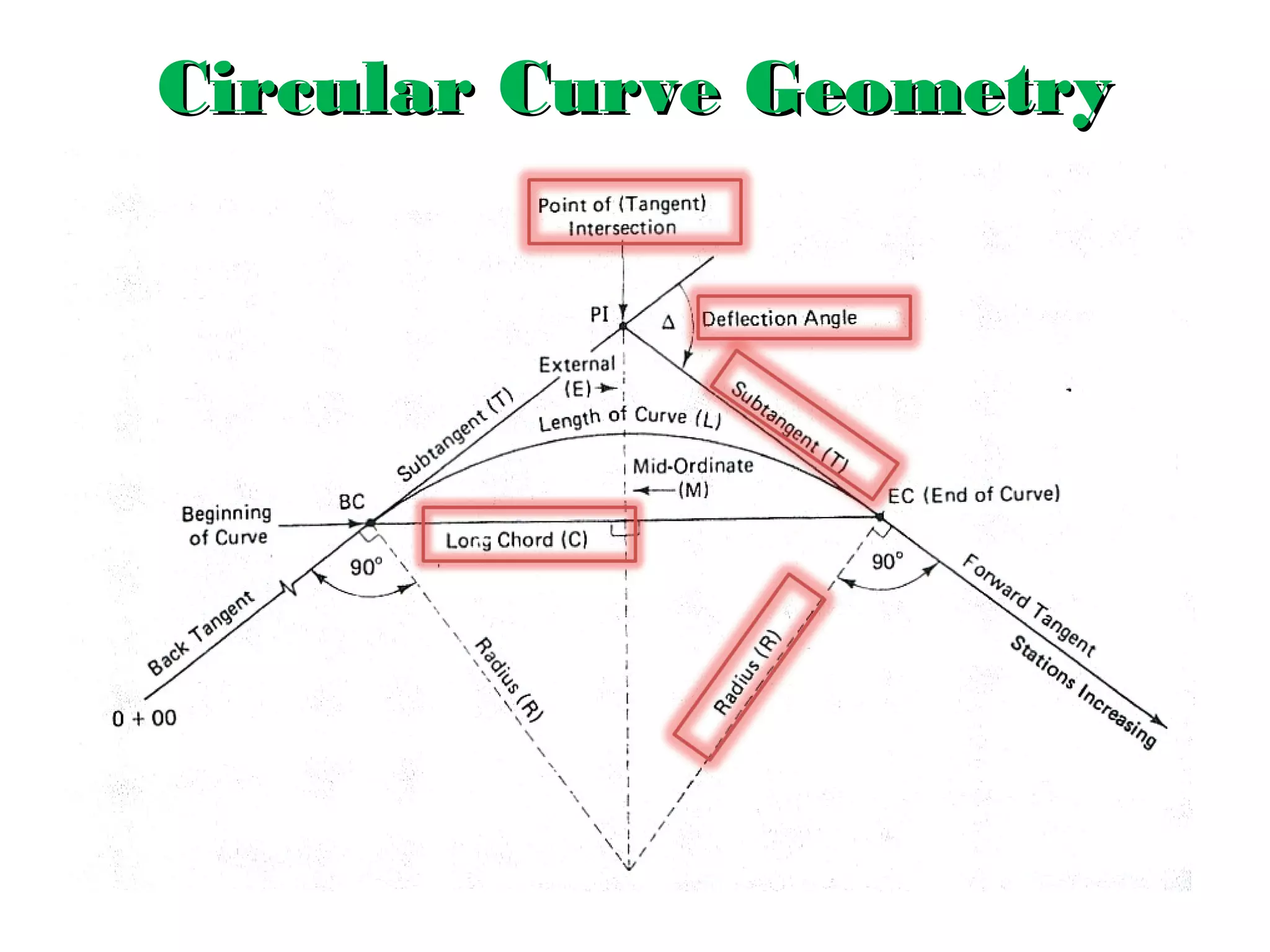
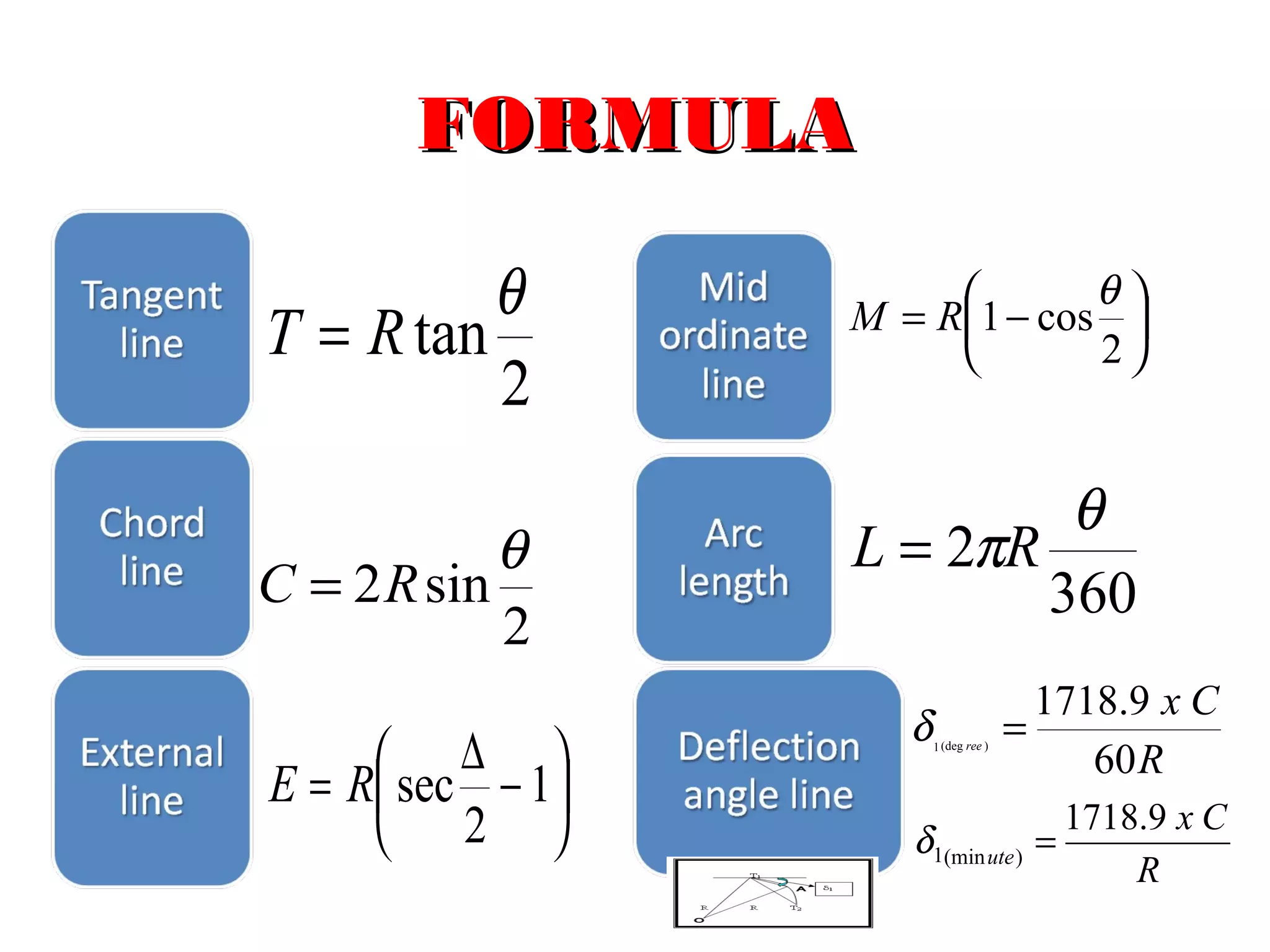
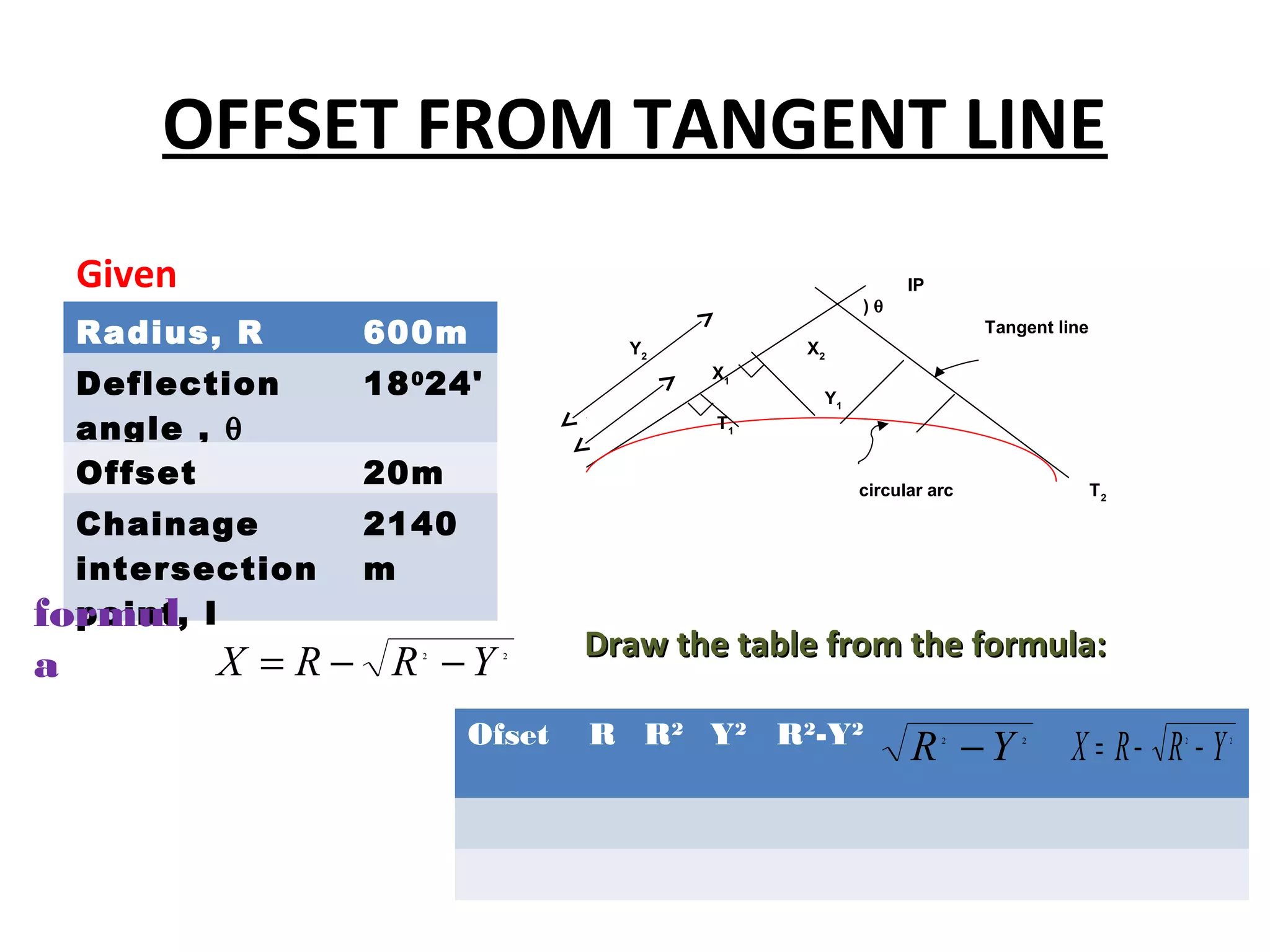
