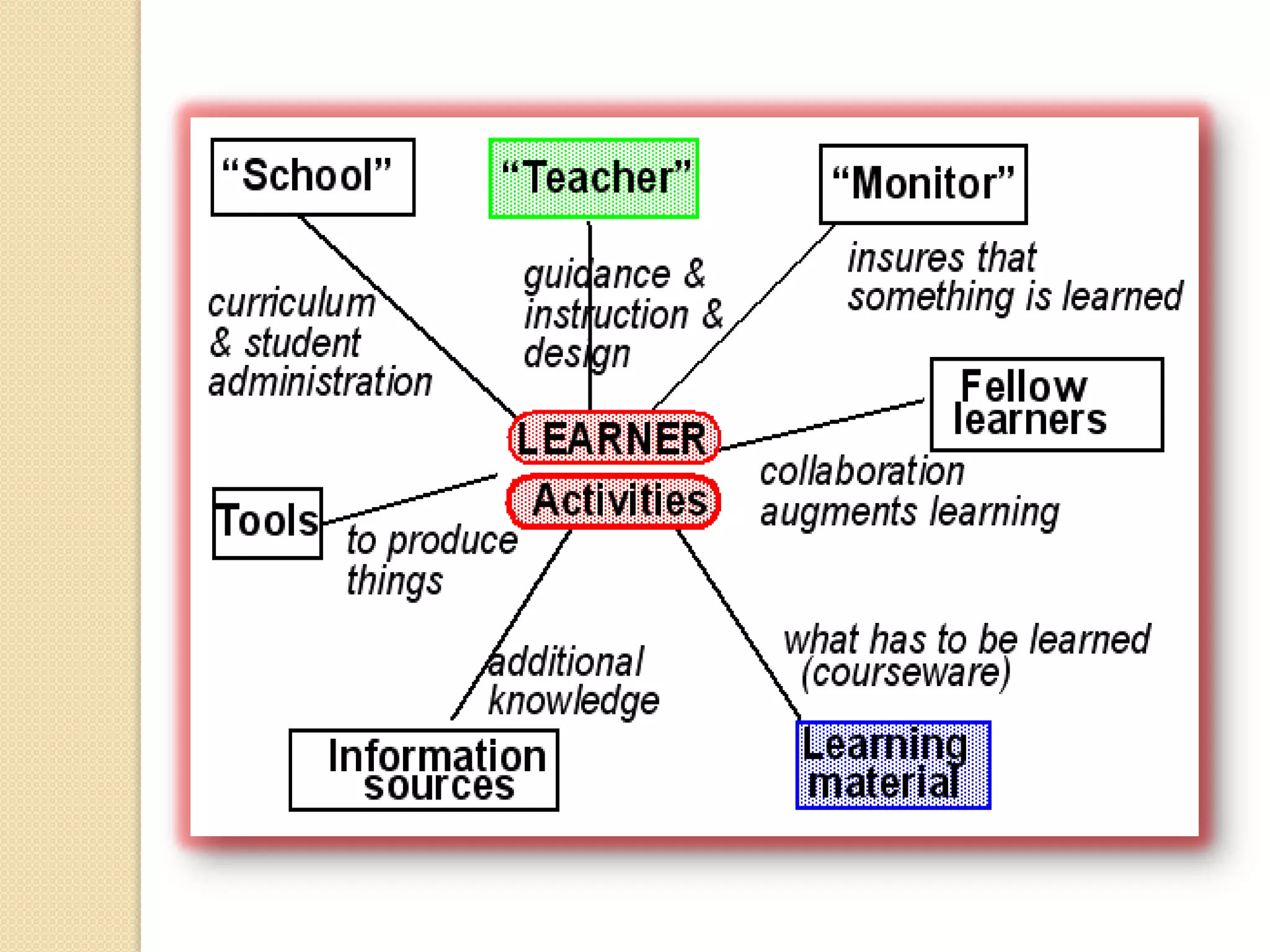
The document discusses the learning environment and its key components. It states that the learning environment refers to the whole range of components and activities where learning takes place. It includes the physical classroom space as well as instructional features, tools, resources, and interactions that facilitate learning. An ideal learning environment is constructivist in nature, engages learners through hands-on activities, and provides scaffolds and support to help students problem solve.