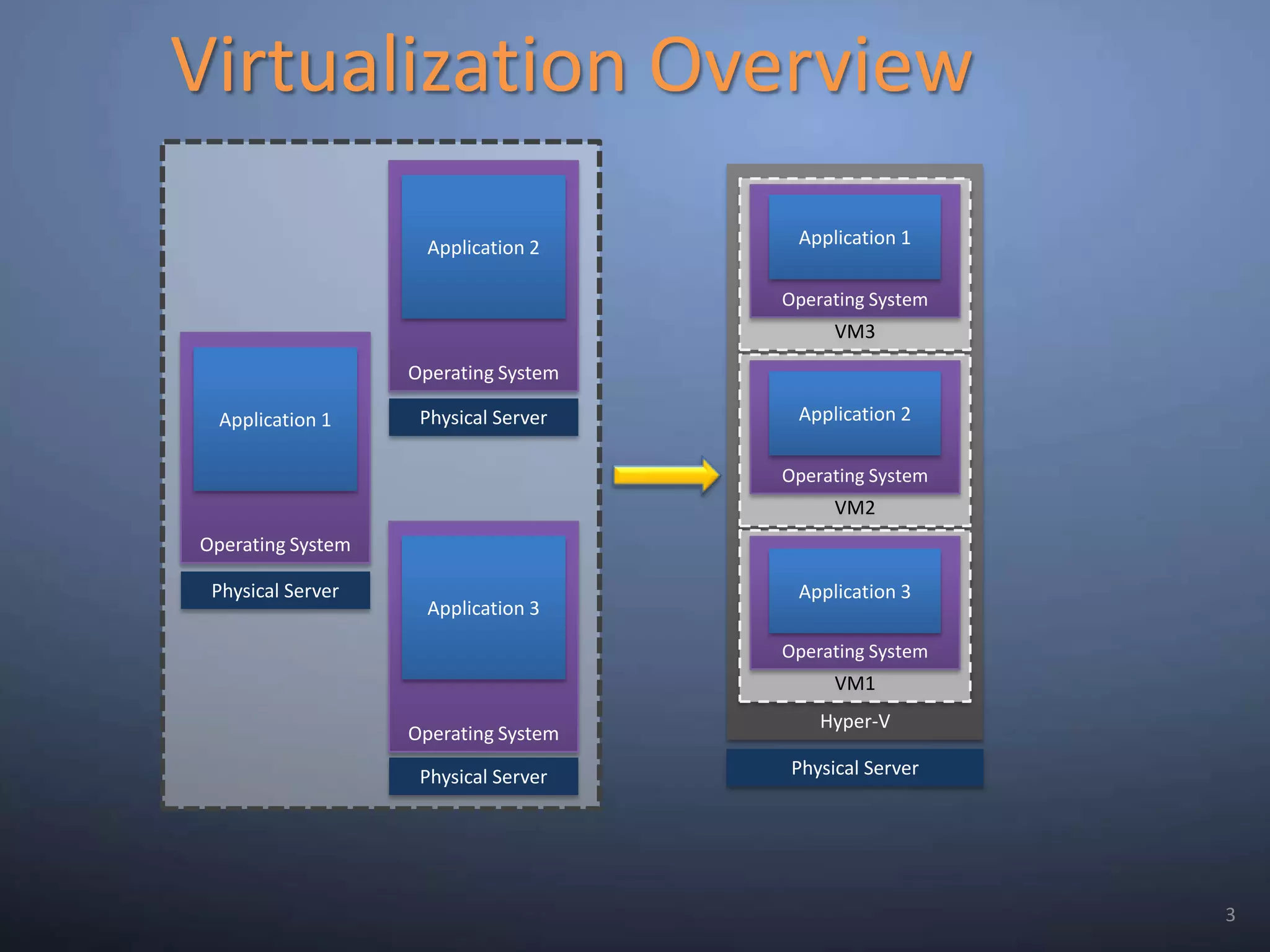
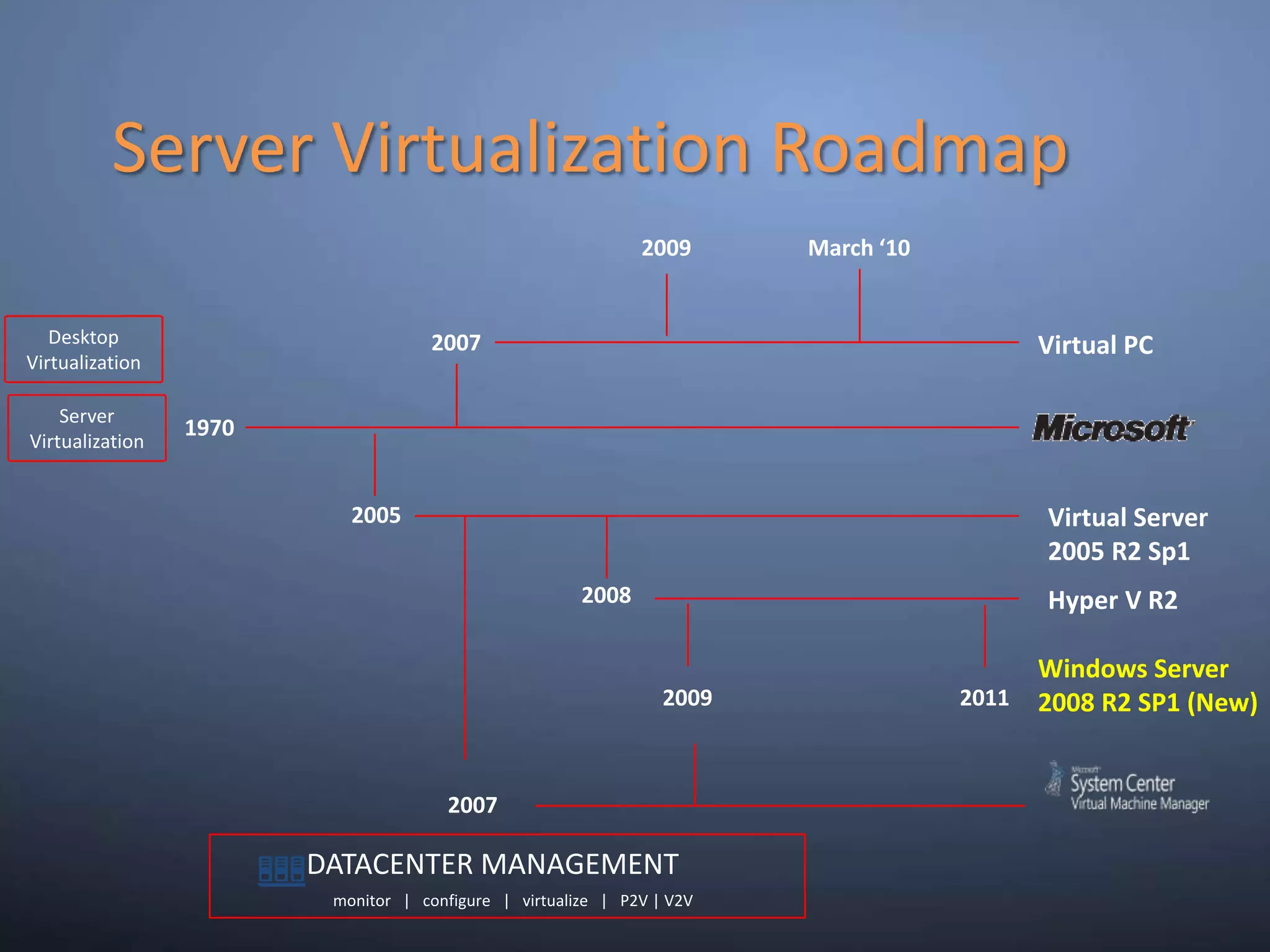
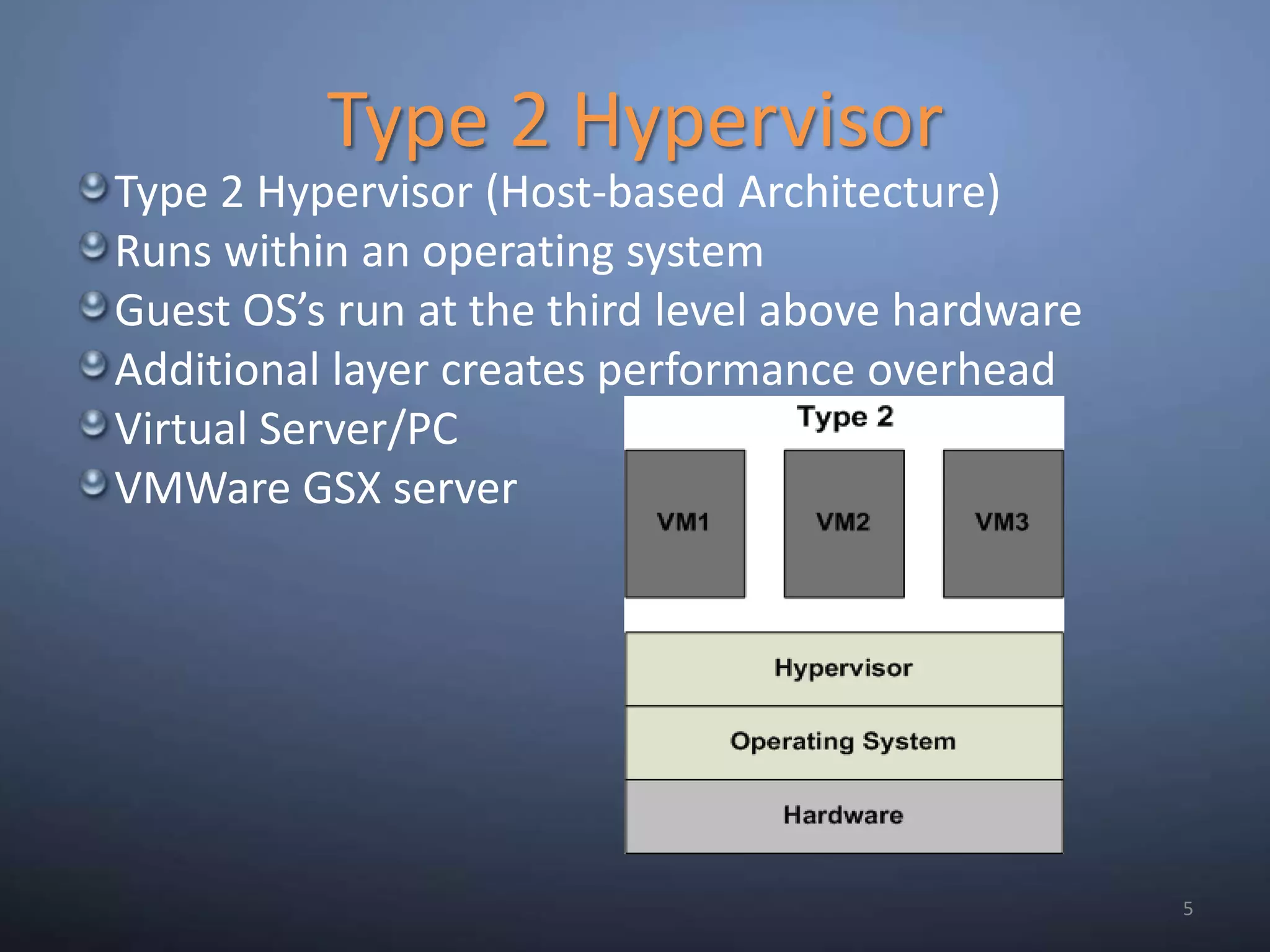
