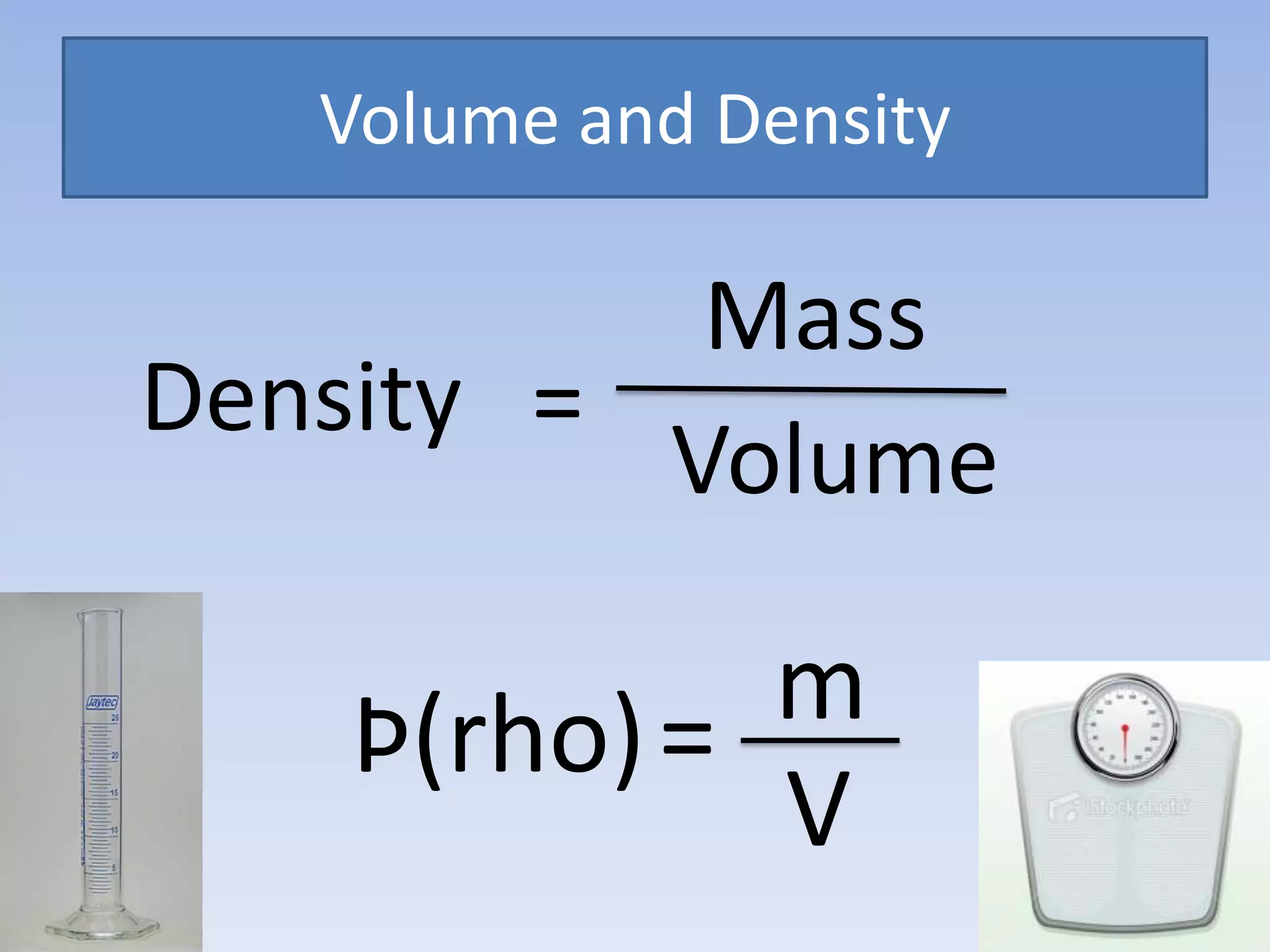
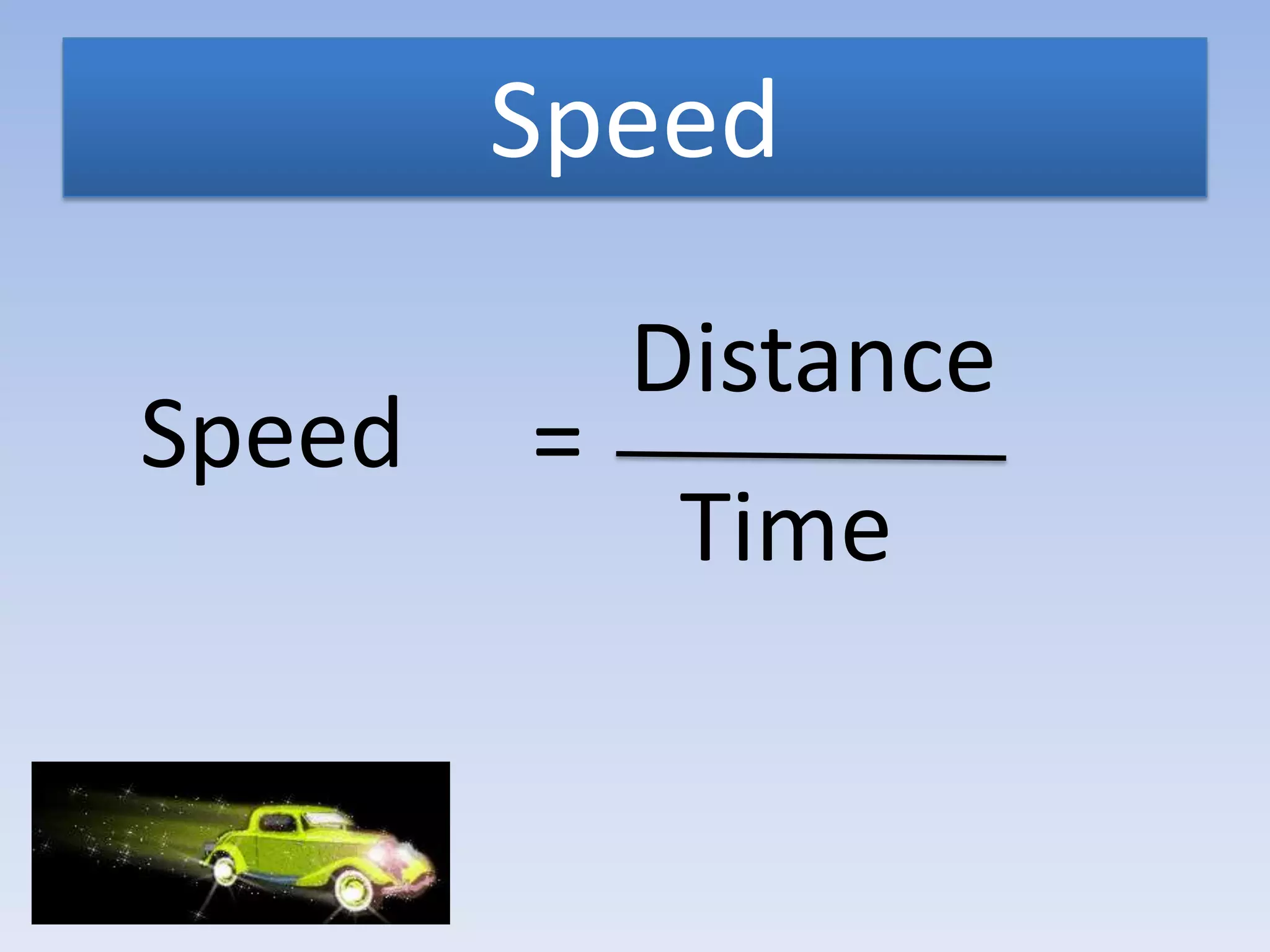
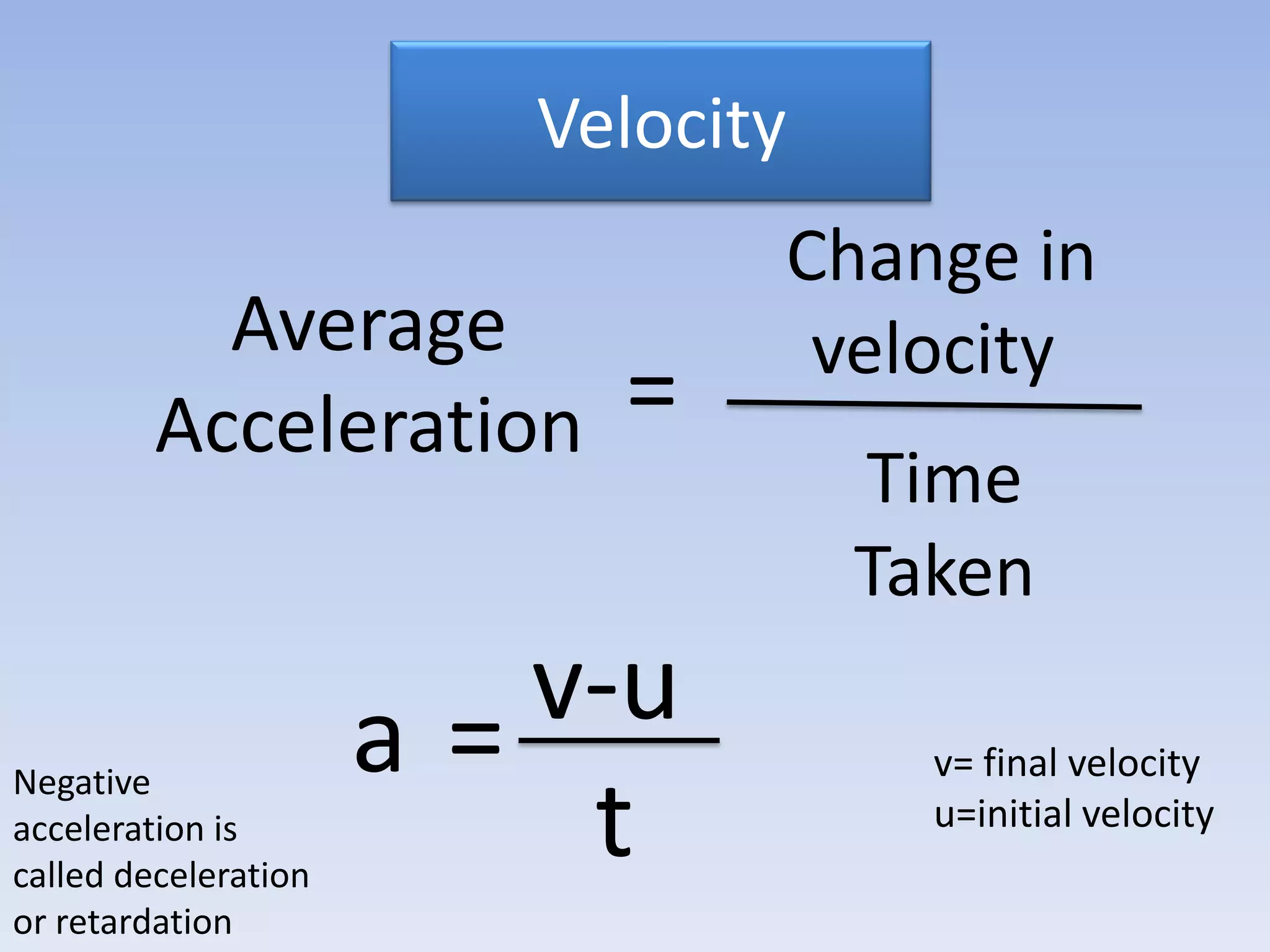
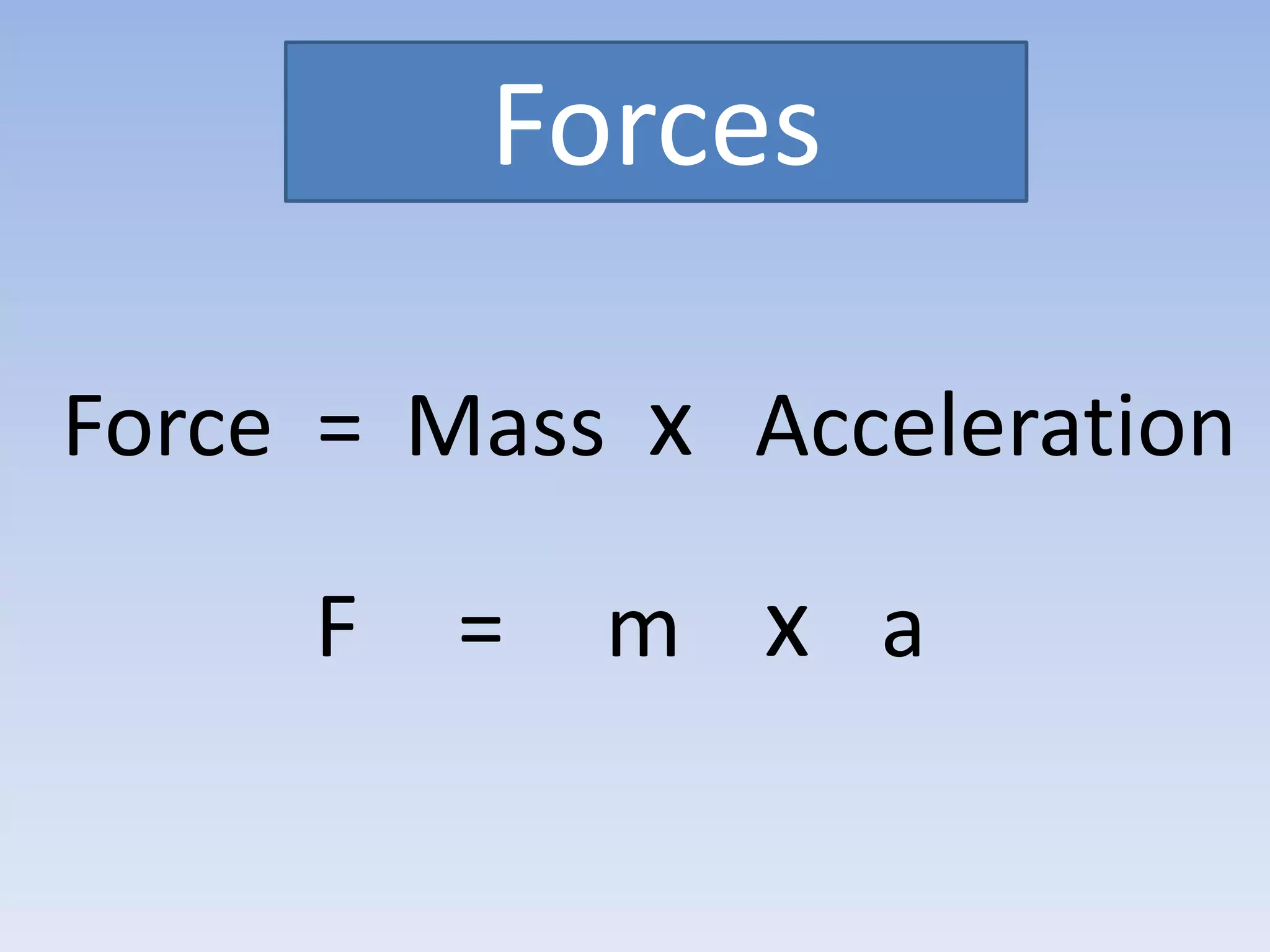
