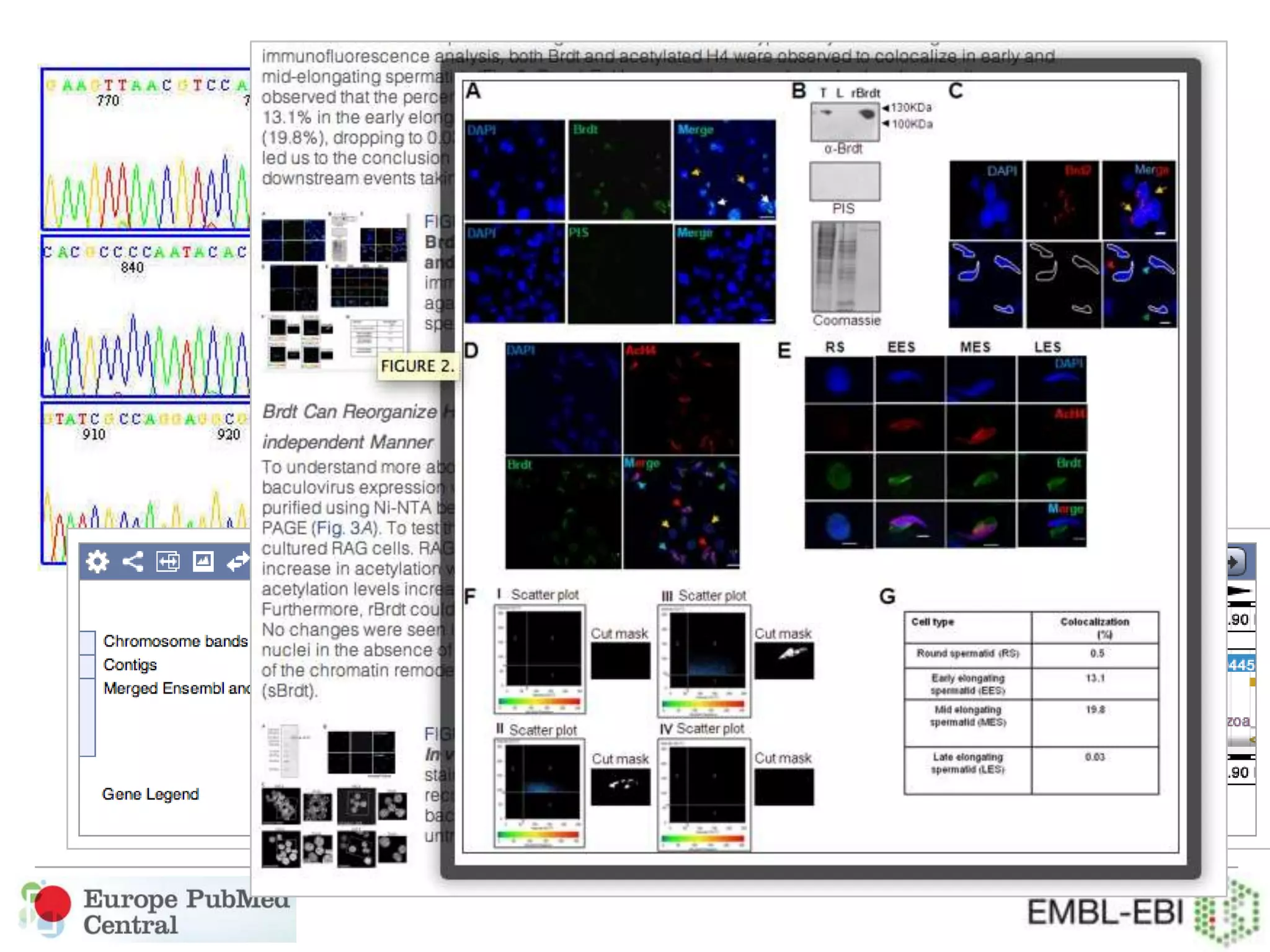
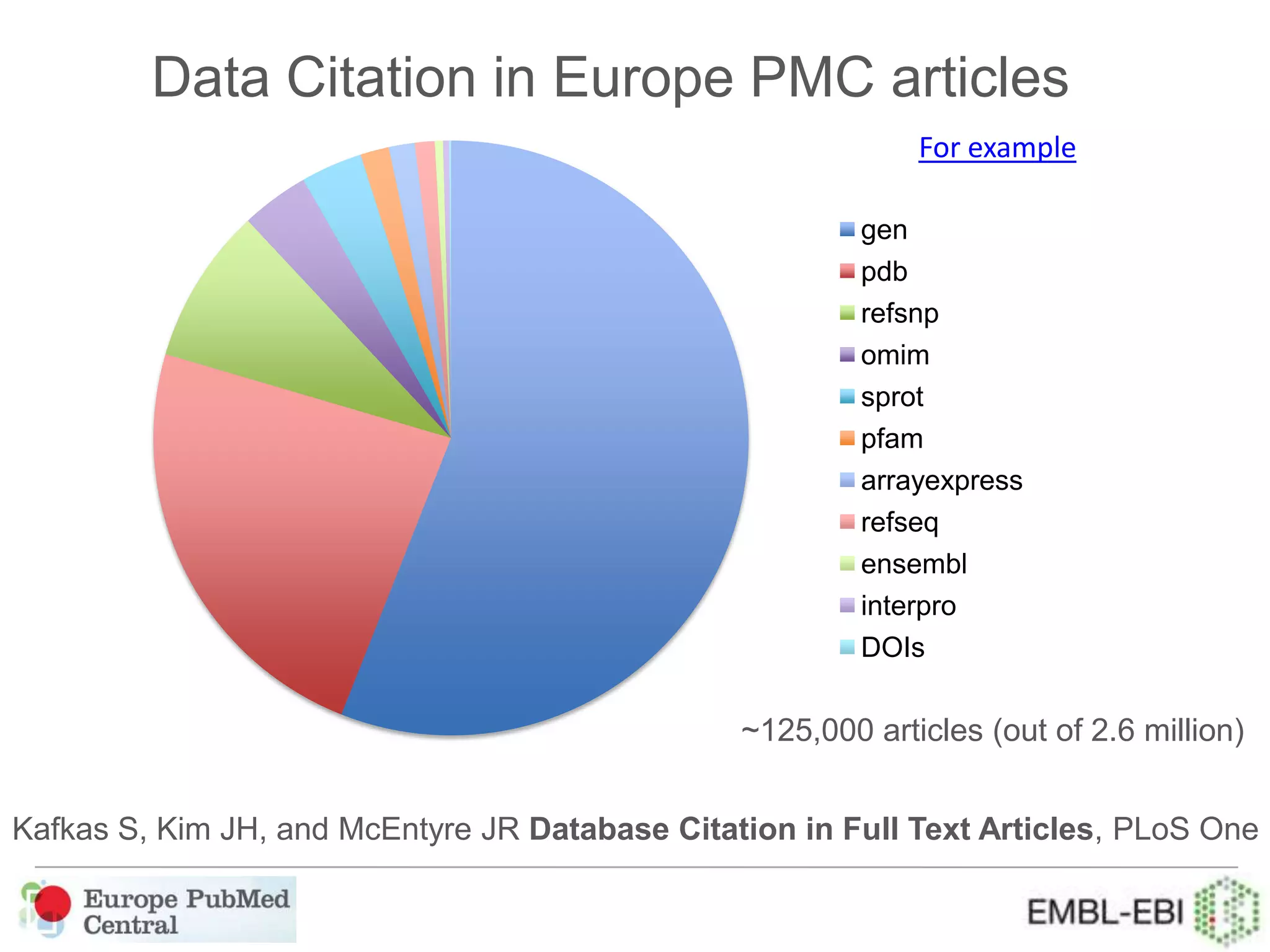
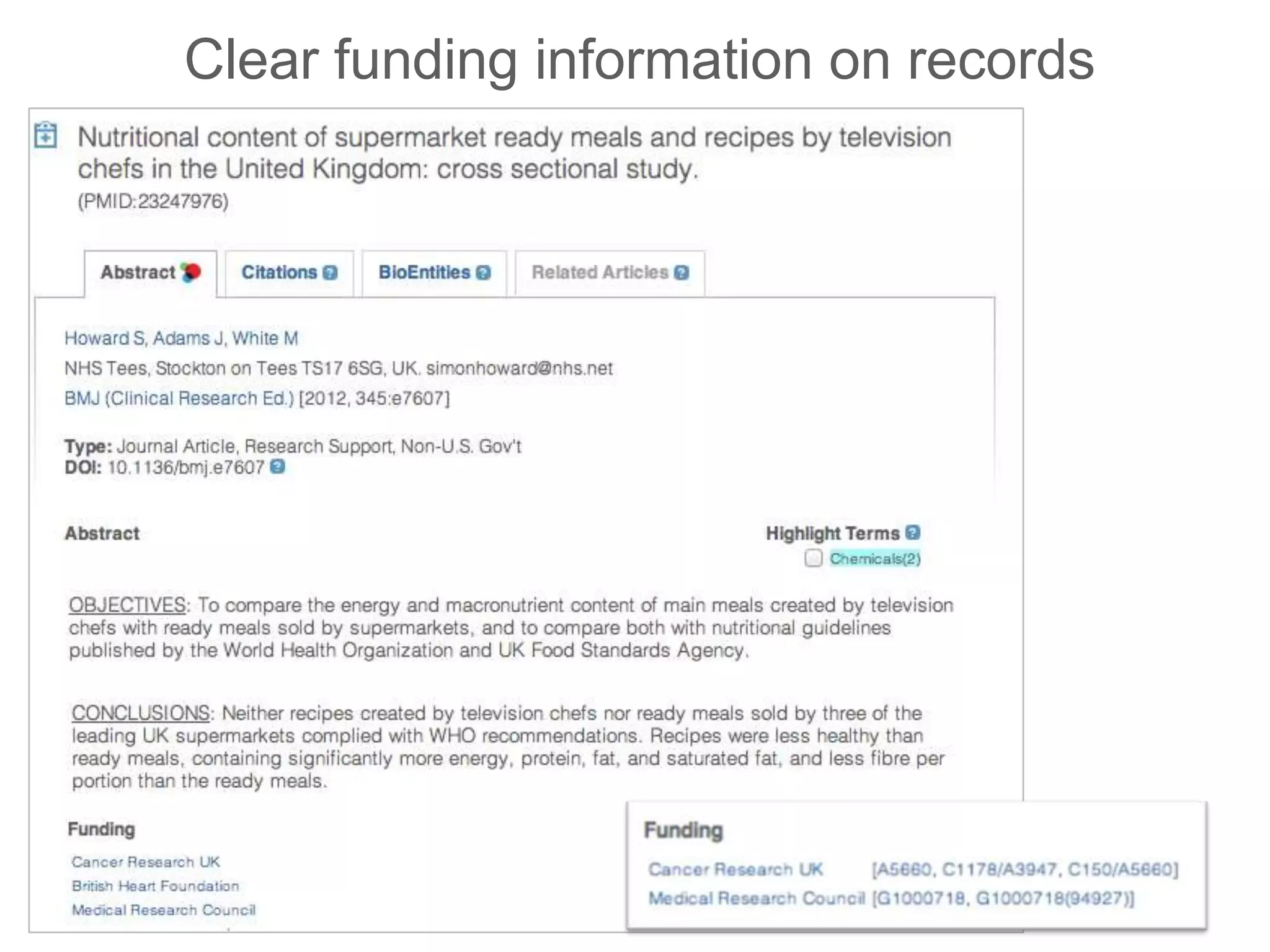
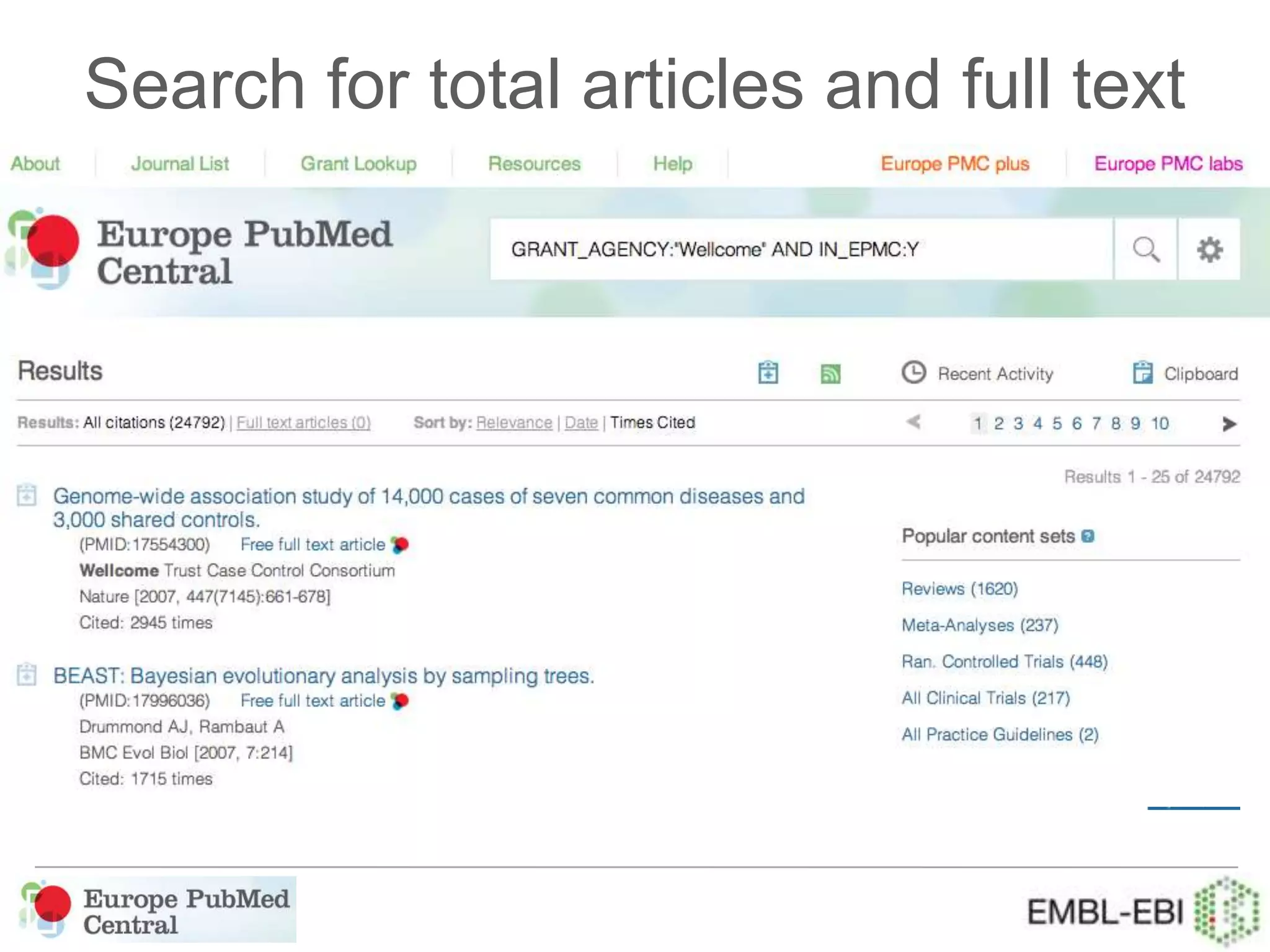