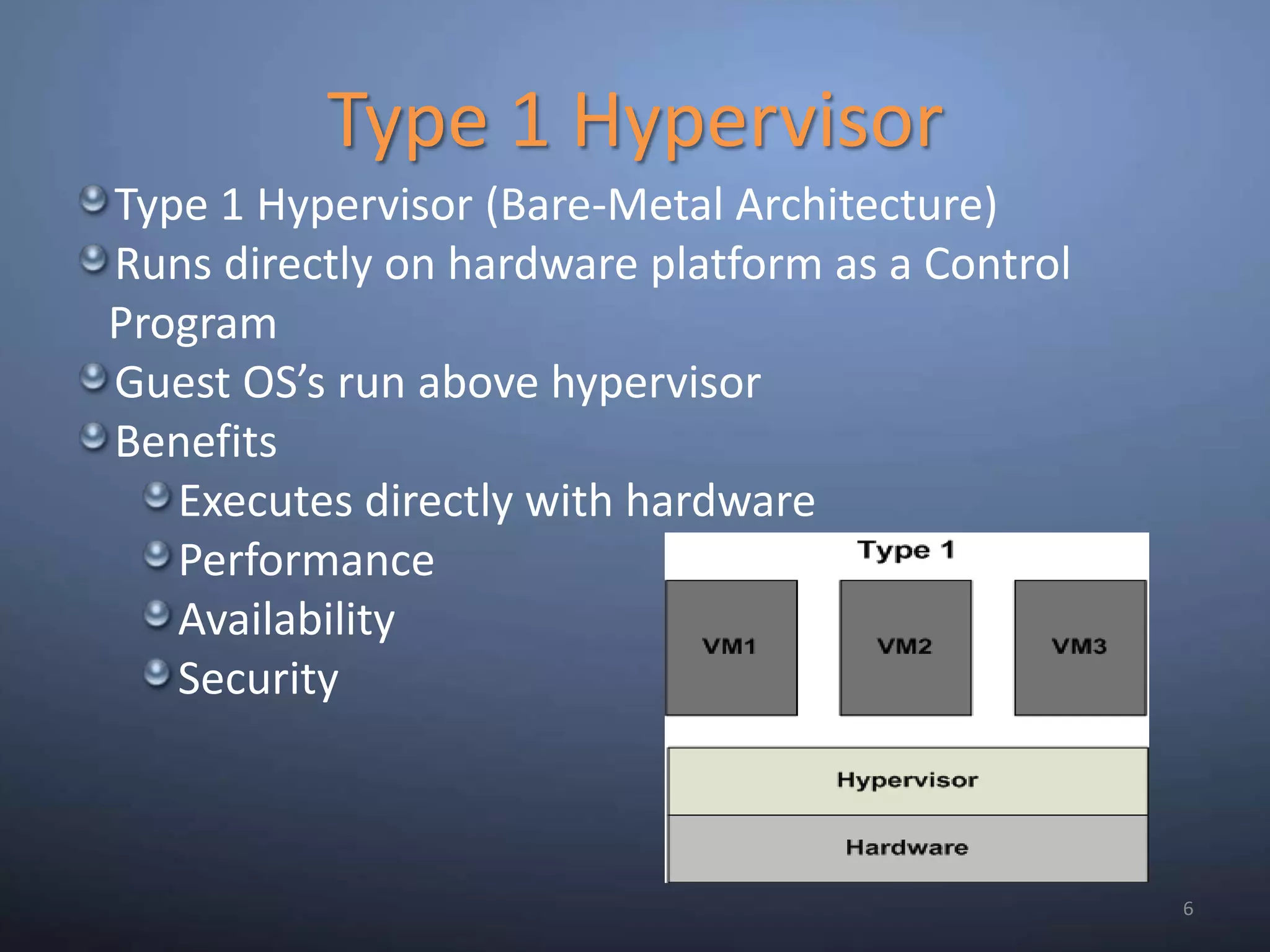
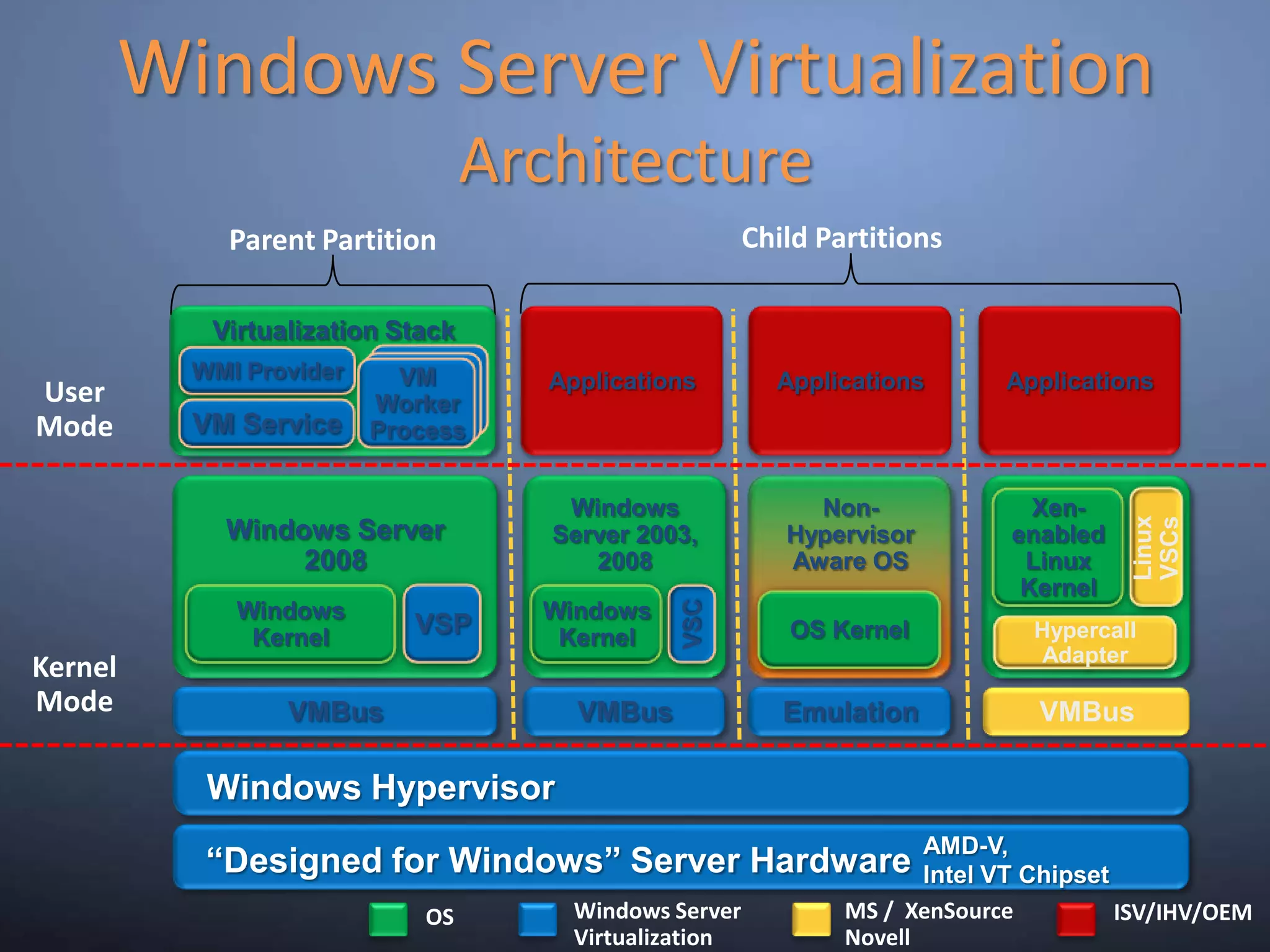
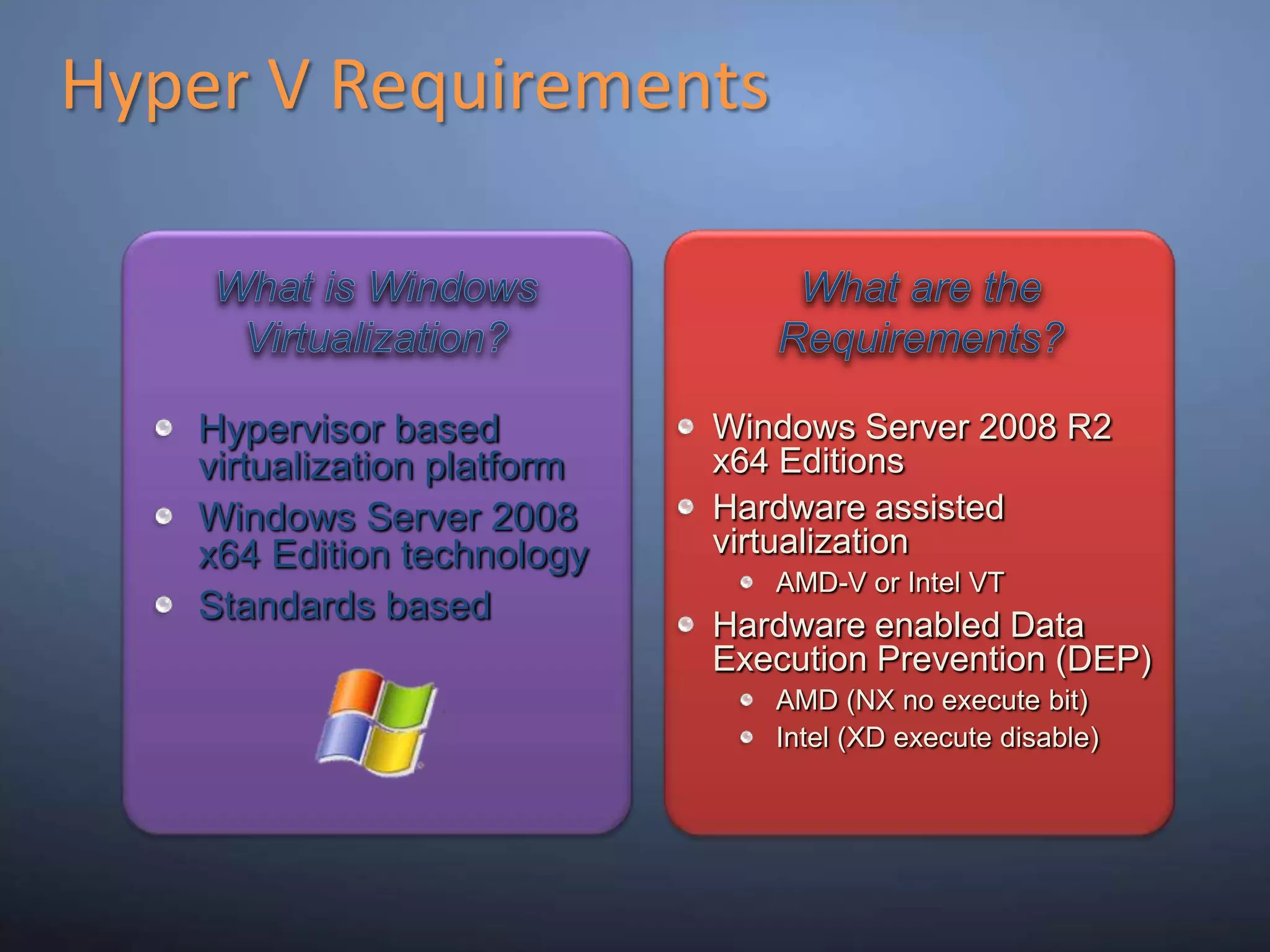
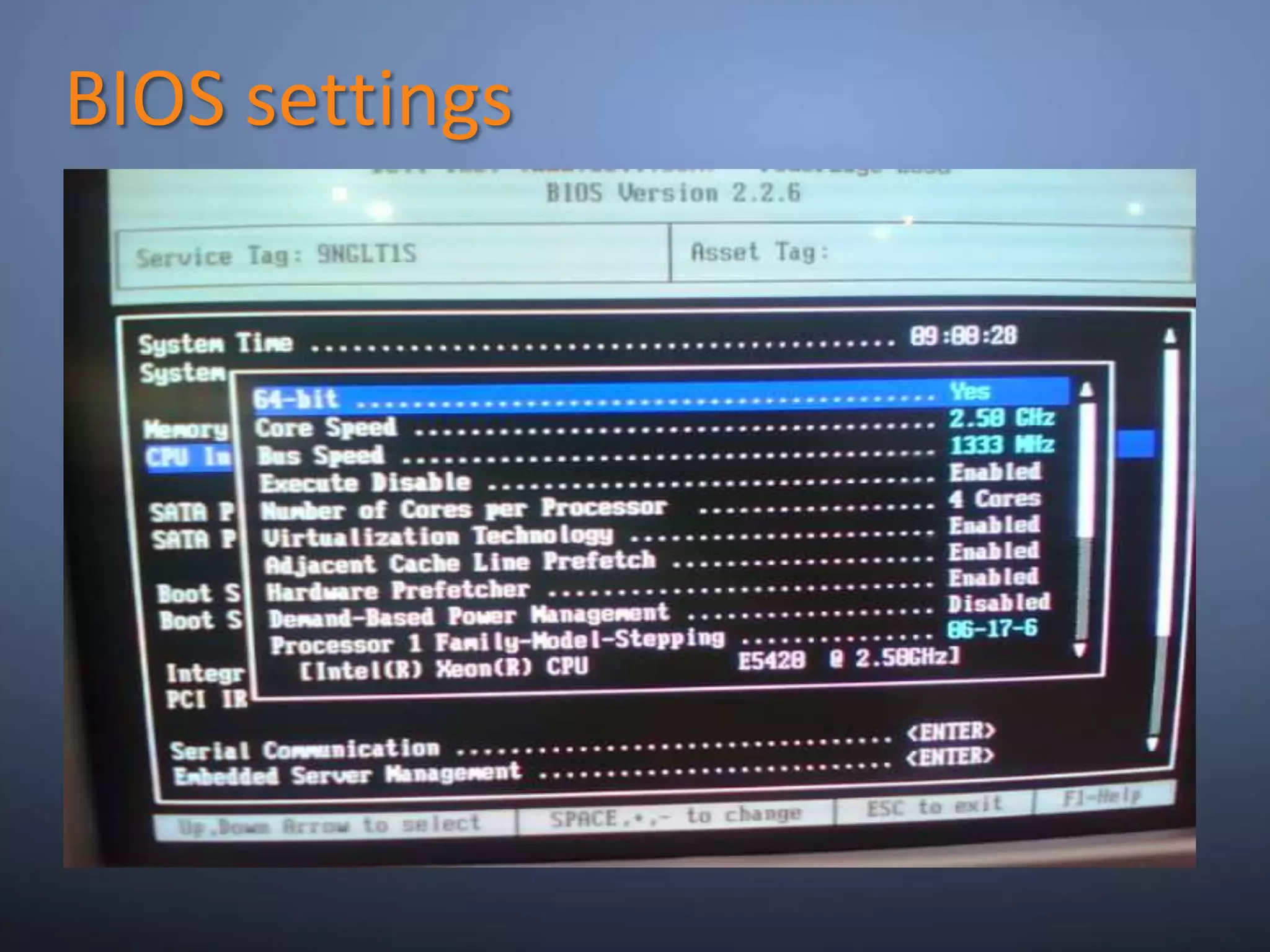