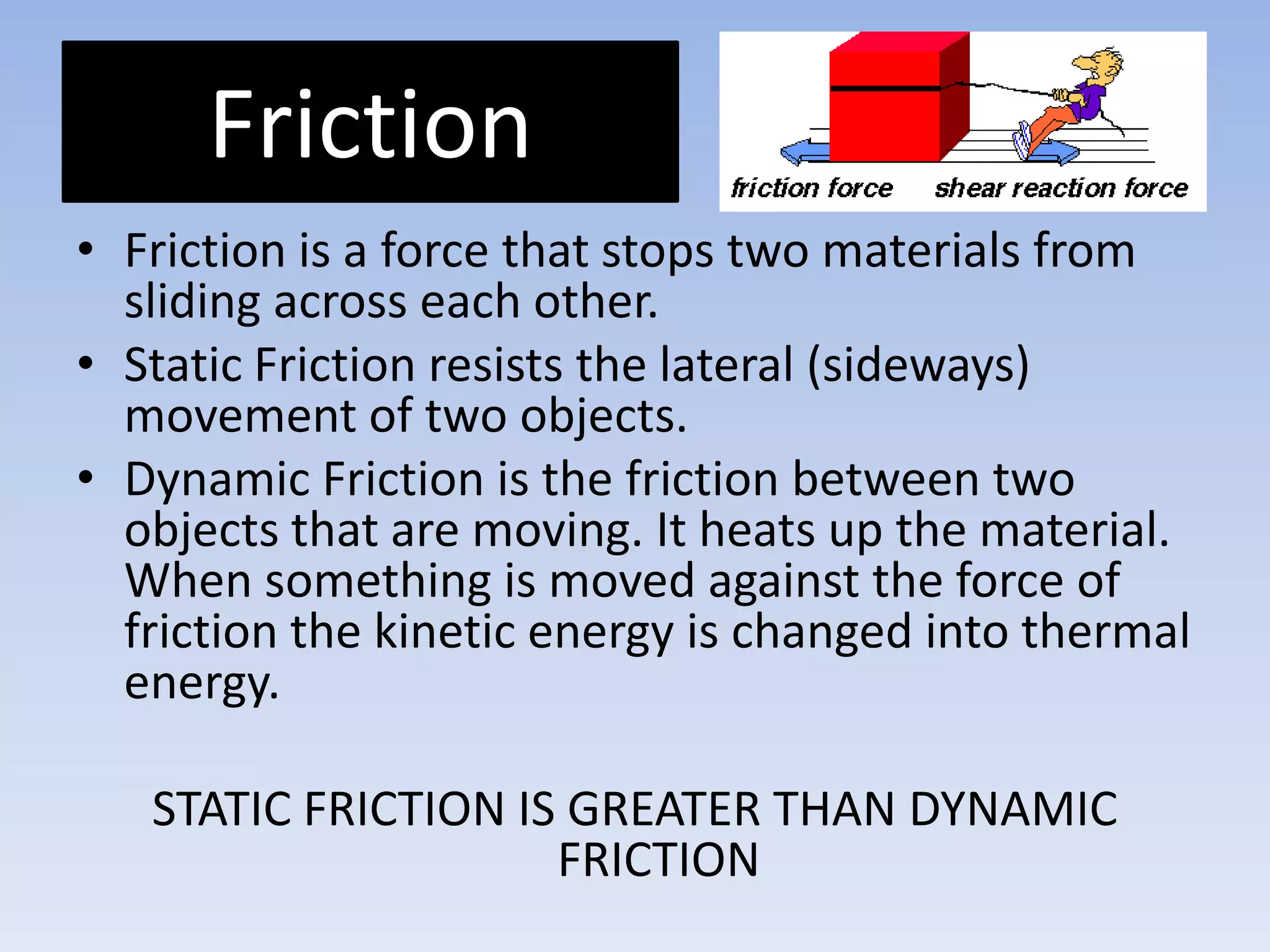
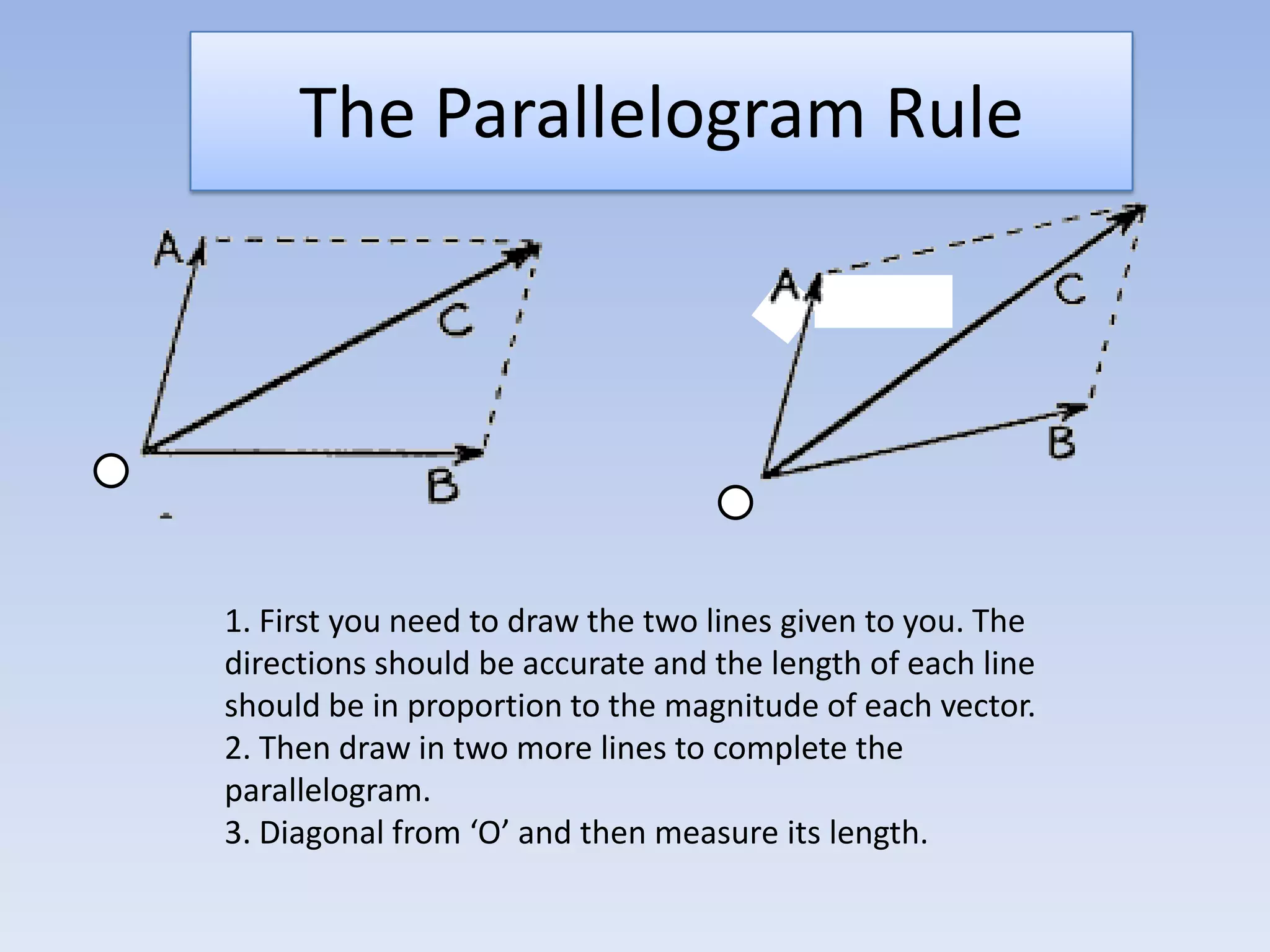
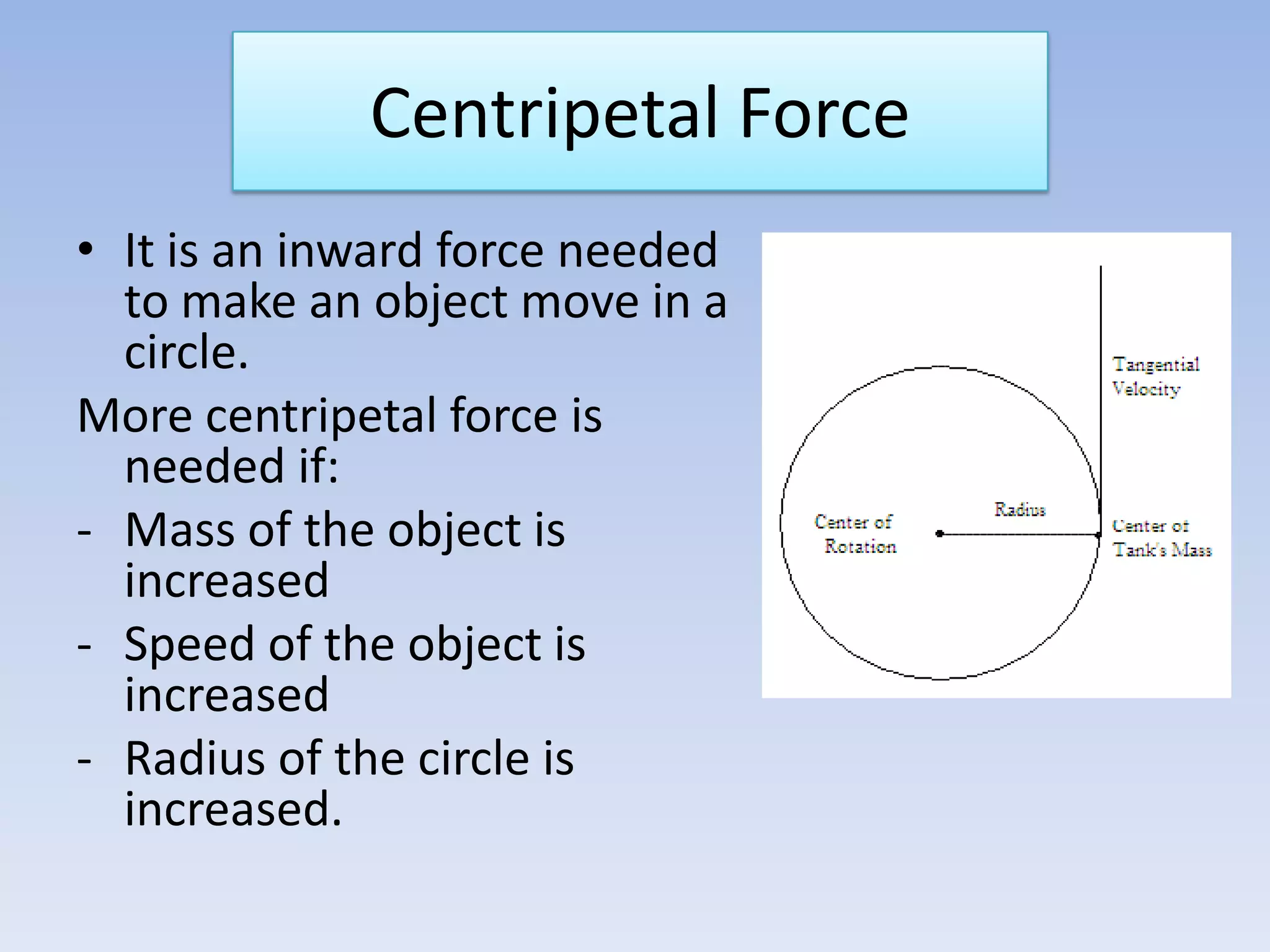
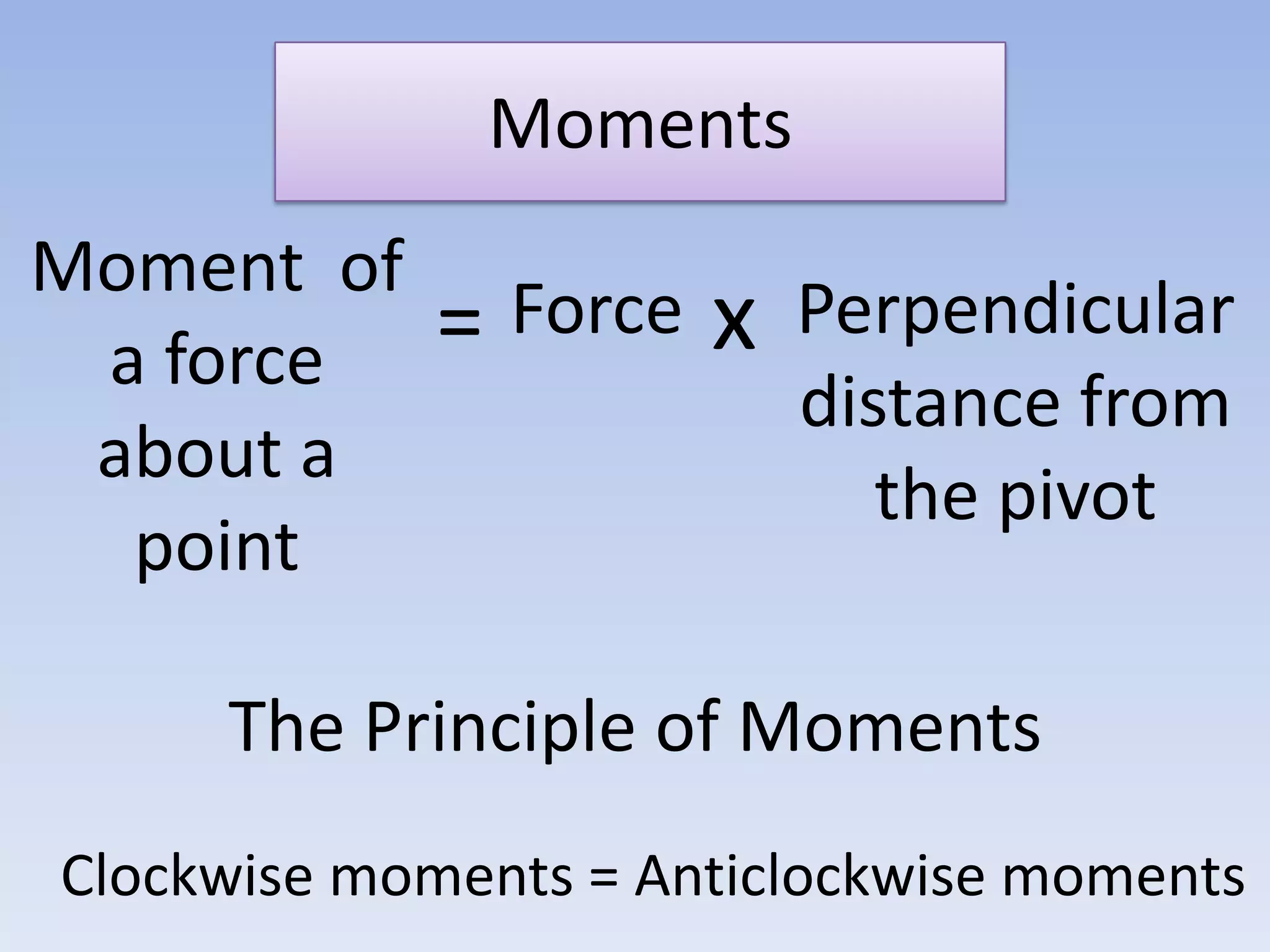
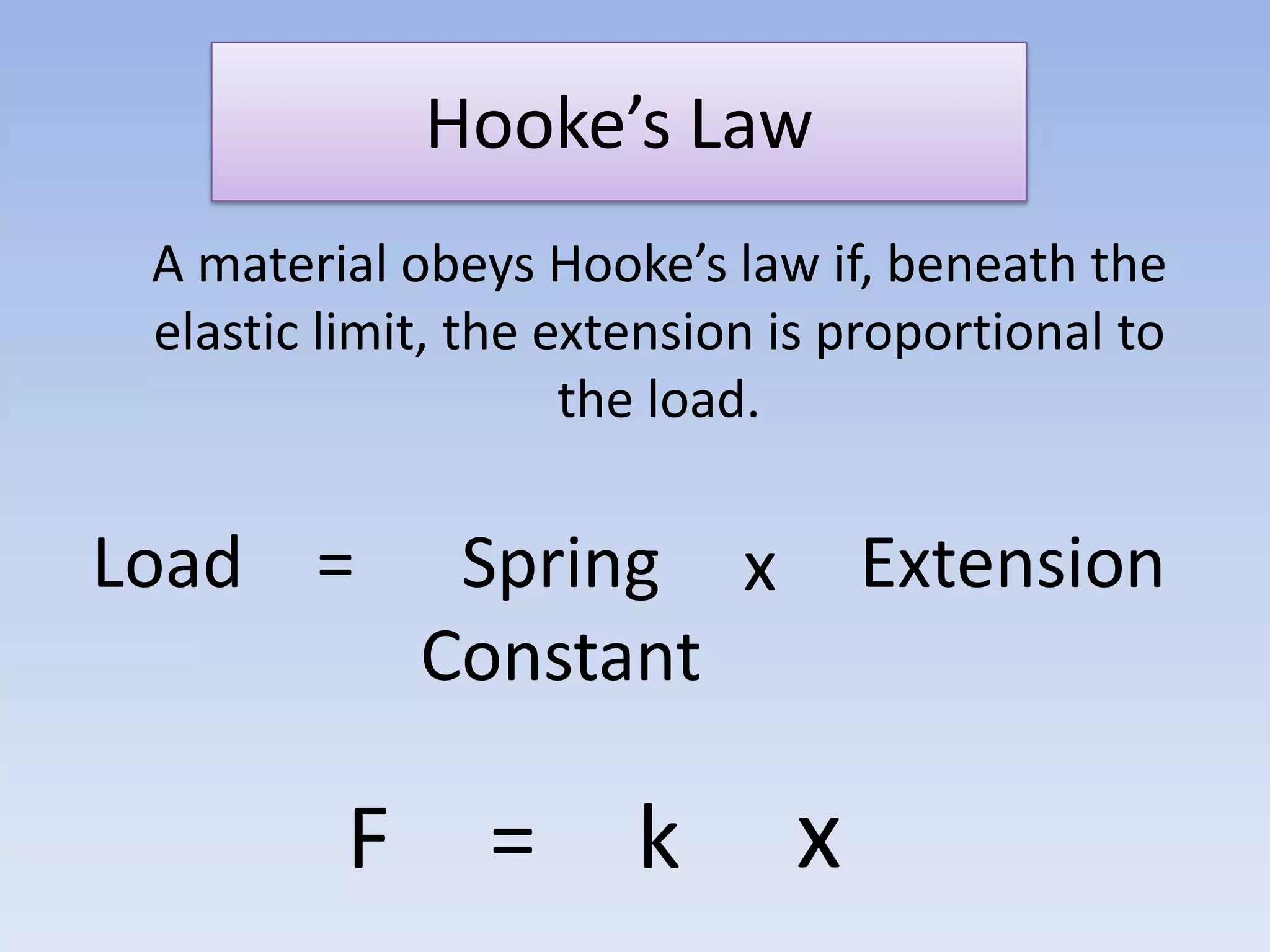
