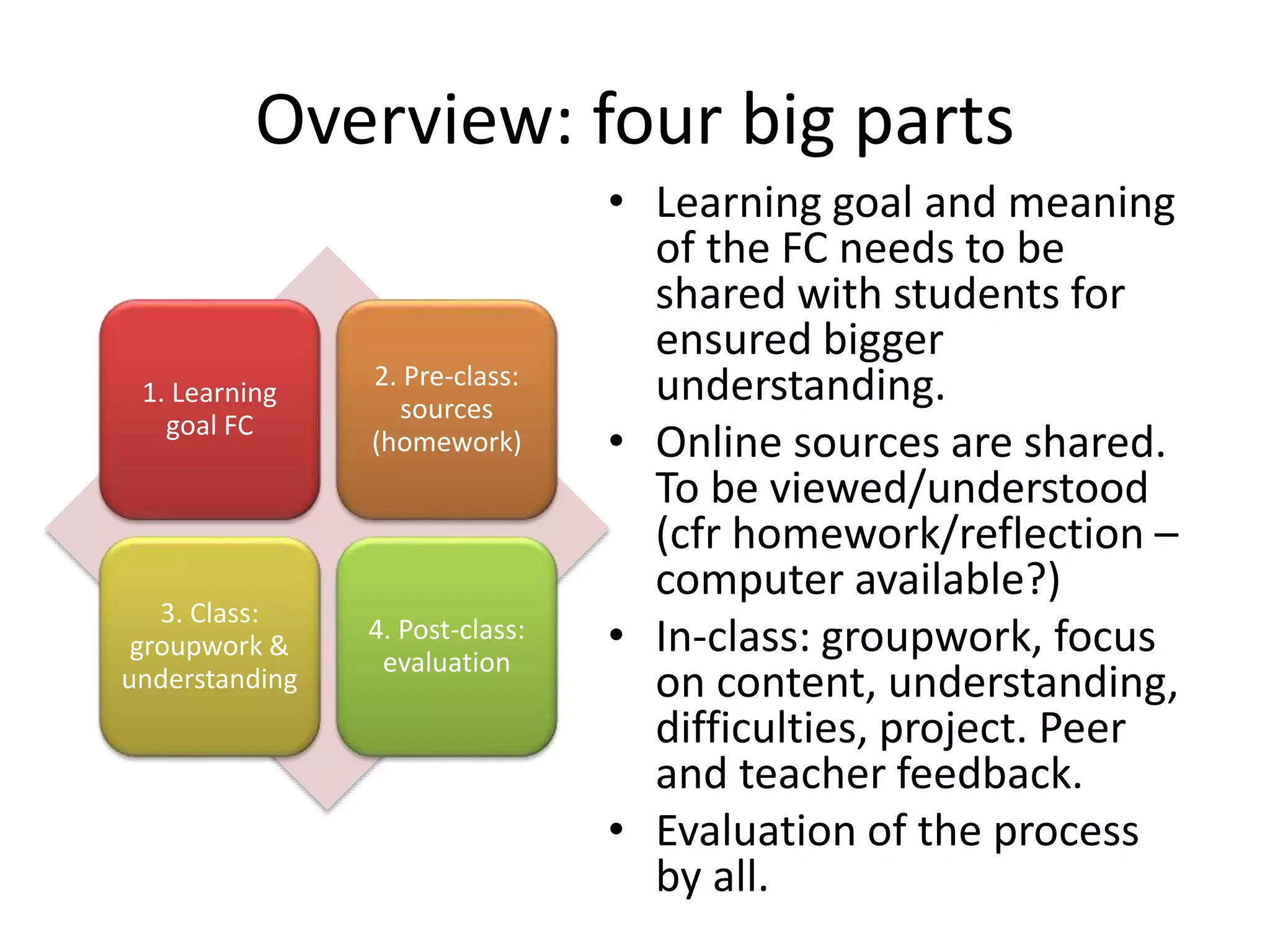
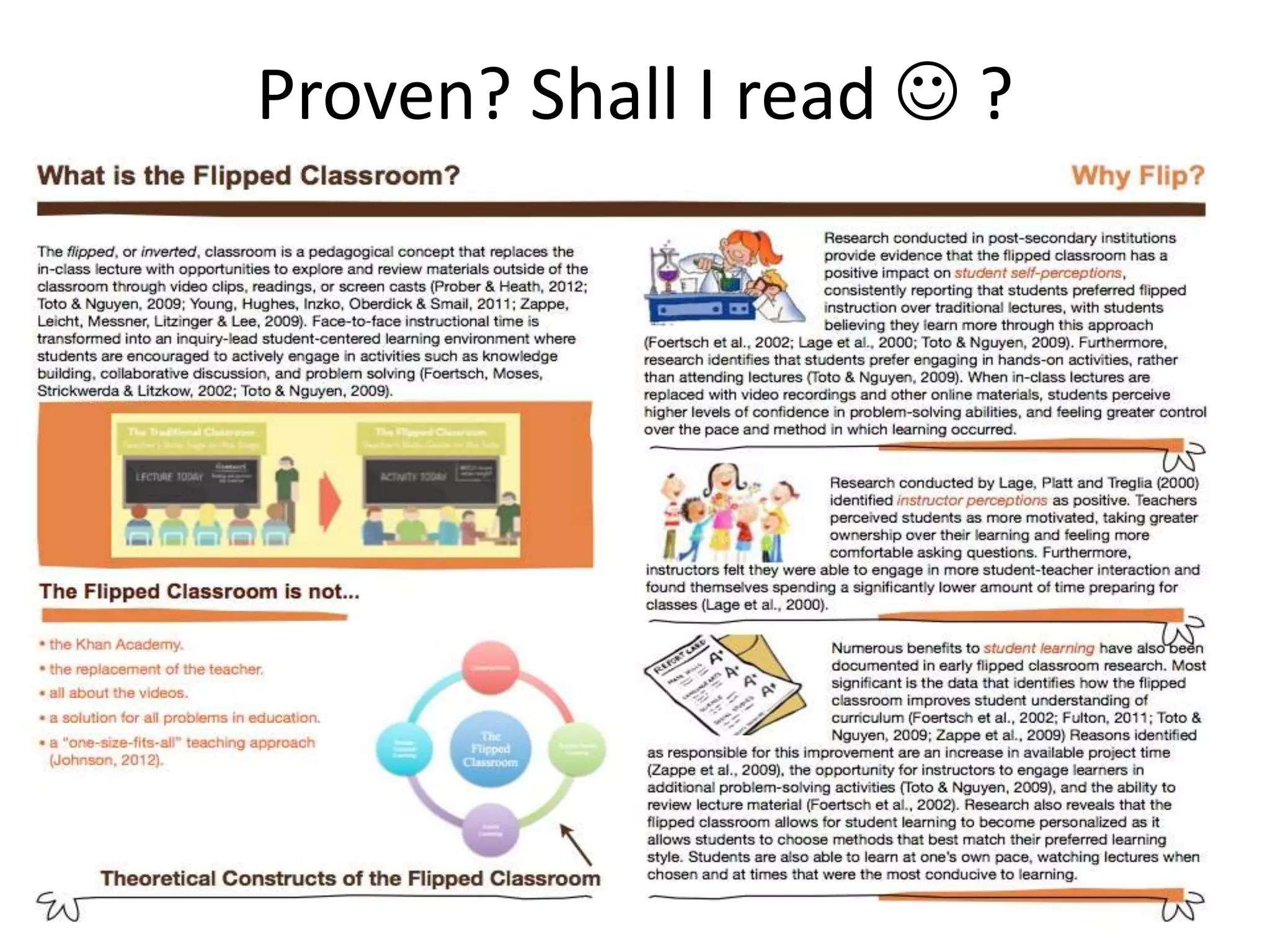
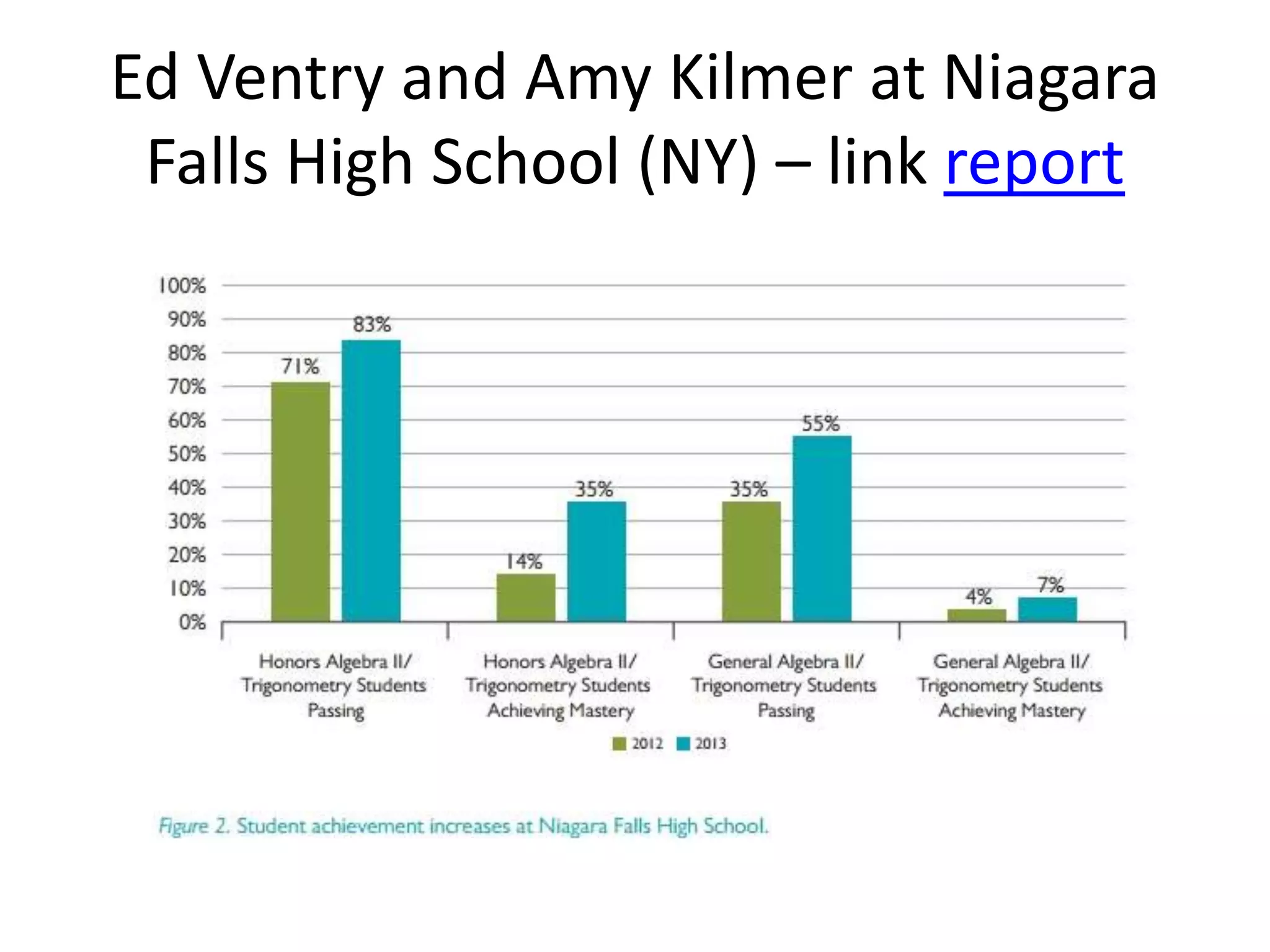
