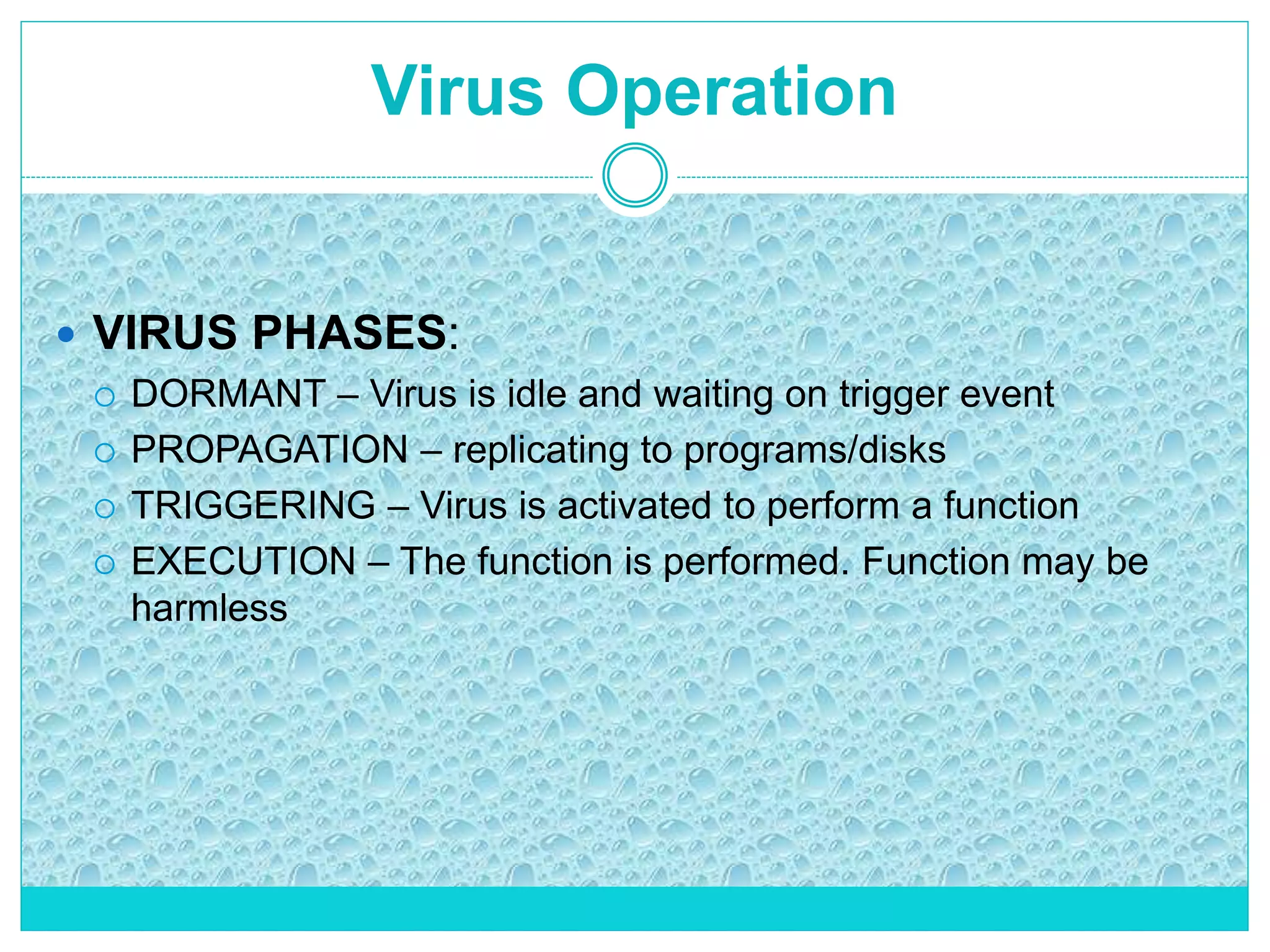