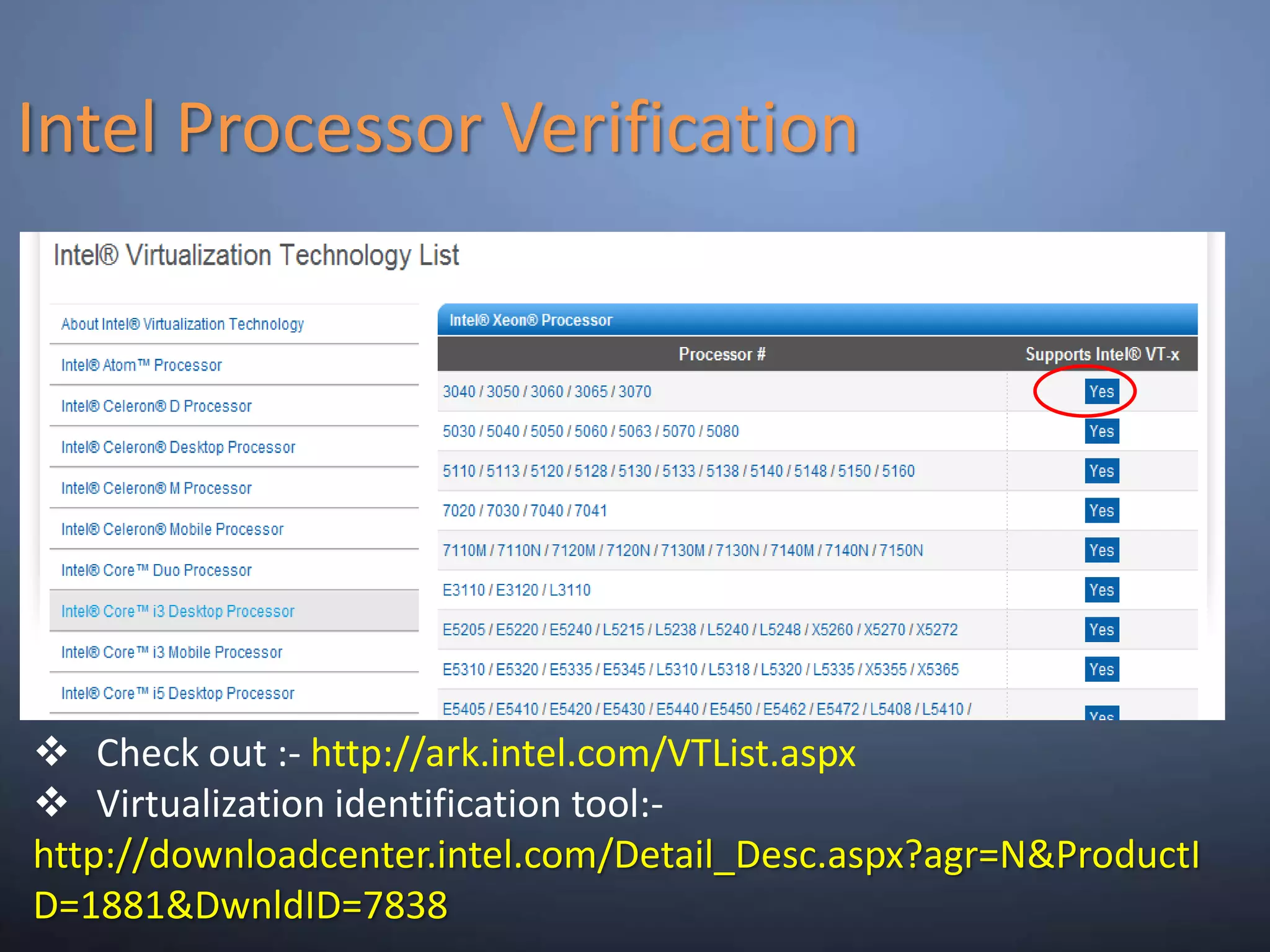
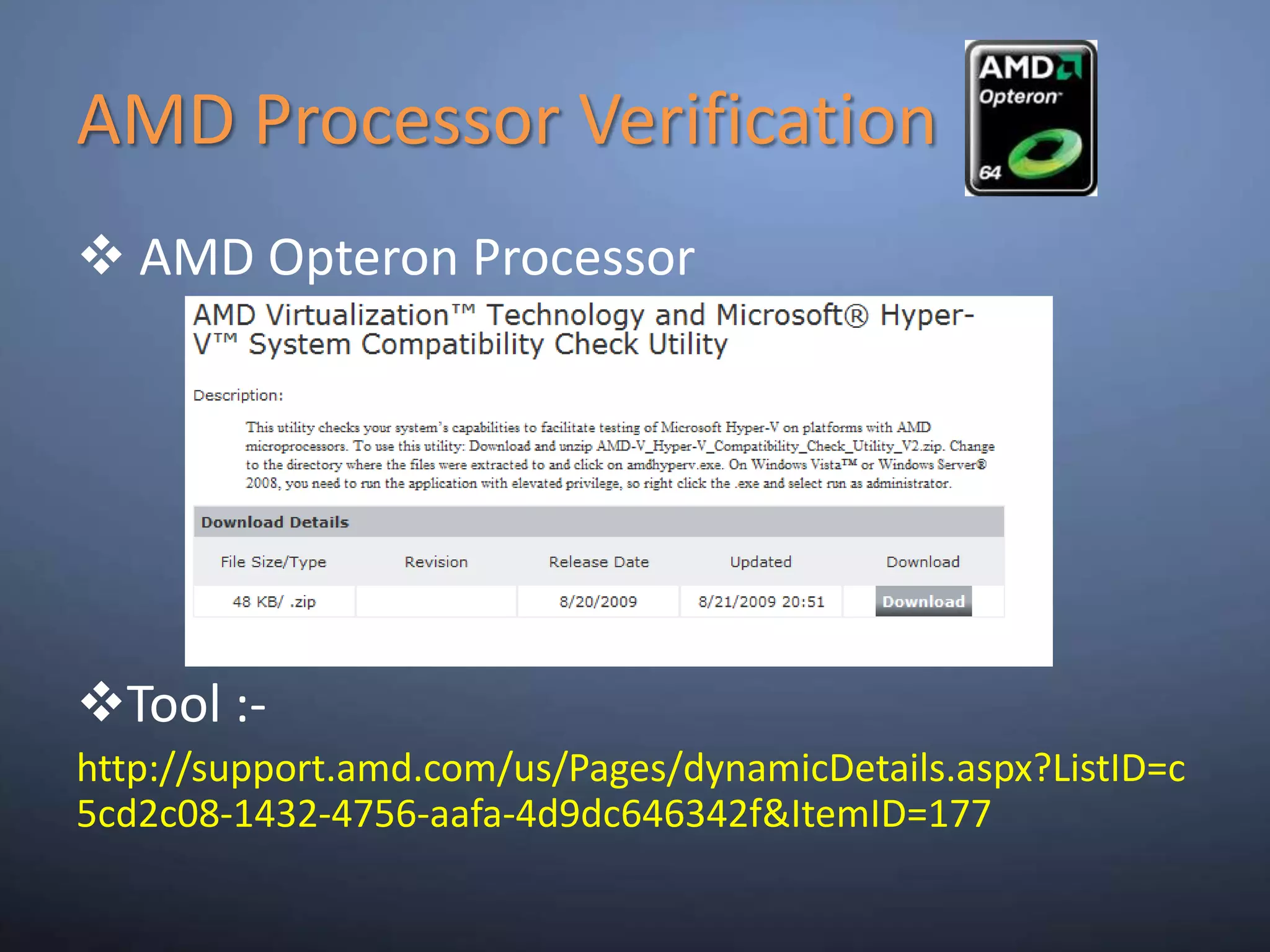
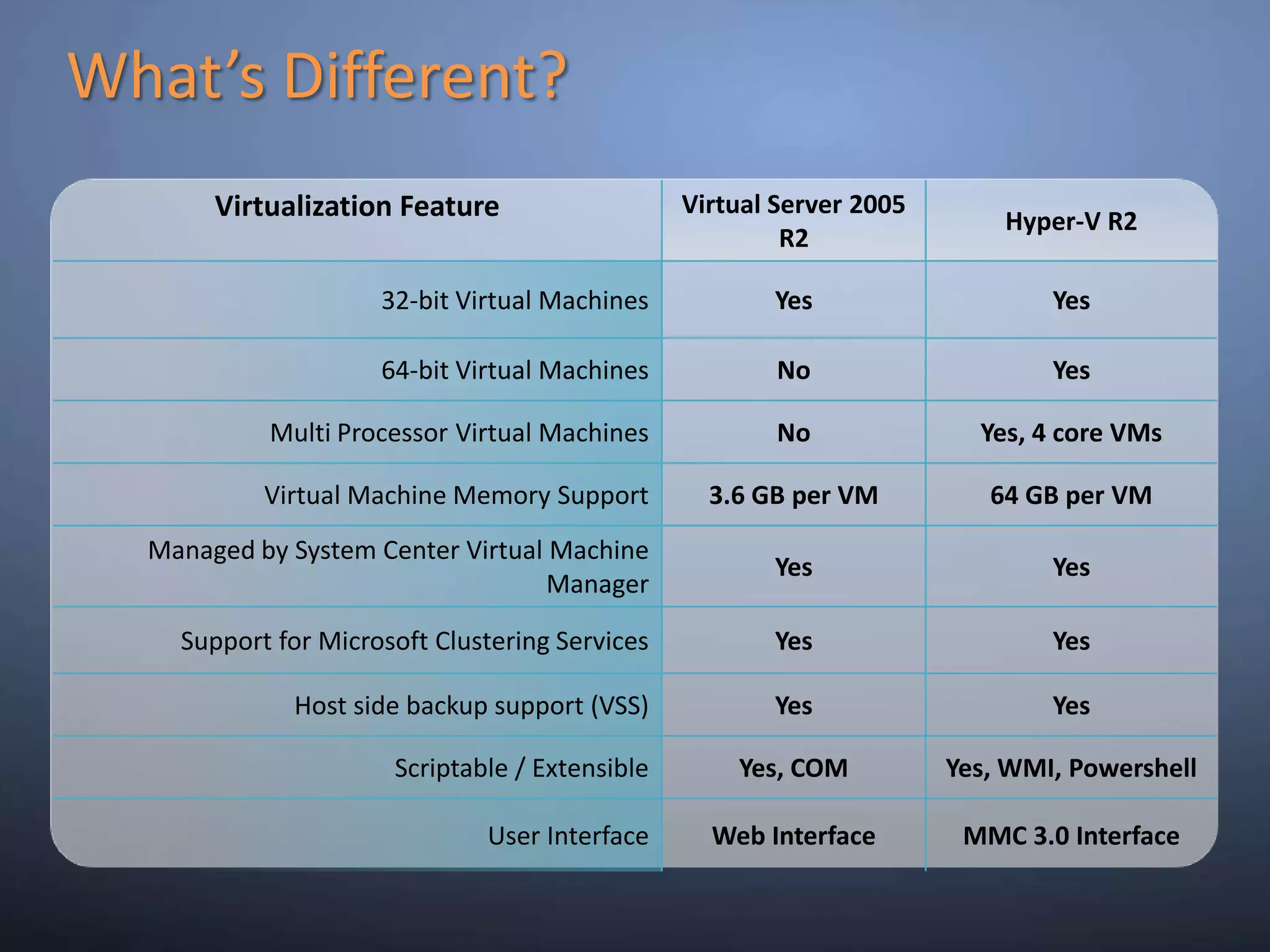
