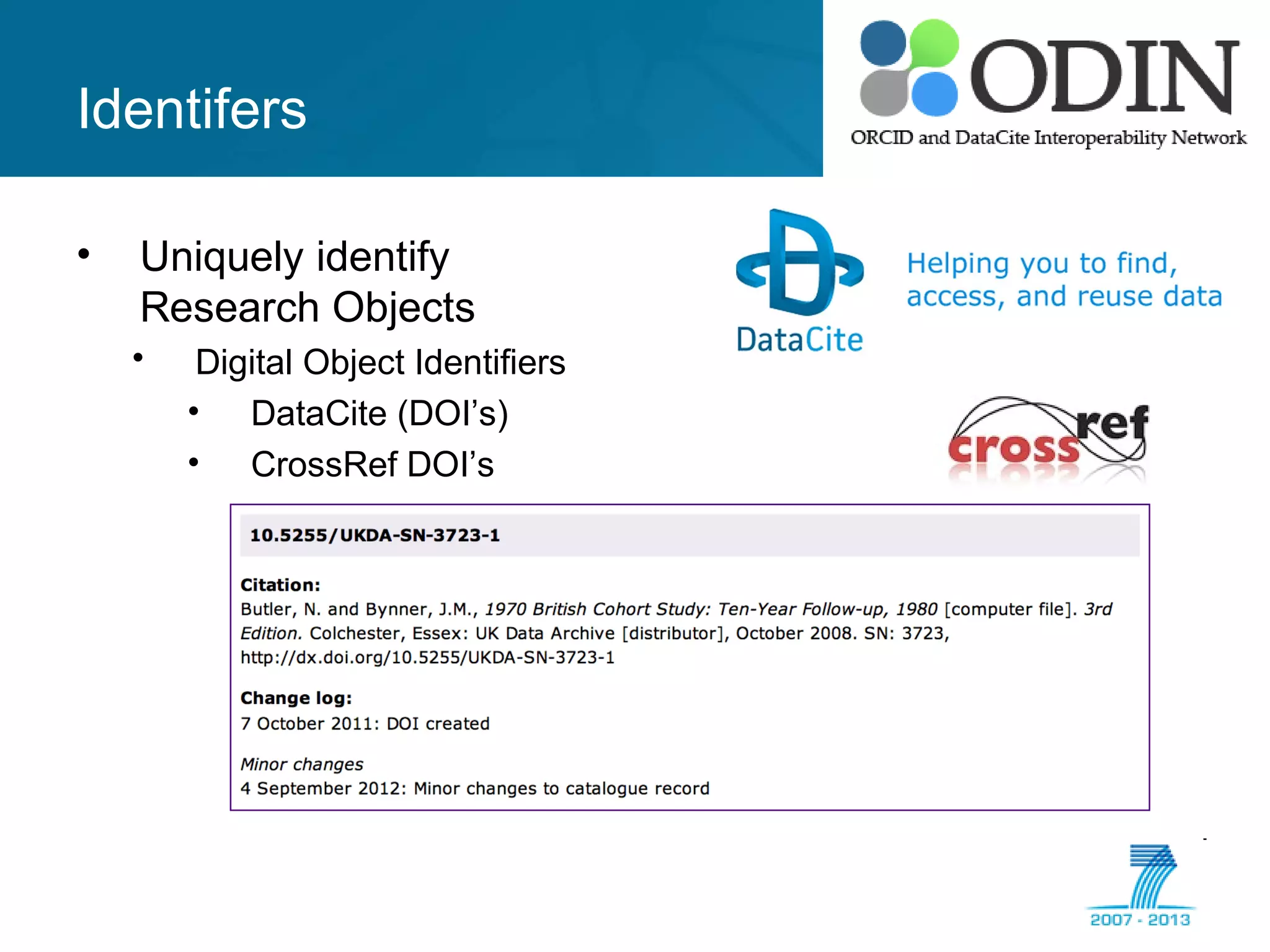
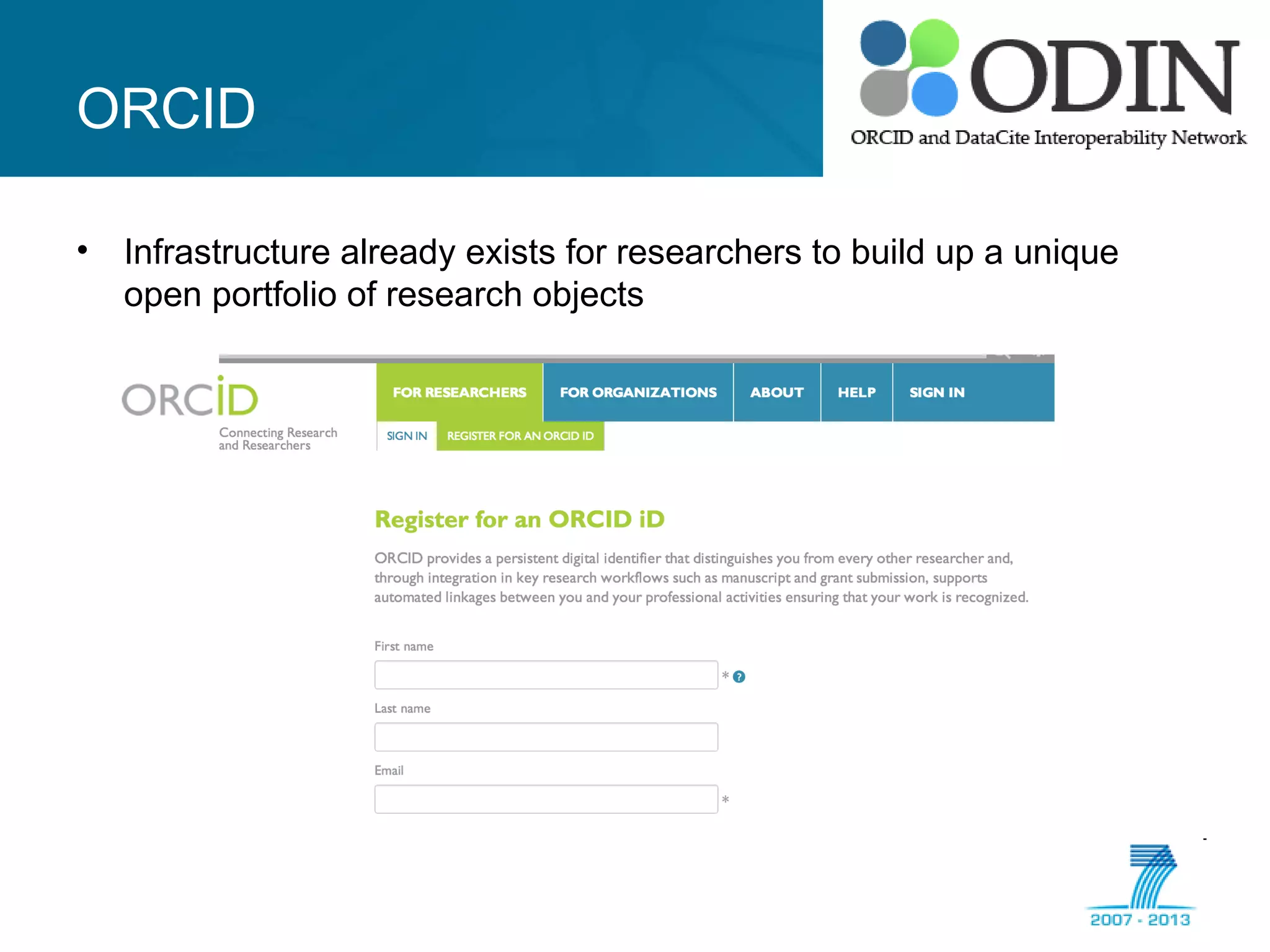
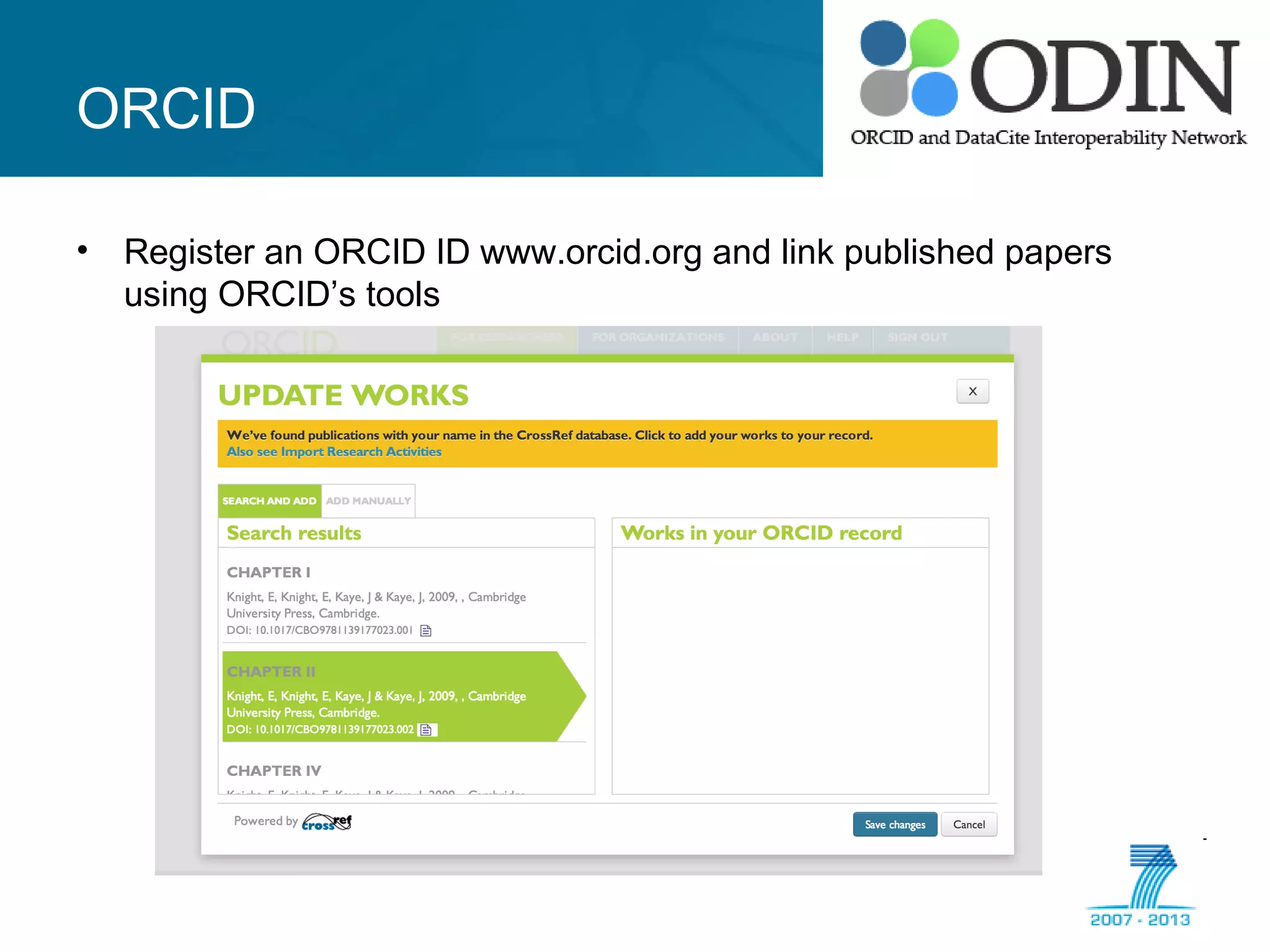