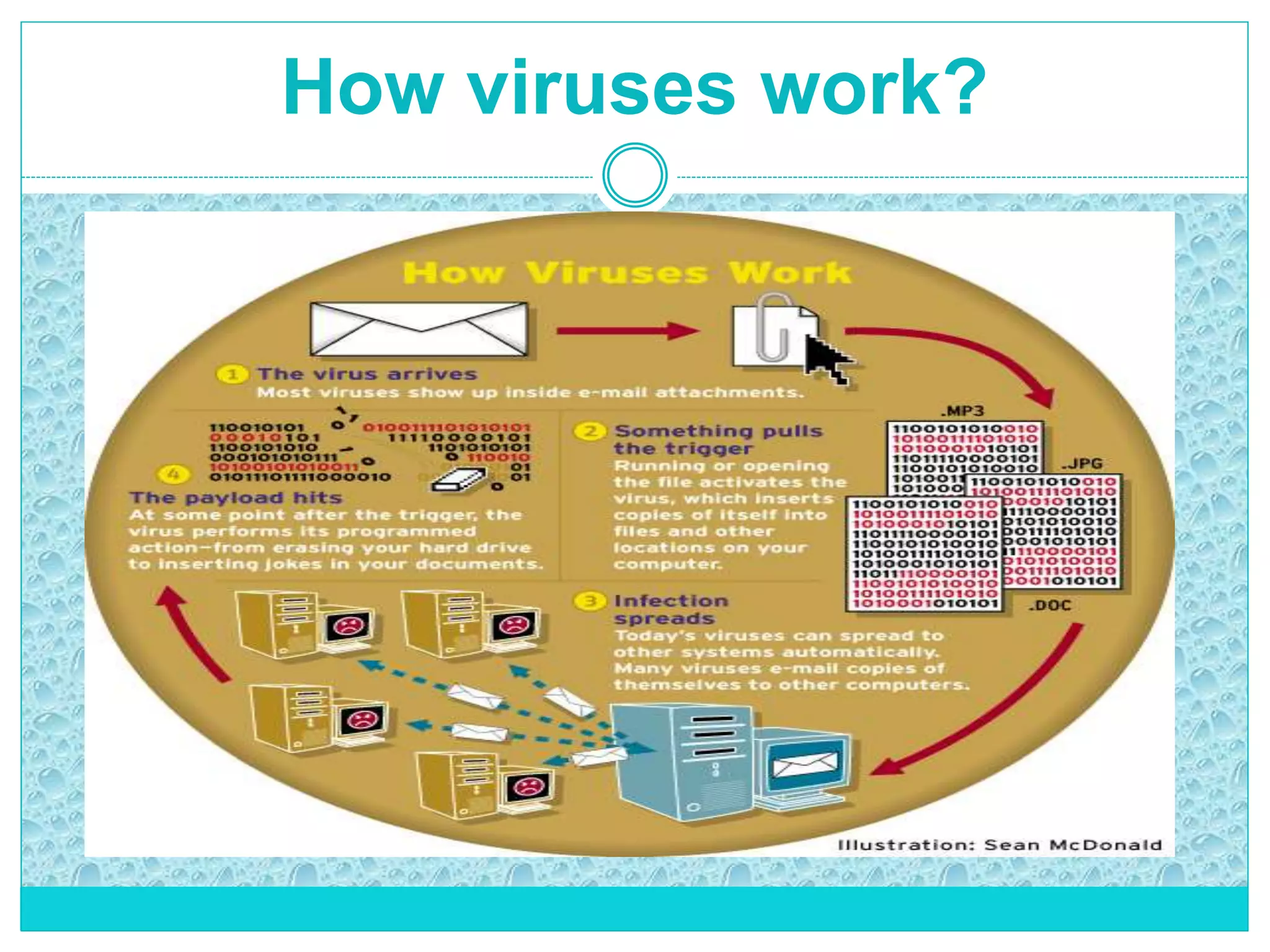