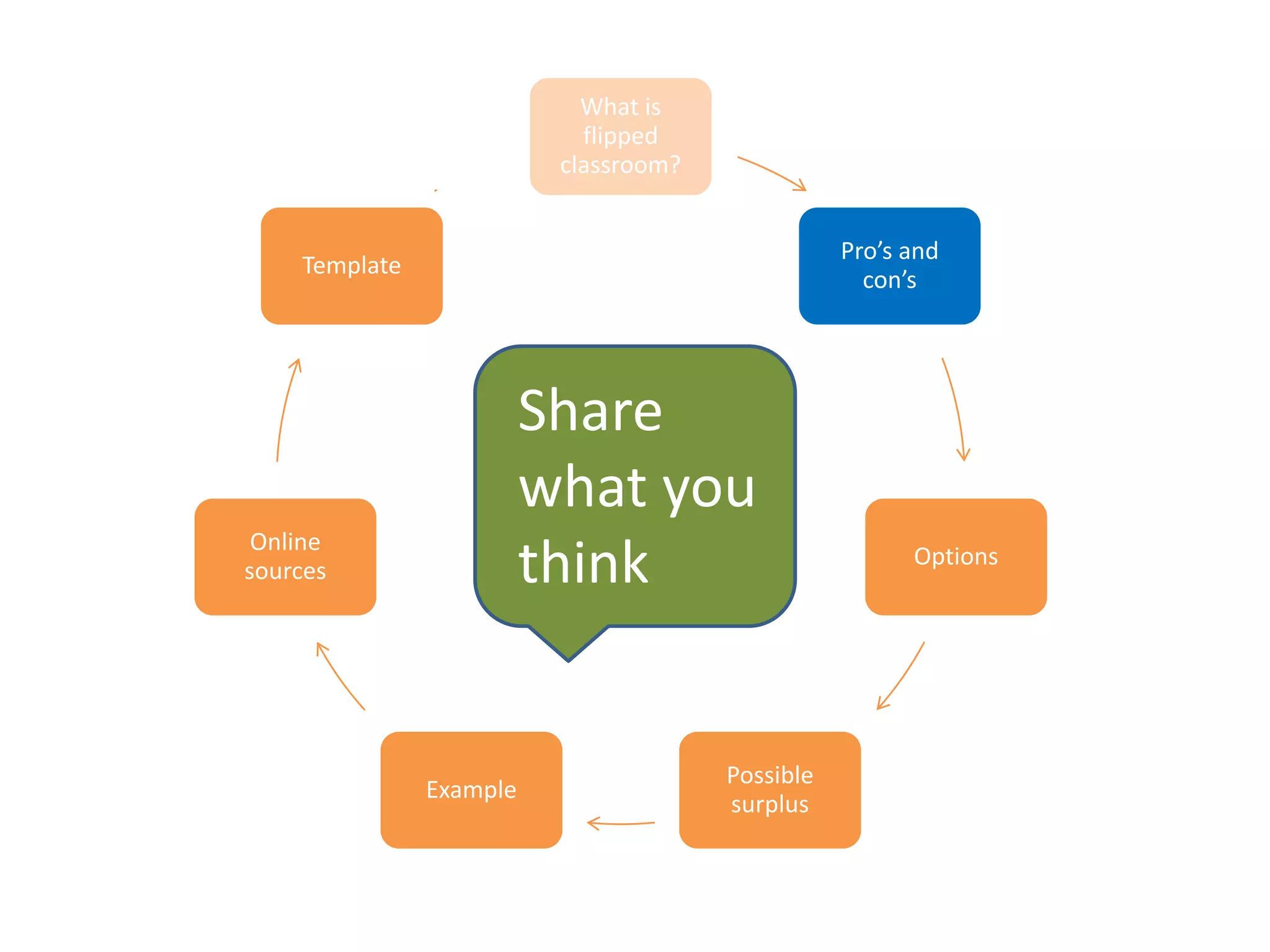
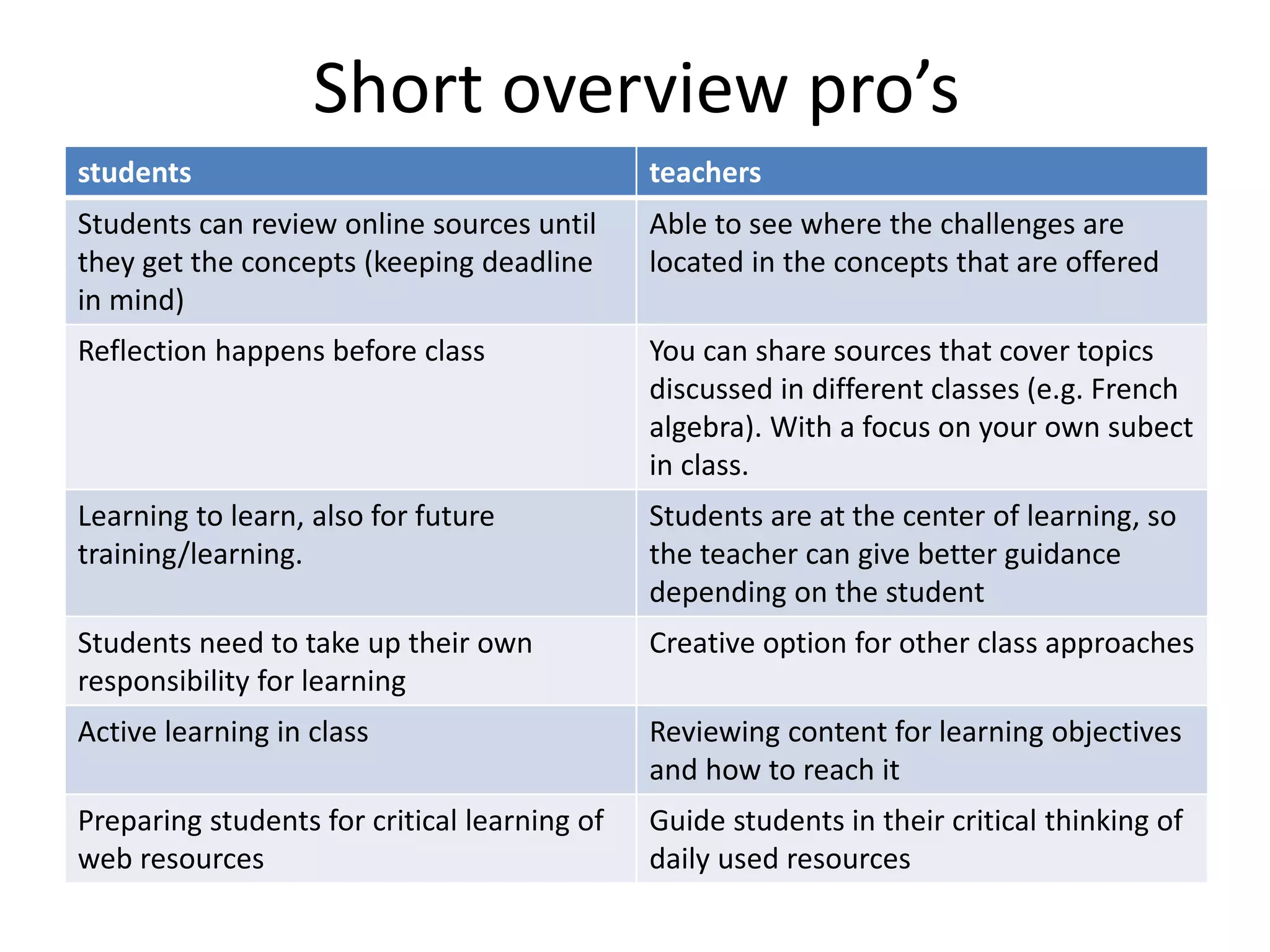
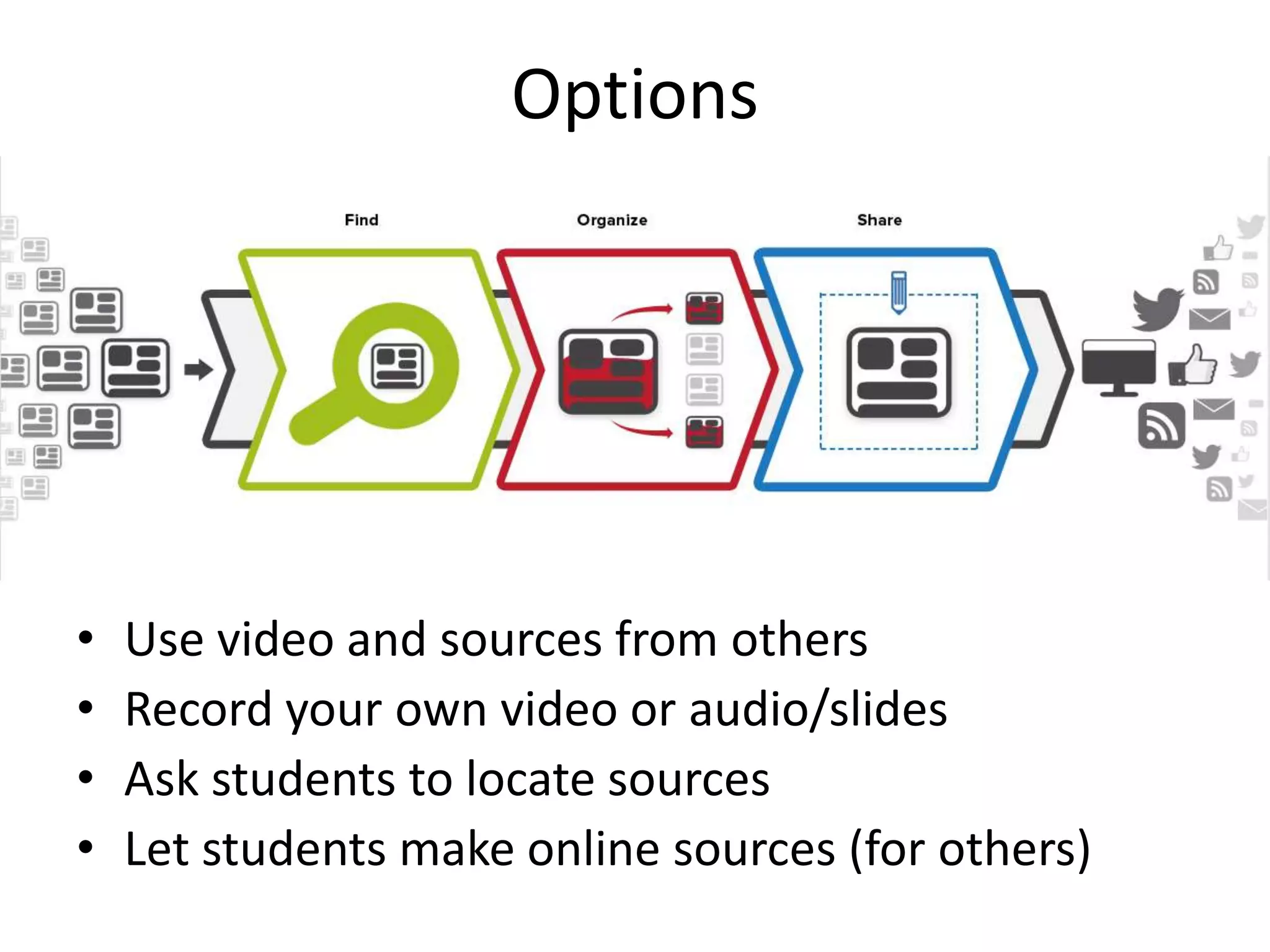