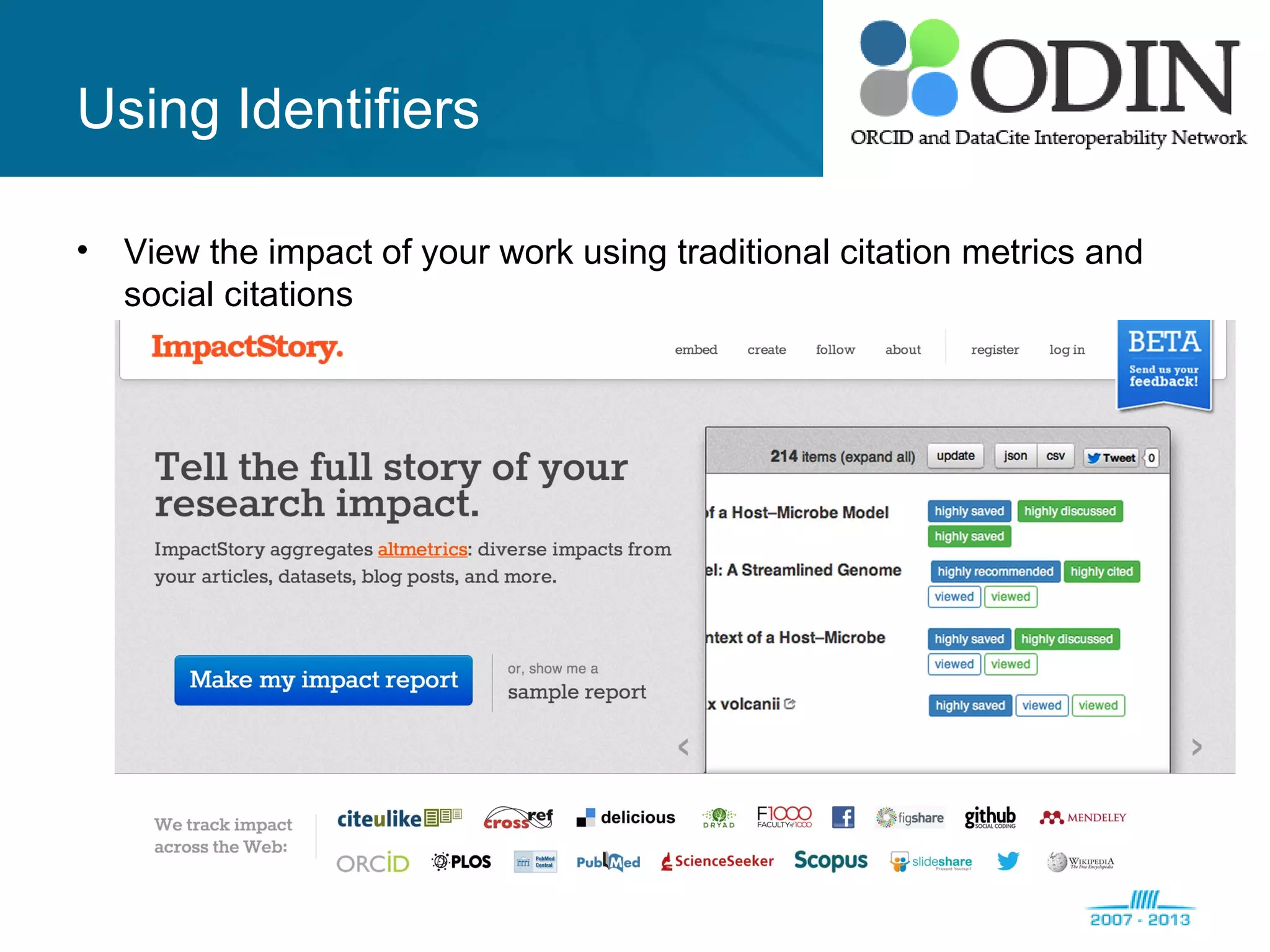
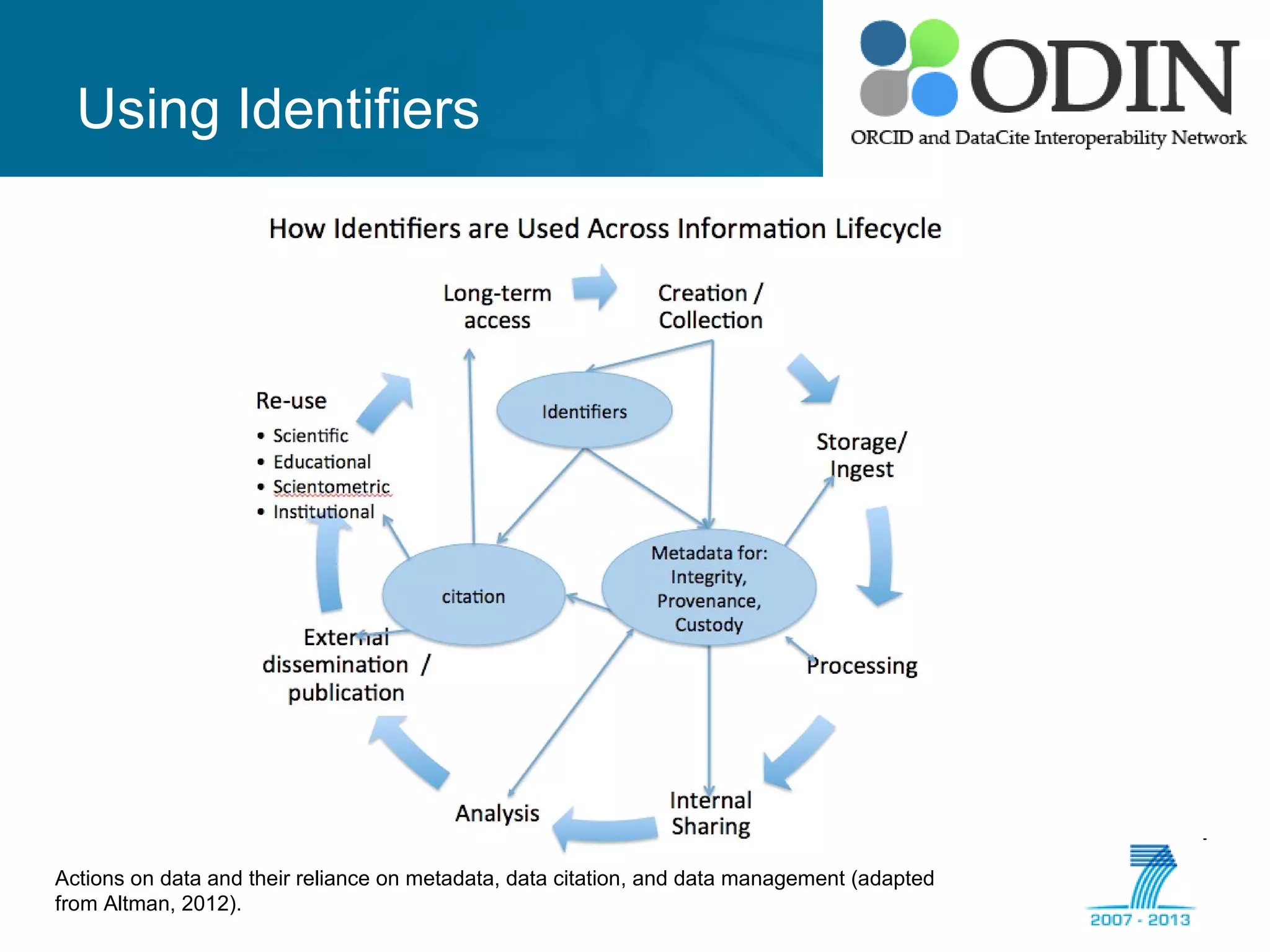
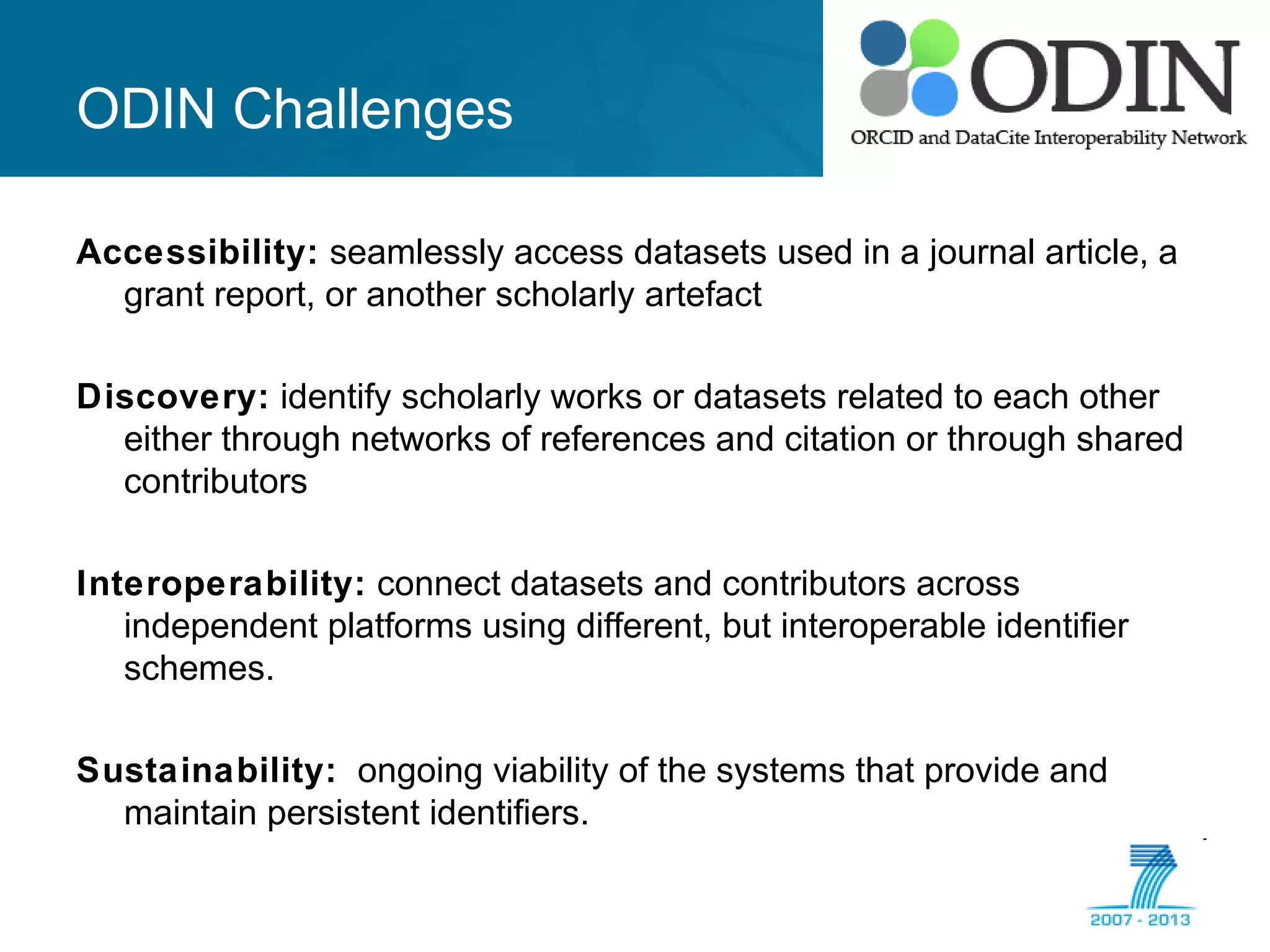