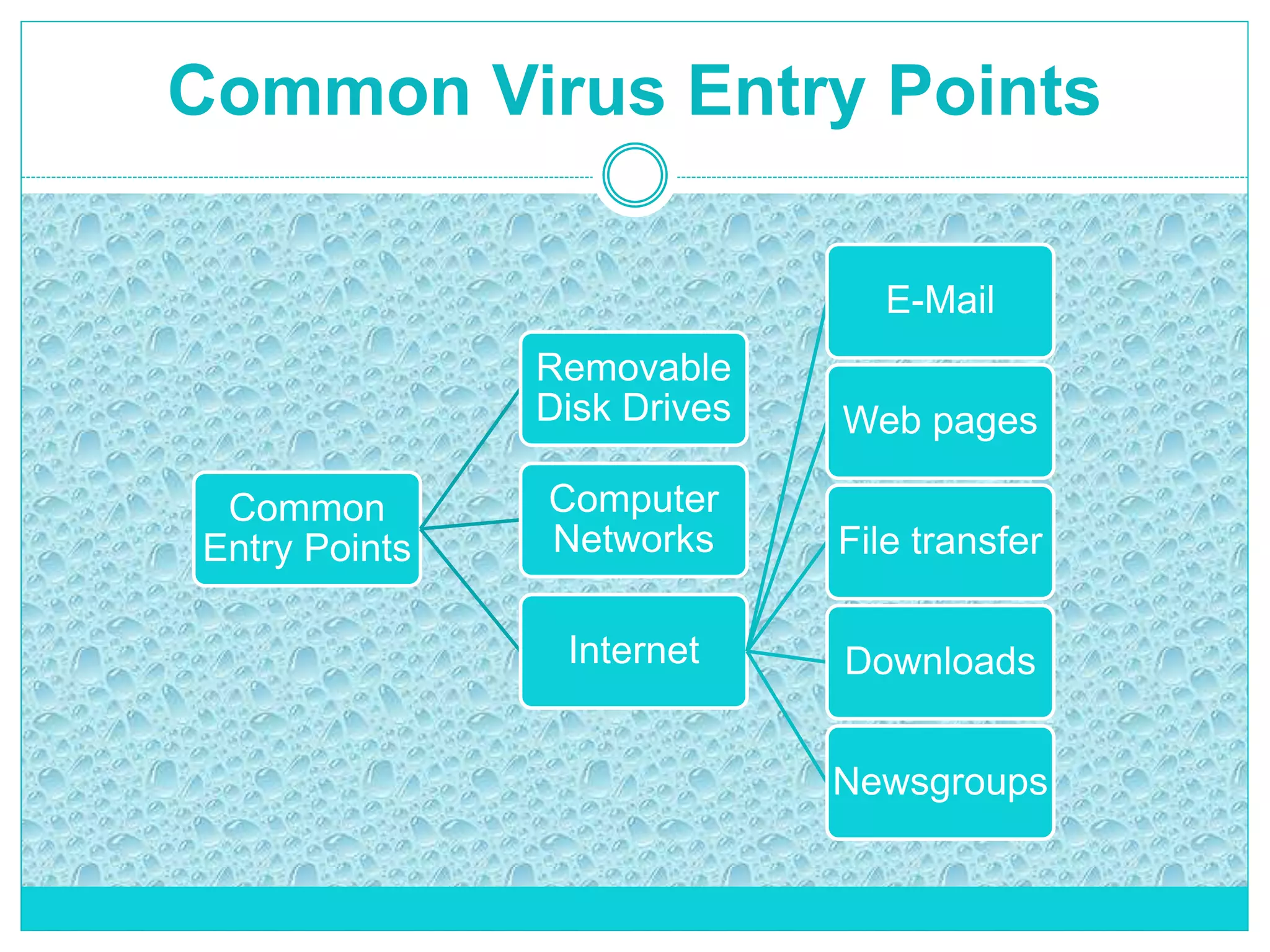
