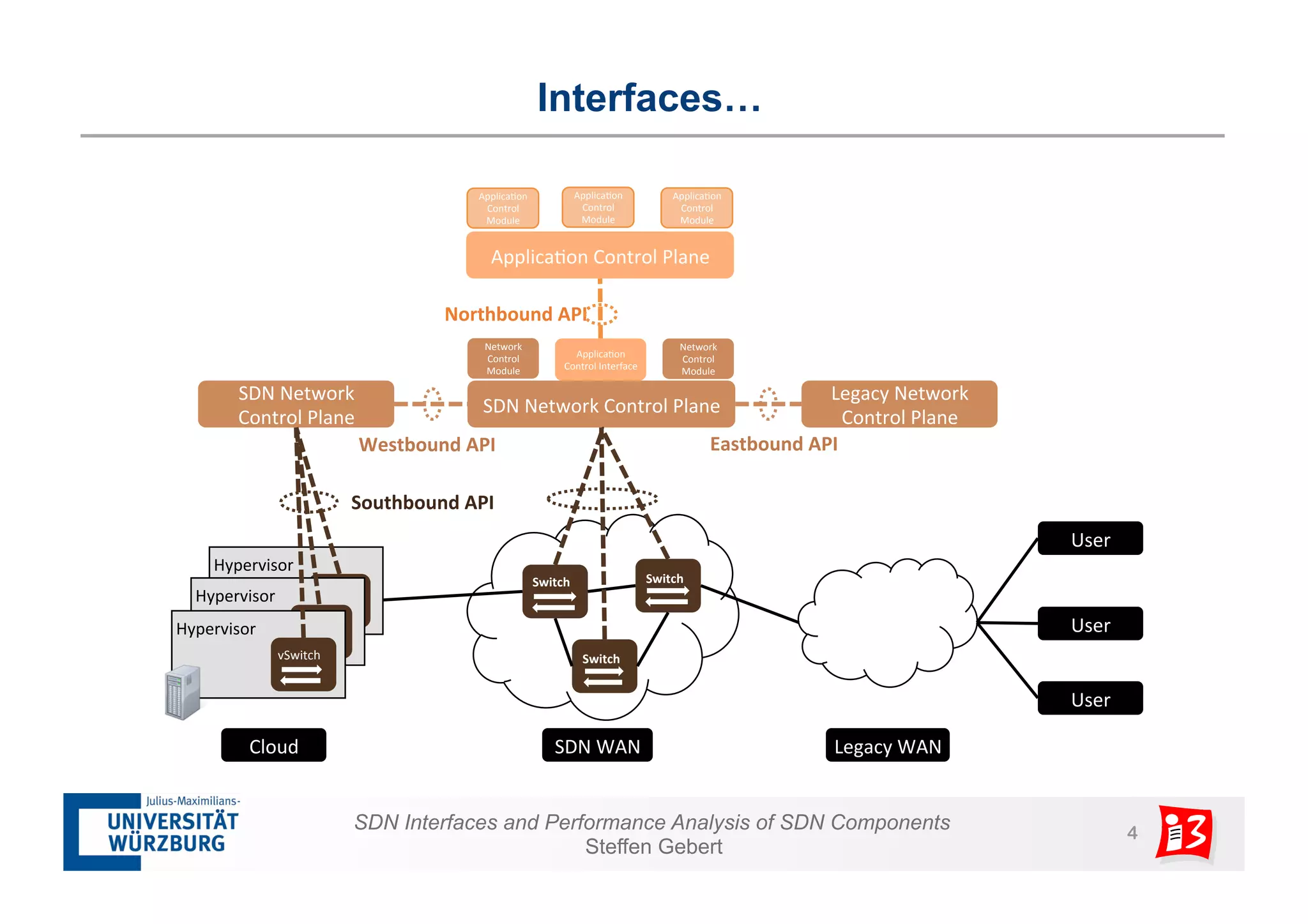
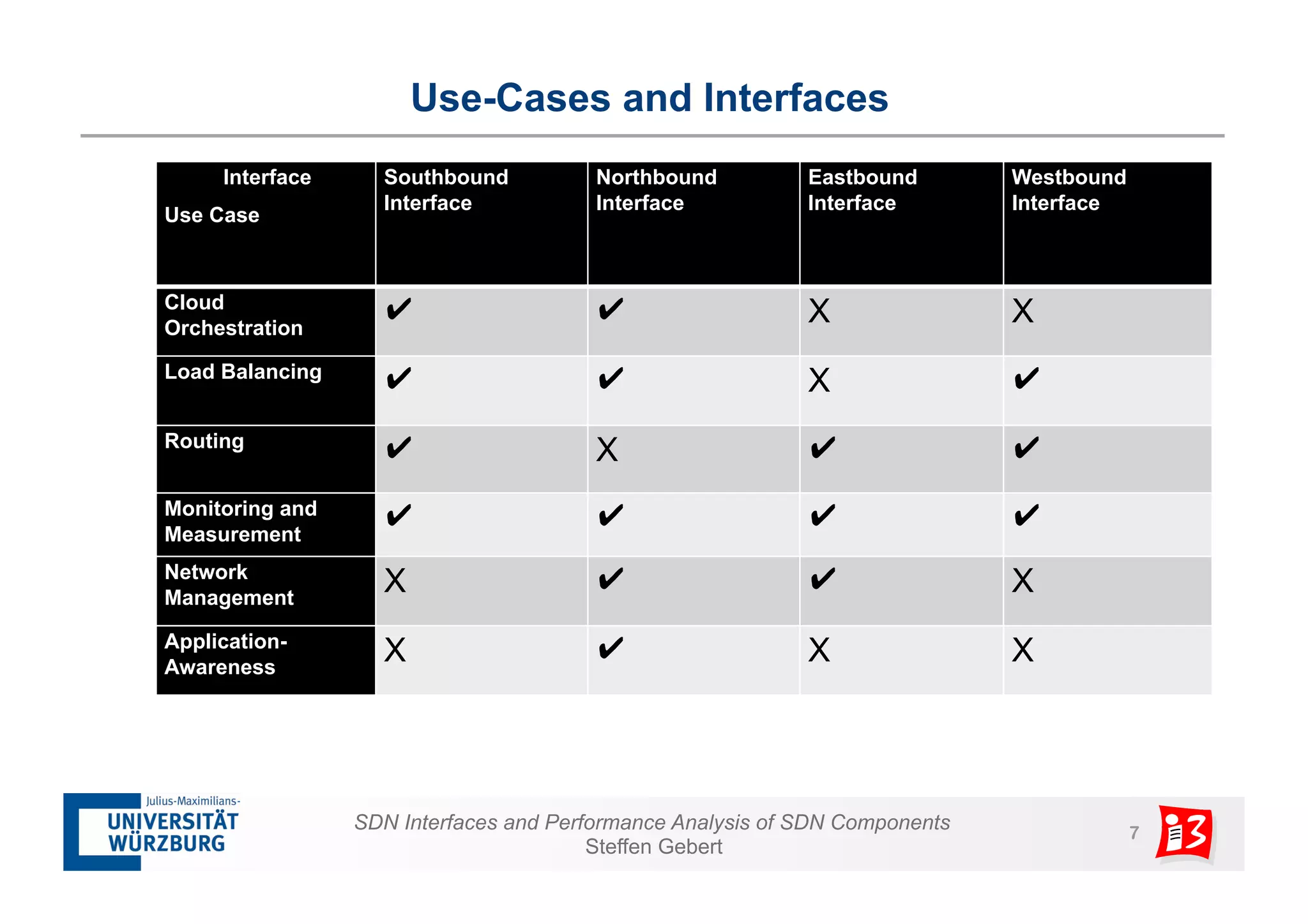
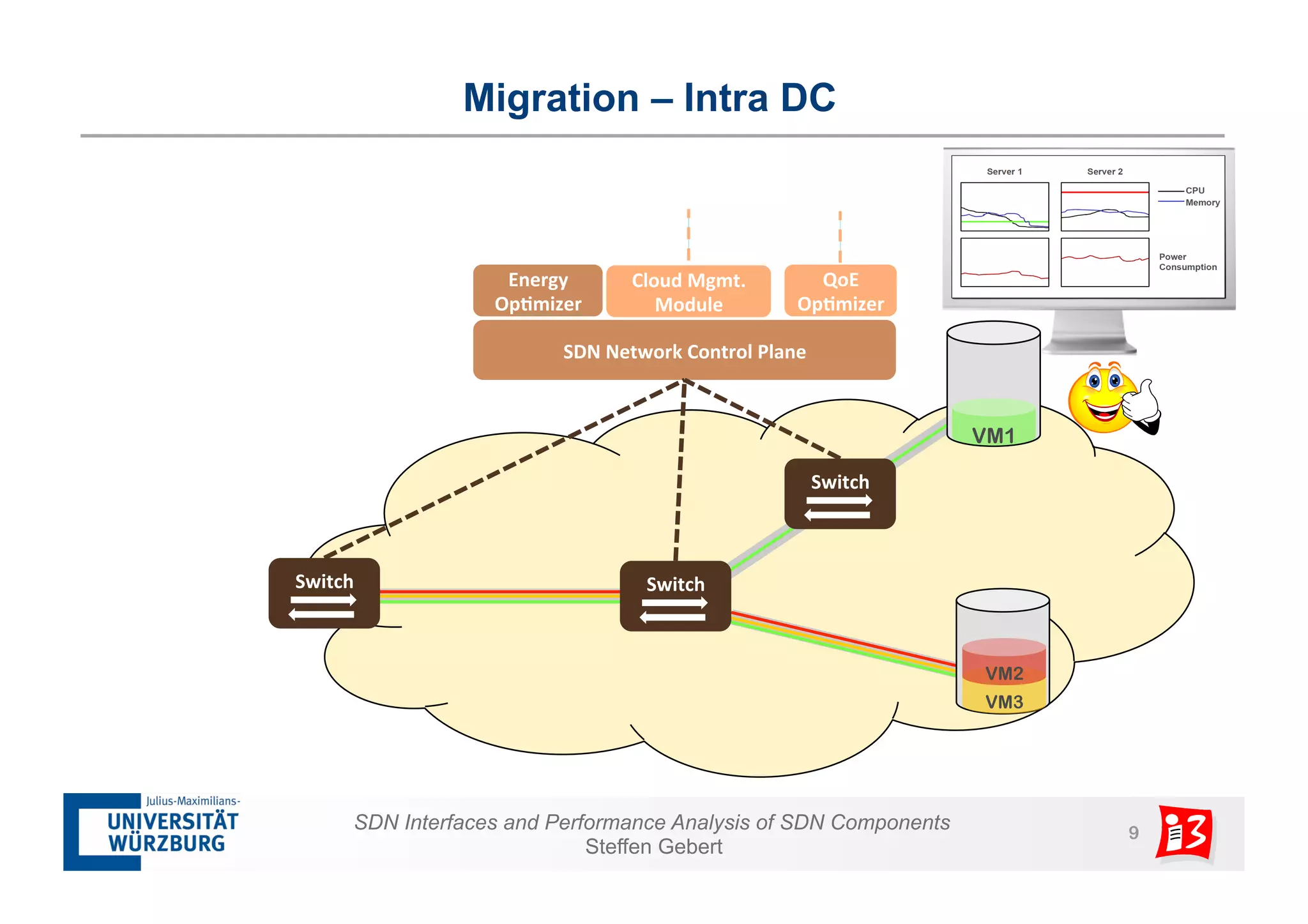
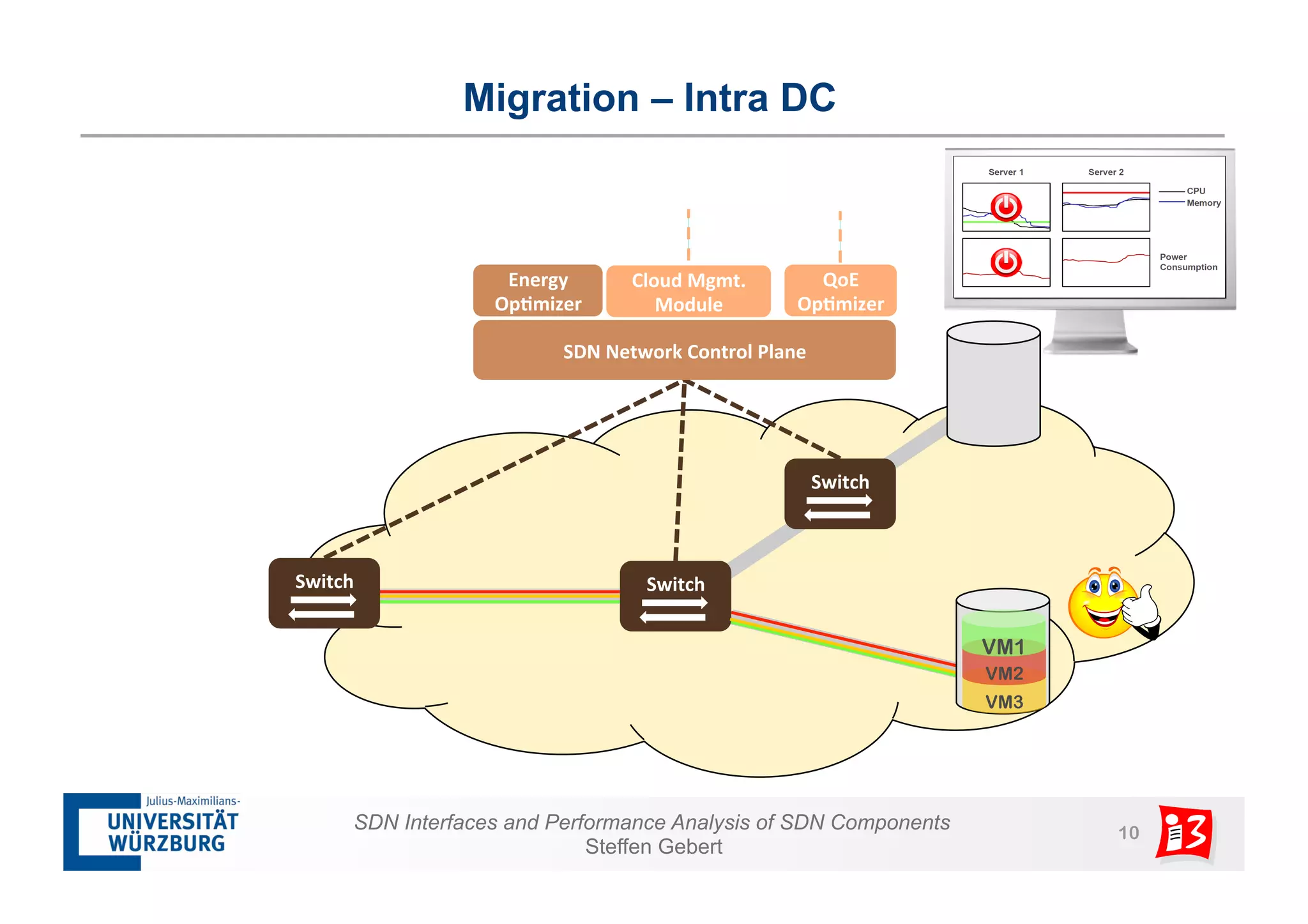