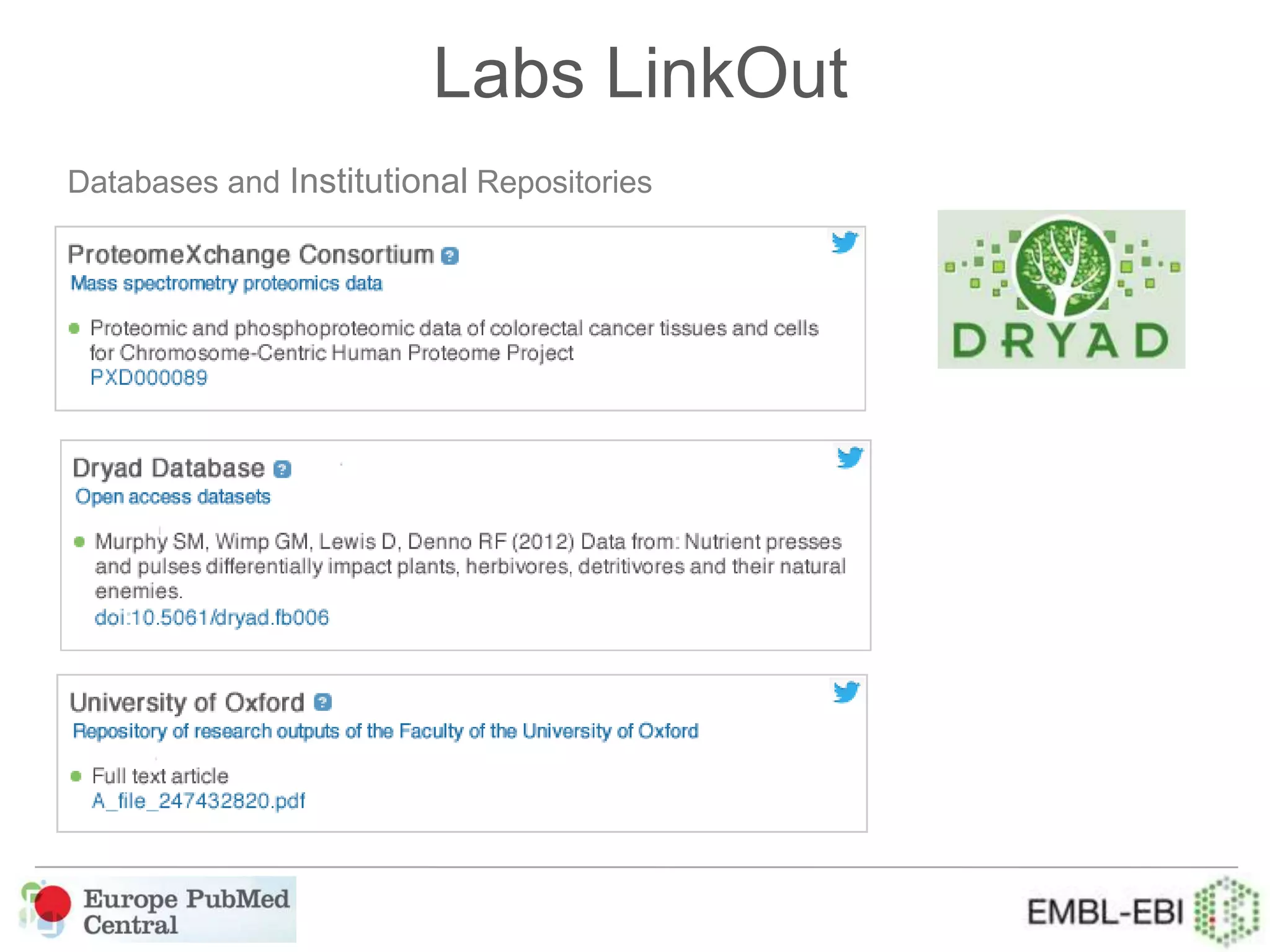
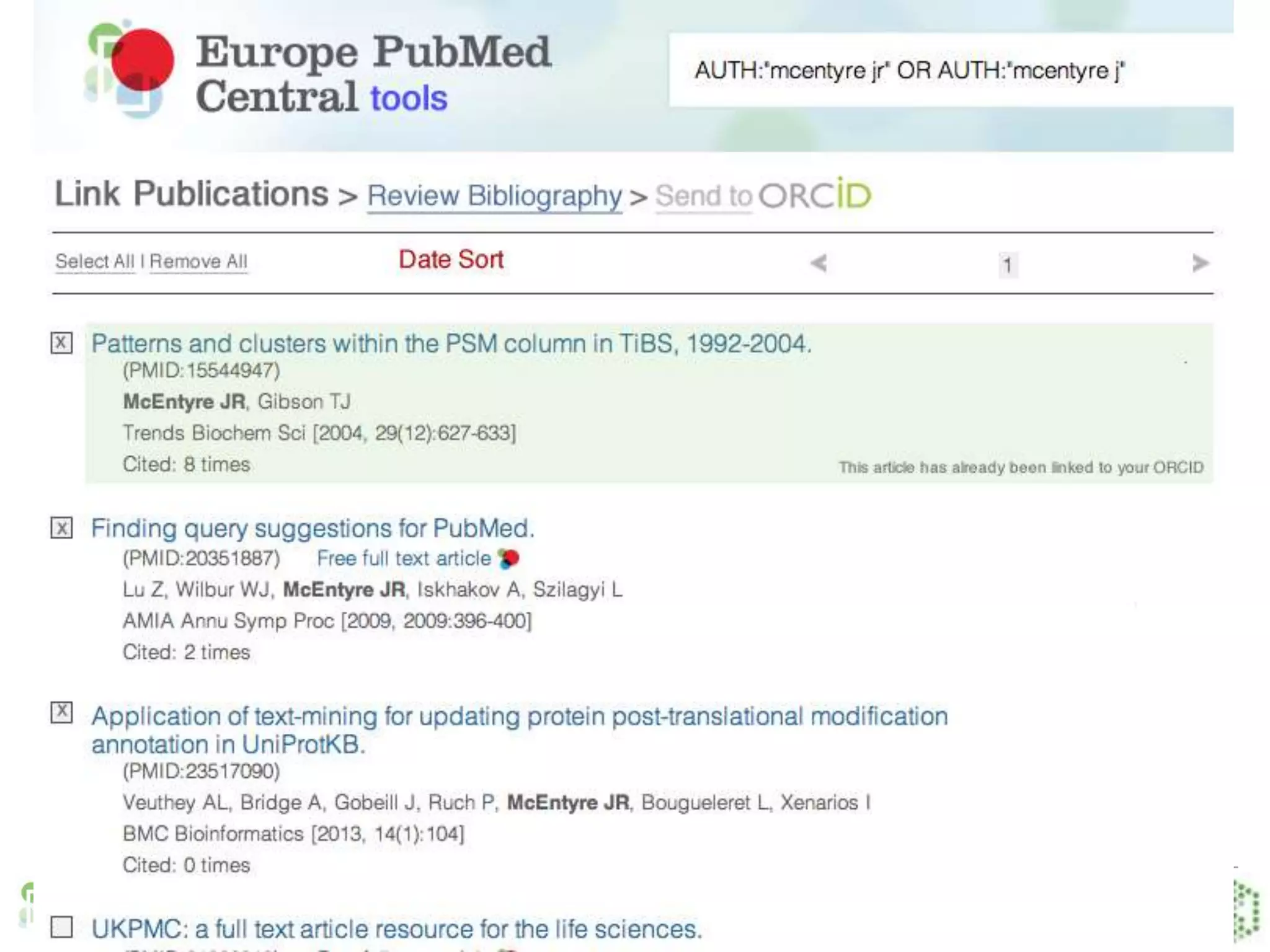
This document provides an overview of Europe PubMed Central, a repository for life science literature built in collaboration with PubMed Central USA and Canada. It contains over 28 million abstracts and 2.5 million full text articles, with 600k open access articles. The document outlines reasons to use Europe PMC including integrated searching of abstracts and full text, semantic enrichment of text, and citation linking. It also discusses providing credit for authors, funders, and data through features like author search and linking publications to ORCID profiles. Tools are being developed for database curators to monitor when data is cited in articles.