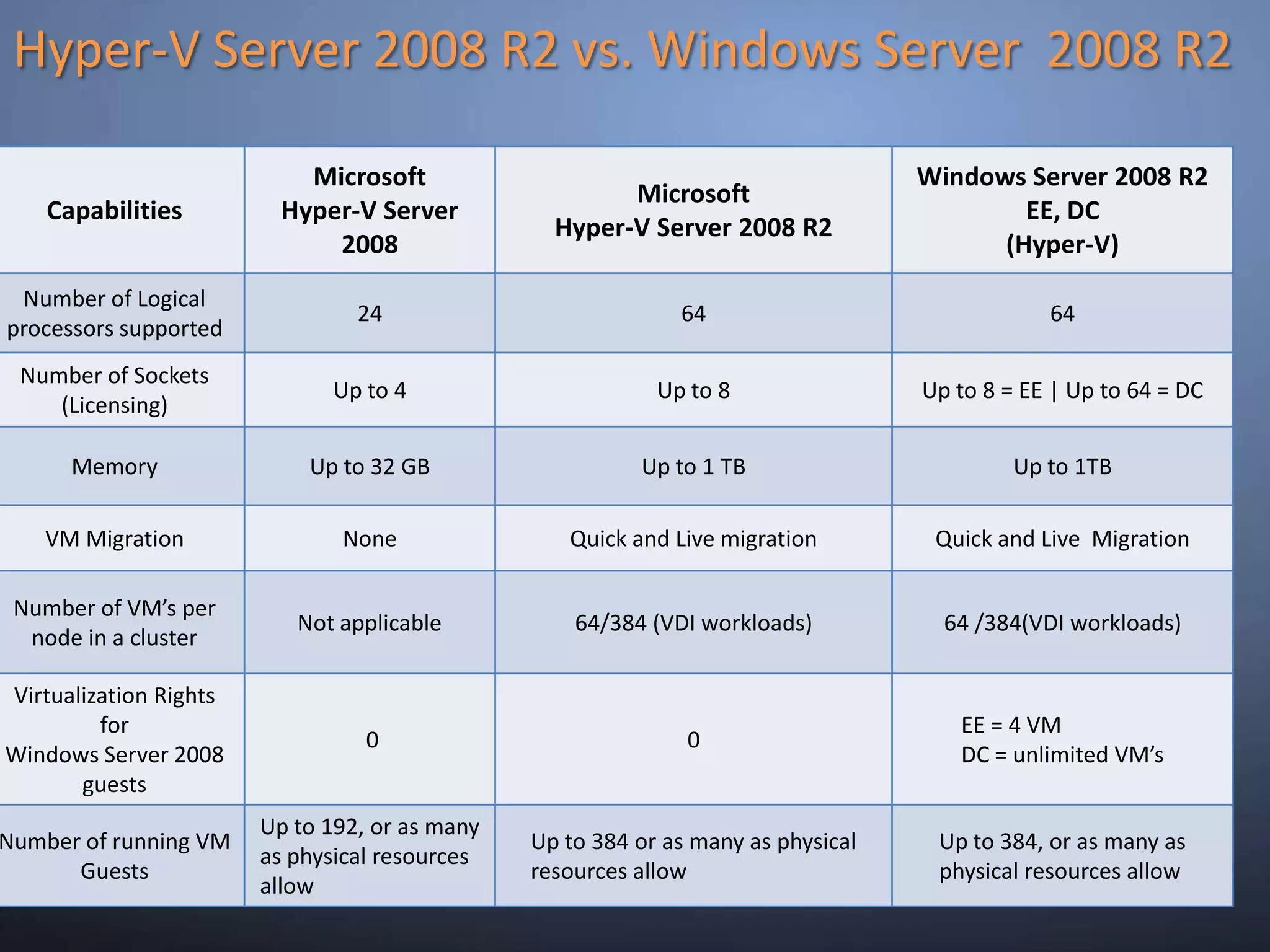
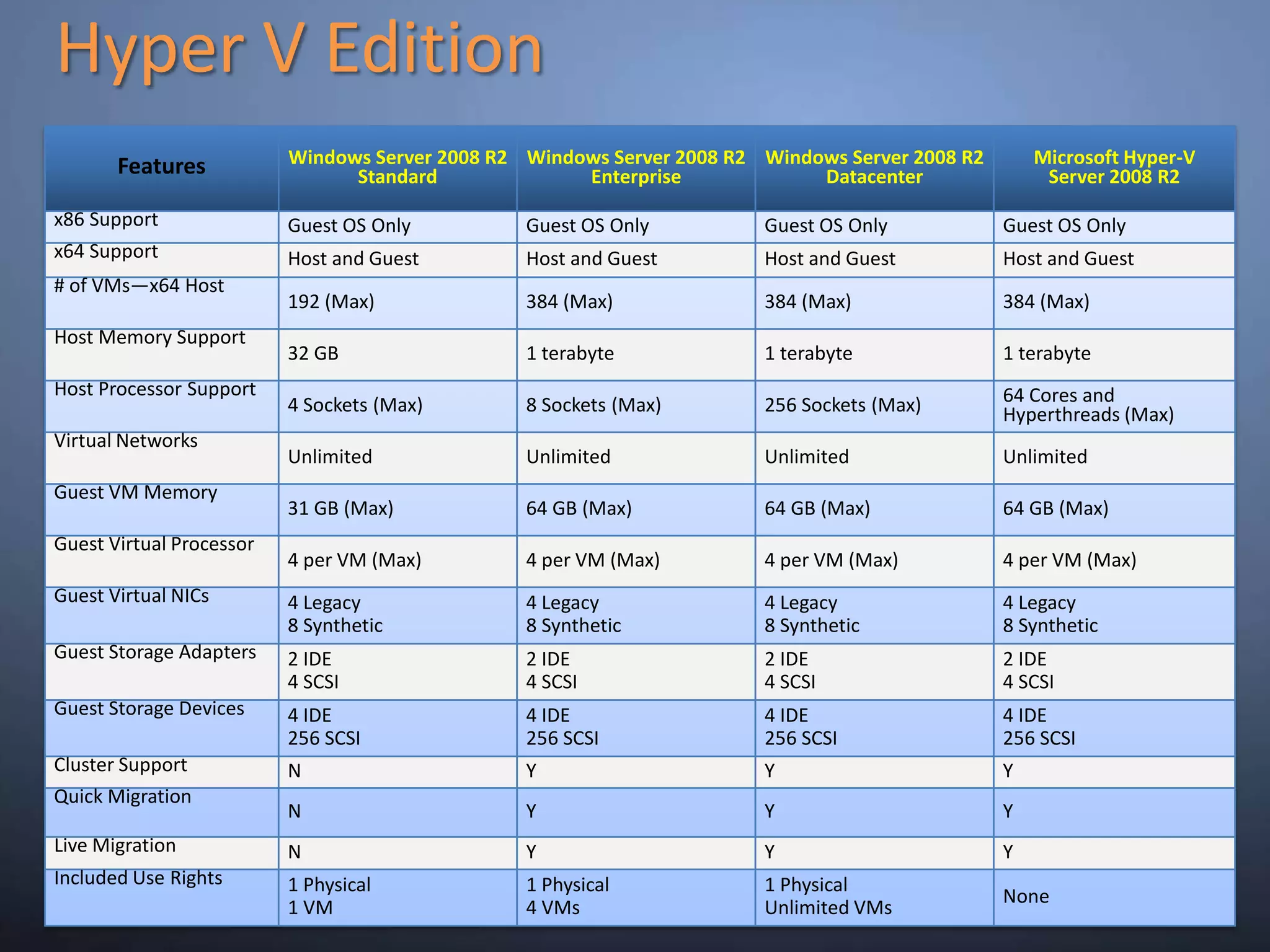
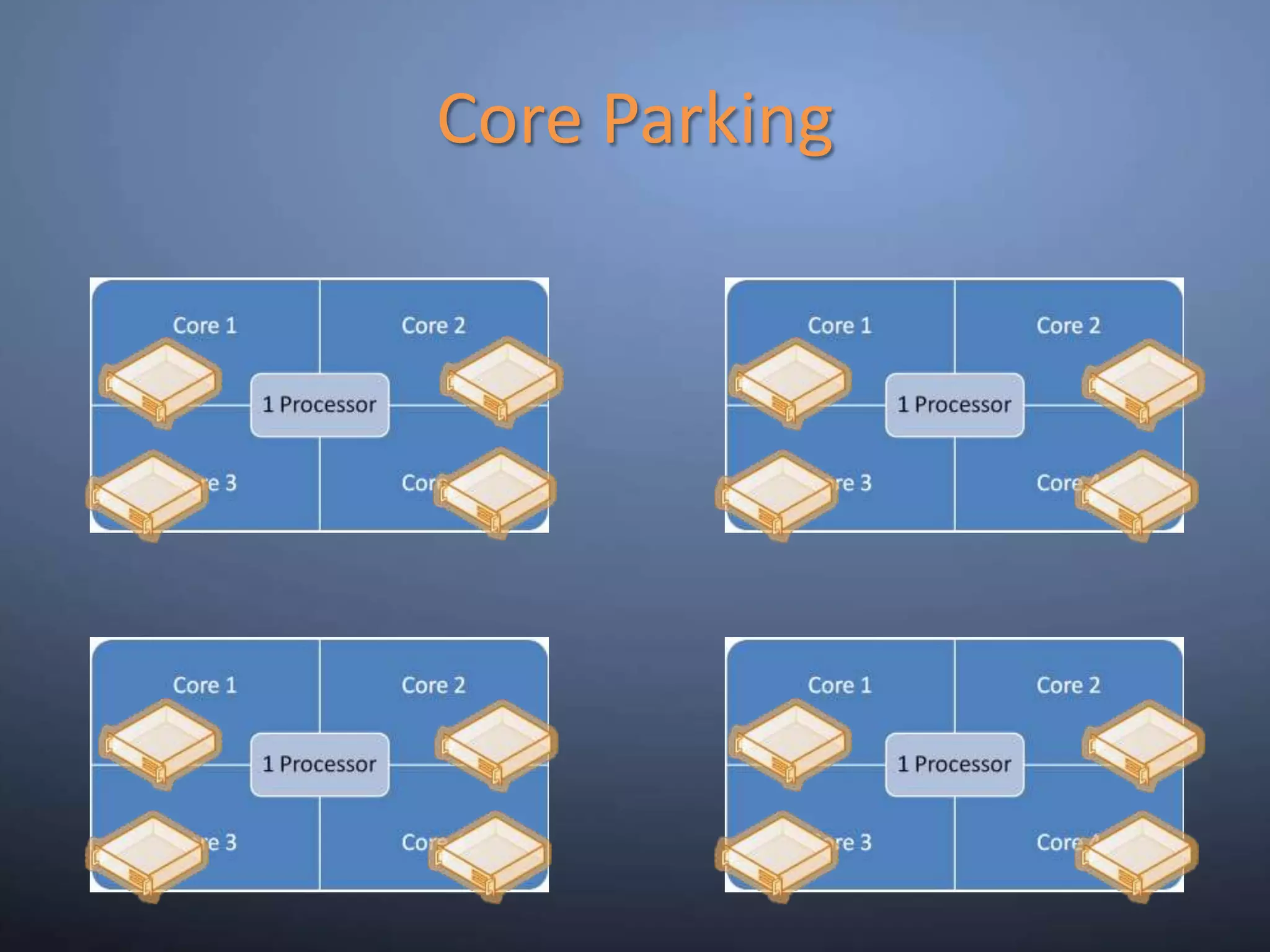