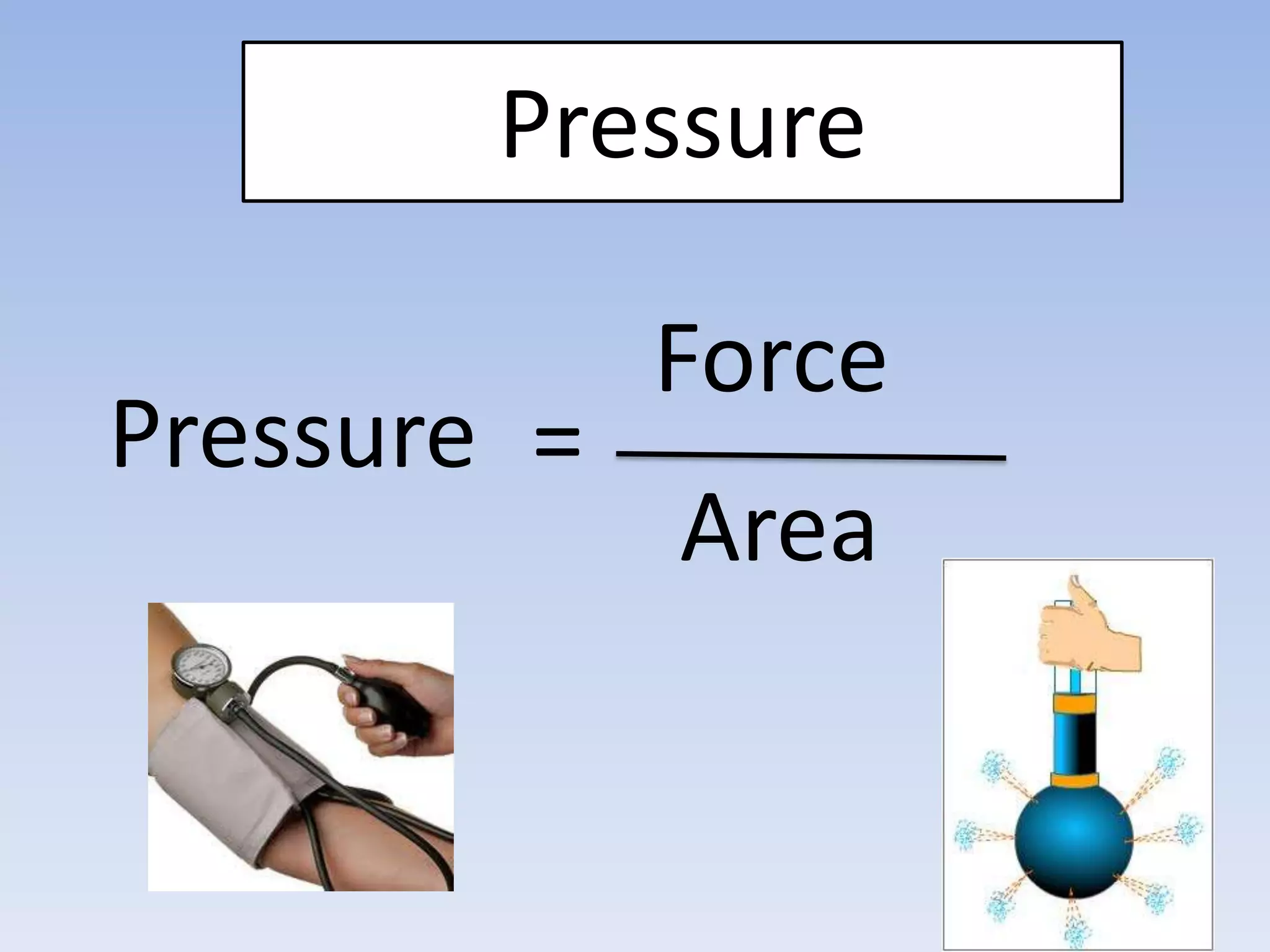
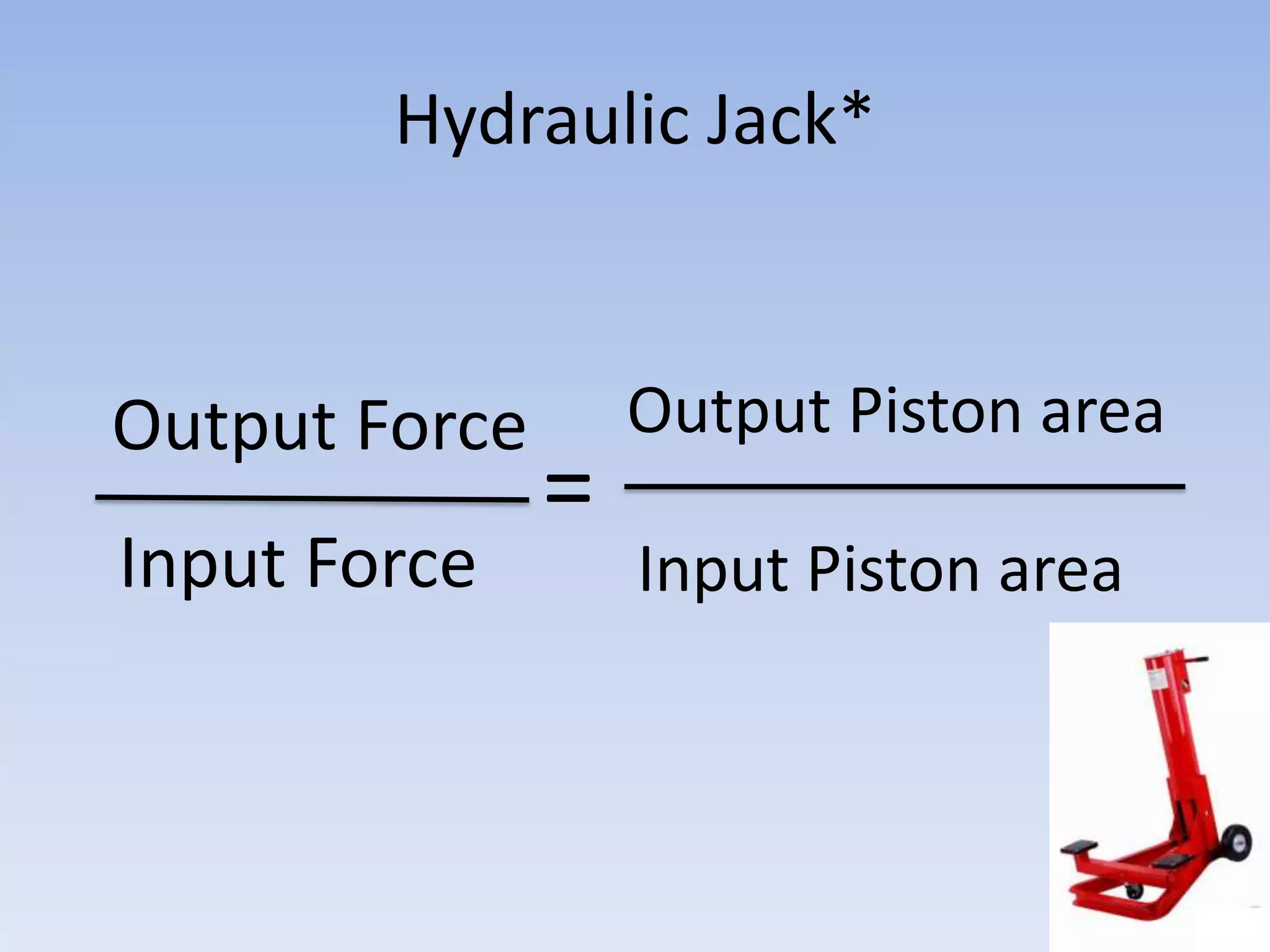
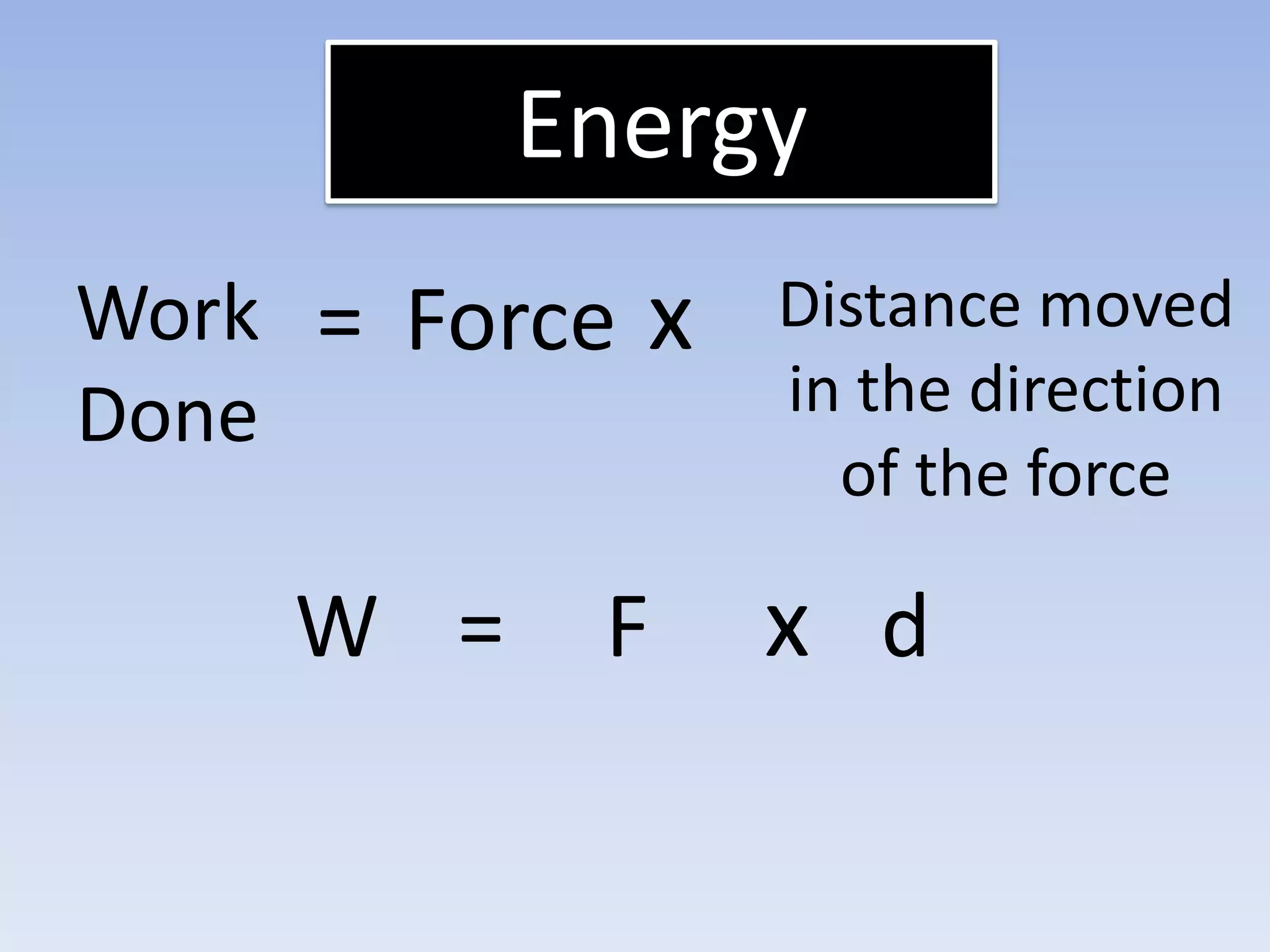
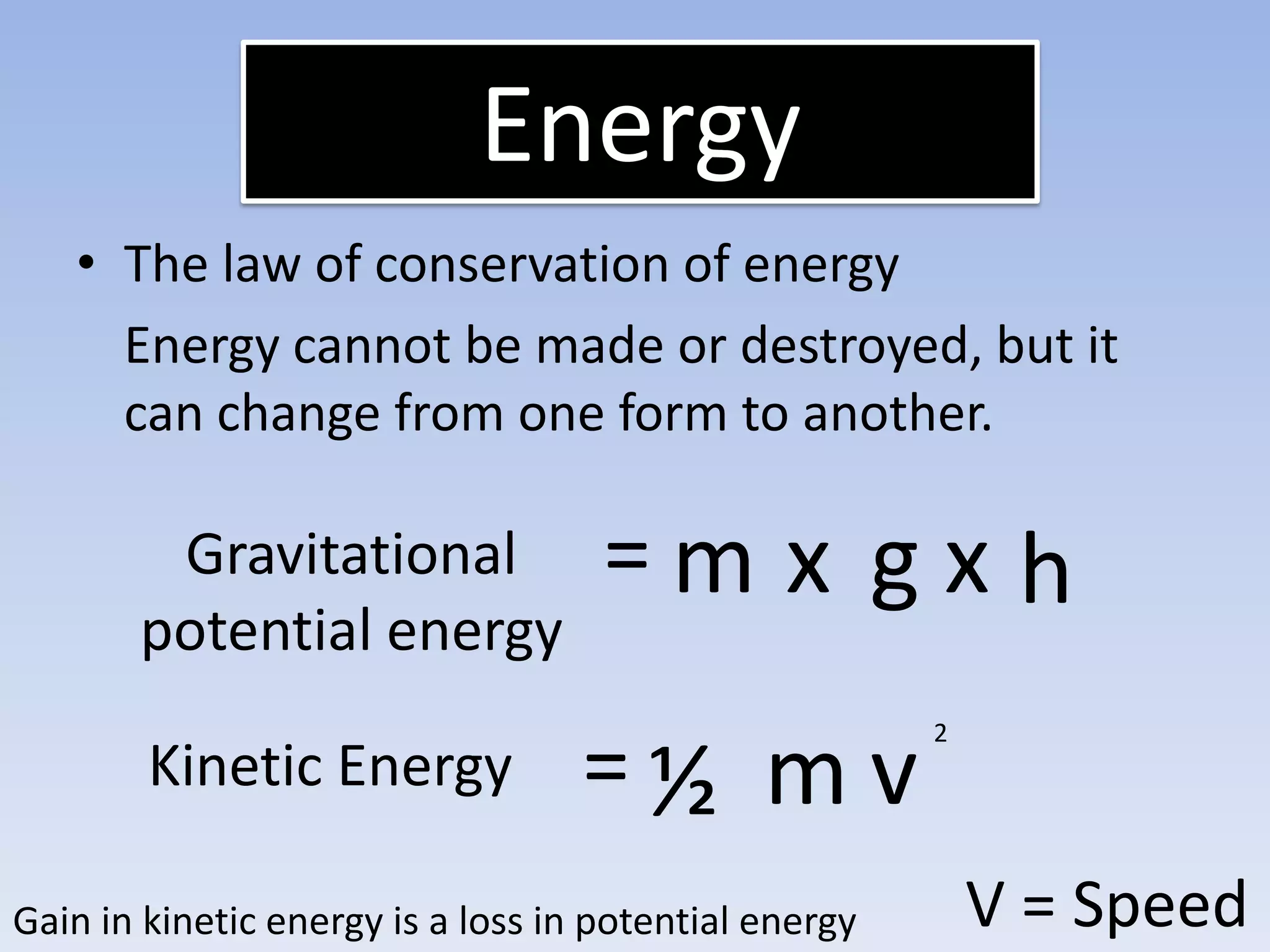