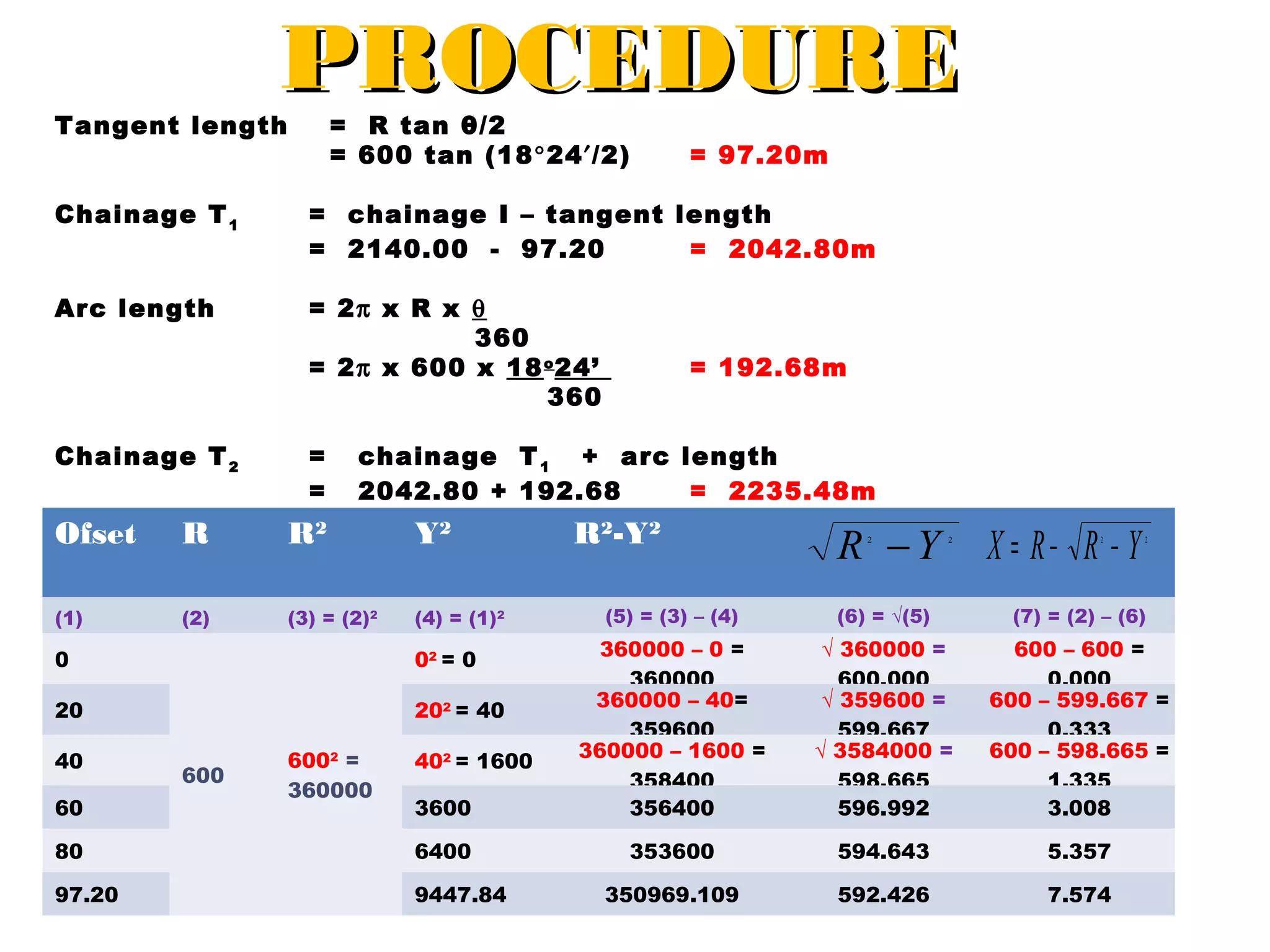
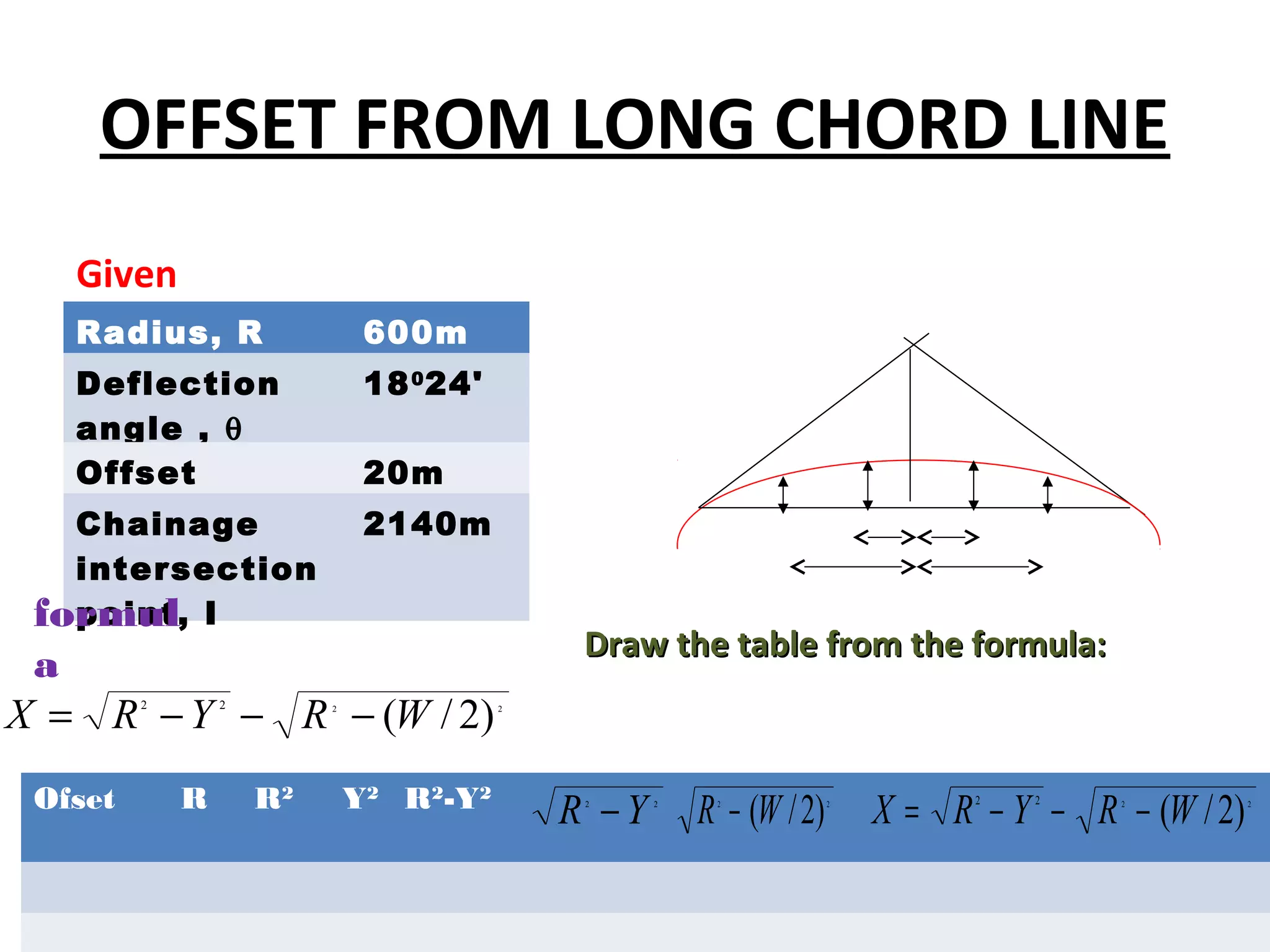
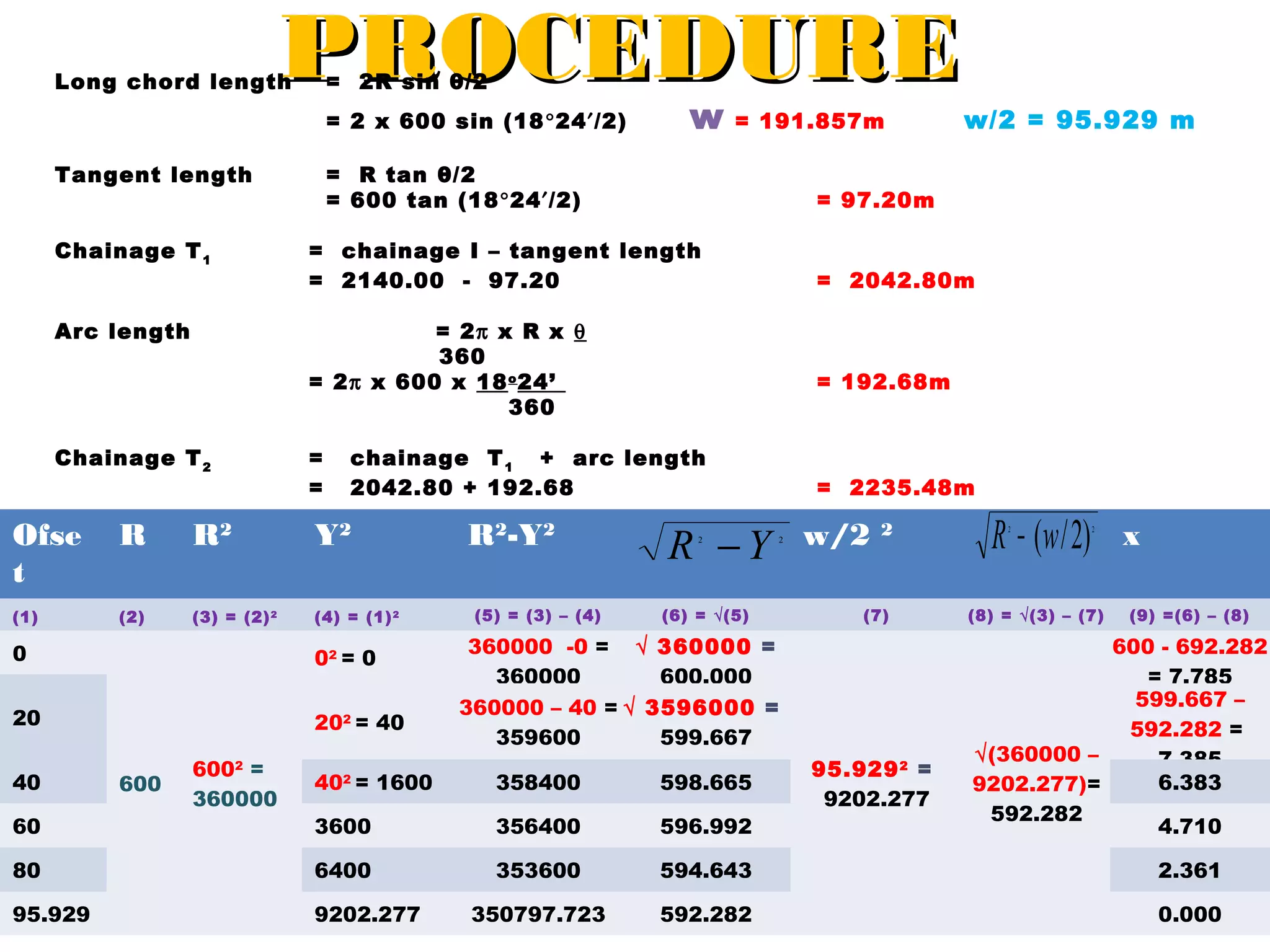
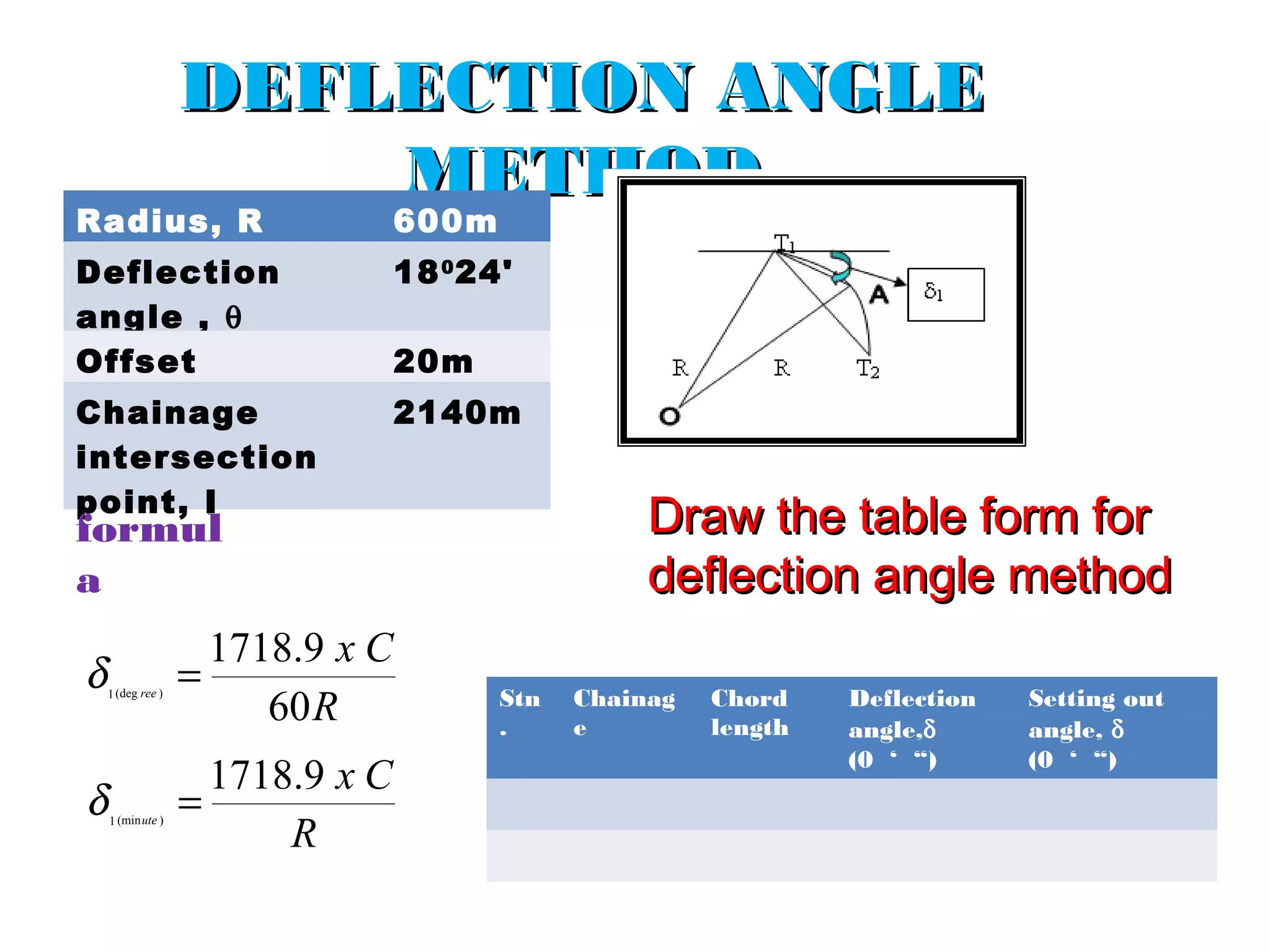
