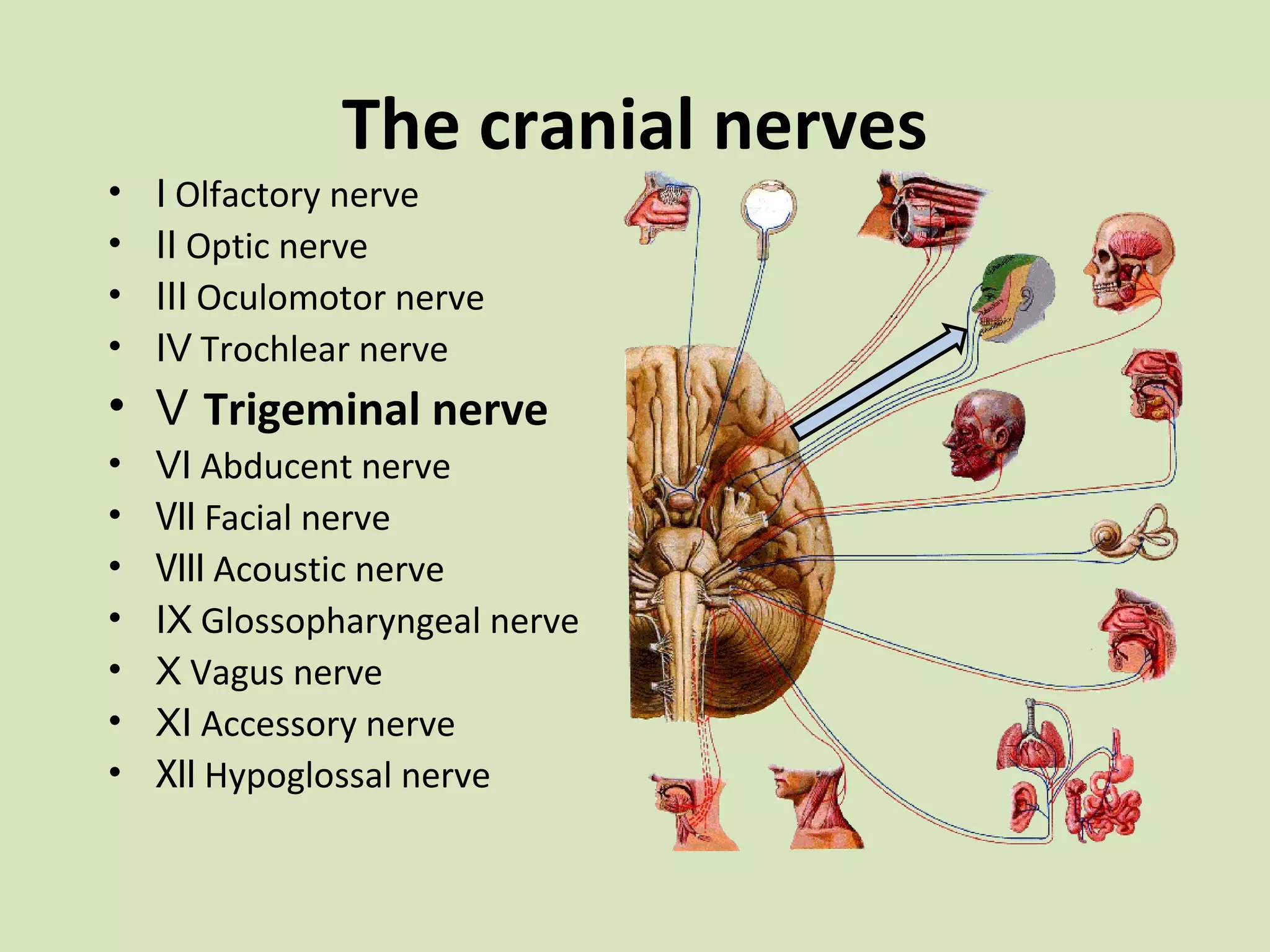
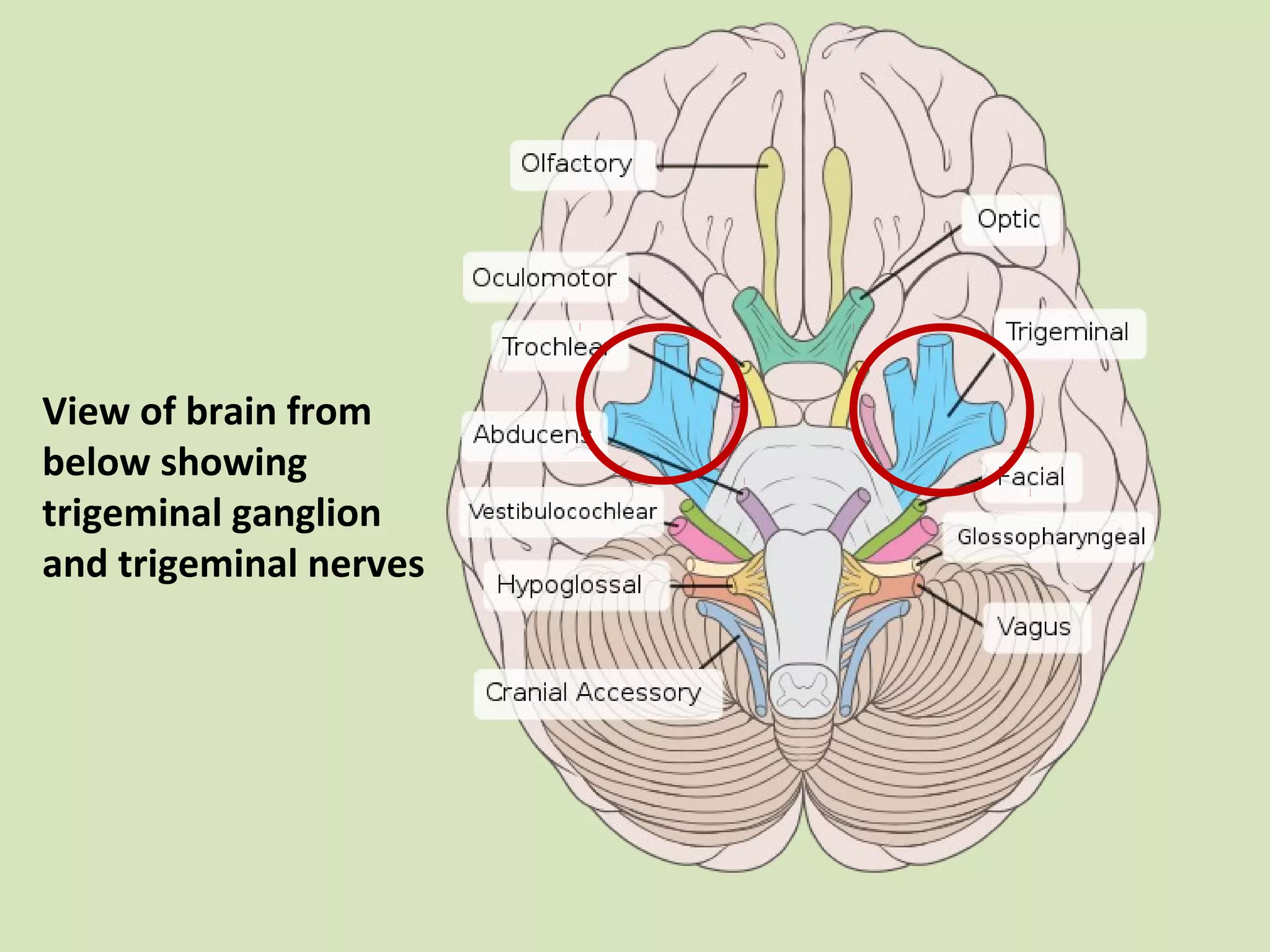
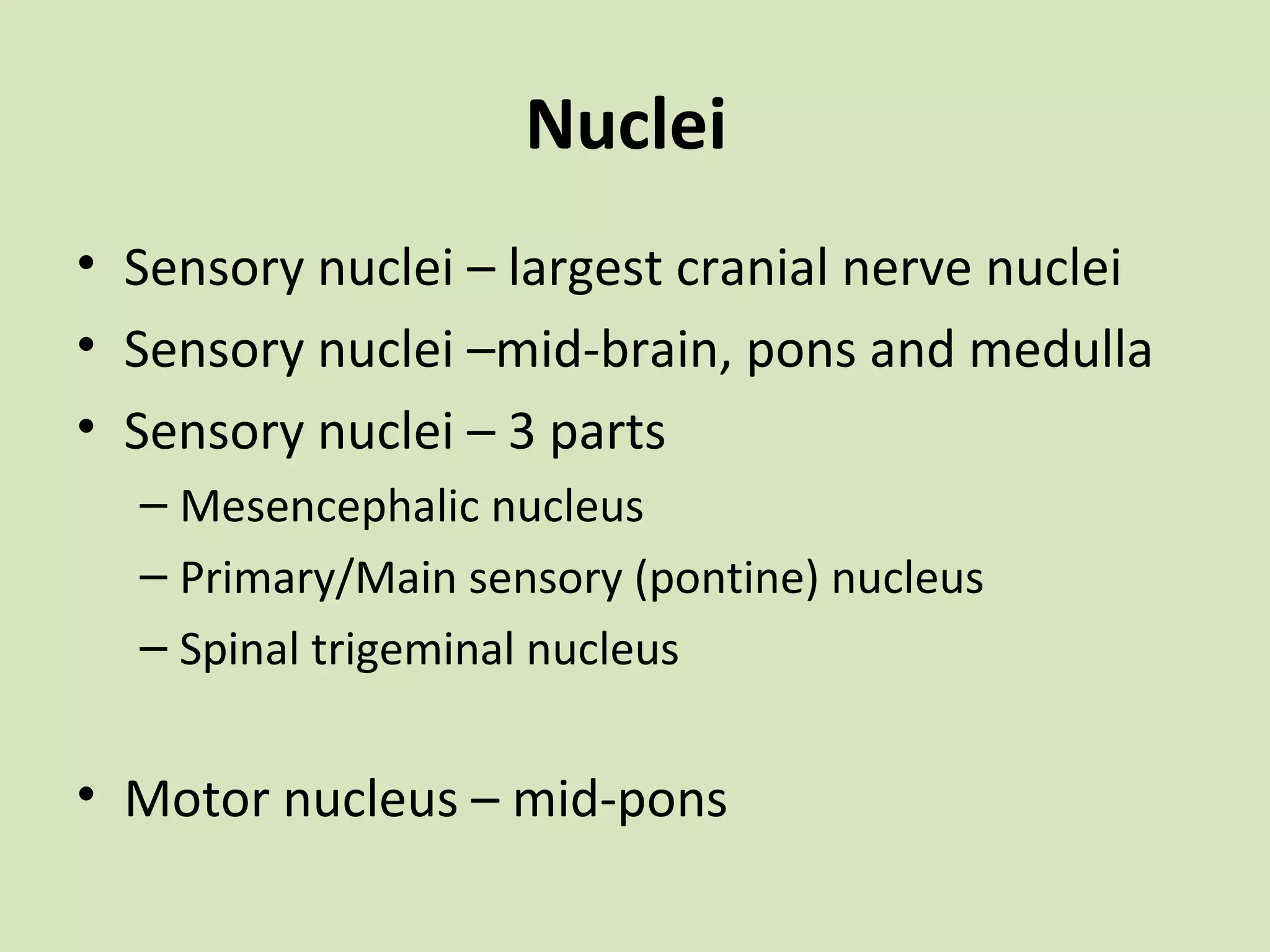