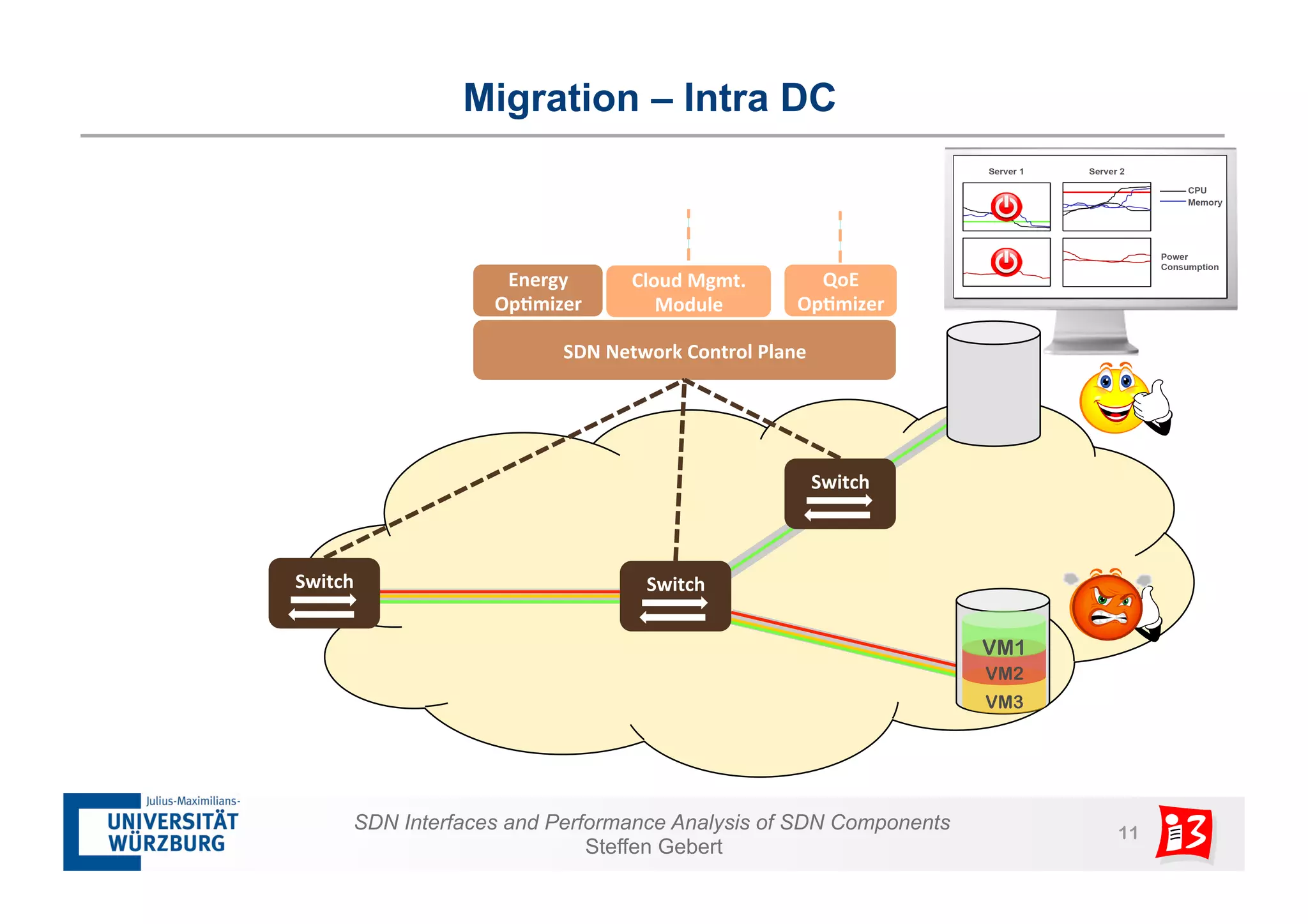
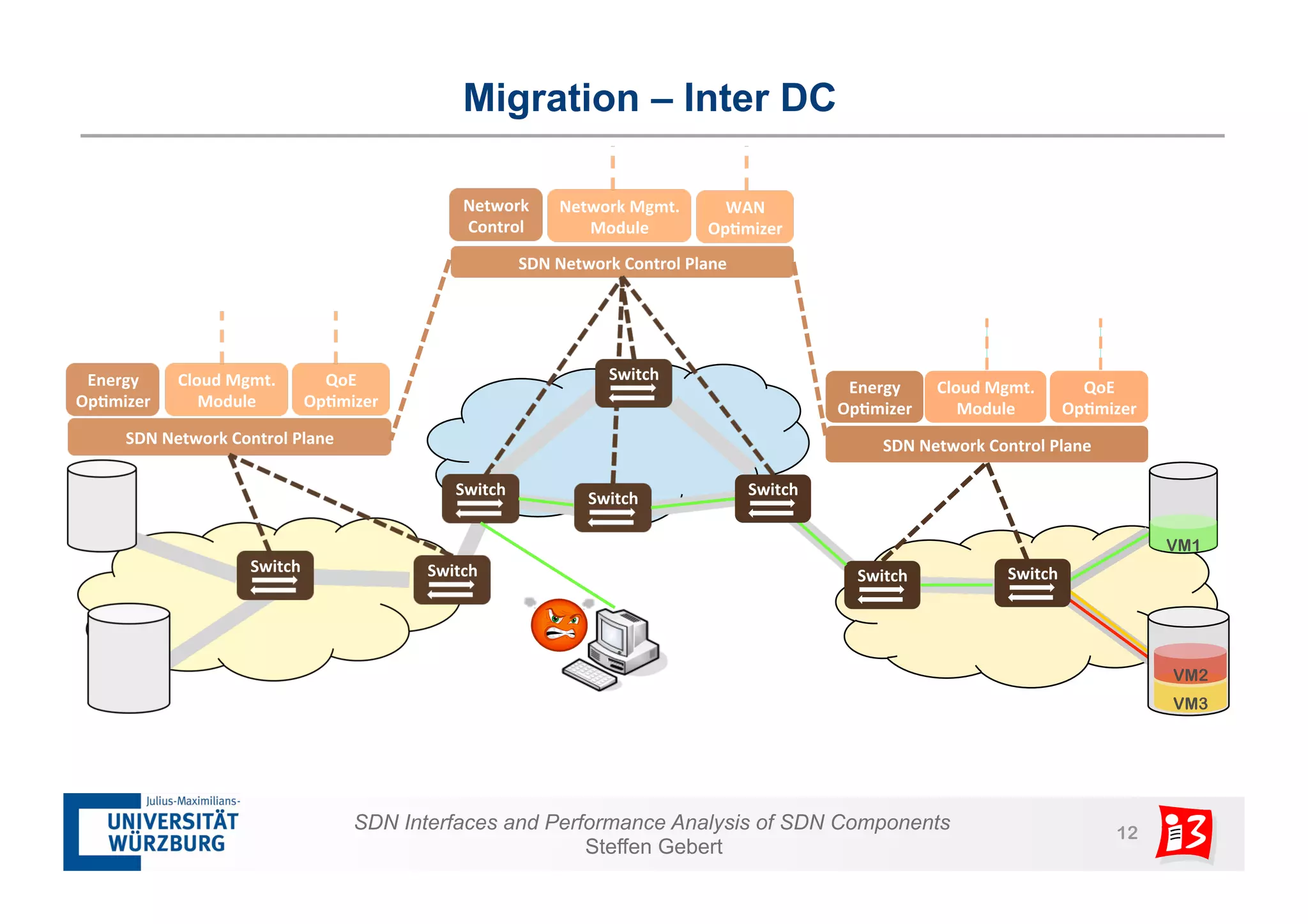
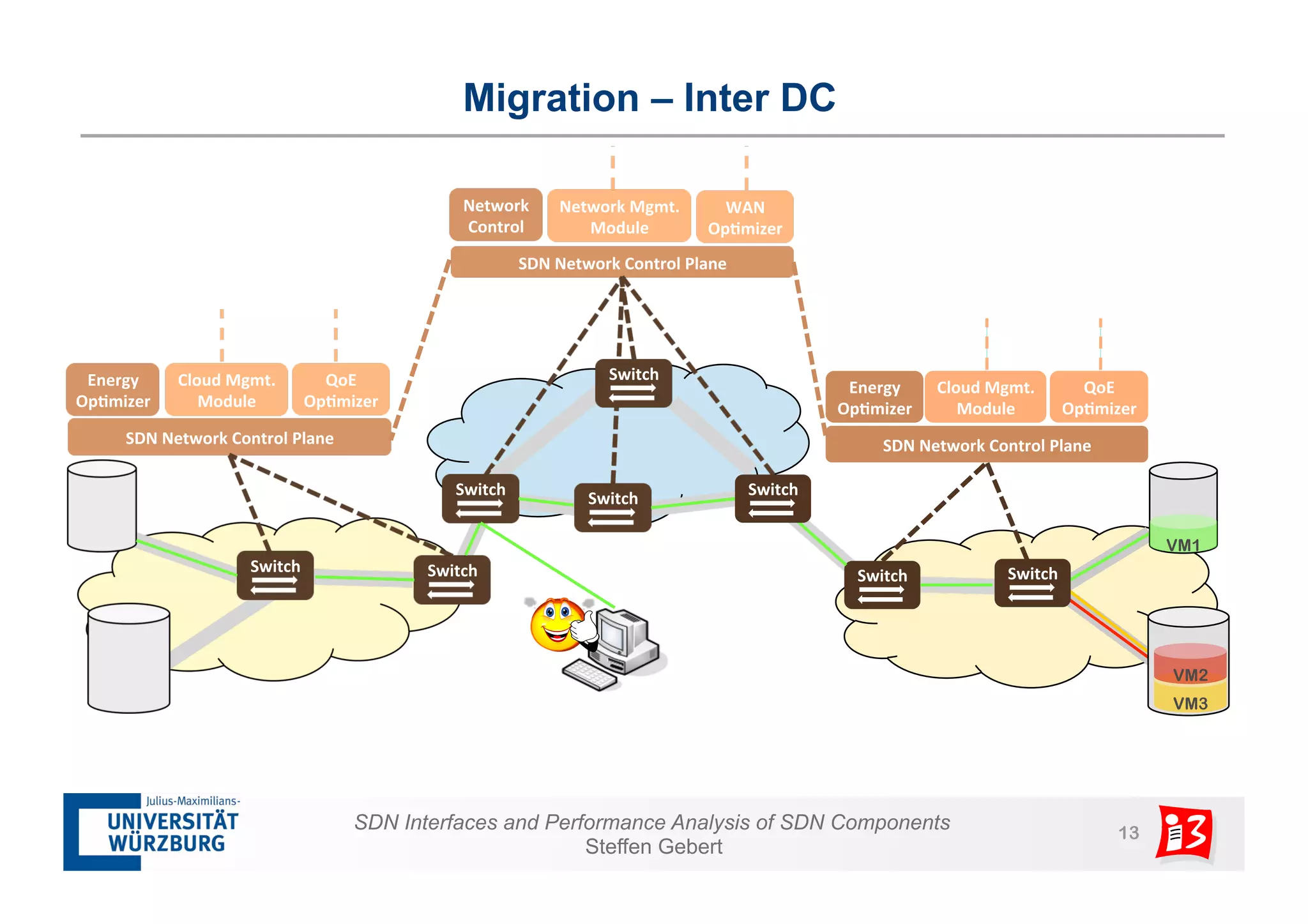
