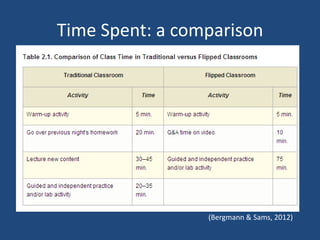
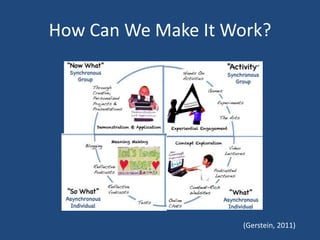
The document defines the flipped classroom model as one where traditional lecture content is delivered at home via video and class time is used for applied learning activities. It explores how this changes the instructional landscape by making the home the lecture space and class the collaboration/problem solving space. Potential benefits discussed include allowing students to work at their own pace and enabling teachers to spend more one-on-one time with students, though concerns about the digital divide and lack of interaction are also raised. The document provides resources for implementing flipped learning and encourages teachers to reflect on how it could enhance their lessons.