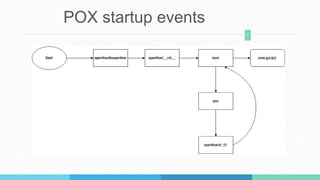
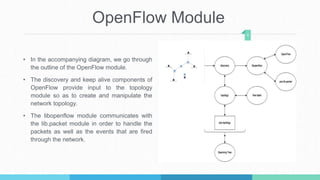
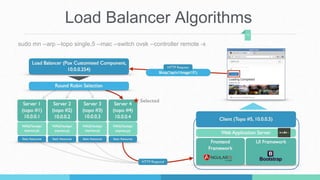
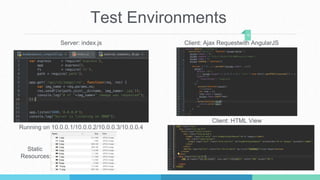
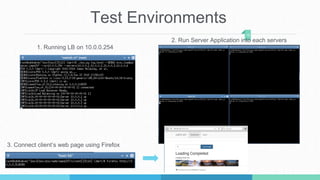
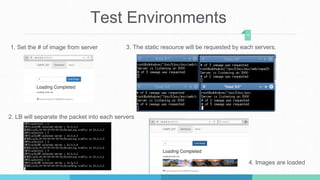
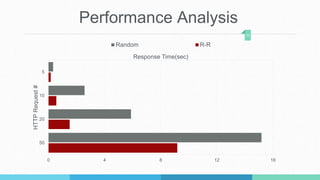
This document describes a student project to implement a software-defined network load balancer using the POX controller. It is divided into two parts: the first part analyzes the POX controller and its OpenFlow module, explaining components like the libopenflow library and discovery module. The second part details the development of a load balancer using a round-robin algorithm to distribute traffic across multiple servers, including modifications made to the POX code and testing in a Mininet environment to analyze performance.