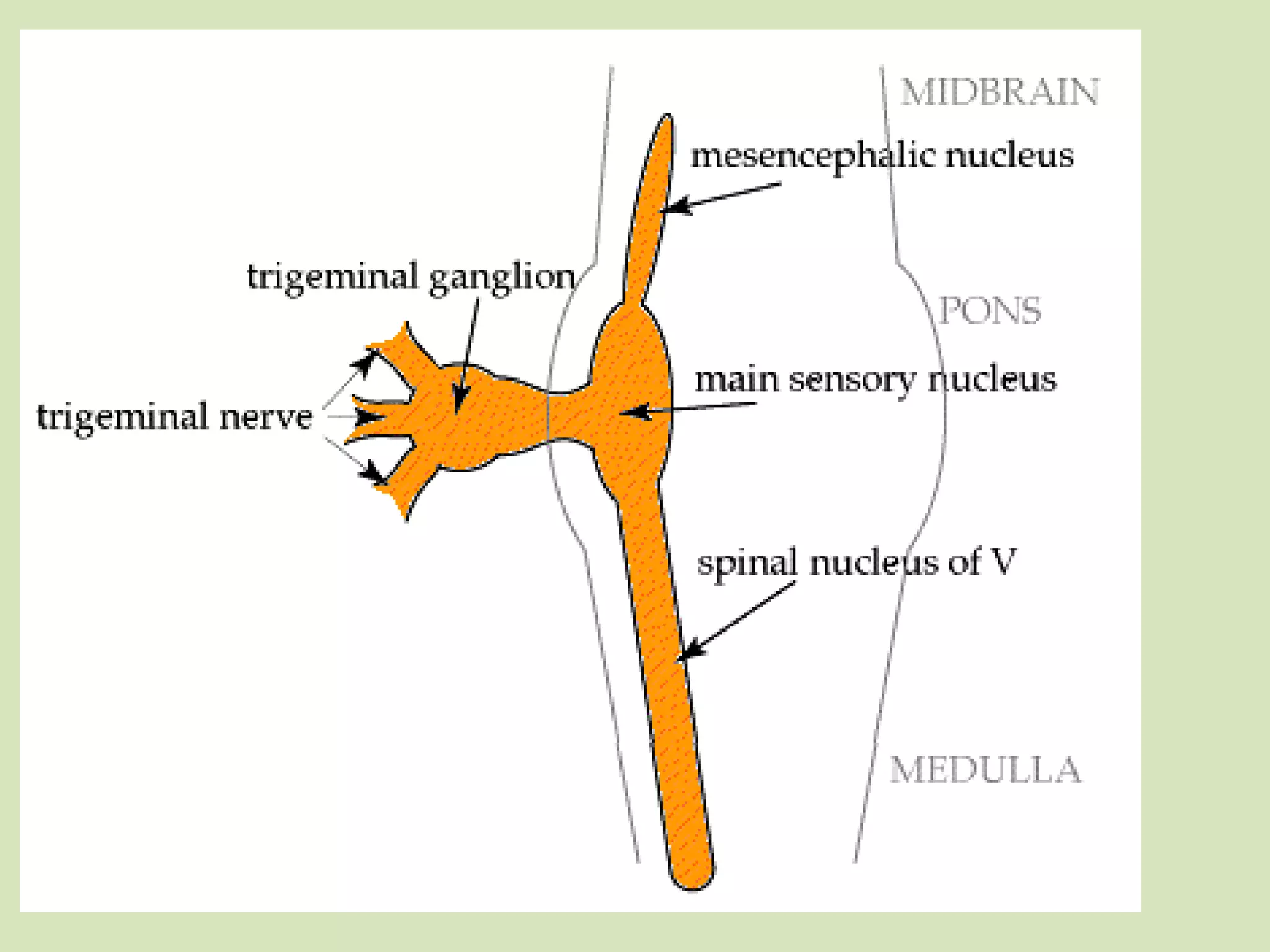
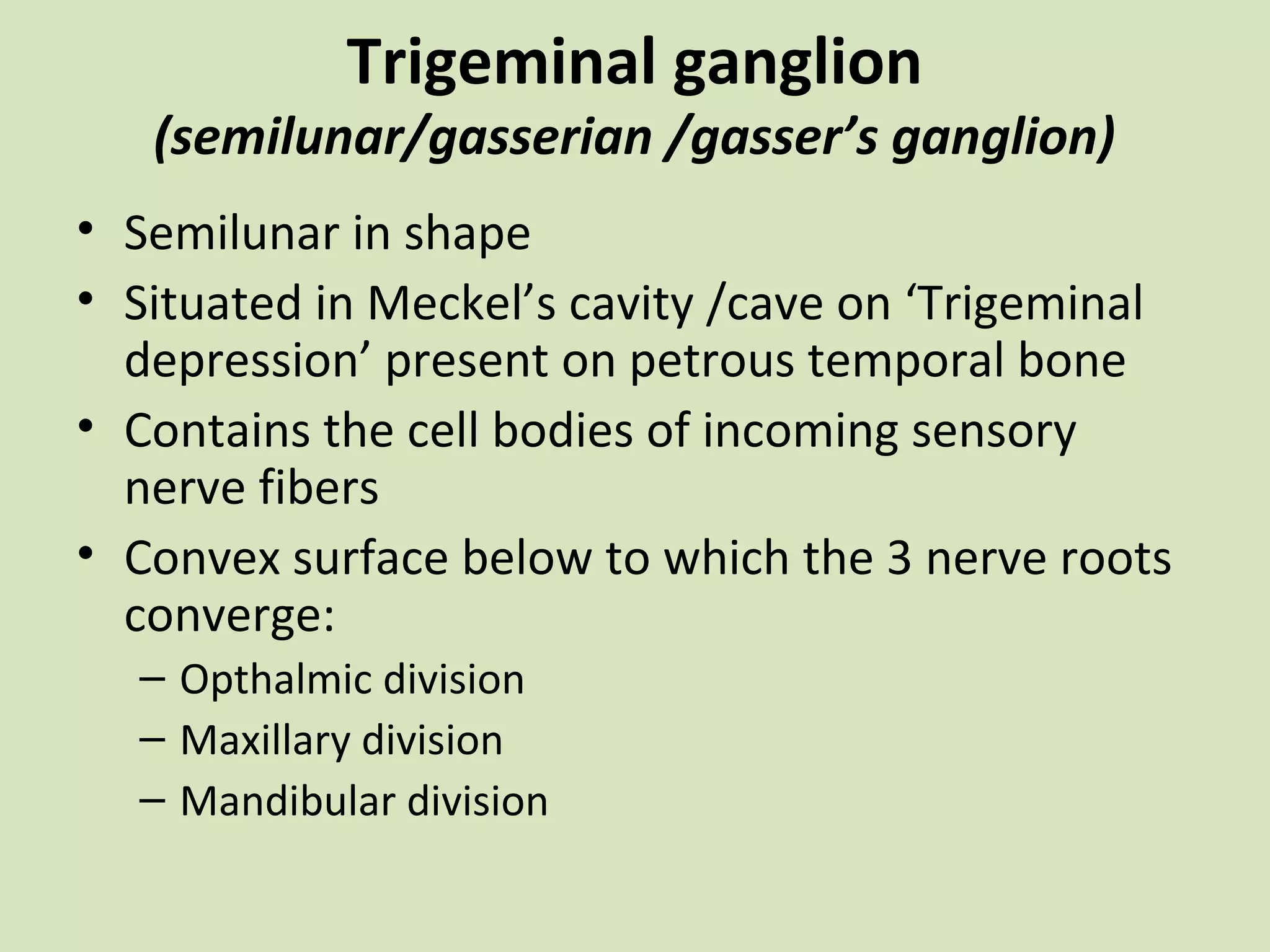