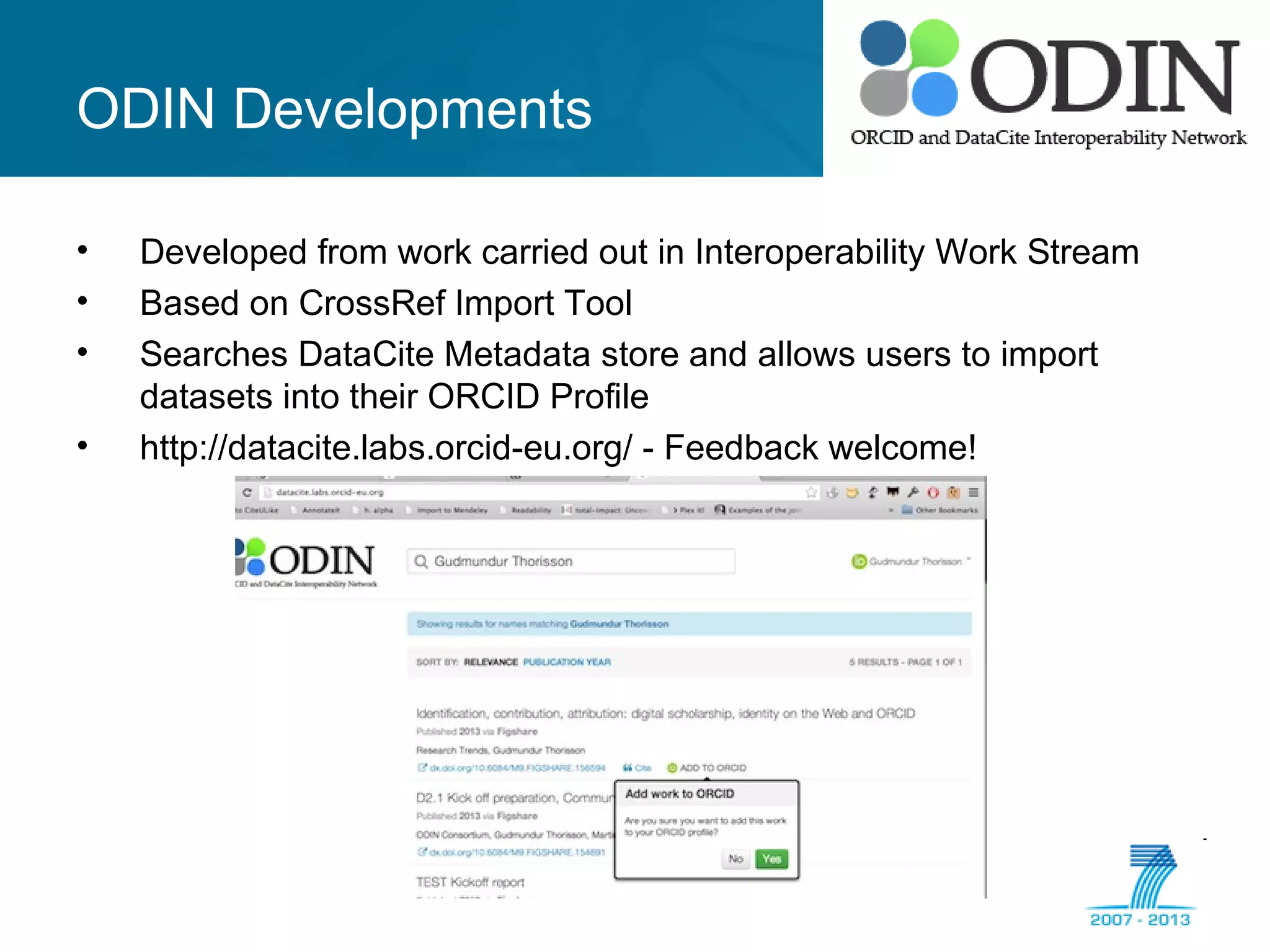
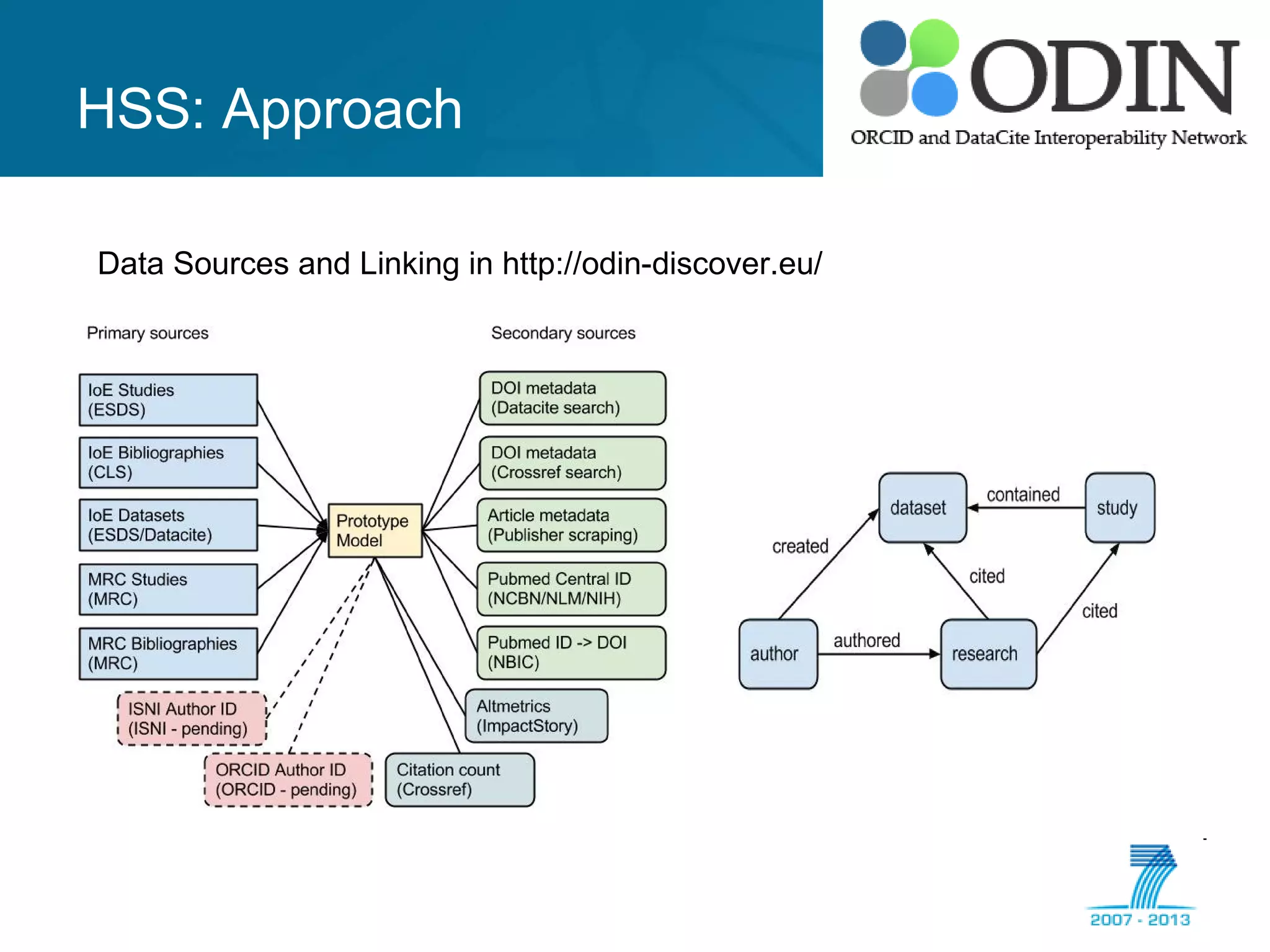
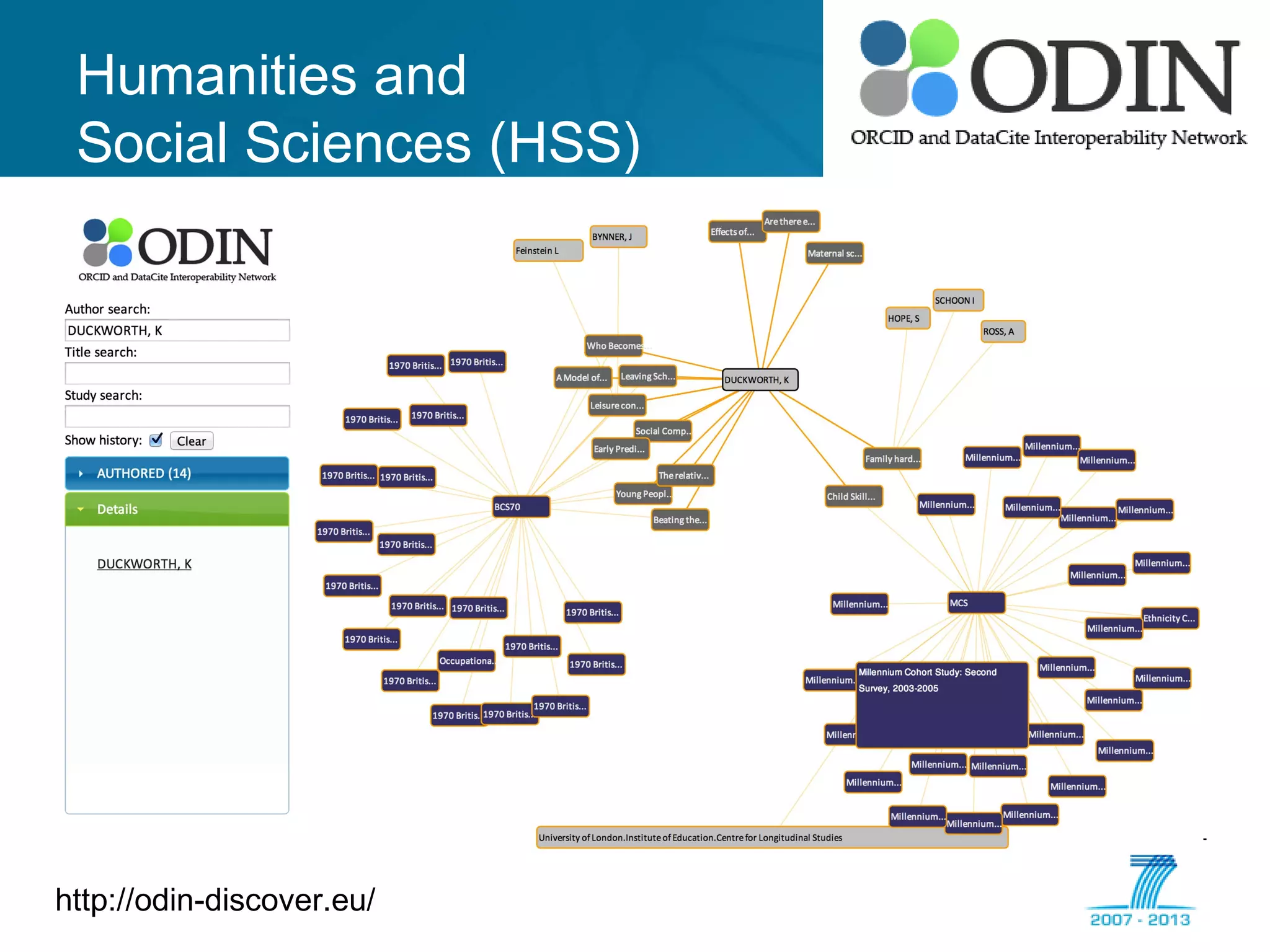