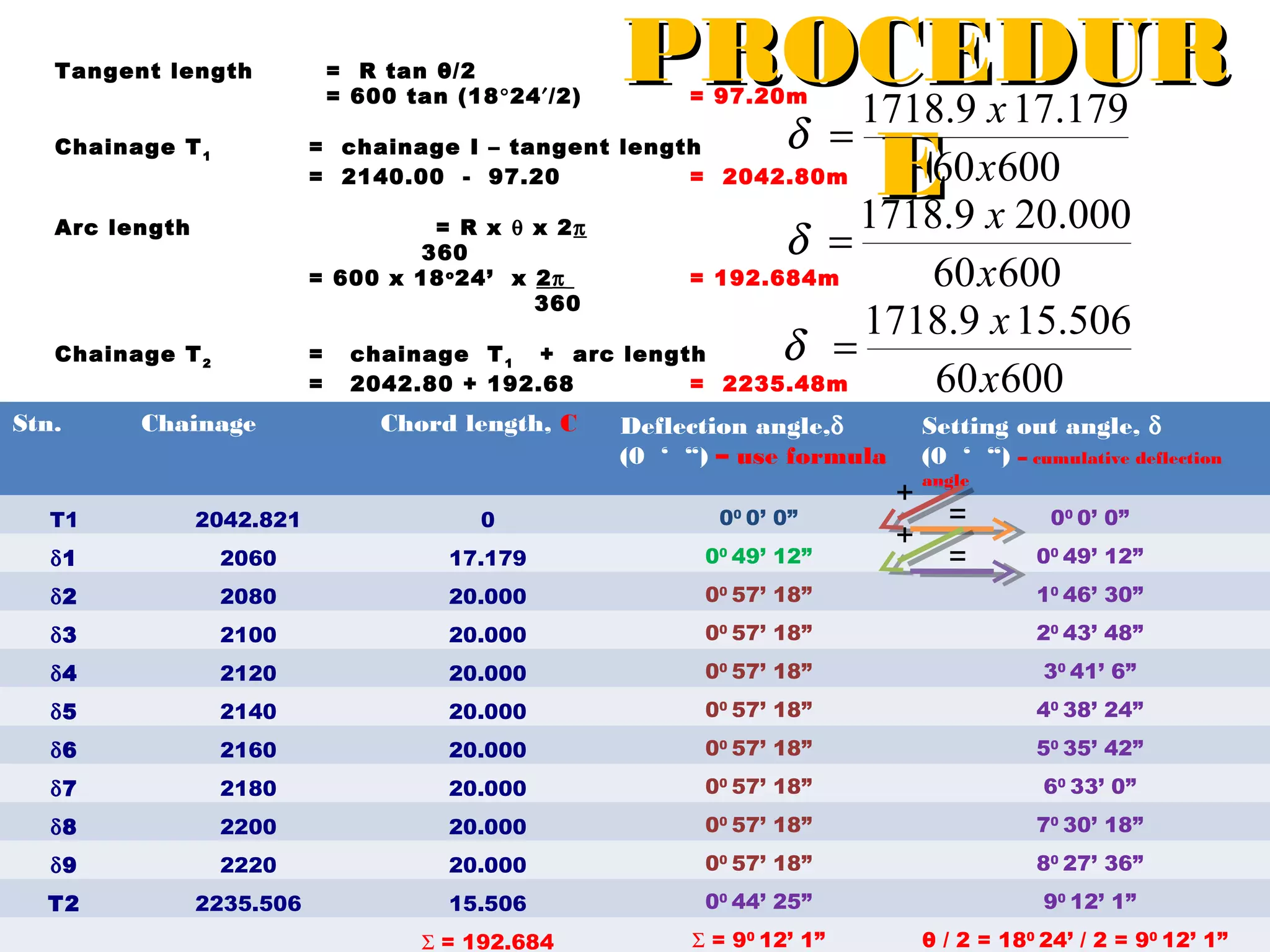
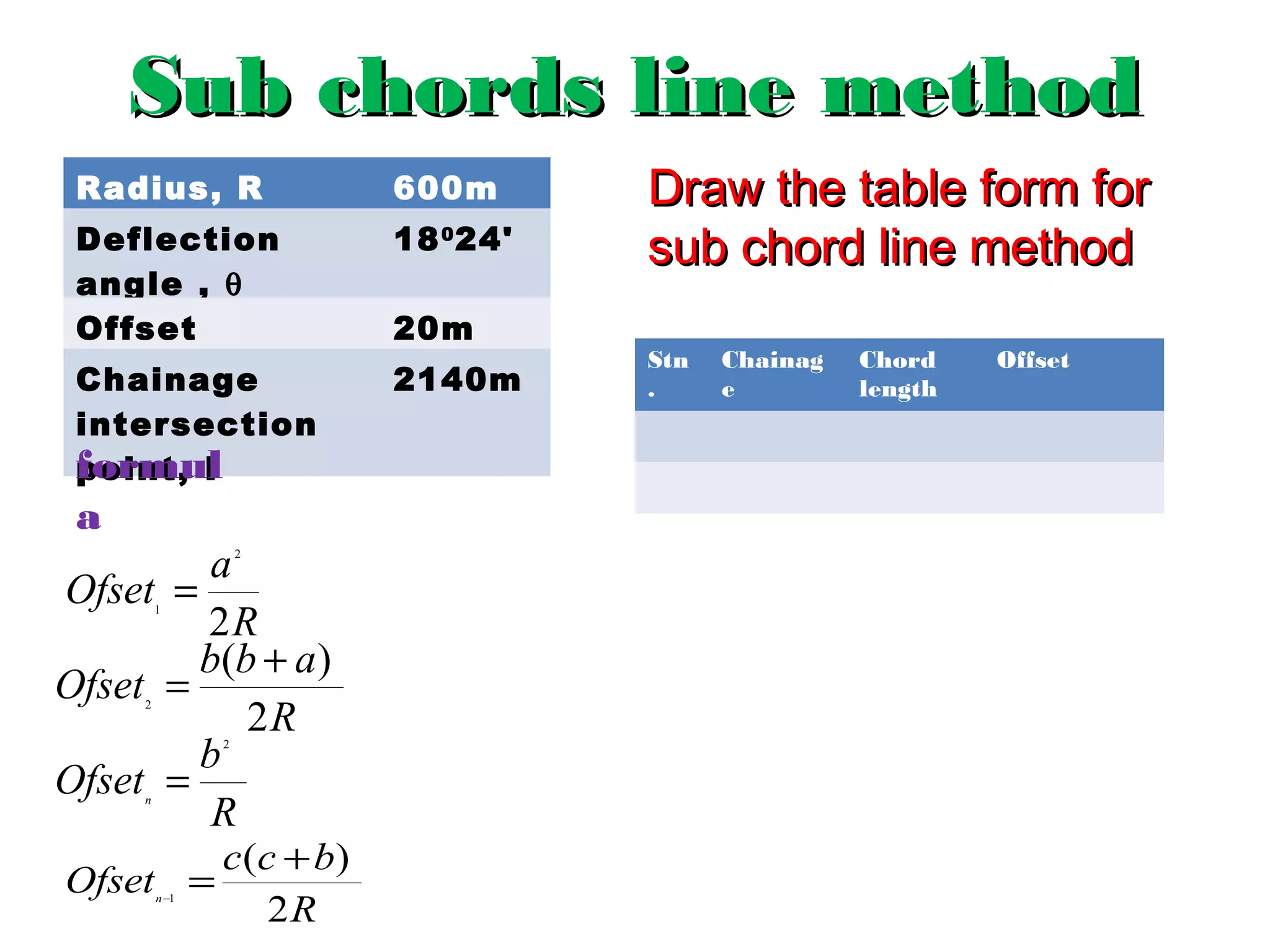
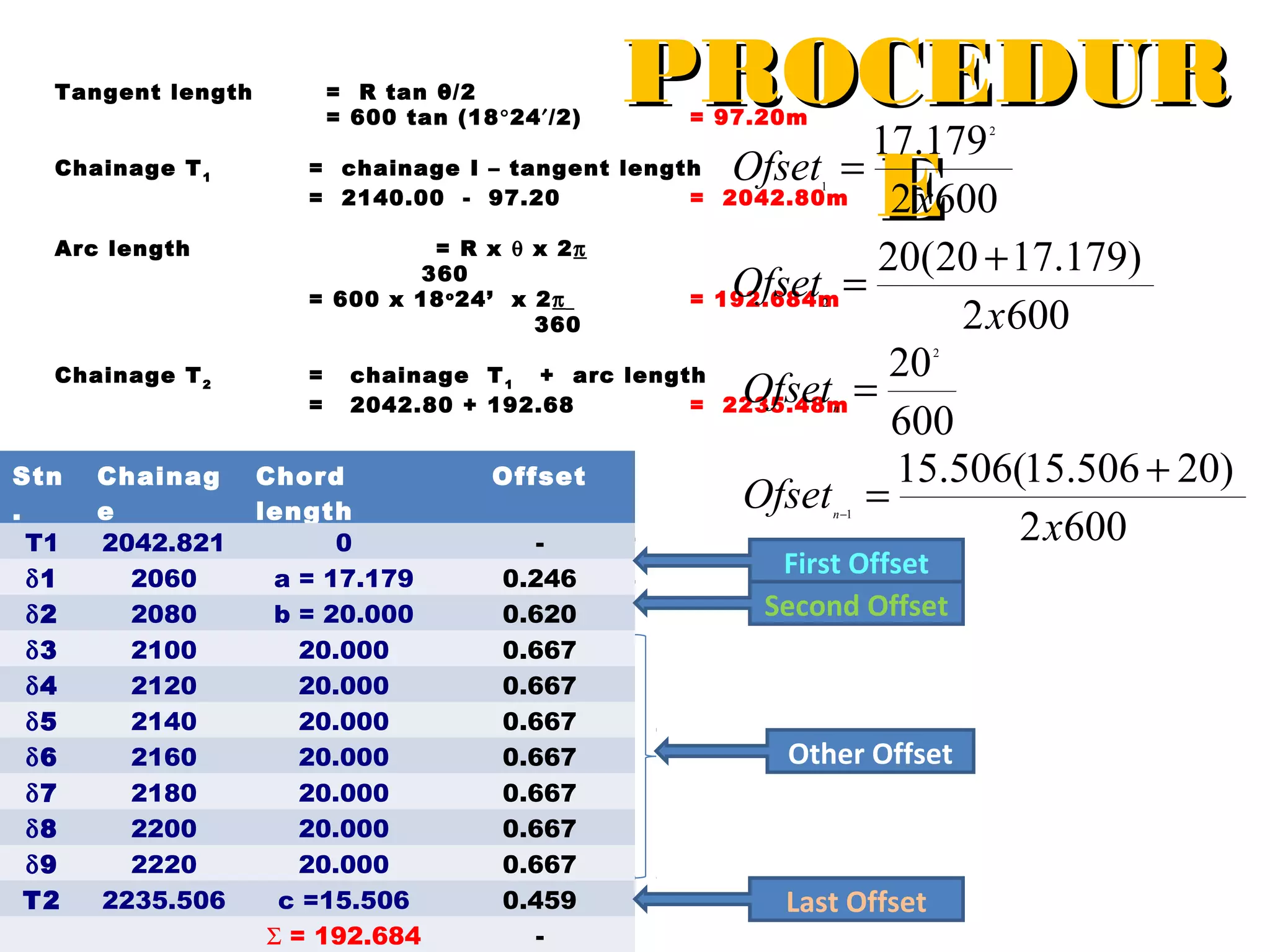