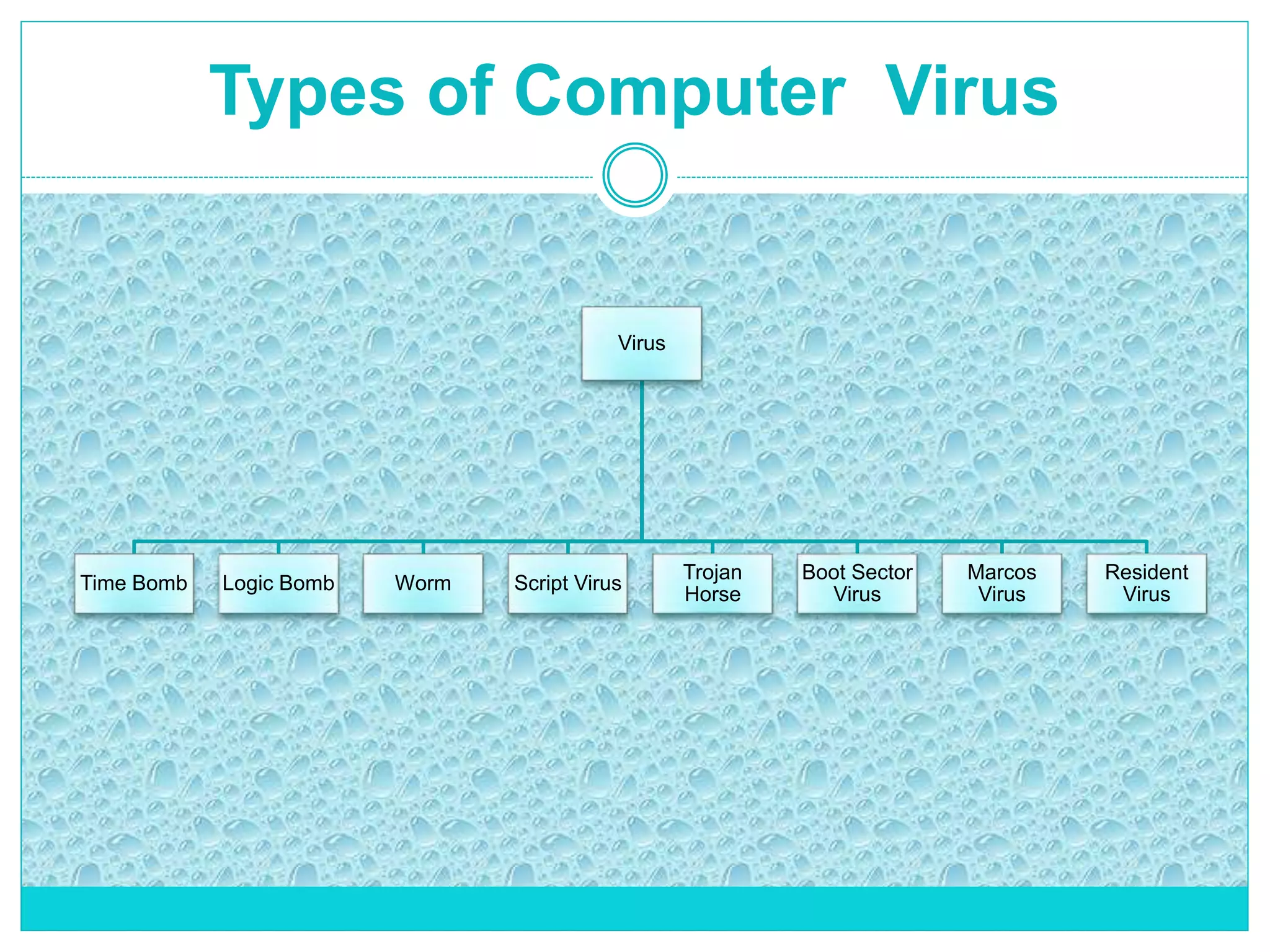
