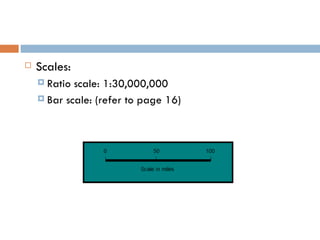
The document provides an overview of the key concepts in world geography that geographers use to study the world, including the five themes of geography. It discusses location, place, region, movement, and human-environment interaction. It also outlines the main tools geographers use, including globes, maps, and data. Geographers rely on maps to show different types of information about the world, such as physical features, political boundaries, themes, and movement.