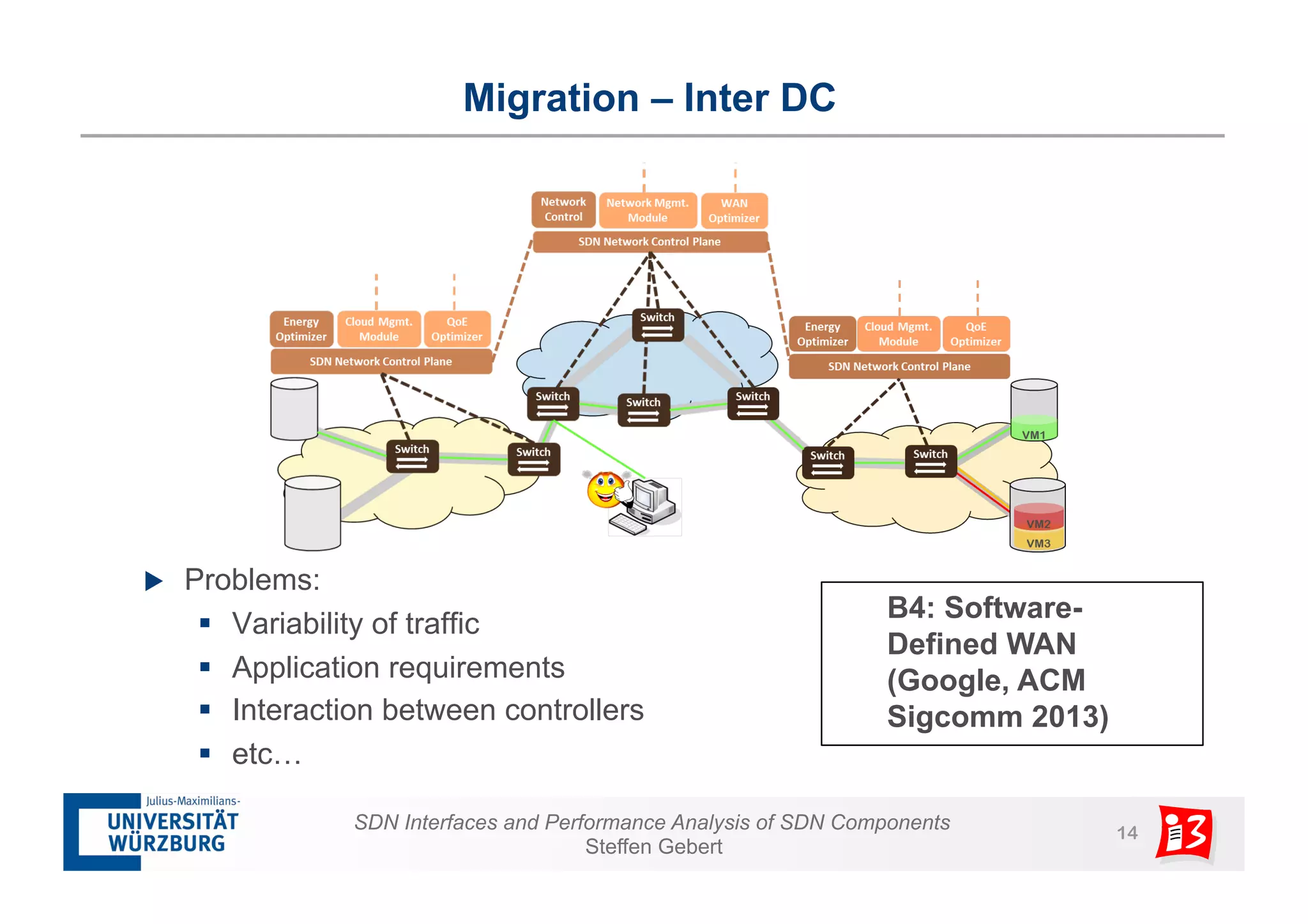
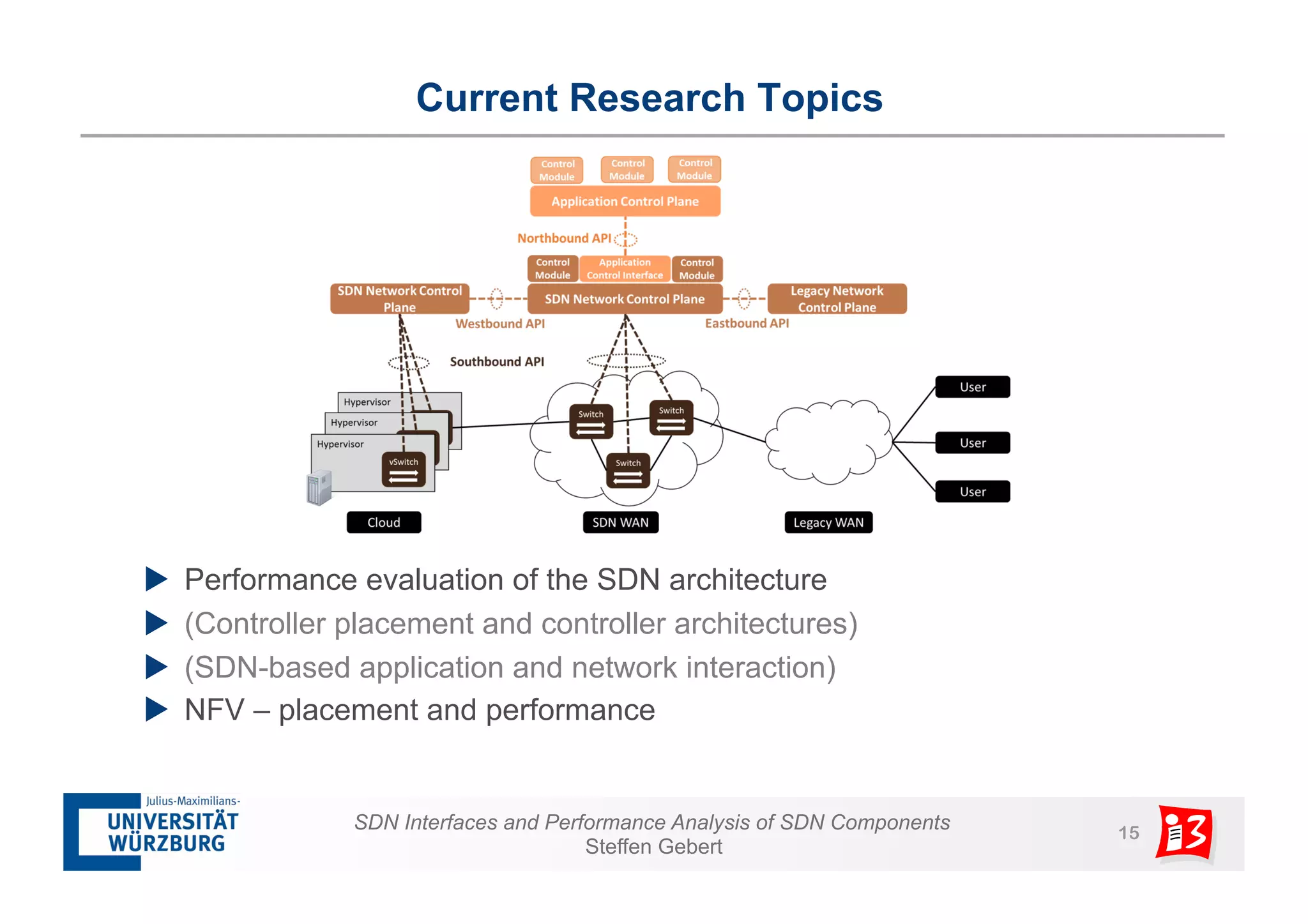
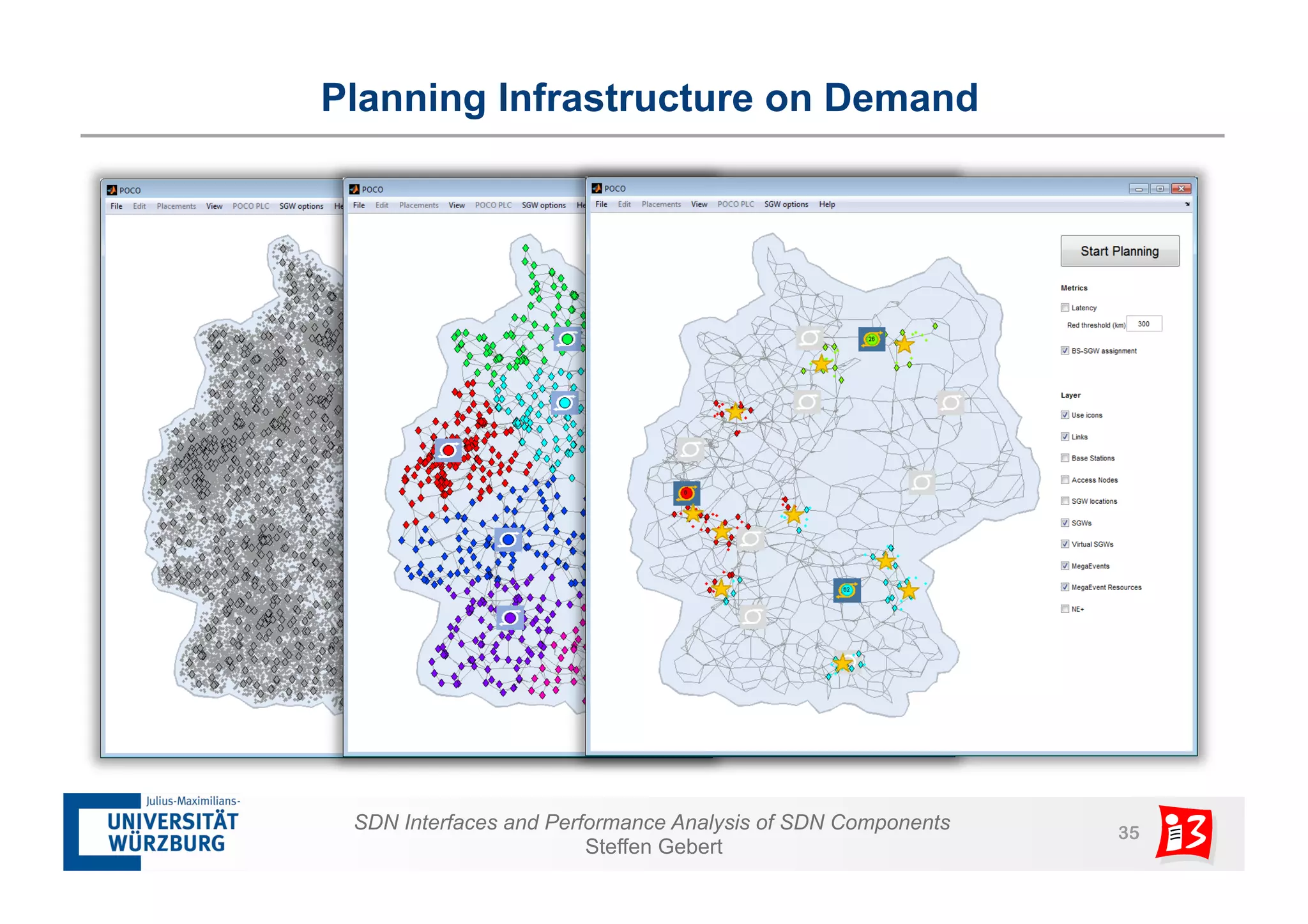
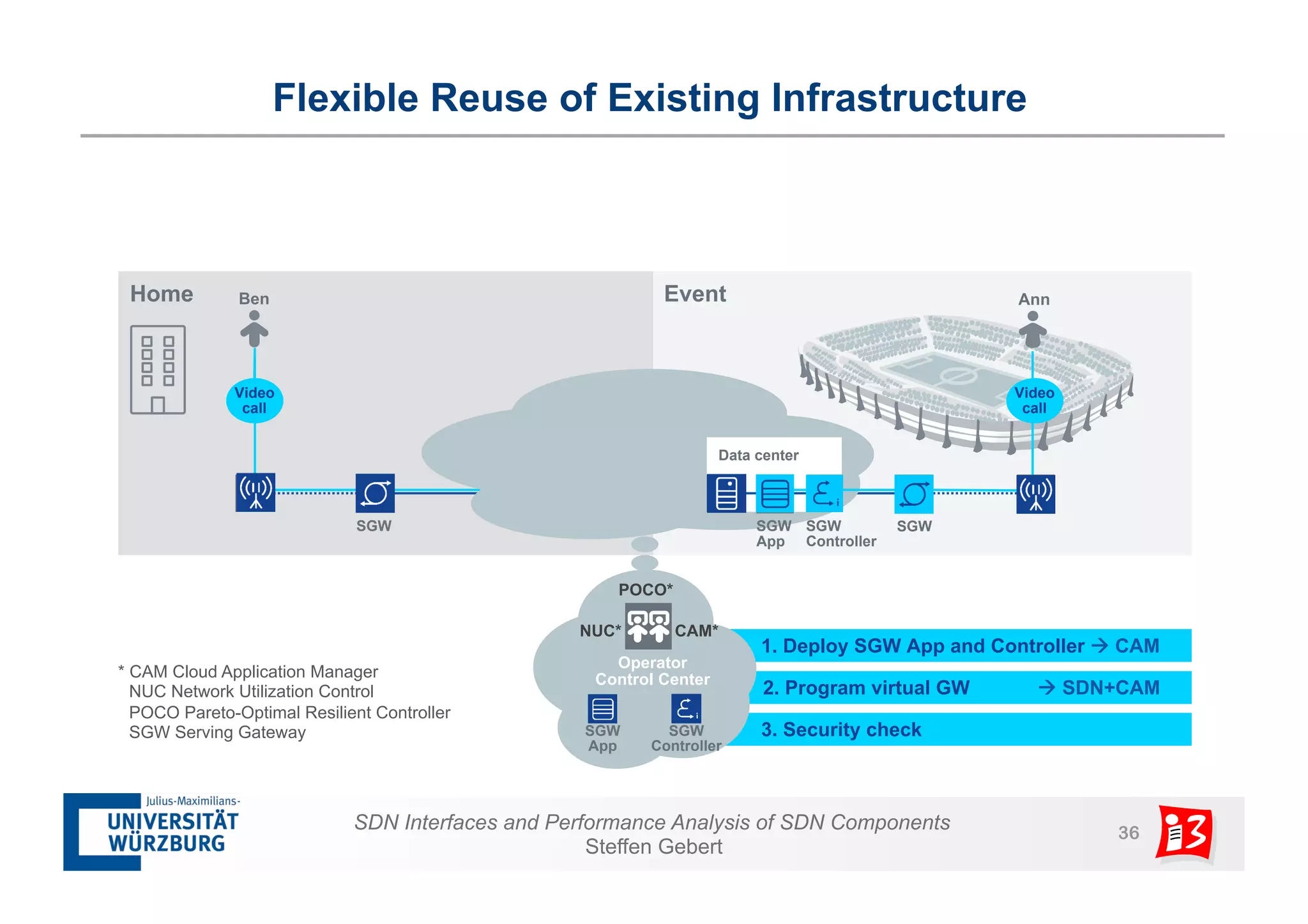