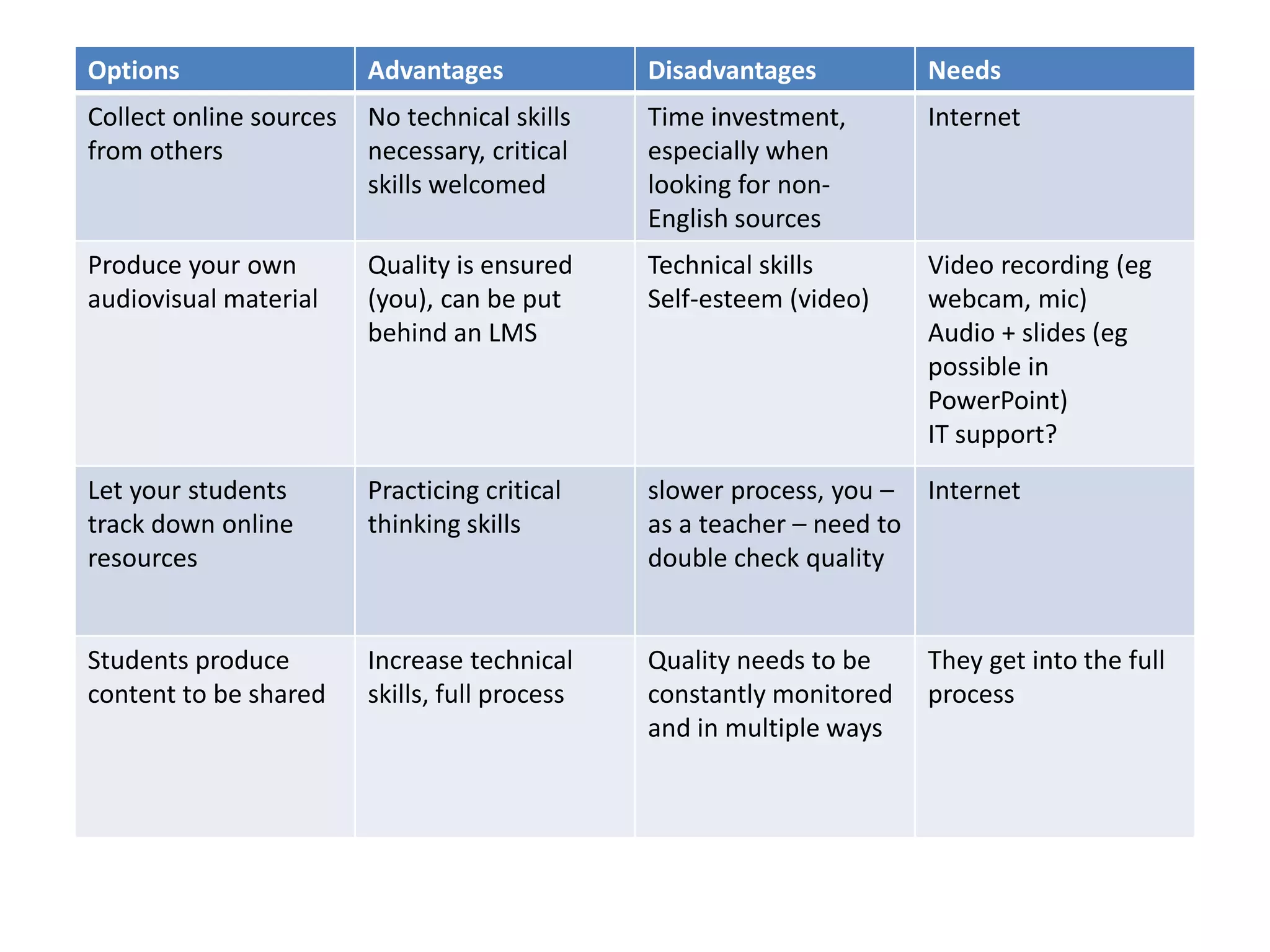
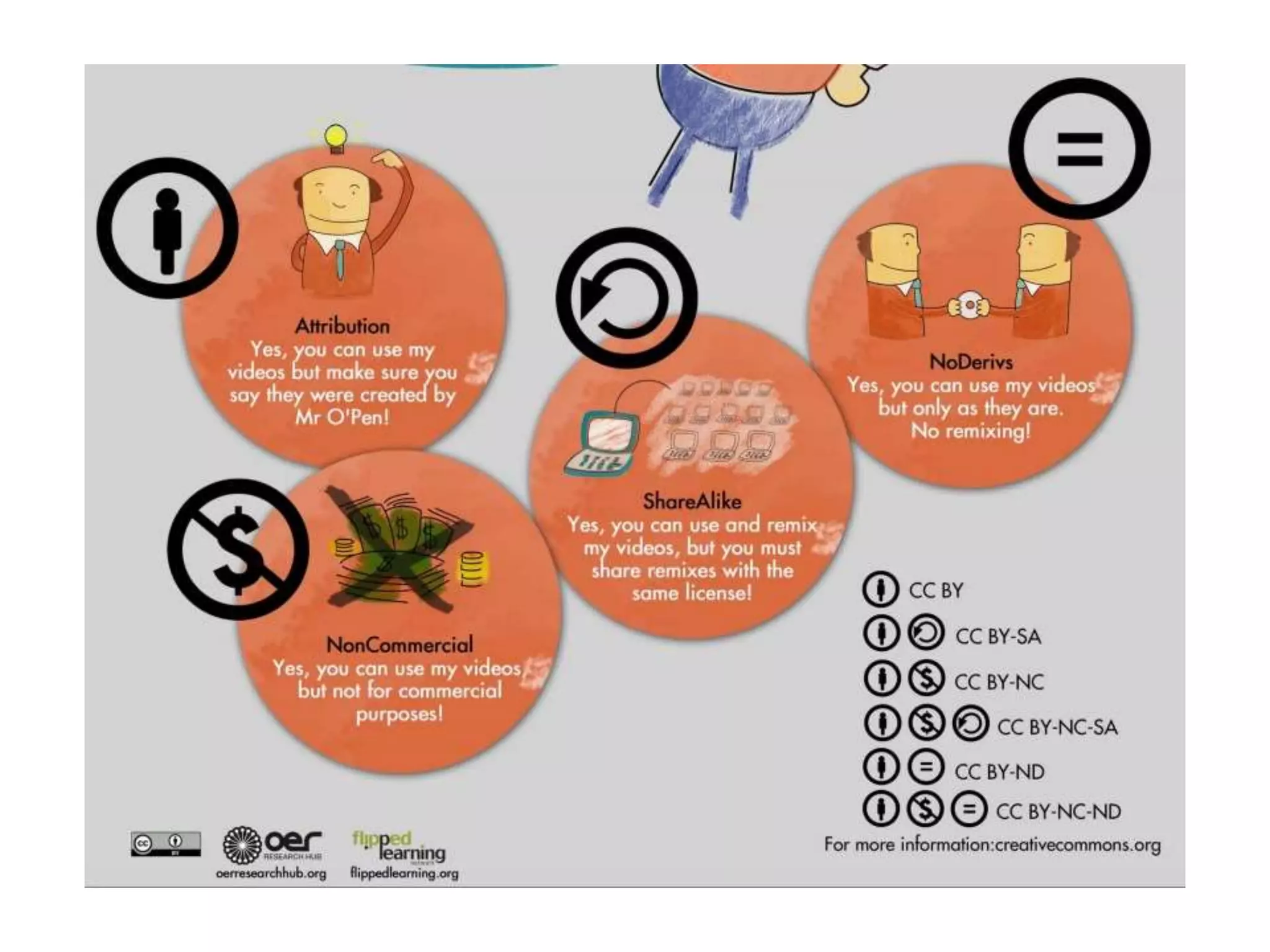