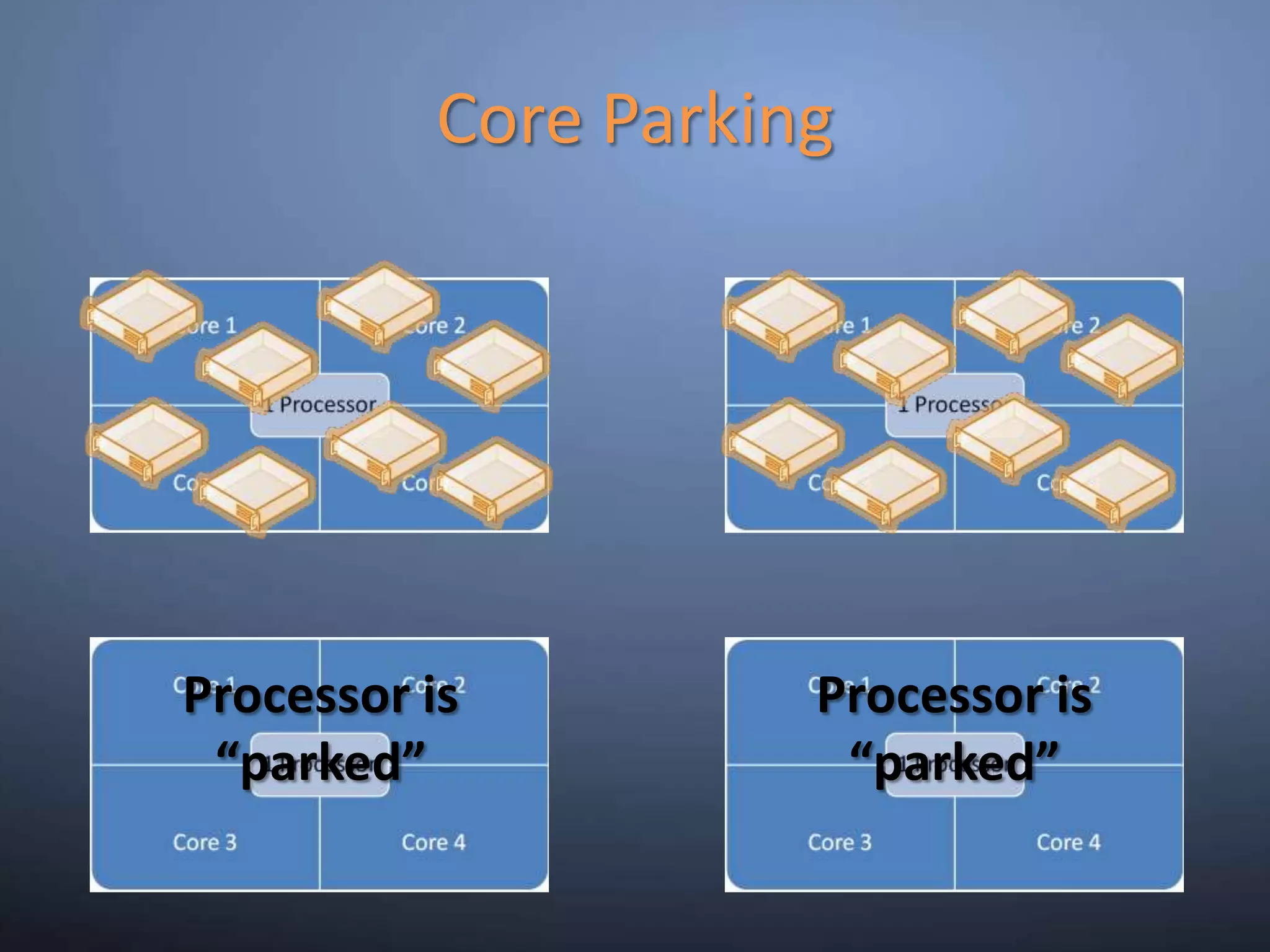
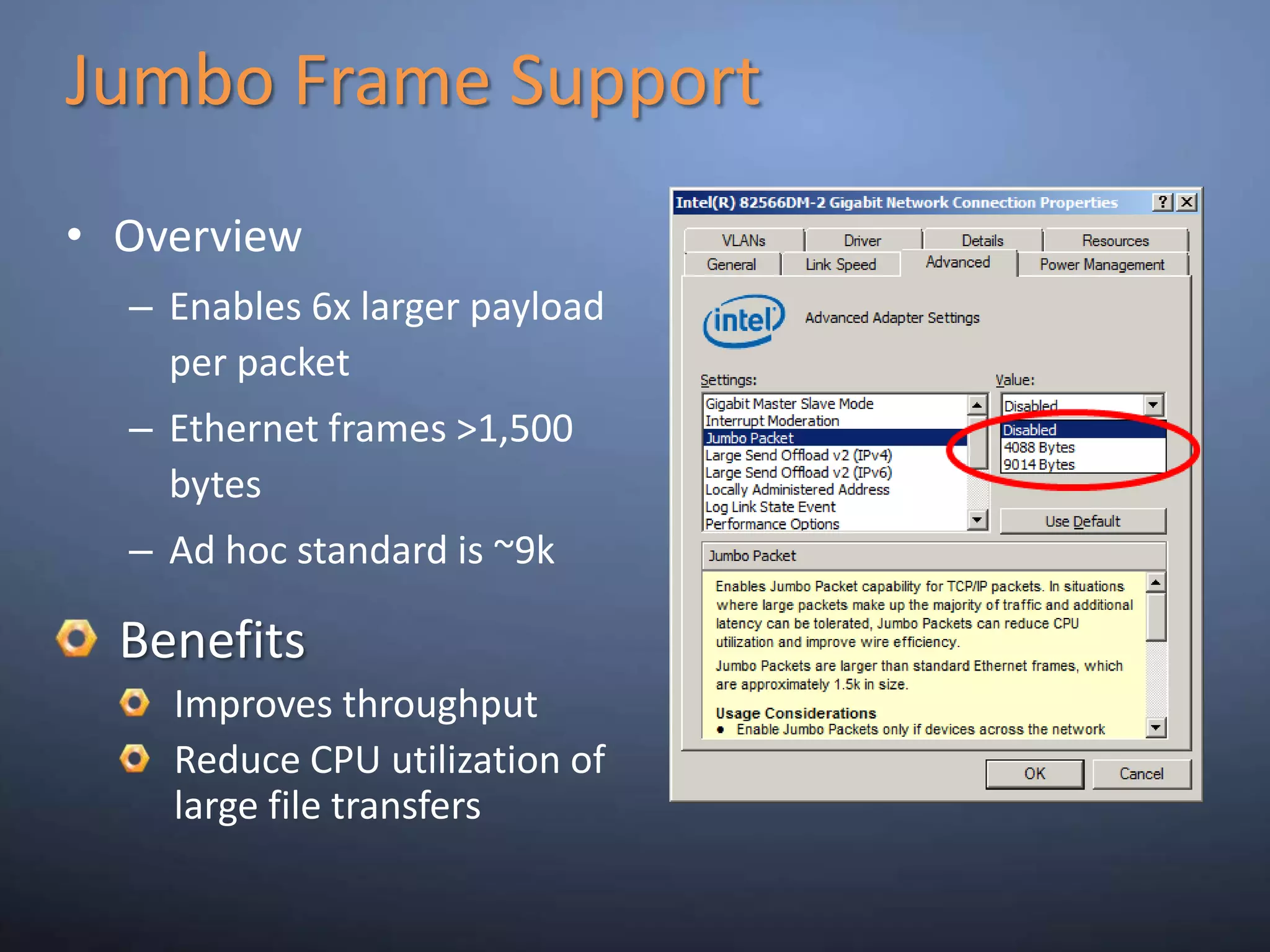
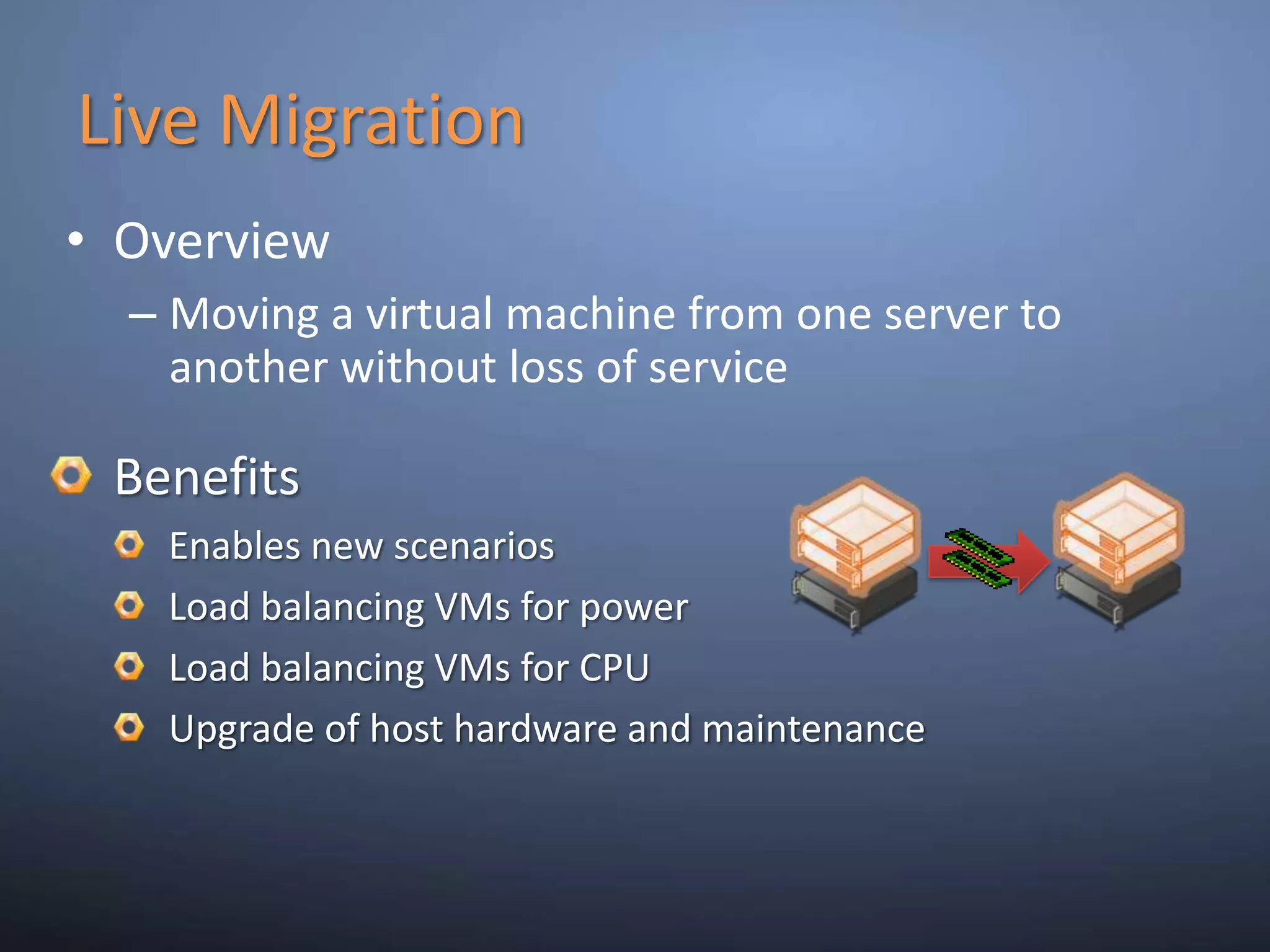
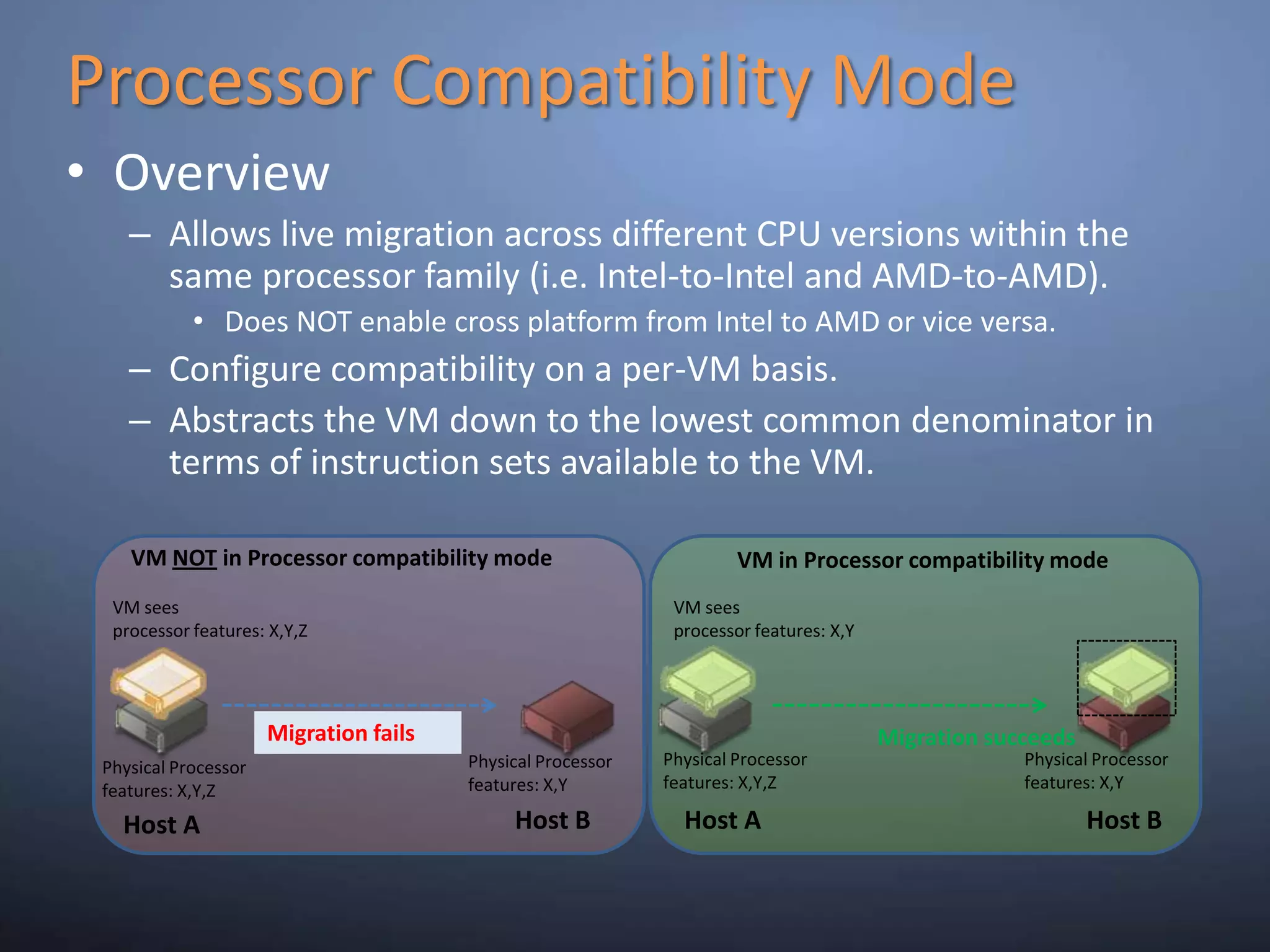
This document provides an overview and summary of key capabilities in Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V. It discusses the virtualization roadmap, requirements for running Hyper-V, supported guest operating systems, new features like core parking, live migration and cluster shared volumes. The document also announces upcoming demonstrations and training on using Hyper-V.