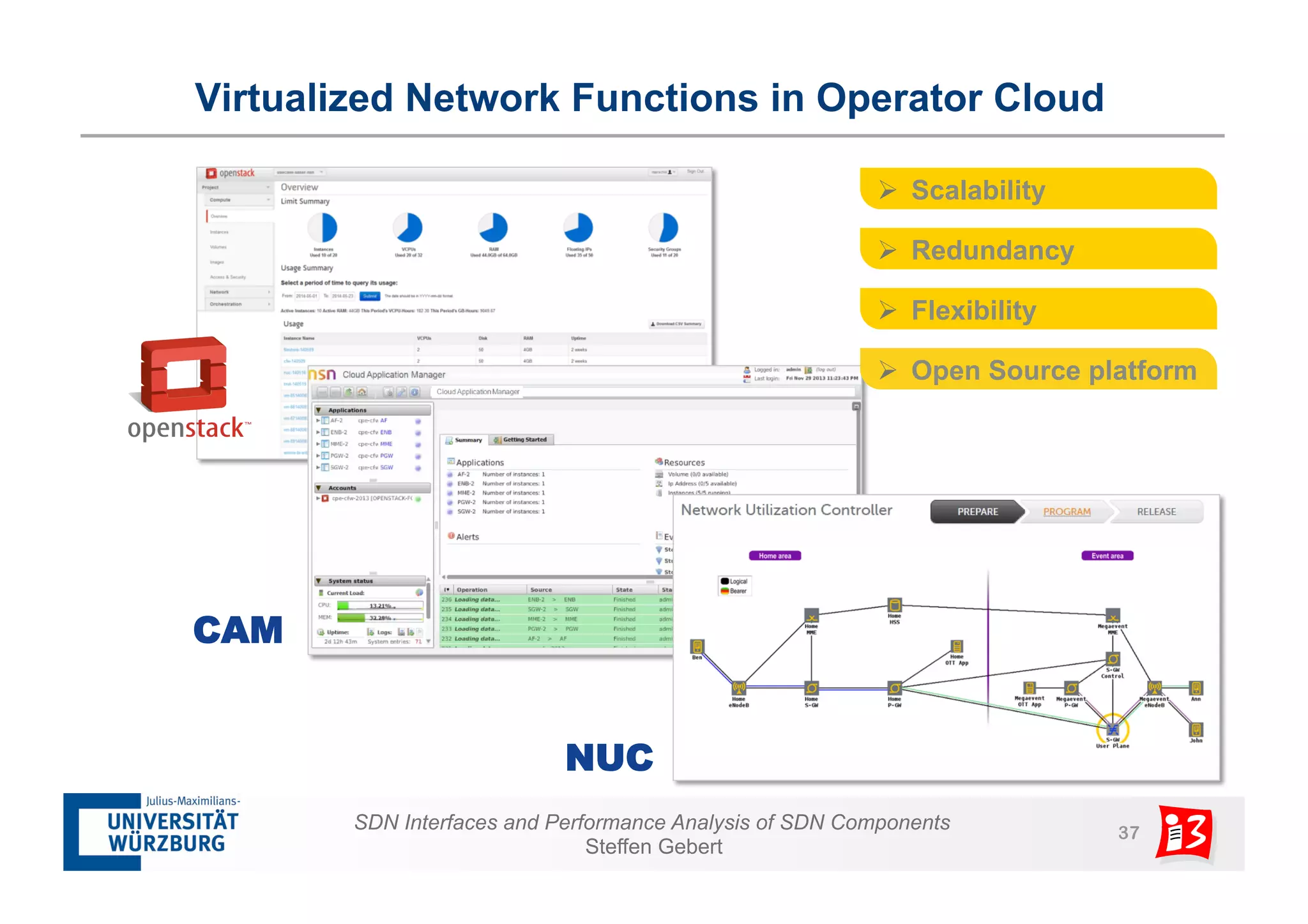
1. The document discusses SDN interfaces, performance analysis of SDN components, and network