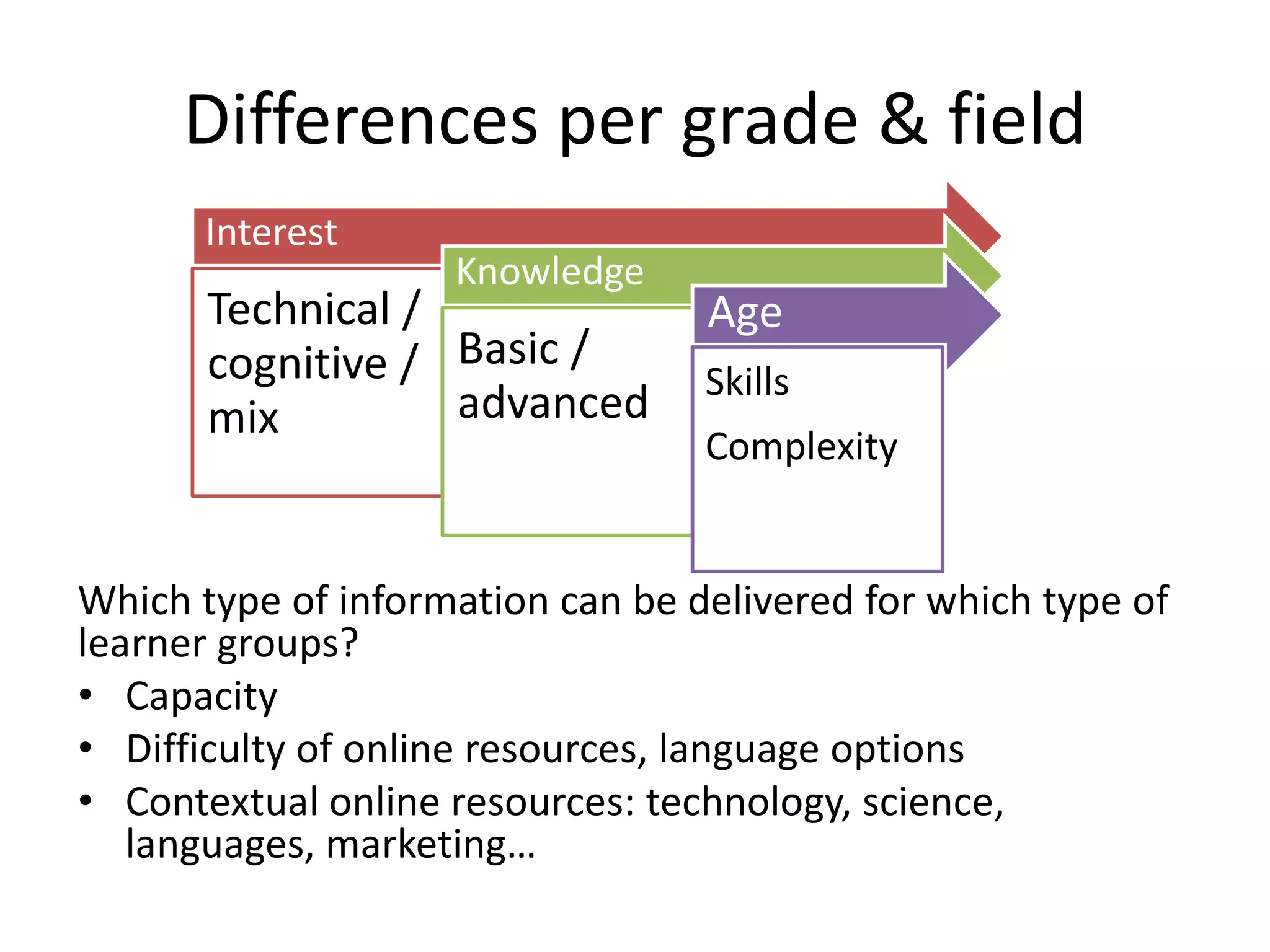
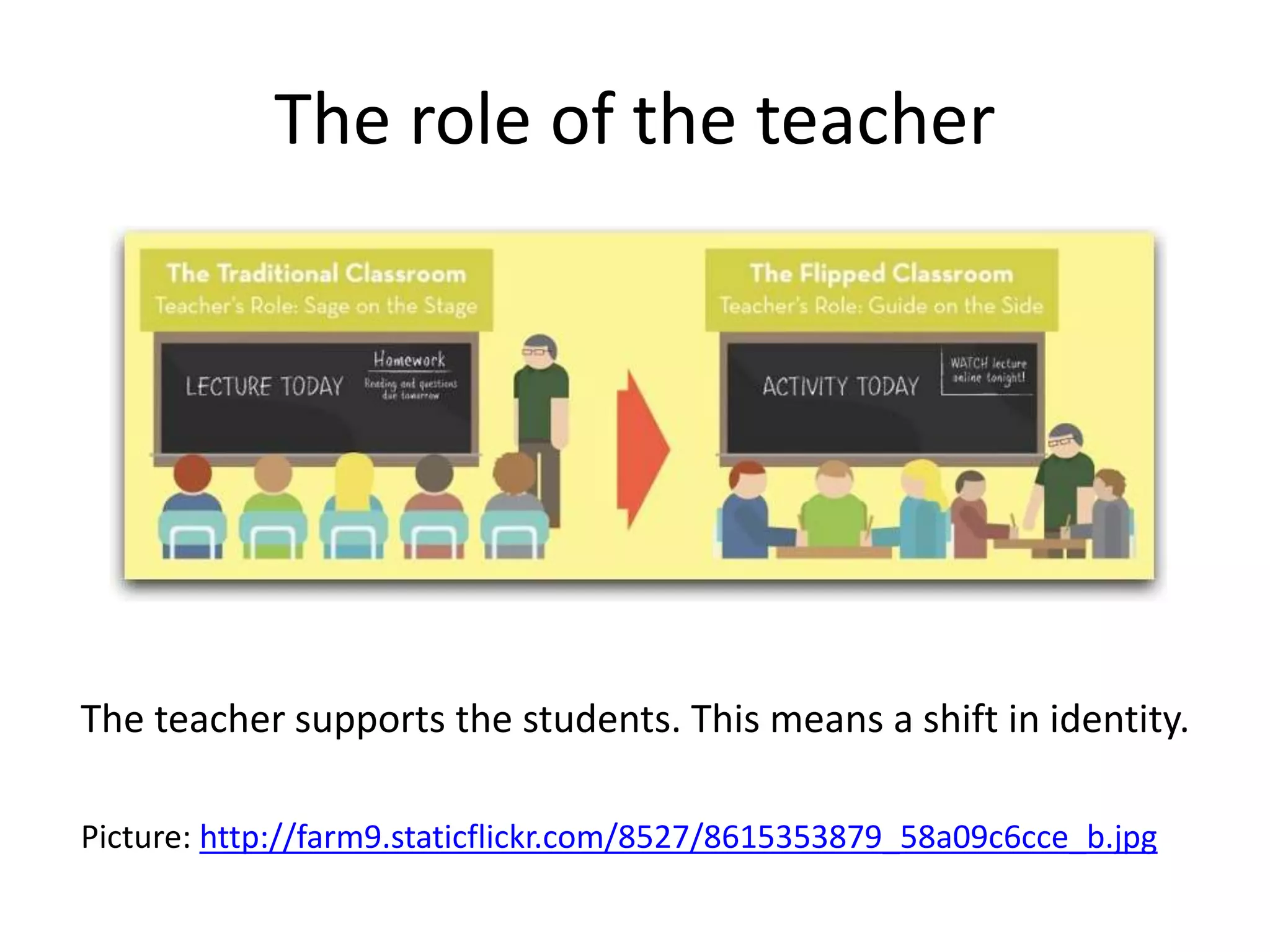
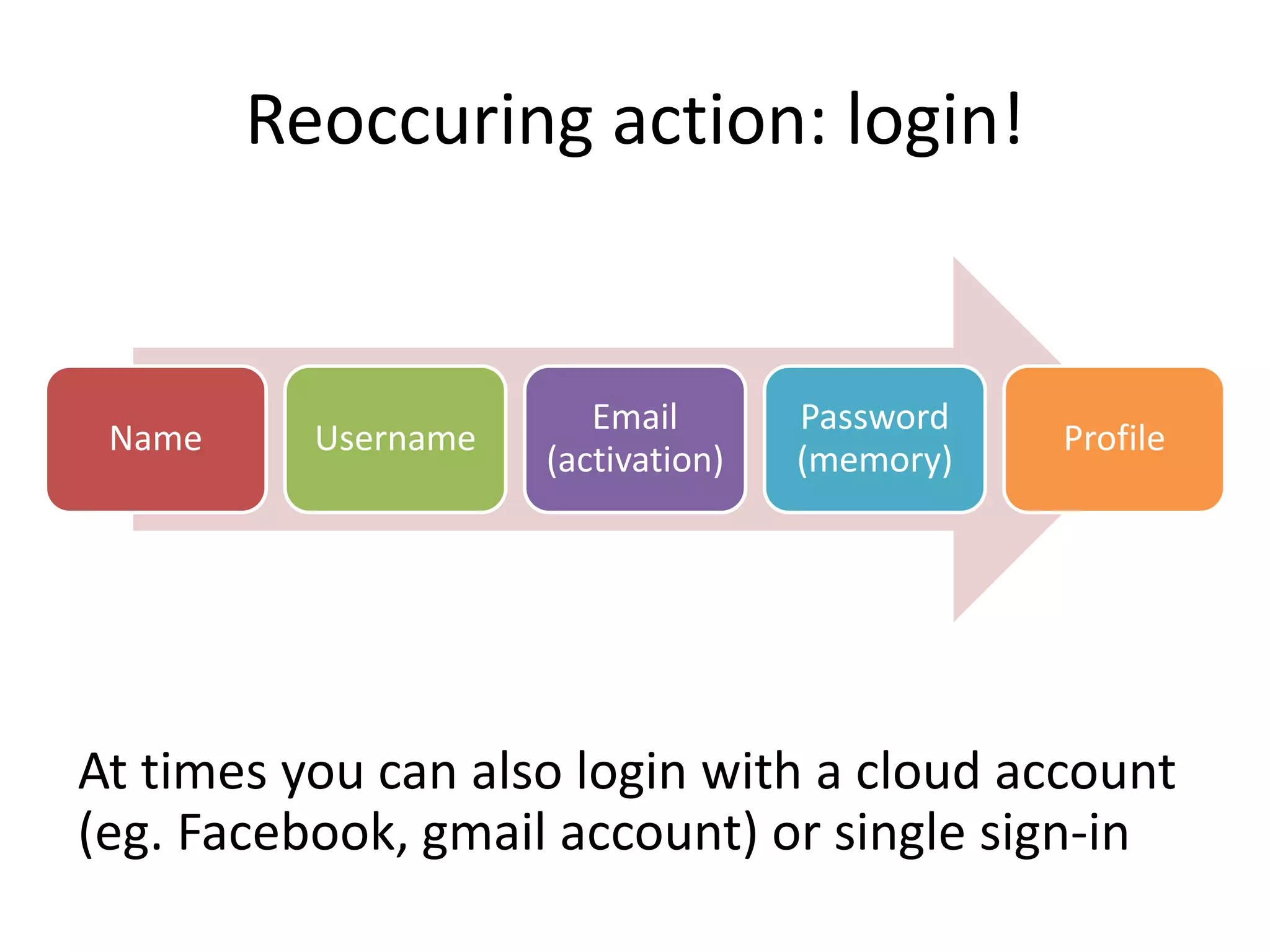
The document provides an overview of the flipped classroom model, detailing its origins, benefits, and challenges. It emphasizes the importance of student-centered learning, where students engage with online resources before class and utilize classroom time for interactive activities. Various options for implementing the flipped classroom approach are discussed, alongside the necessary considerations regarding resource selection and teacher preparation time.