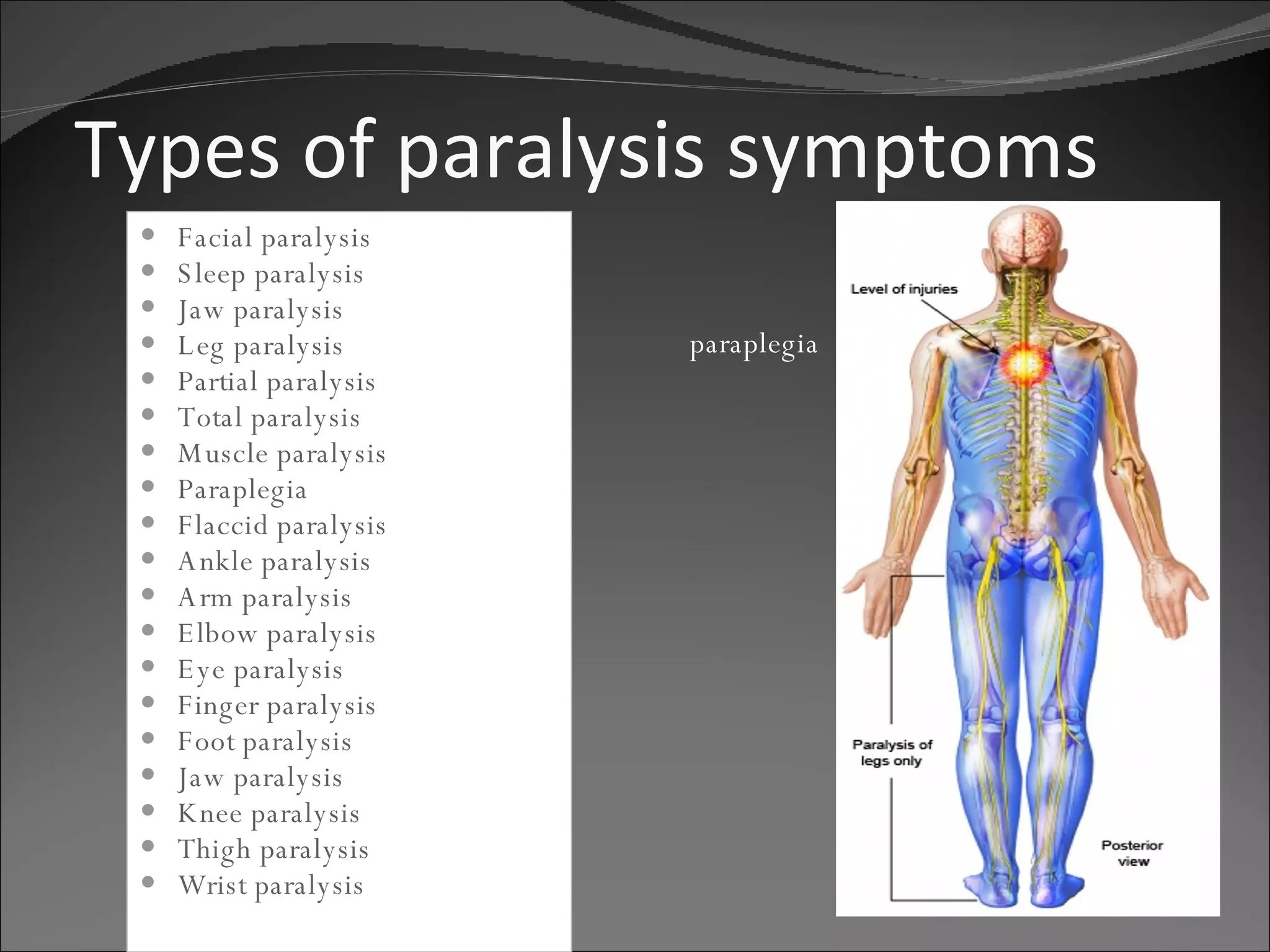
Paralysis is the complete loss of muscle function for one or more muscle groups and often includes loss of feeling in the affected area. It can be caused by damage to upper motor neurons, which convey signals from the brain to the nervous system, or lower motor neurons, which connect to muscles. Signs and symptoms depend on the location and severity of damage and may include numbness, tingling, pain, vision problems, speech difficulties, and breathing issues. Treatments focus on physical and occupational therapy to regain mobility, muscle strength, and independence through techniques like range of motion exercises and home modifications.