functions virtualization.
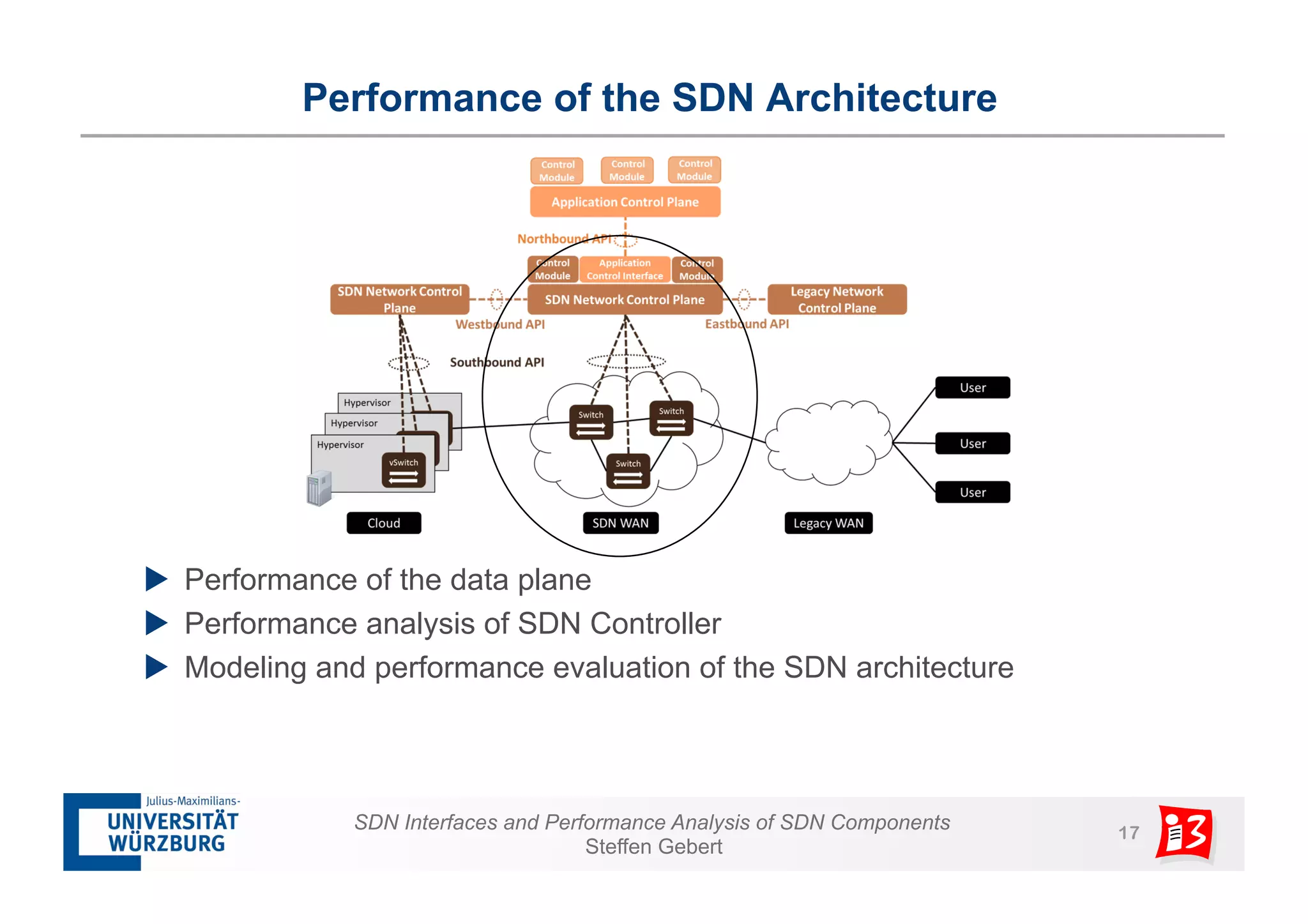
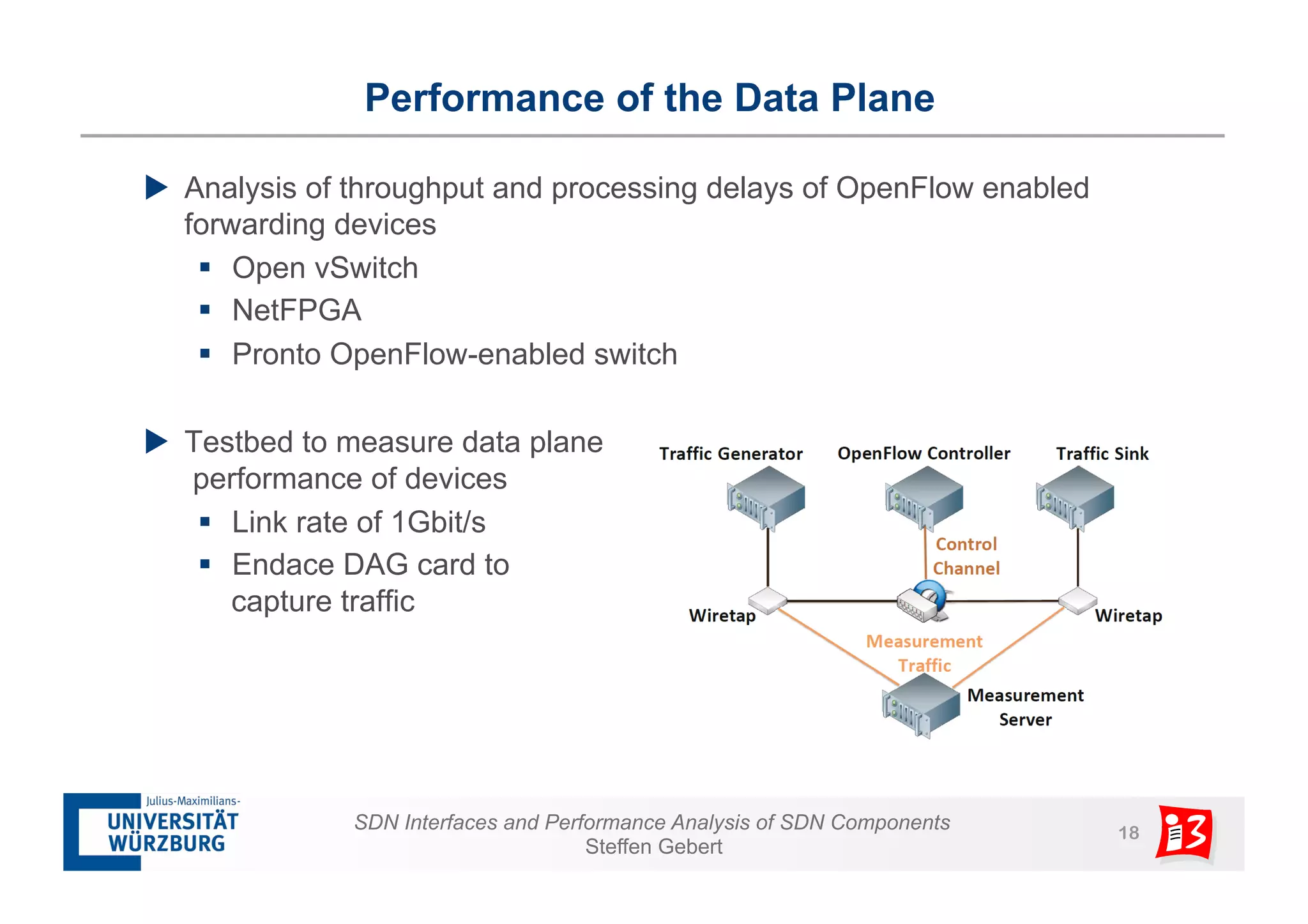
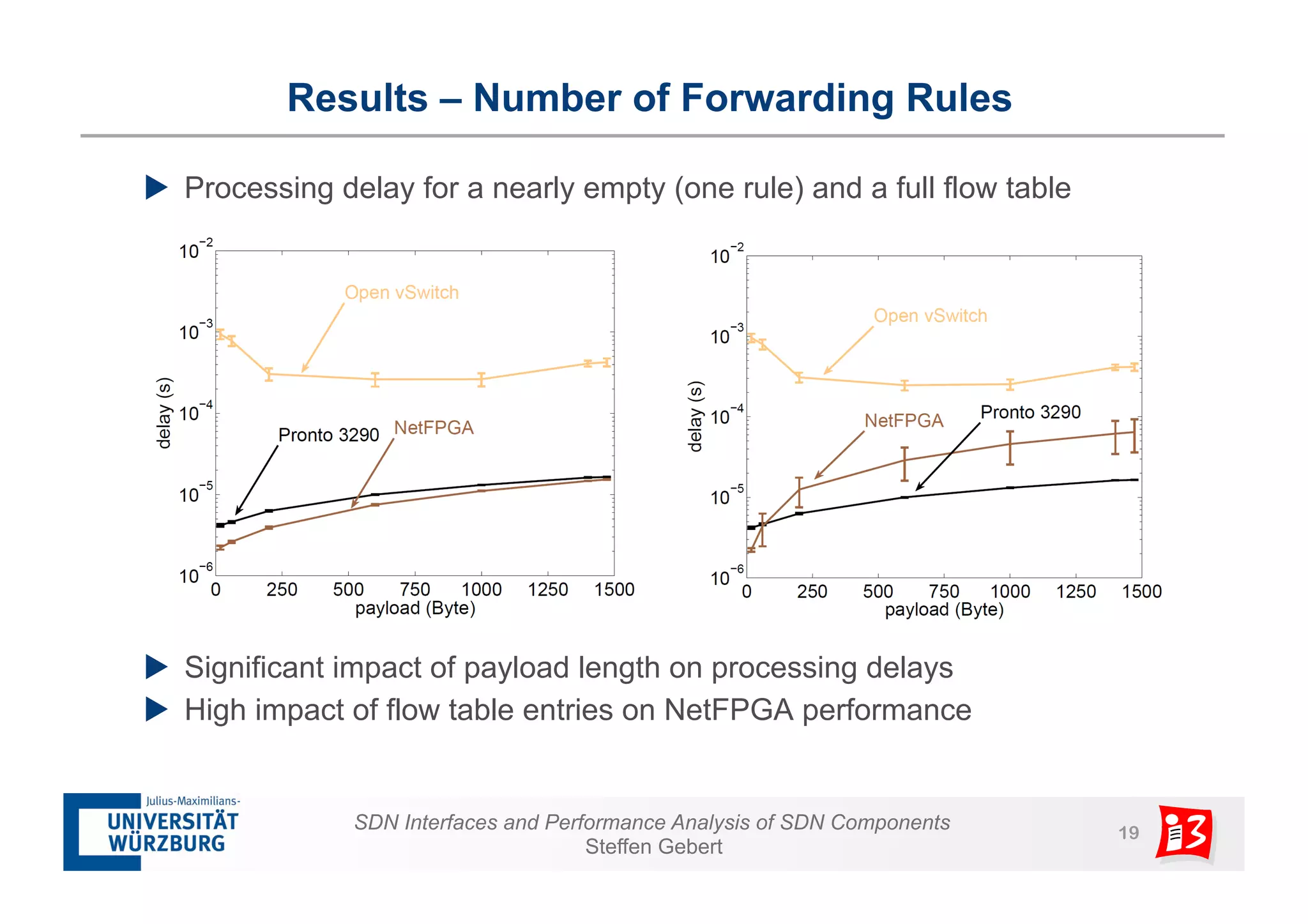