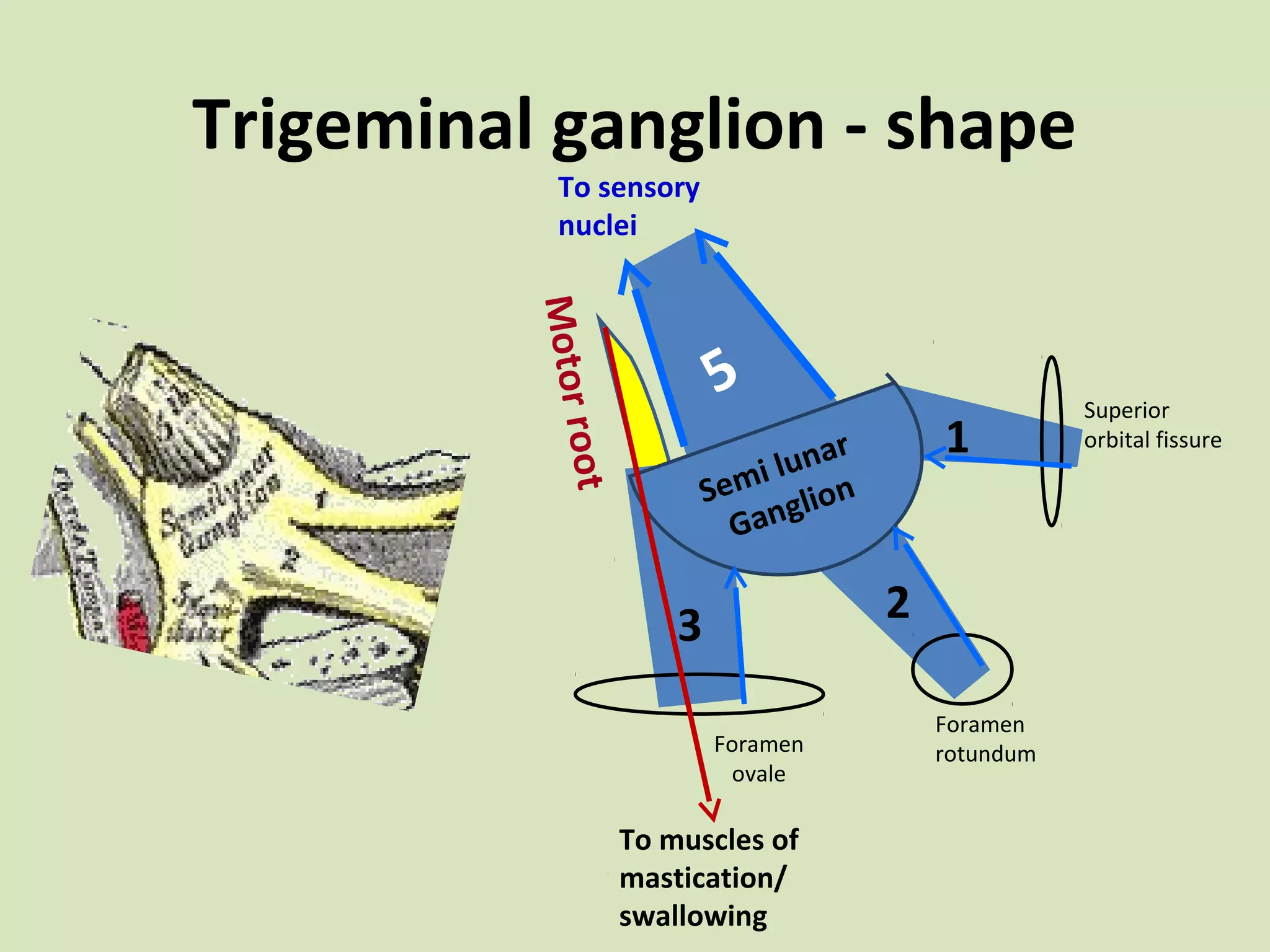
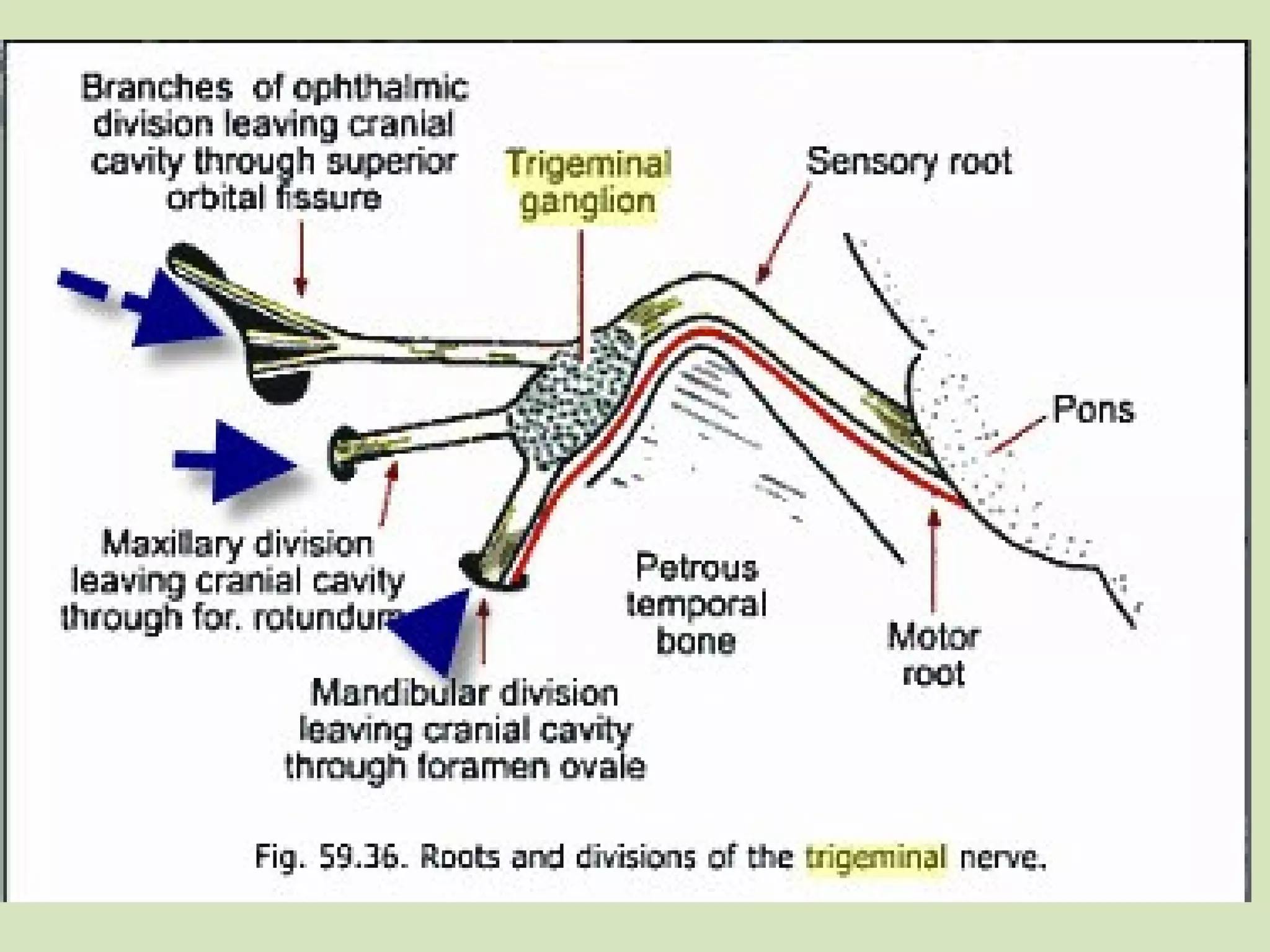
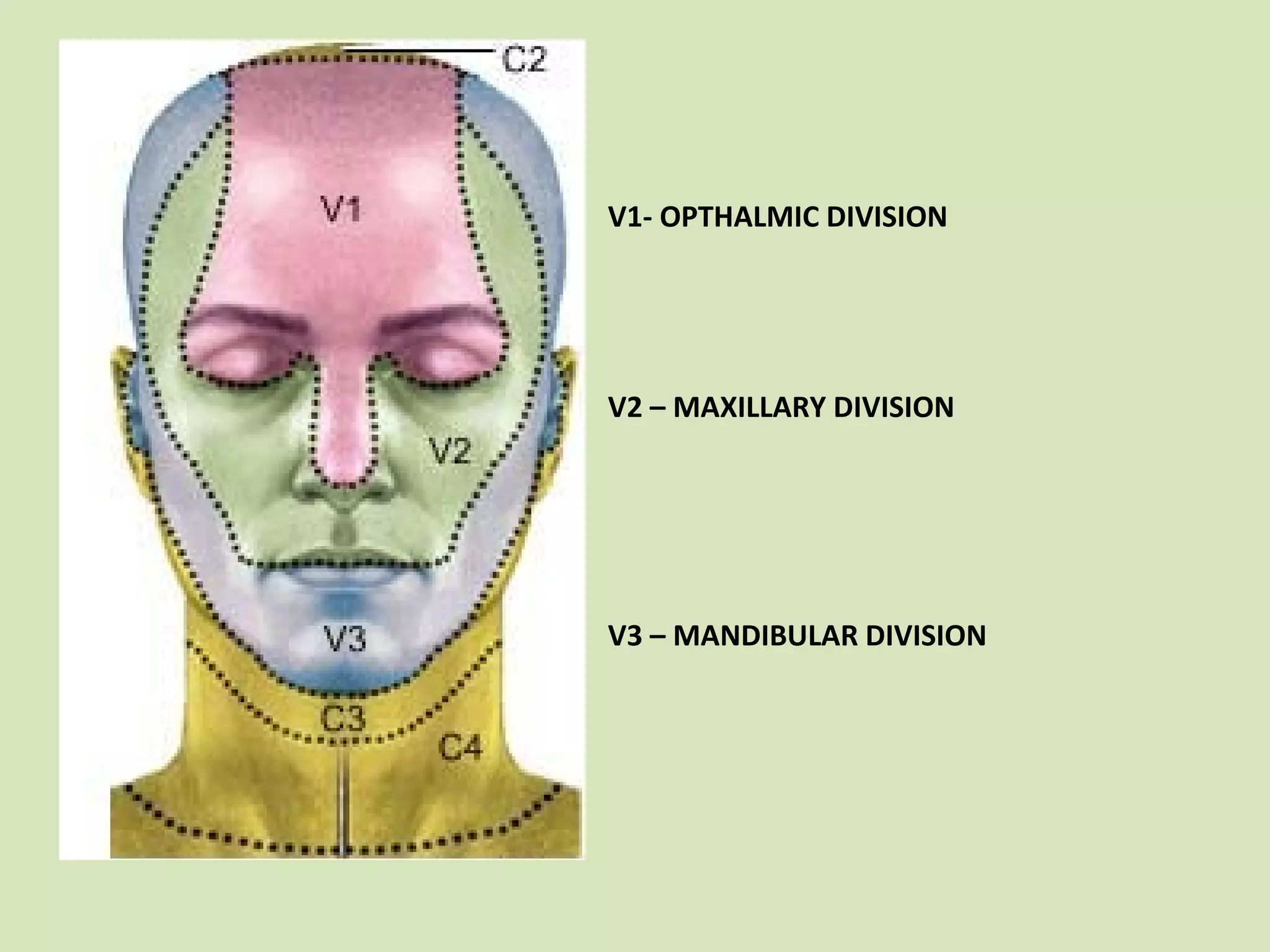