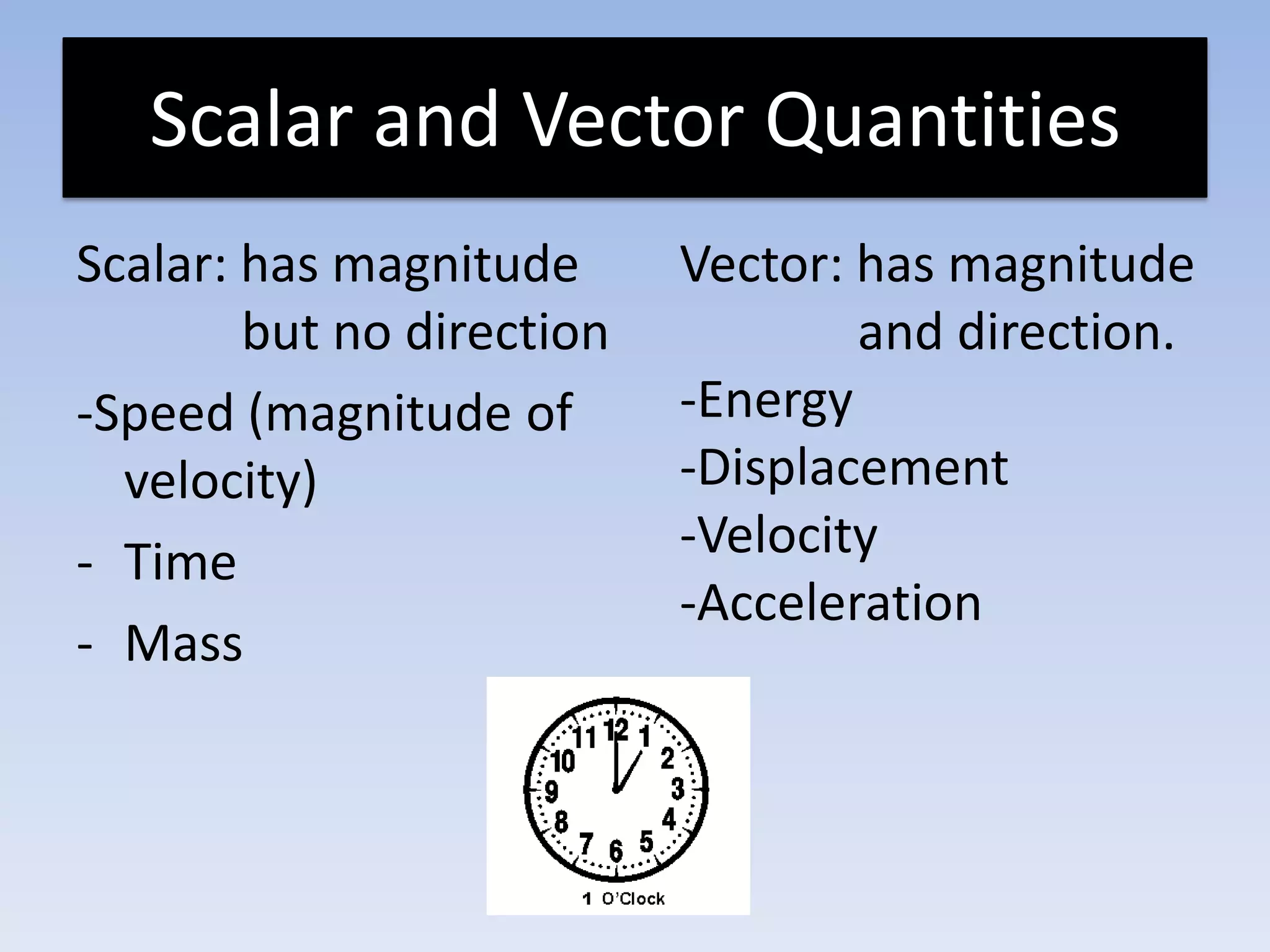
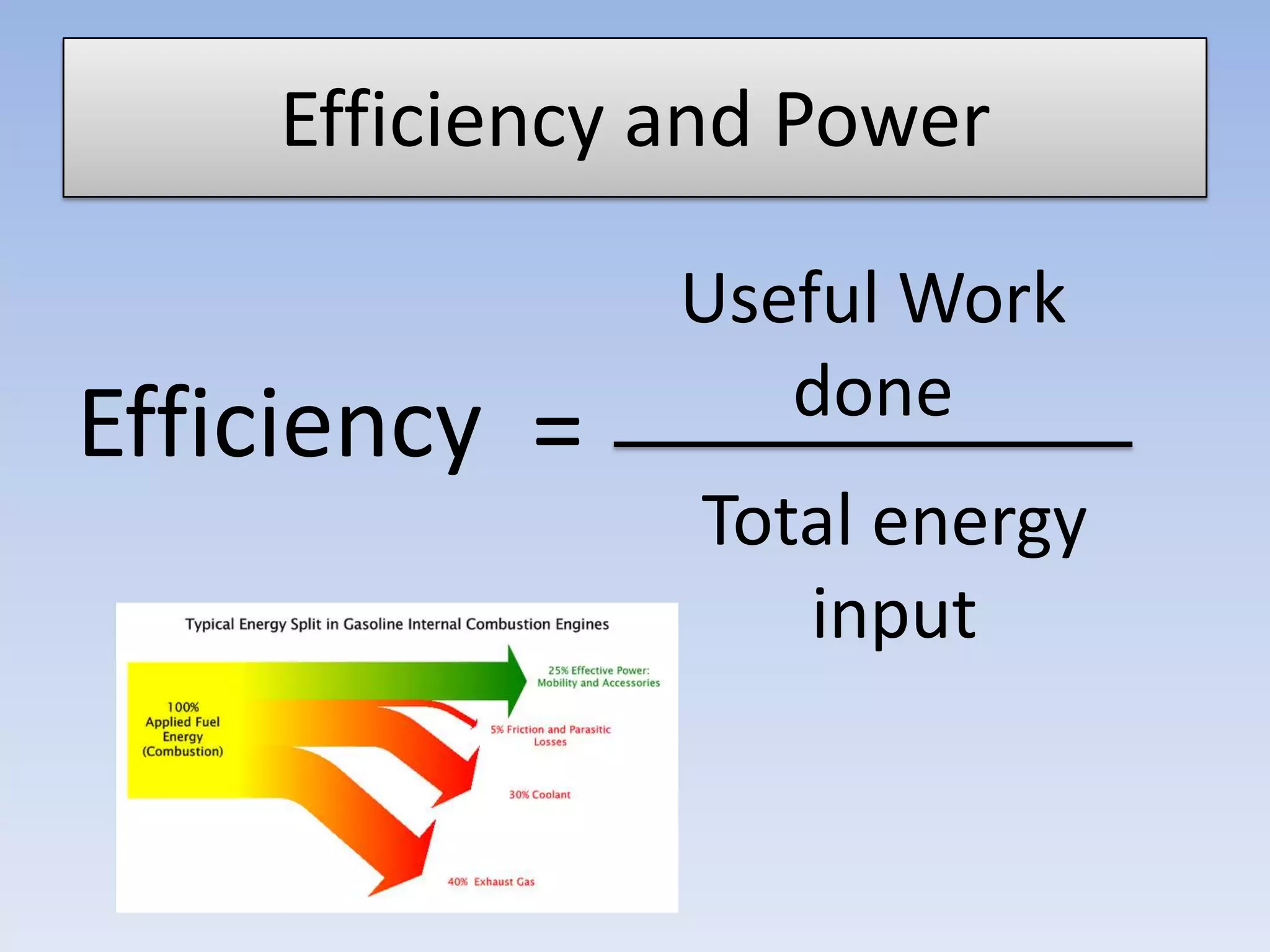
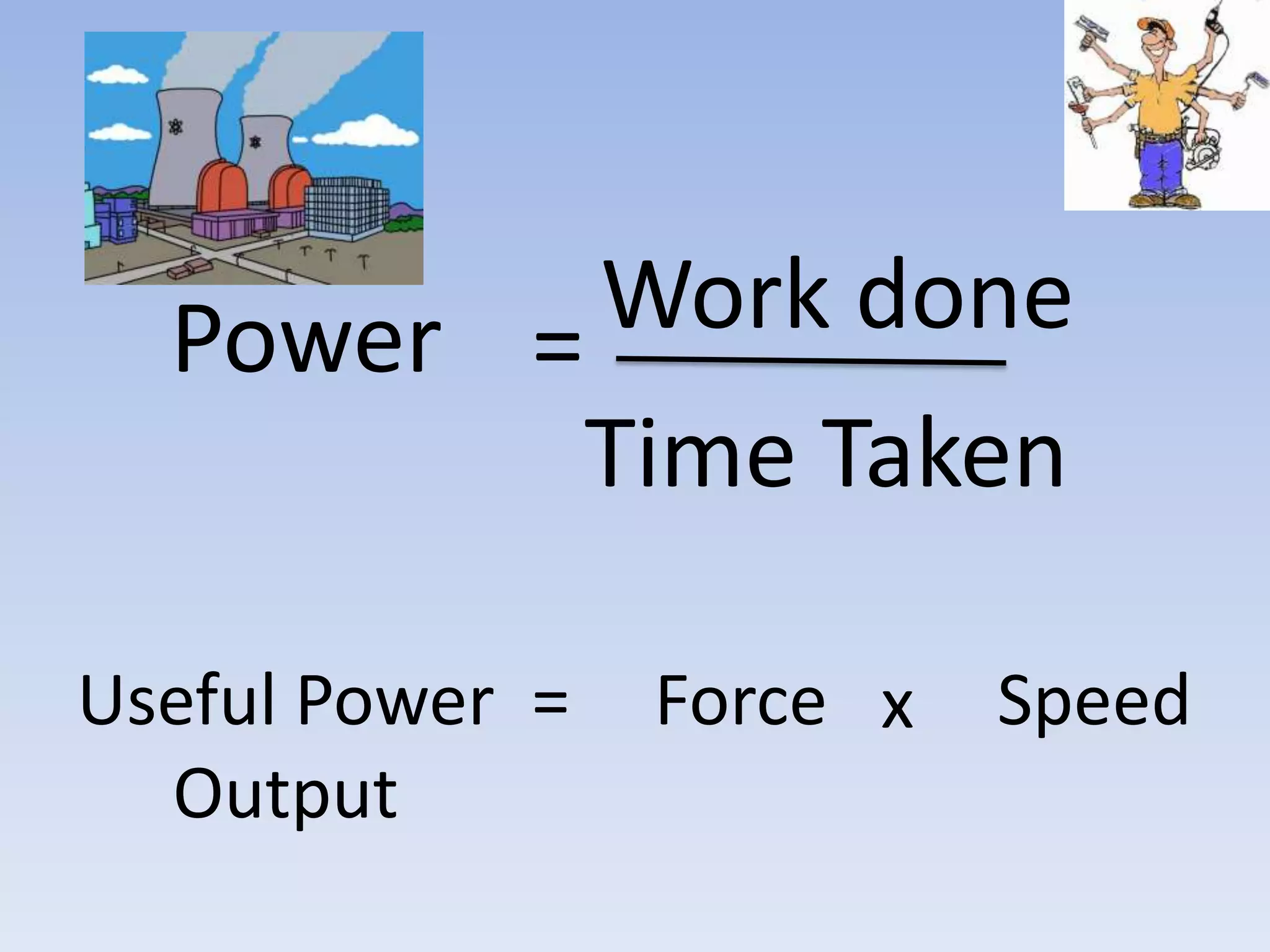
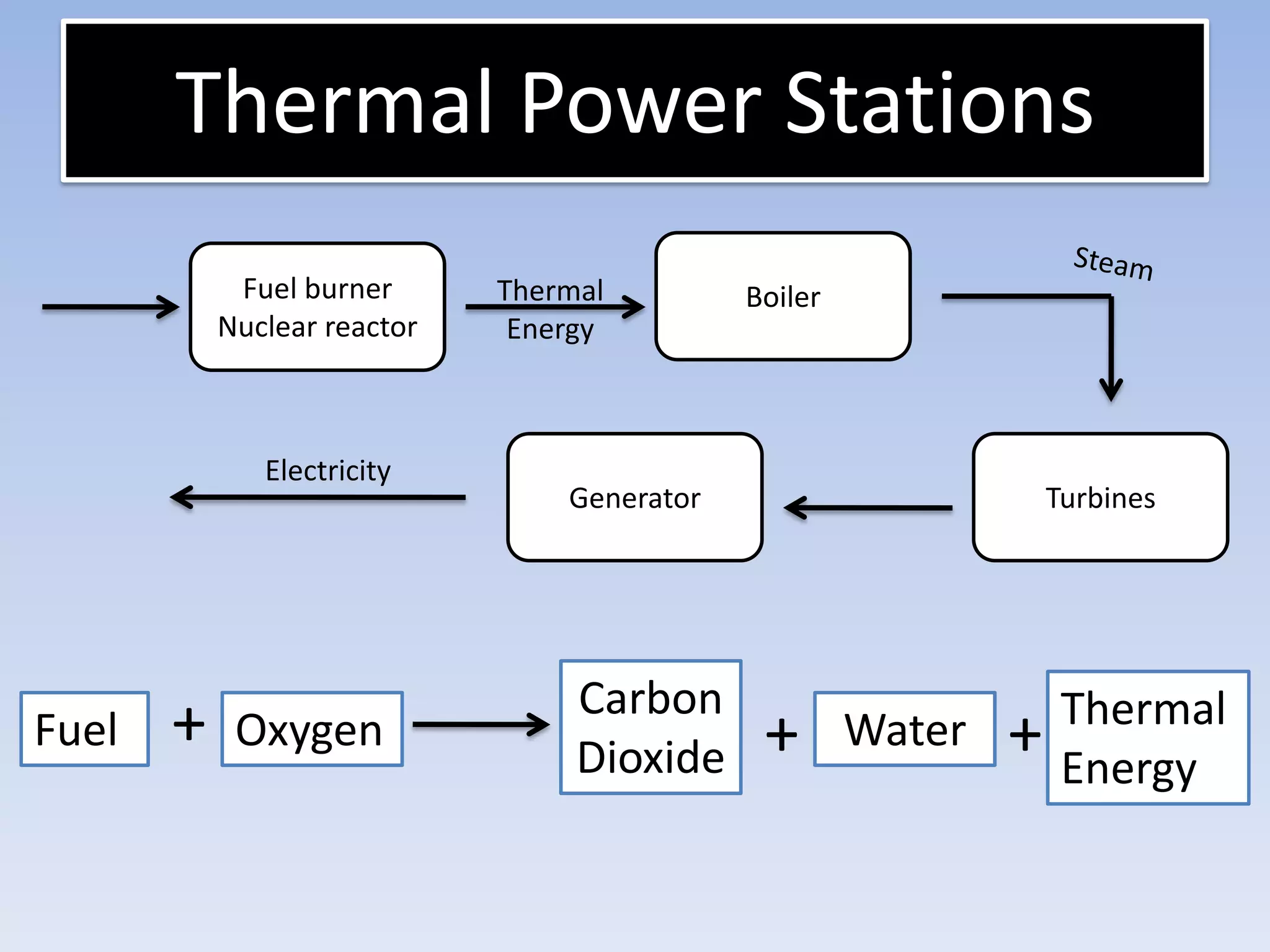