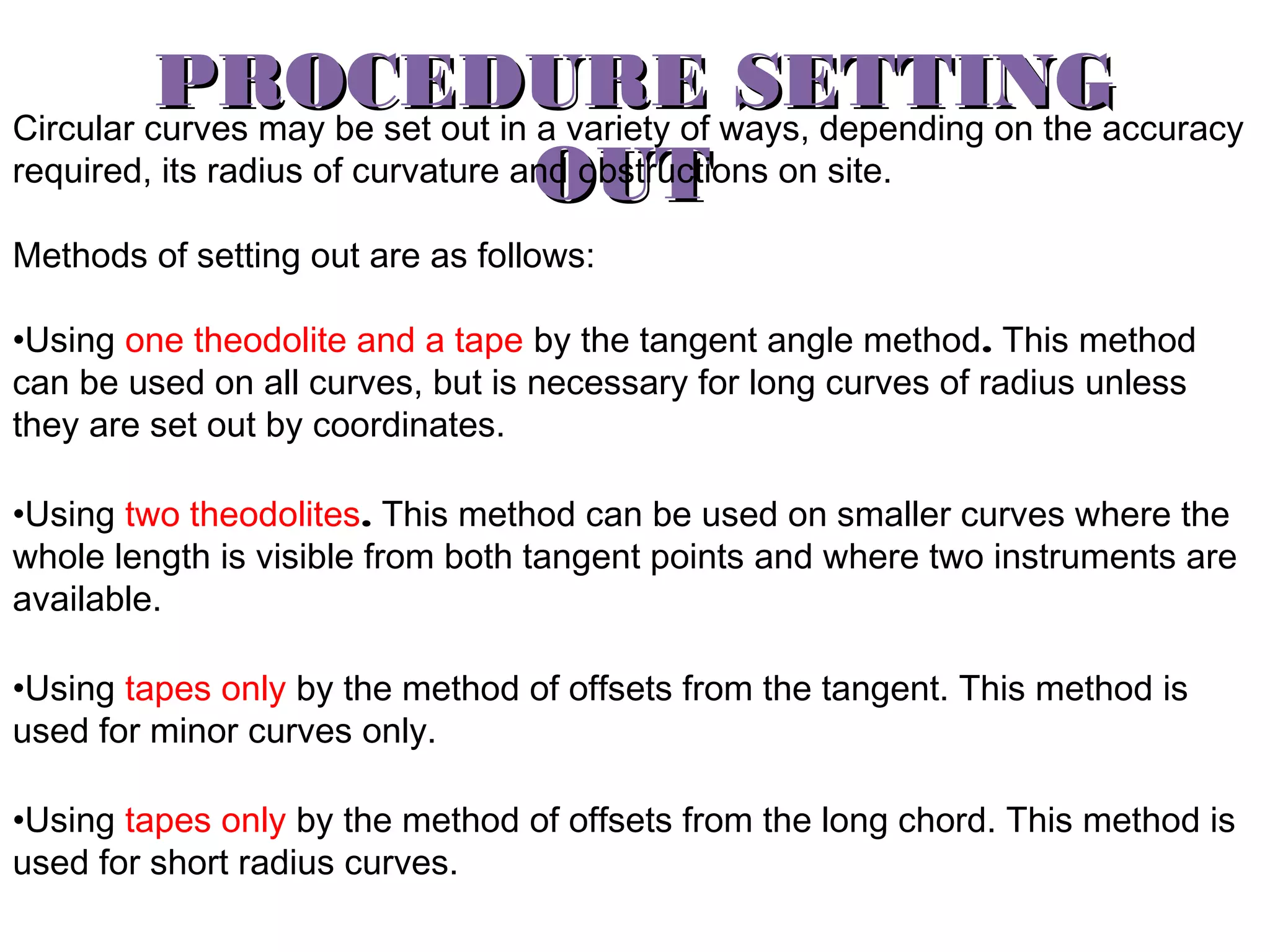
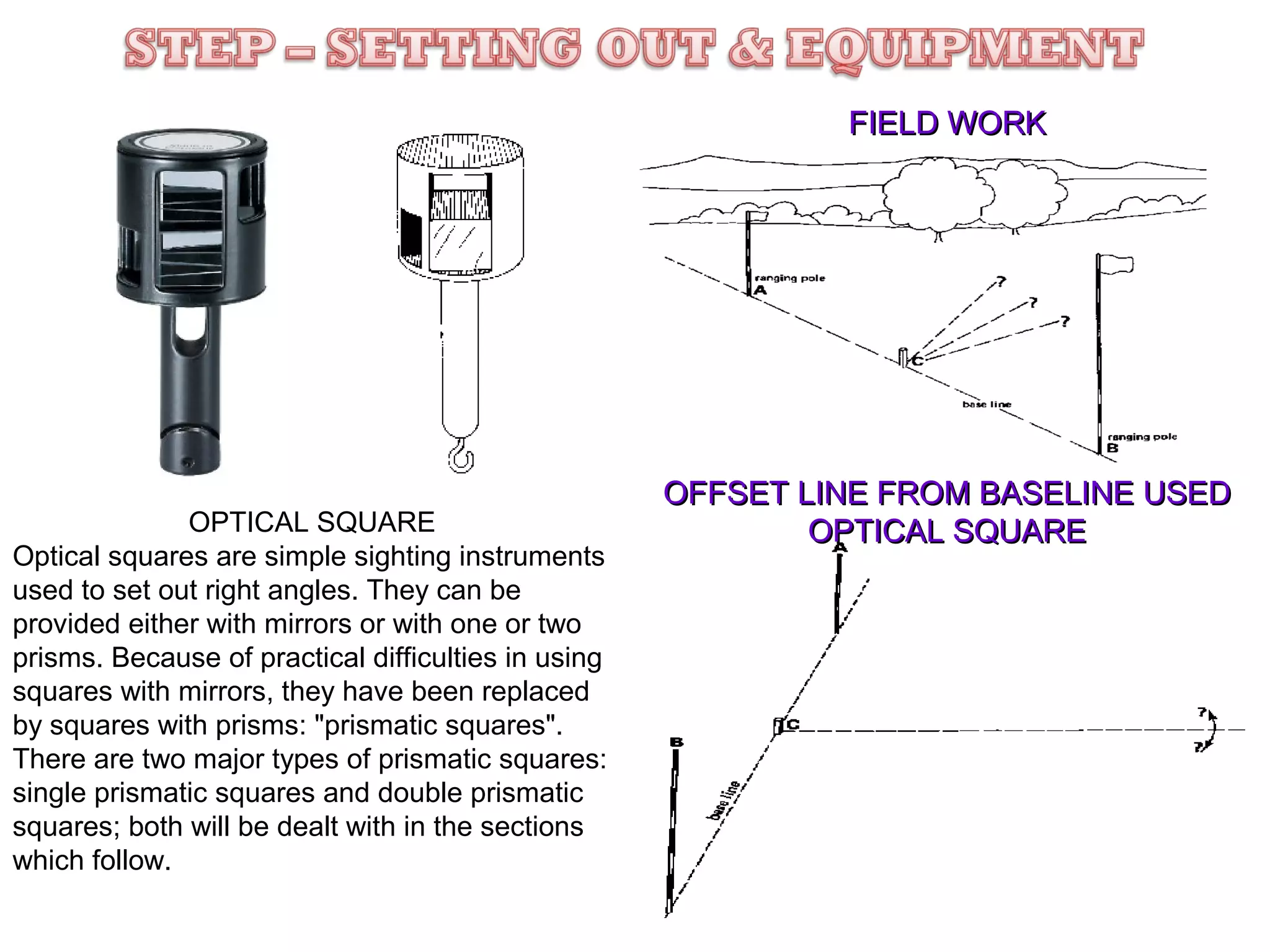
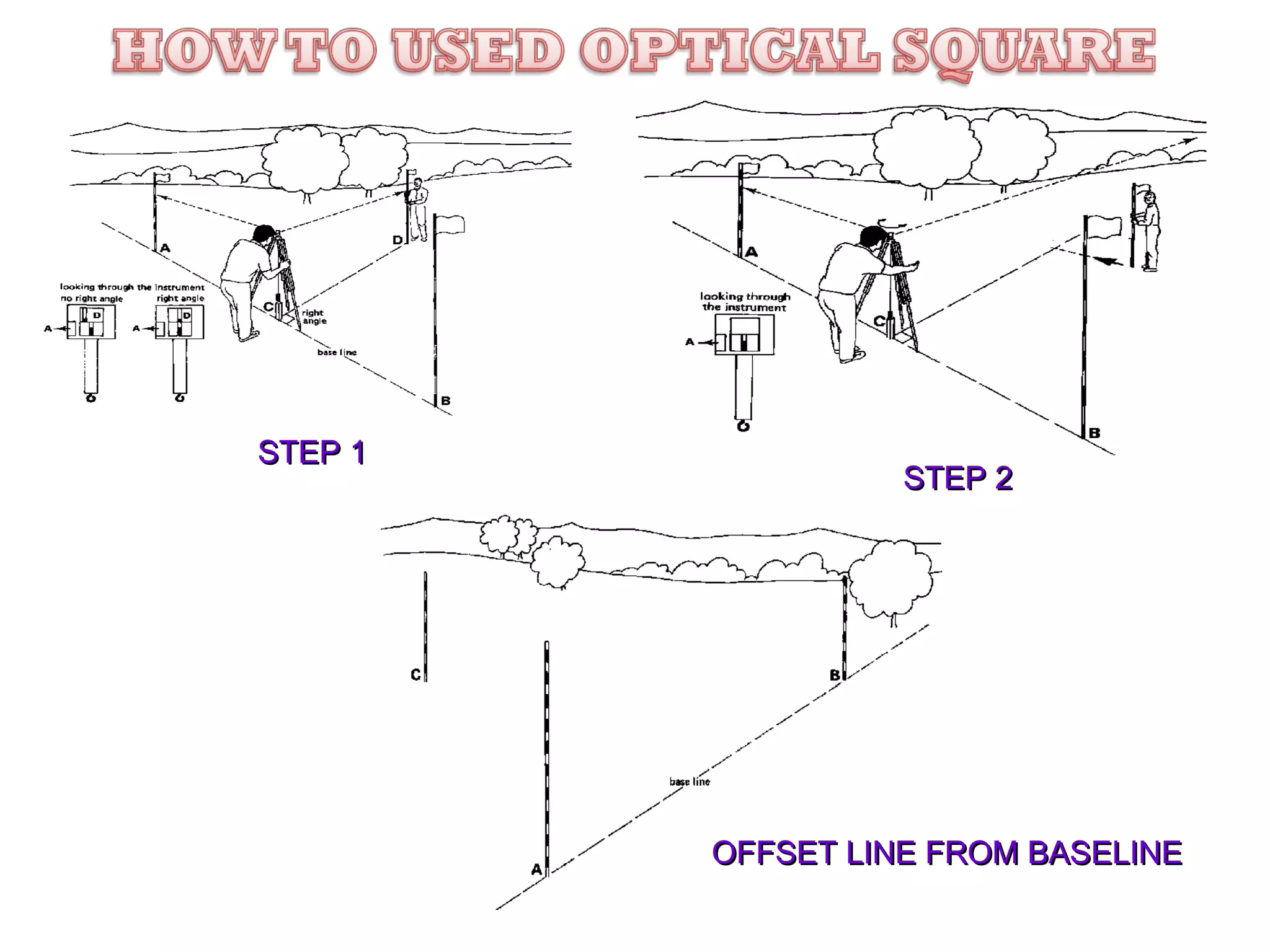
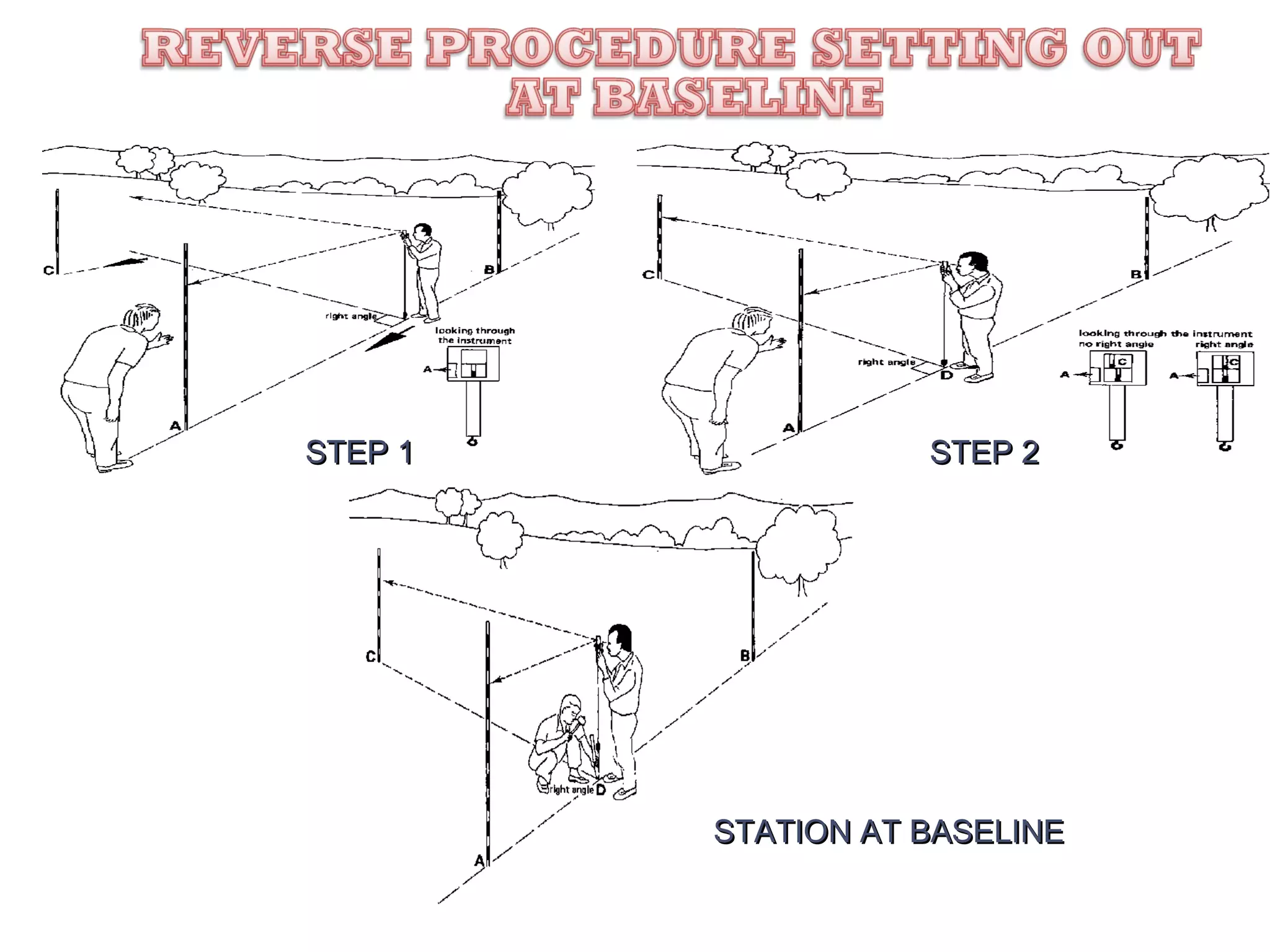