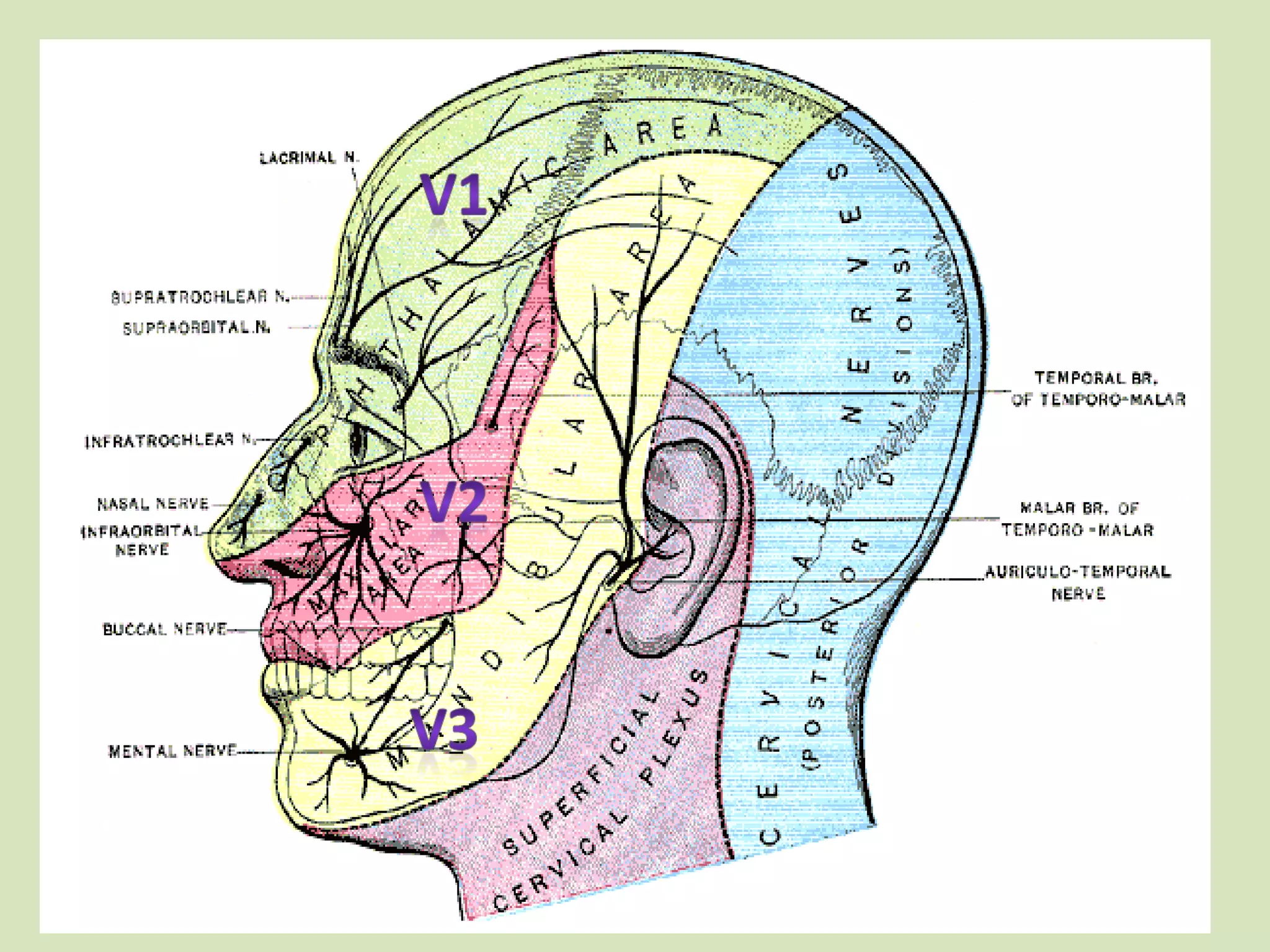
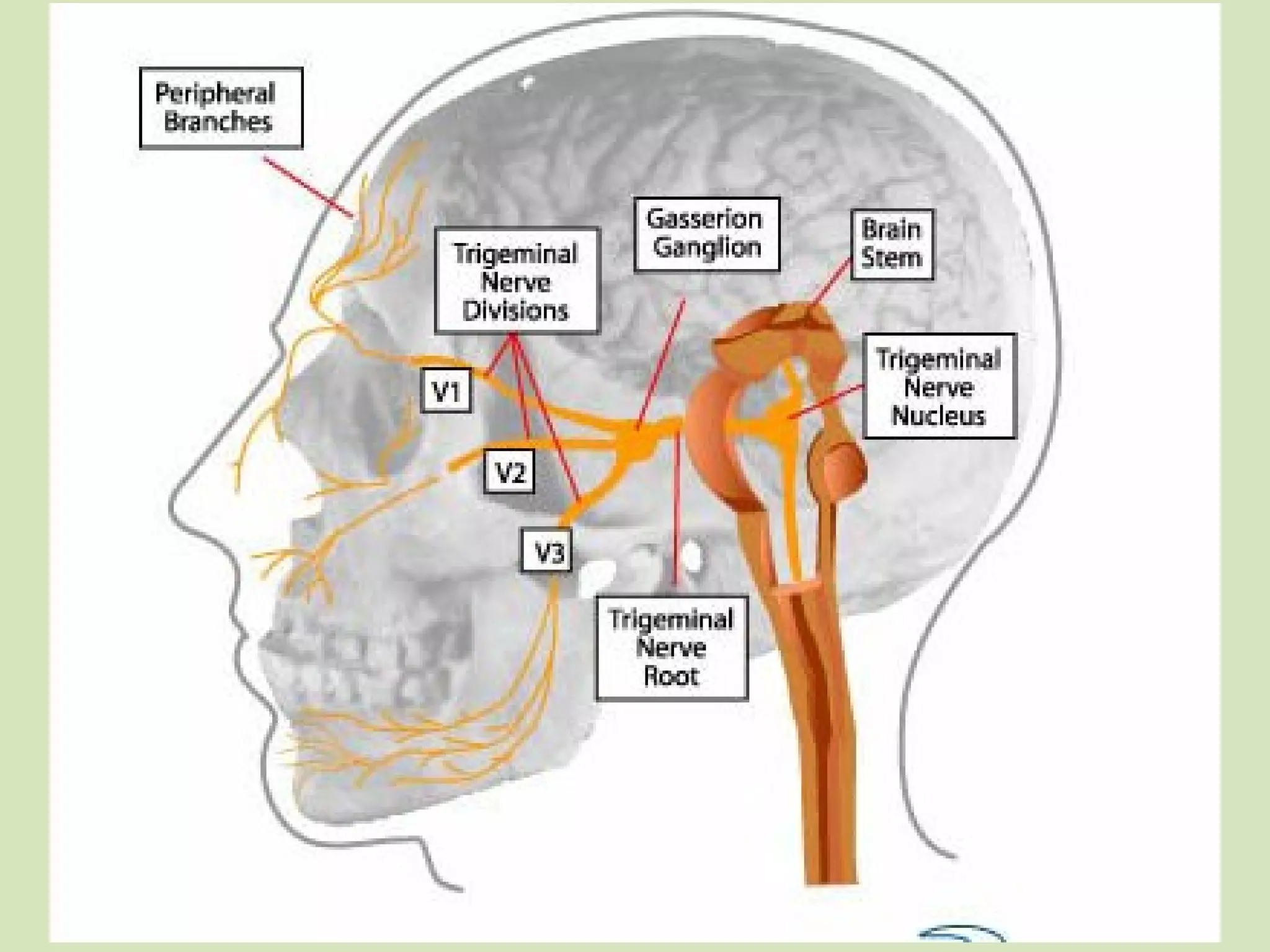
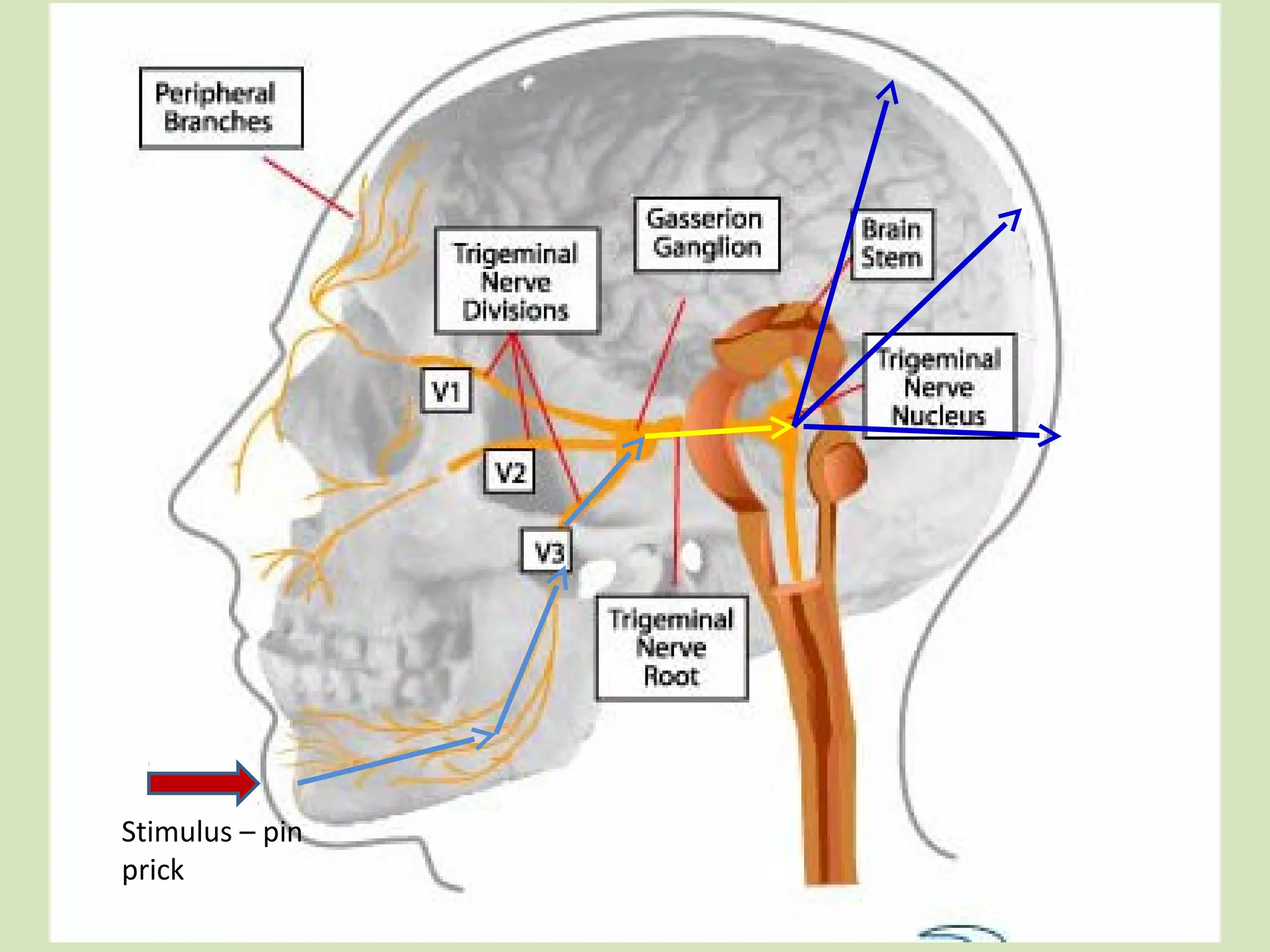
The document provides an overview of cranial nerves, focusing on the trigeminal nerve, which is the fifth cranial nerve and the largest. It explains the trigeminal nerve's mixed function, sensory innervation of the face, and its three divisions—ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. Additionally, it discusses the importance of understanding dermatomes for diagnosing nerve injuries and the effects of nerve blocks.