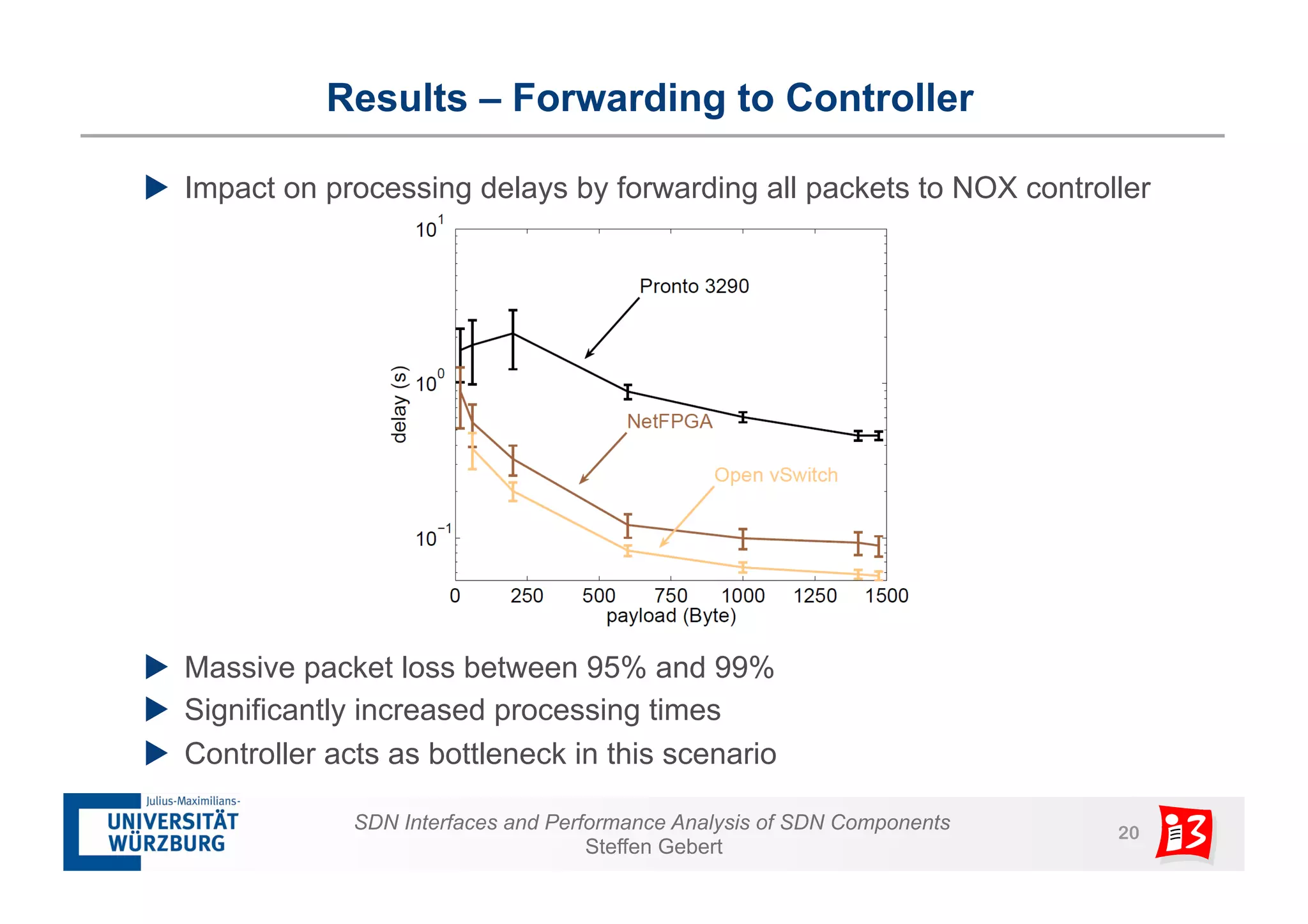
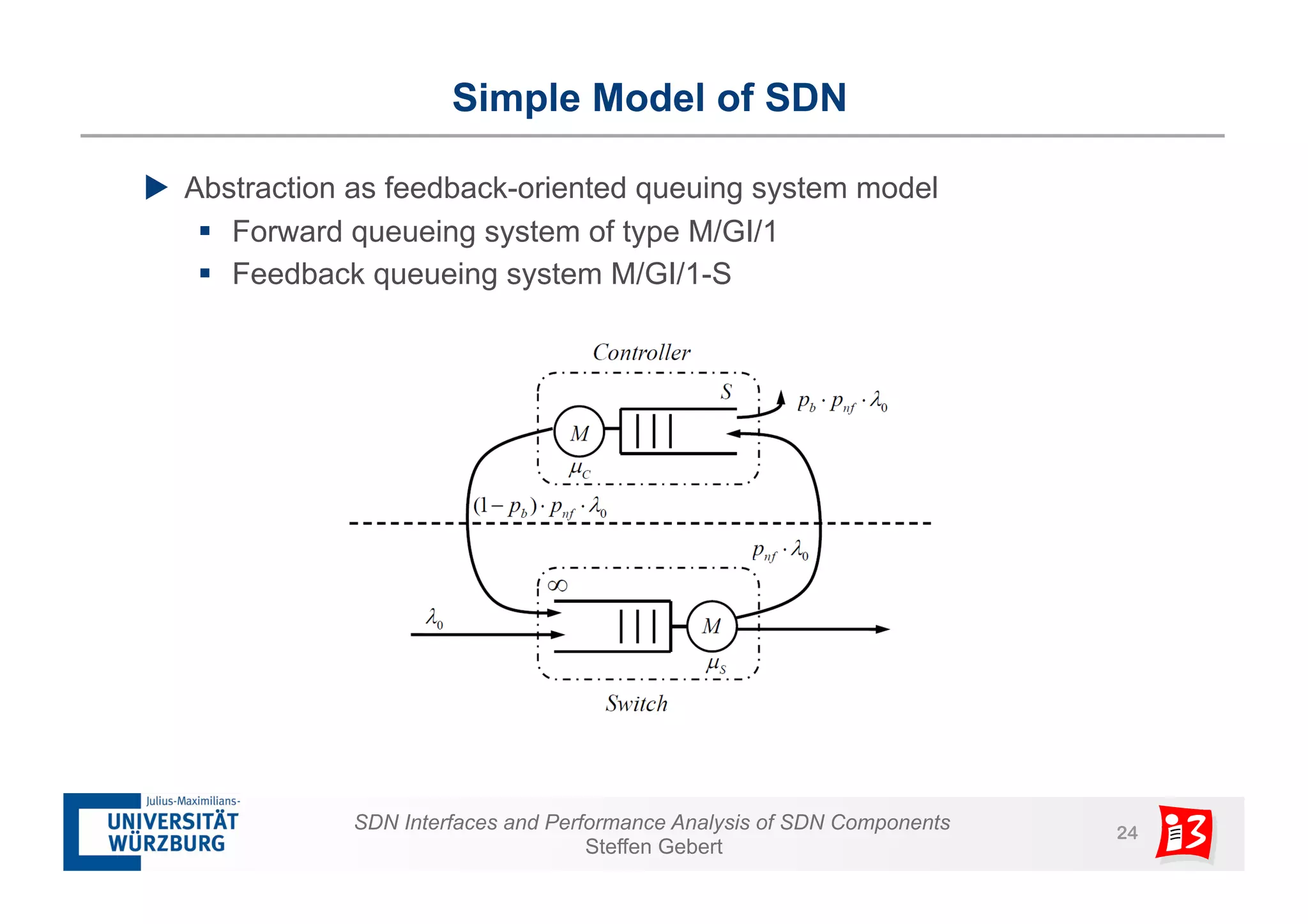
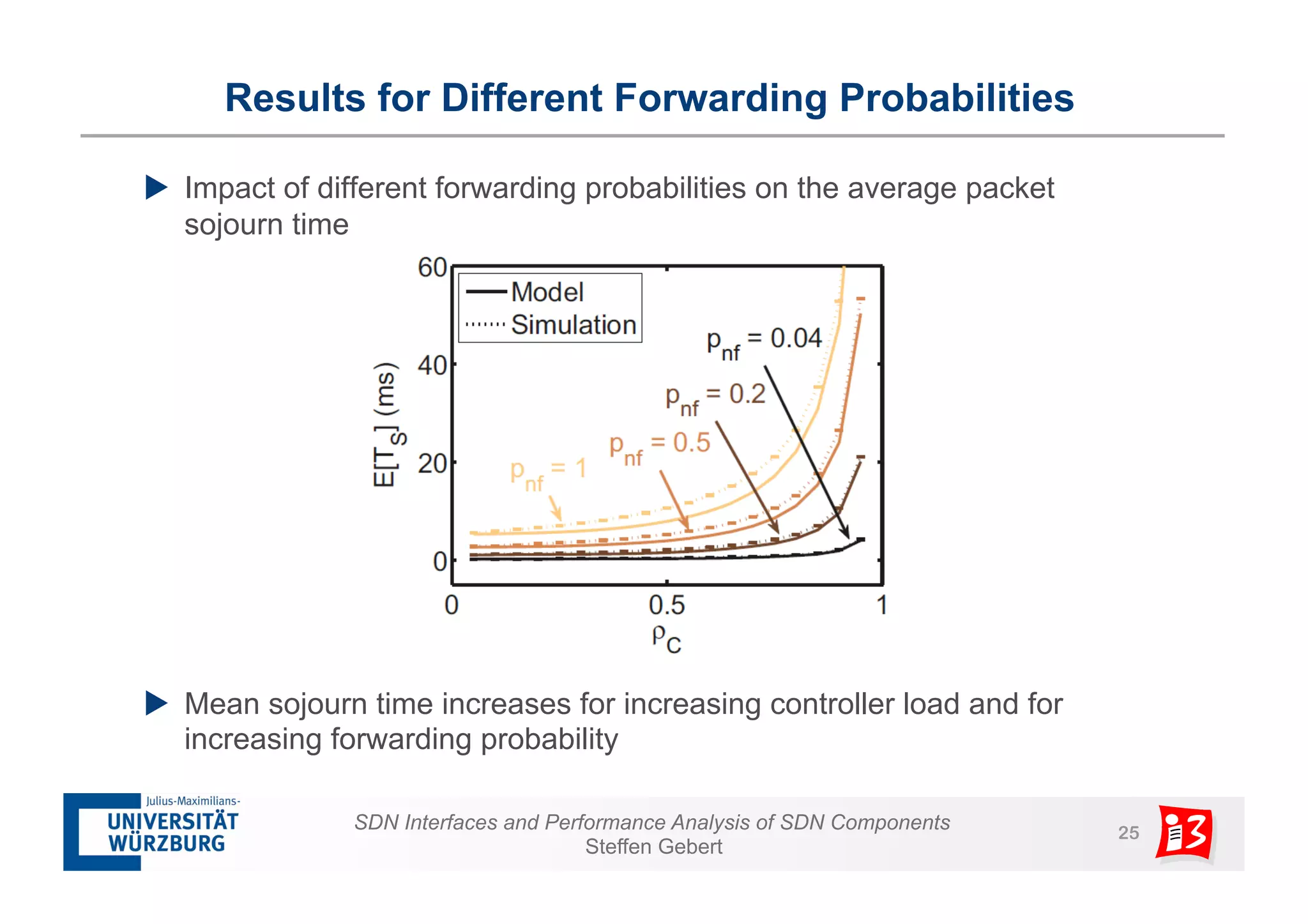
2. It analyzes the performance of SDN controllers and the data plane, and provides models to evaluate the performance of the SDN architecture under different conditions.