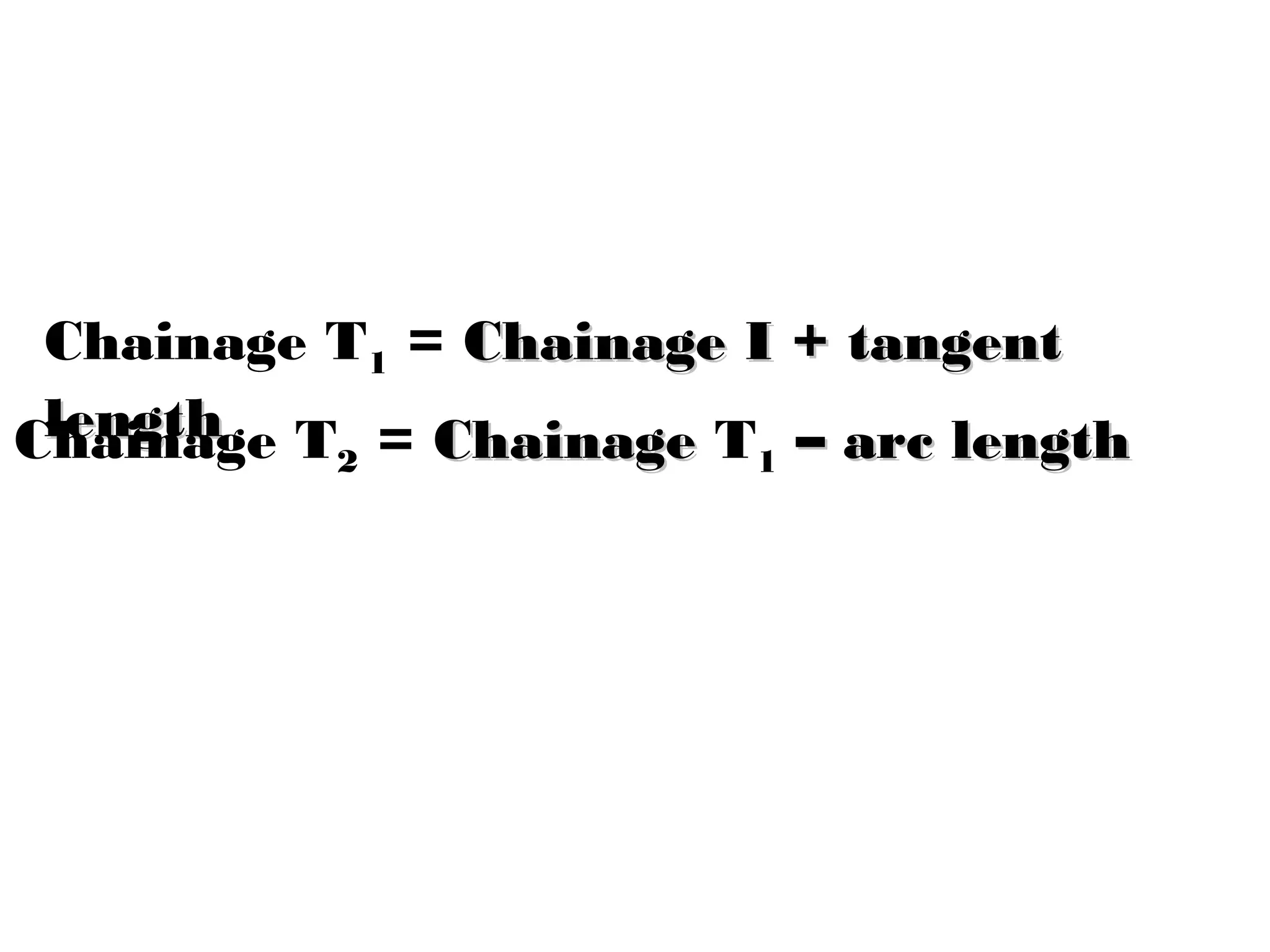Circular curves are used to connect two straight sections of roads, railways, or other infrastructure. There are several common methods for setting out circular curves in the field, including using offsets from the tangent line, offsets from the long chord line, or using deflection angles. Field work involves using tools like optical squares and tapes to accurately mark the curve based on the chosen setting out method. Practical exercises and field work provide opportunities to apply these techniques hands-on.