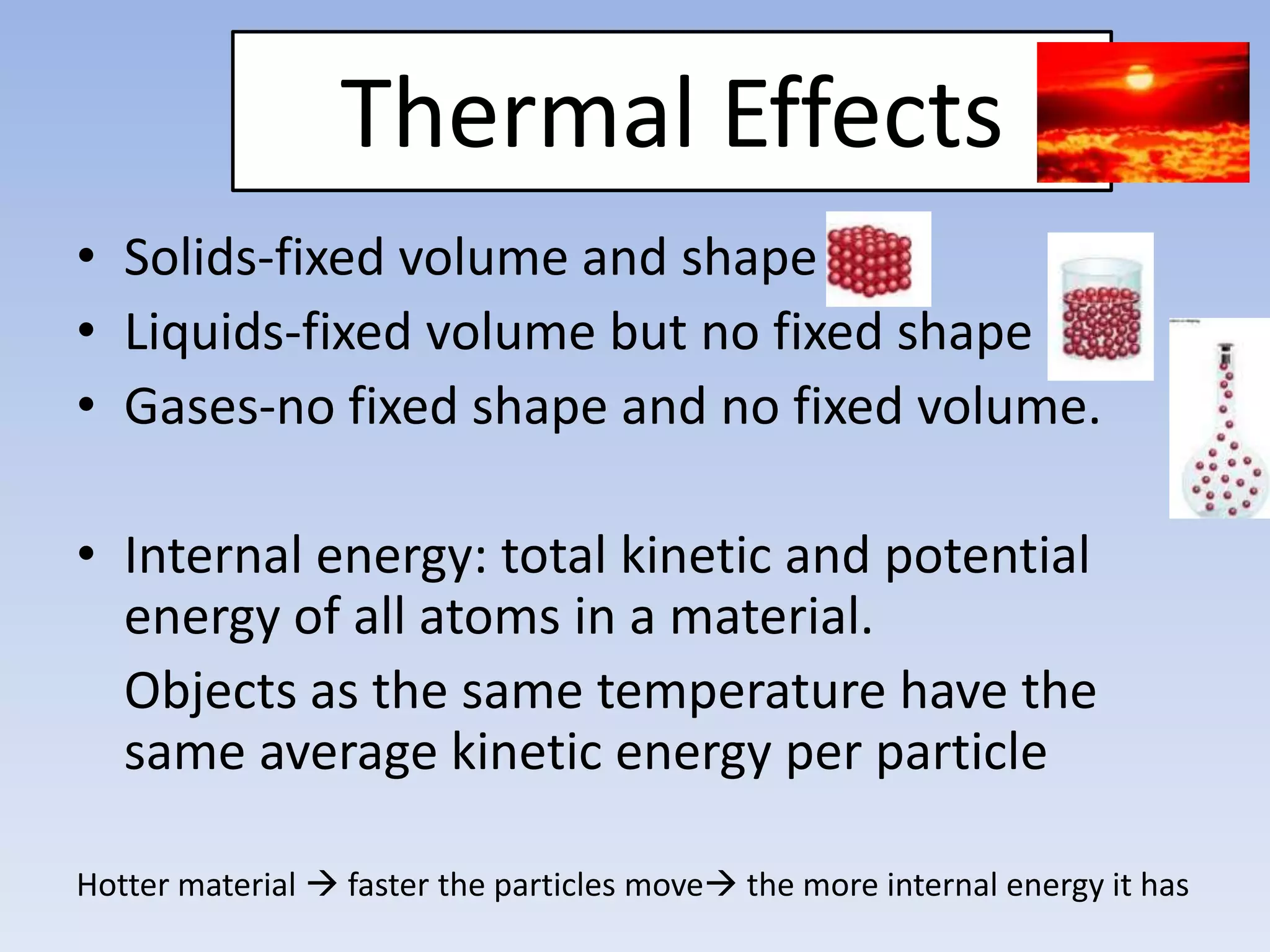
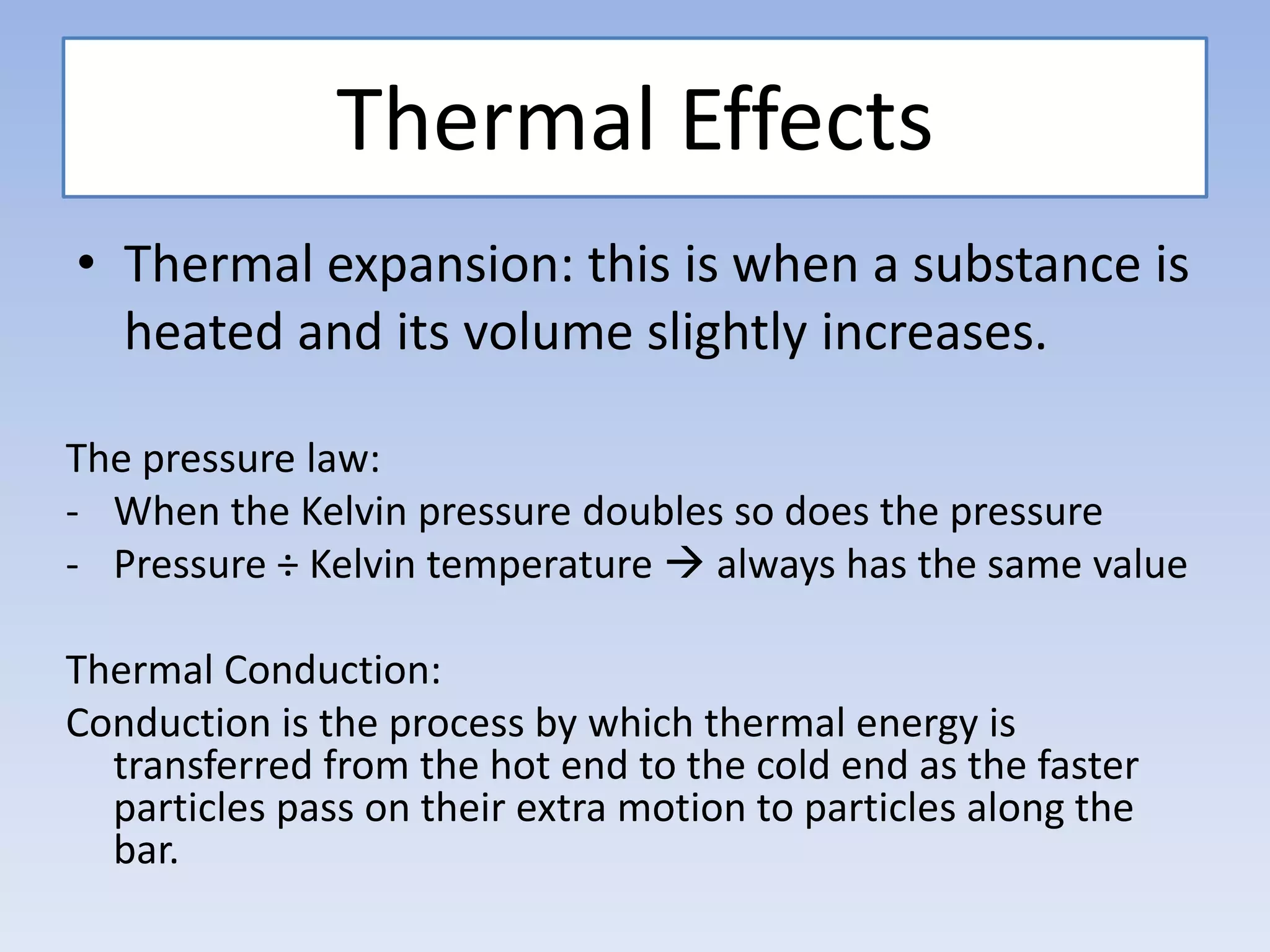
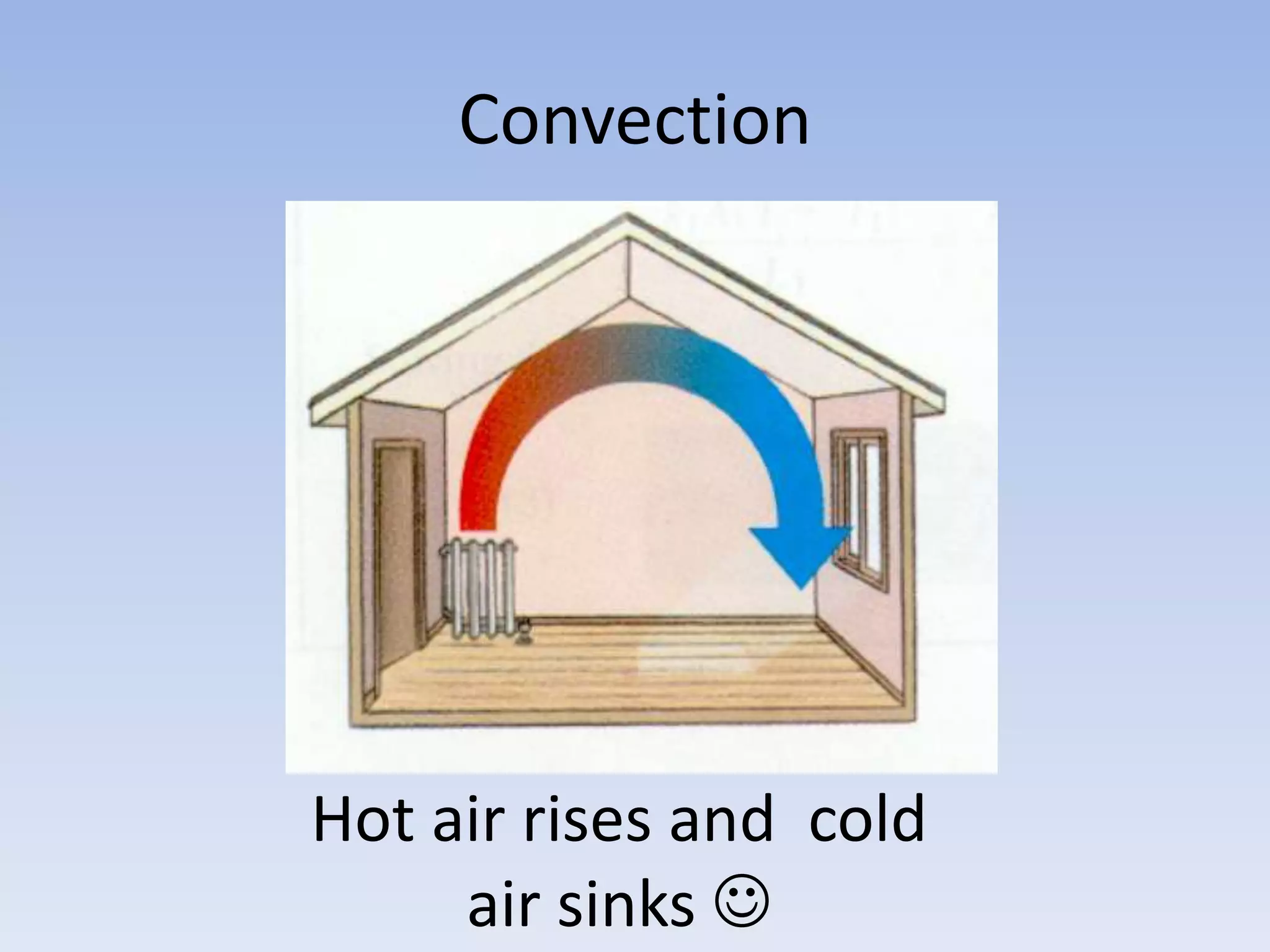
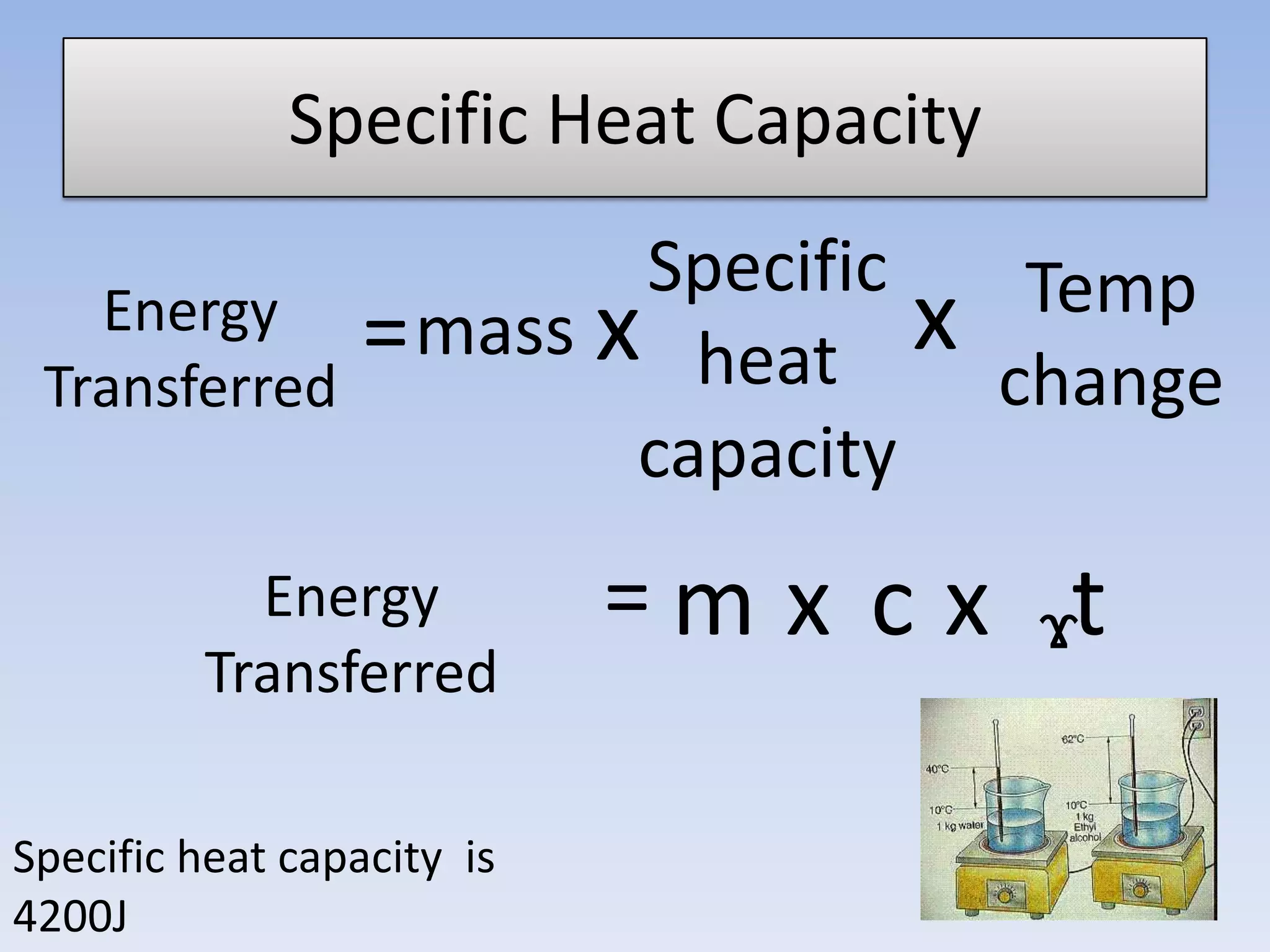