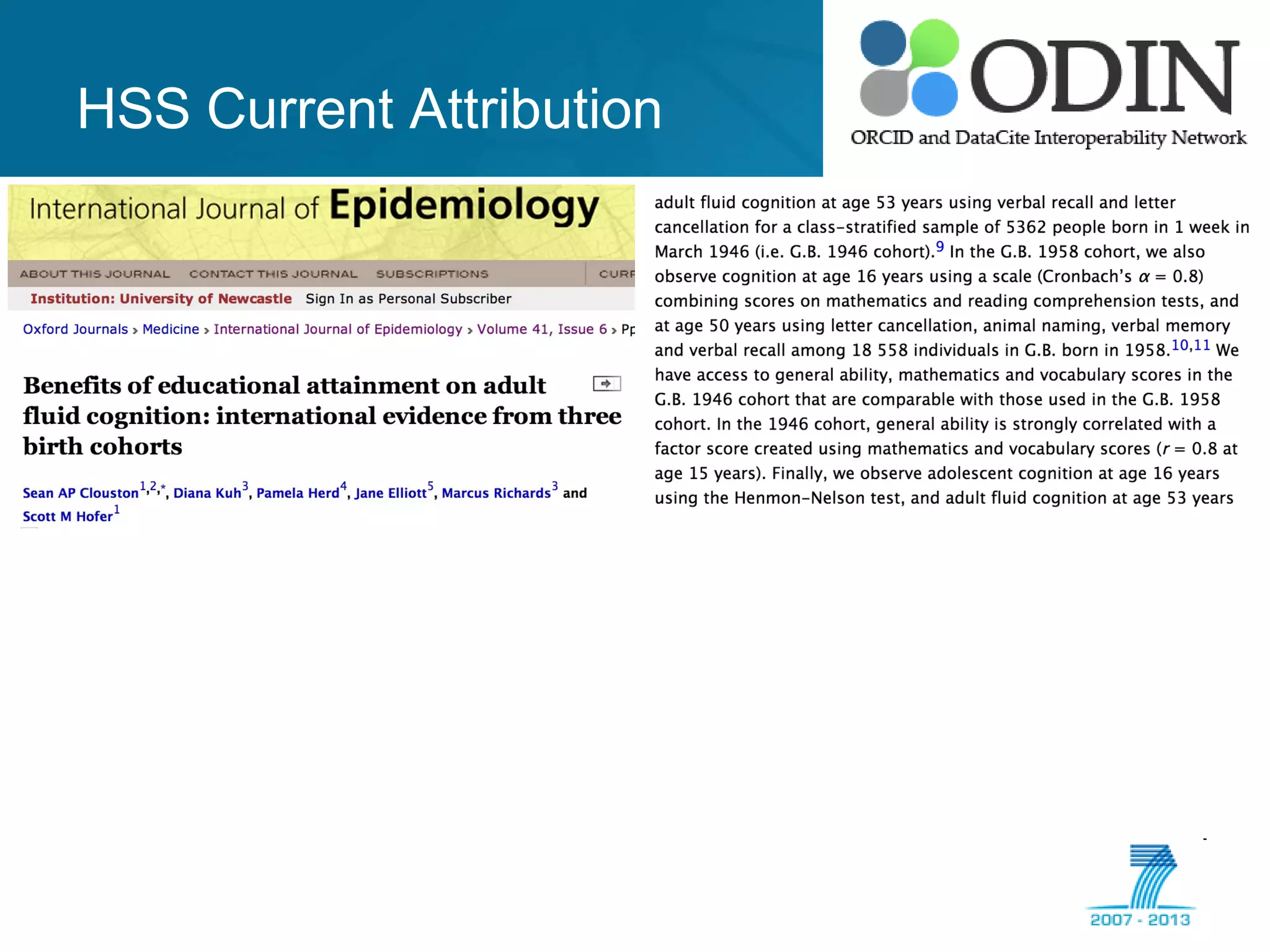
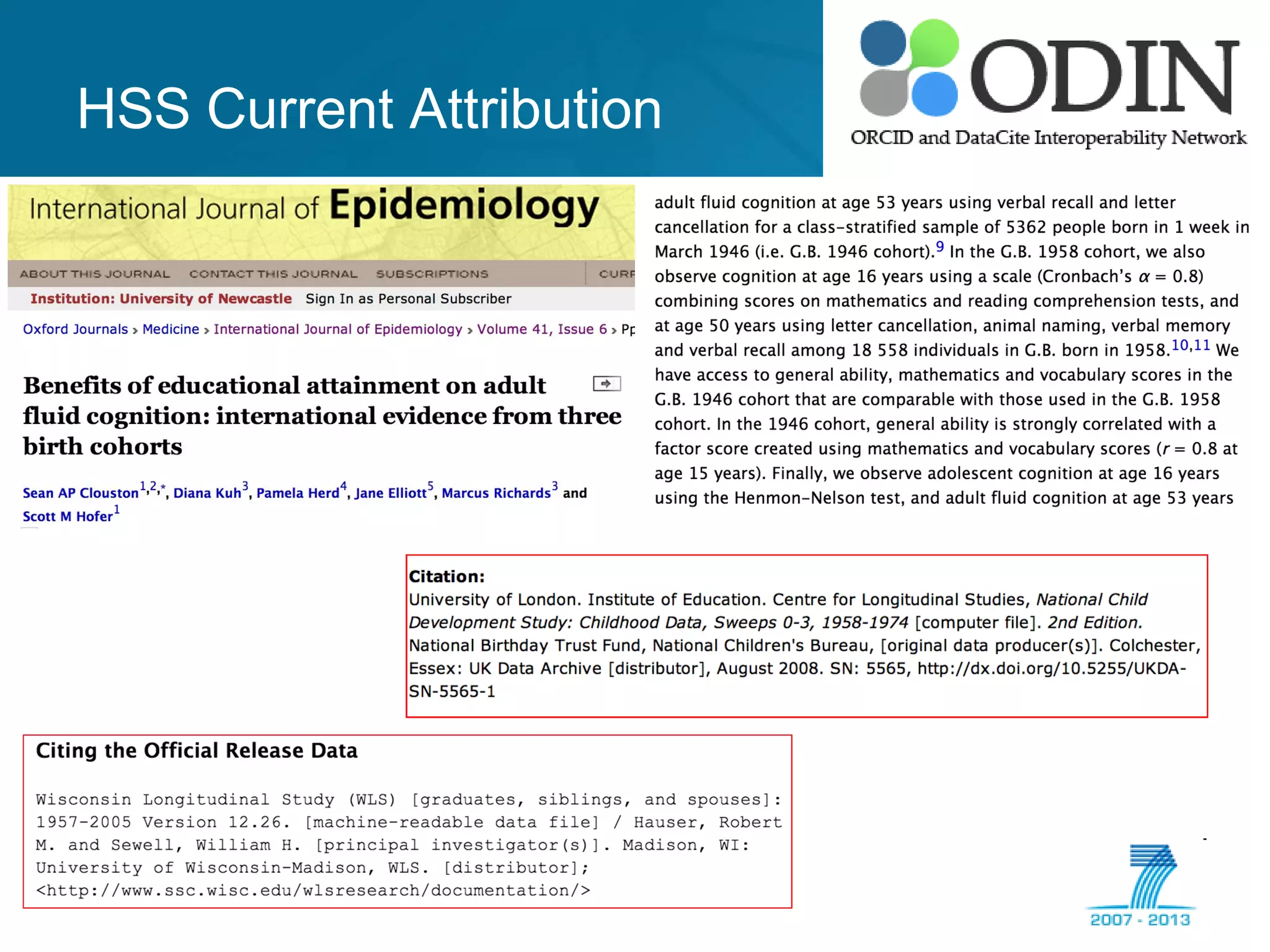
The document outlines the ODIN project, which focuses on enhancing interoperability of identifiers for research objects and contributors in social sciences and high-energy physics. It addresses challenges in accessibility, discovery, interoperability, and sustainability while detailing objectives, developments, and workflows for improving data citation and management. Key initiatives include the use of ORCID for researchers and collaboration with stakeholders to establish effective data linking and citation practices.