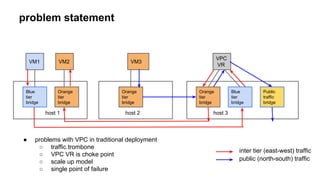
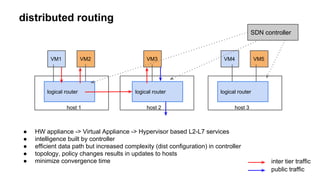
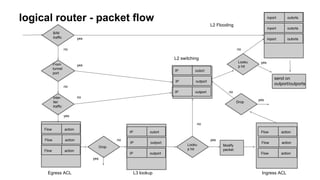
This document discusses using SDN and OpenFlow to implement distributed routing in CloudStack. It describes how traditional VPC deployment has issues like traffic trombone effects and single points of failure. The CloudStack solution uses Open vSwitch bridges on each host configured by a CloudStack controller to act as logical routers, performing distributed routing for east-west traffic within a VPC while continuing to use VPC virtual routers for north-south traffic. It explains how the CloudStack controller populates the OpenFlow tables on each host bridge to implement the distributed routing and ACL policies.