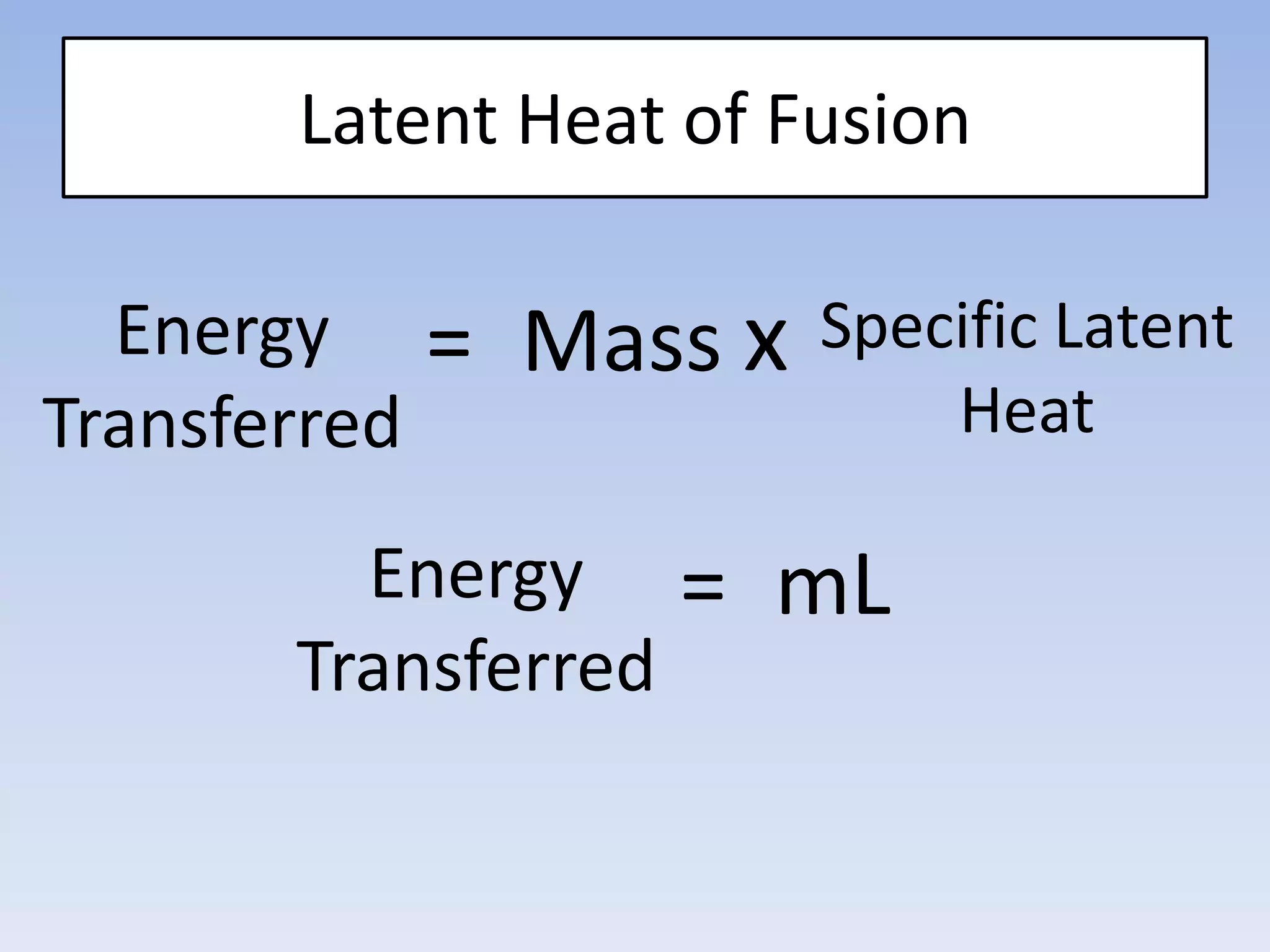
This document provides an overview of key physics concepts covered in the IGCSE syllabus. It discusses topics like volume and density, speed, forces, friction, gravitational force, pressure, energy, thermal effects, and specific heat capacity. For each topic, it outlines relevant formulae and provides 2-3 brief explanatory sentences. The document is intended as a revision guide for students to learn and review the essential information and formulae for multiple areas of the IGCSE physics curriculum.