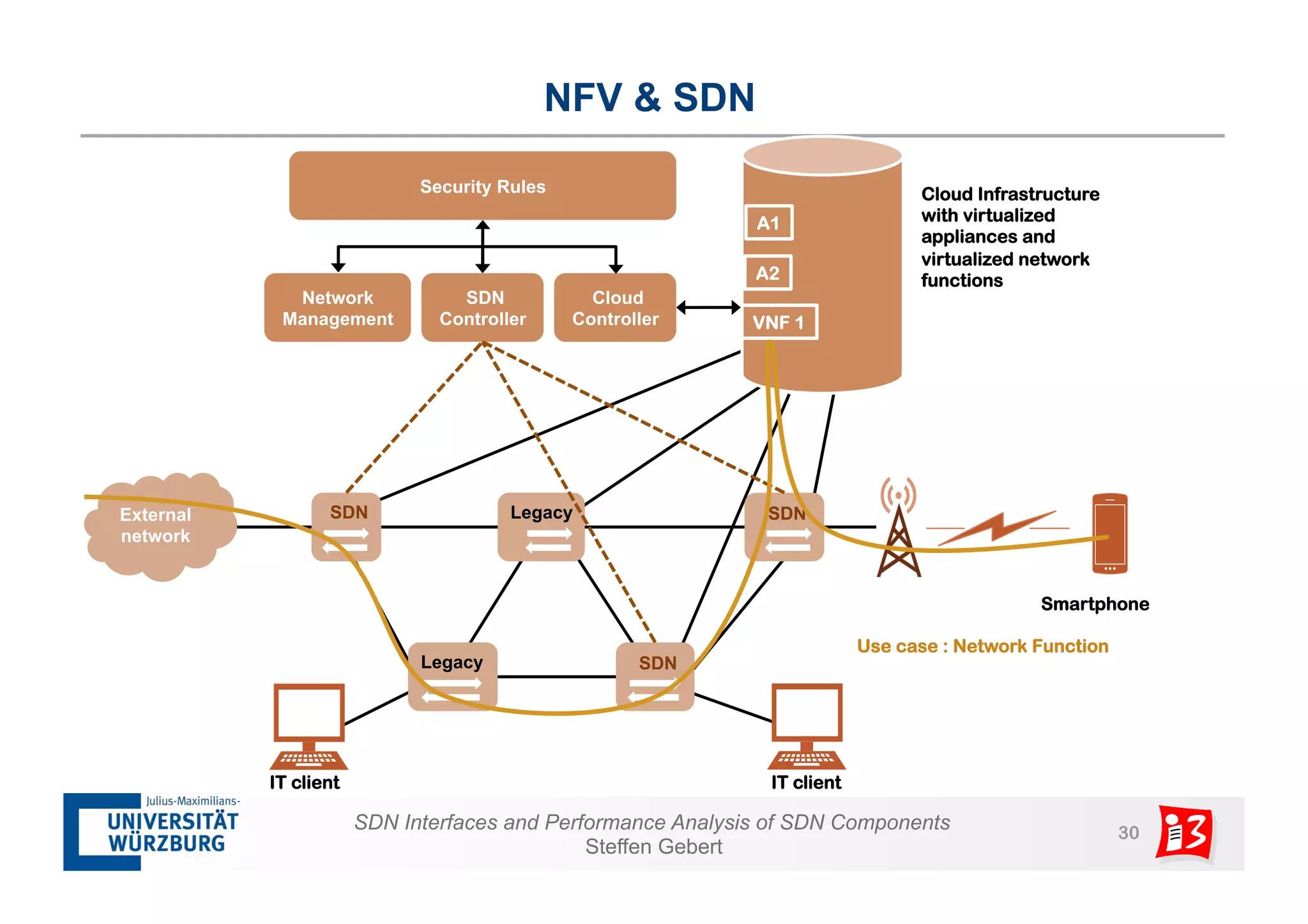
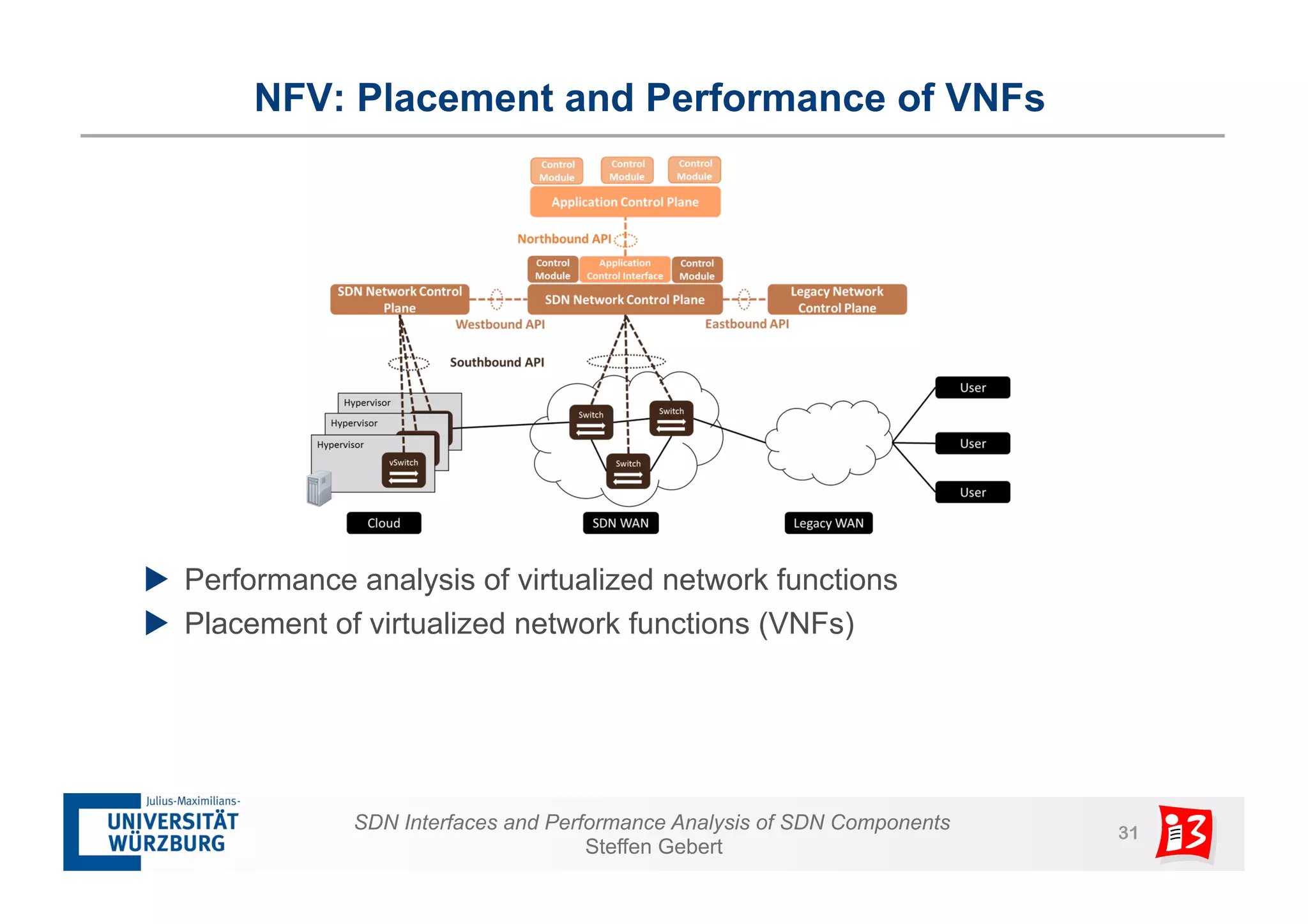
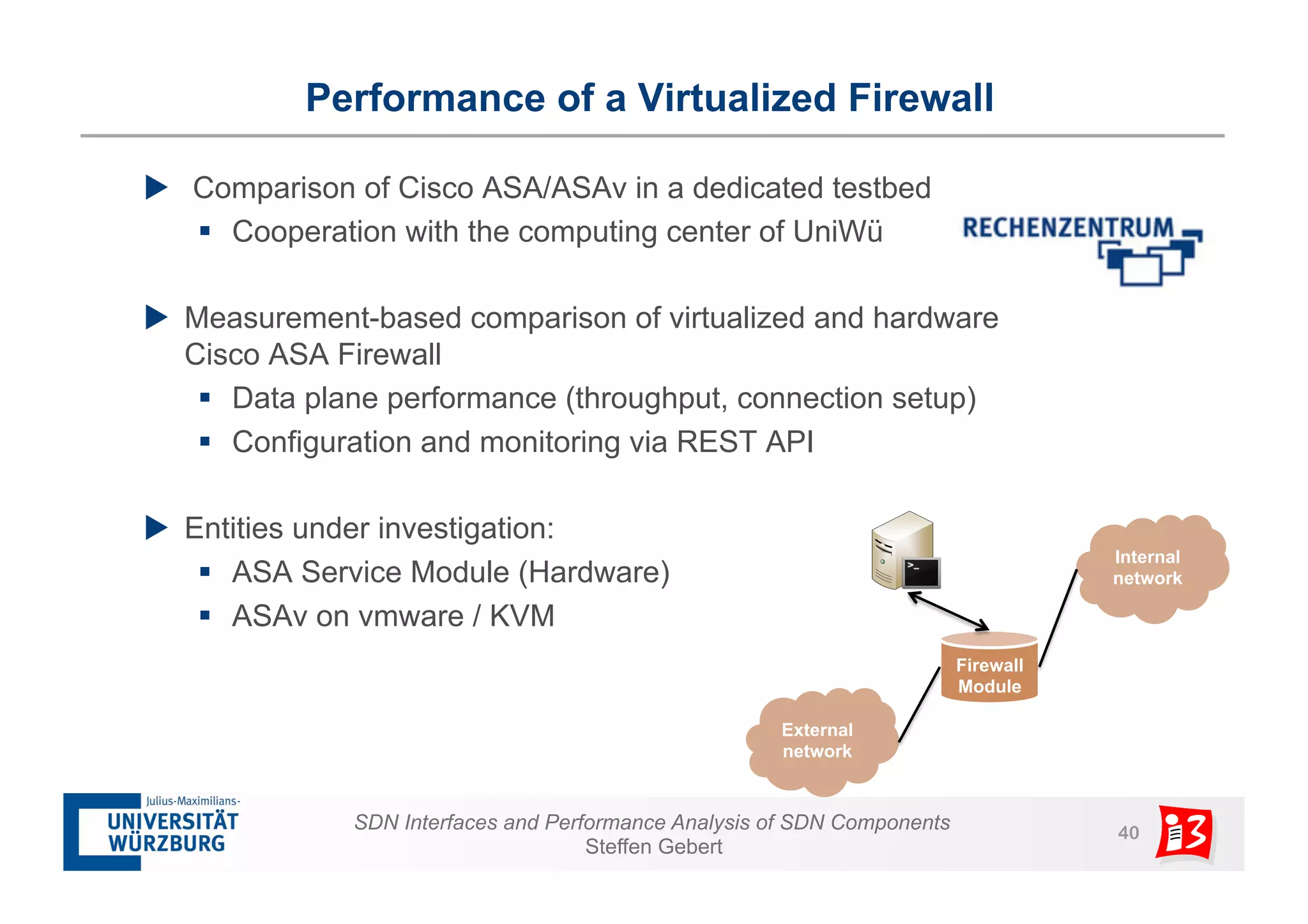
3. The document also examines network functions virtualization, including placement of virtualized network functions and performance evaluation of a virtualized firewall.