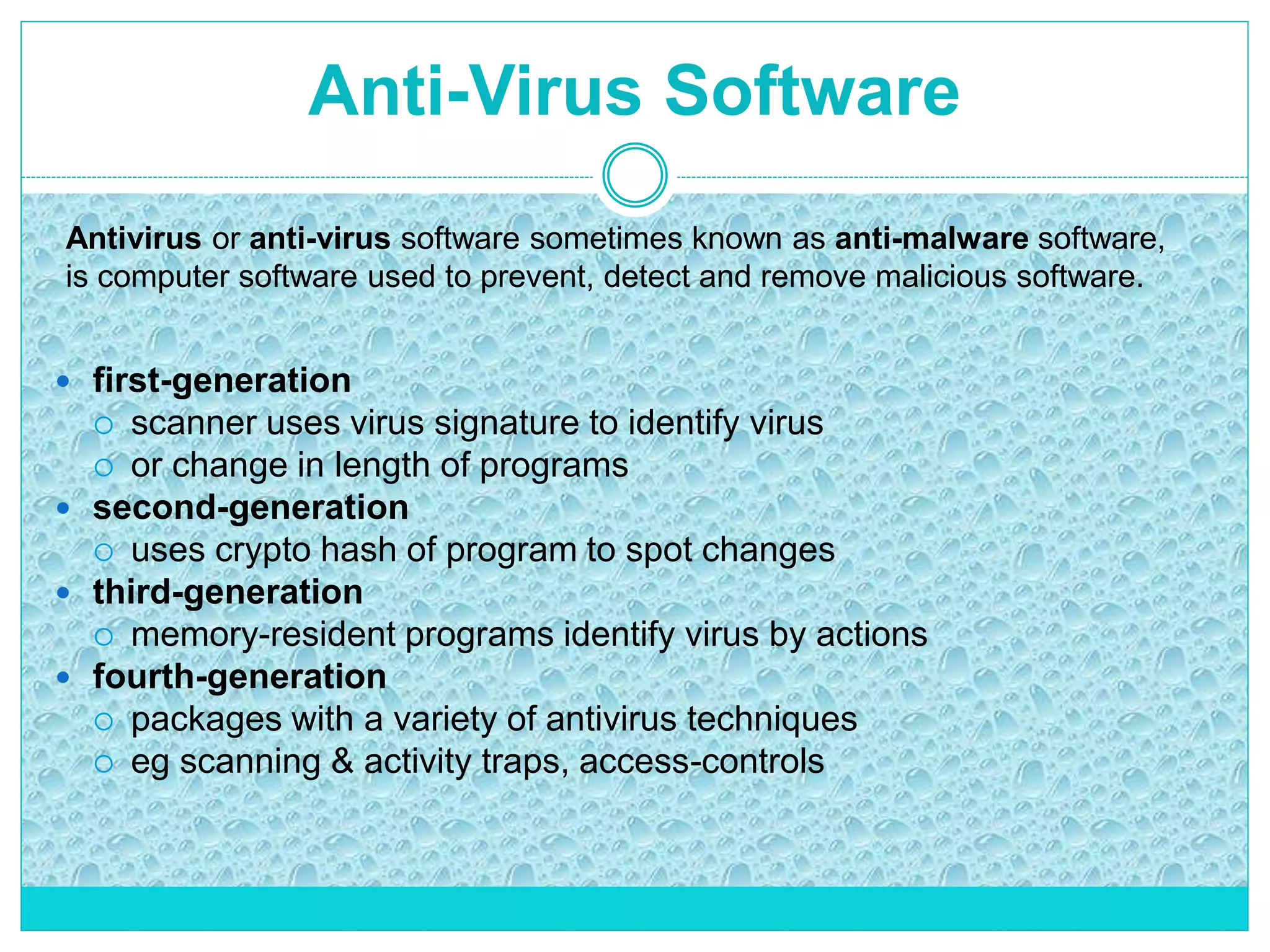
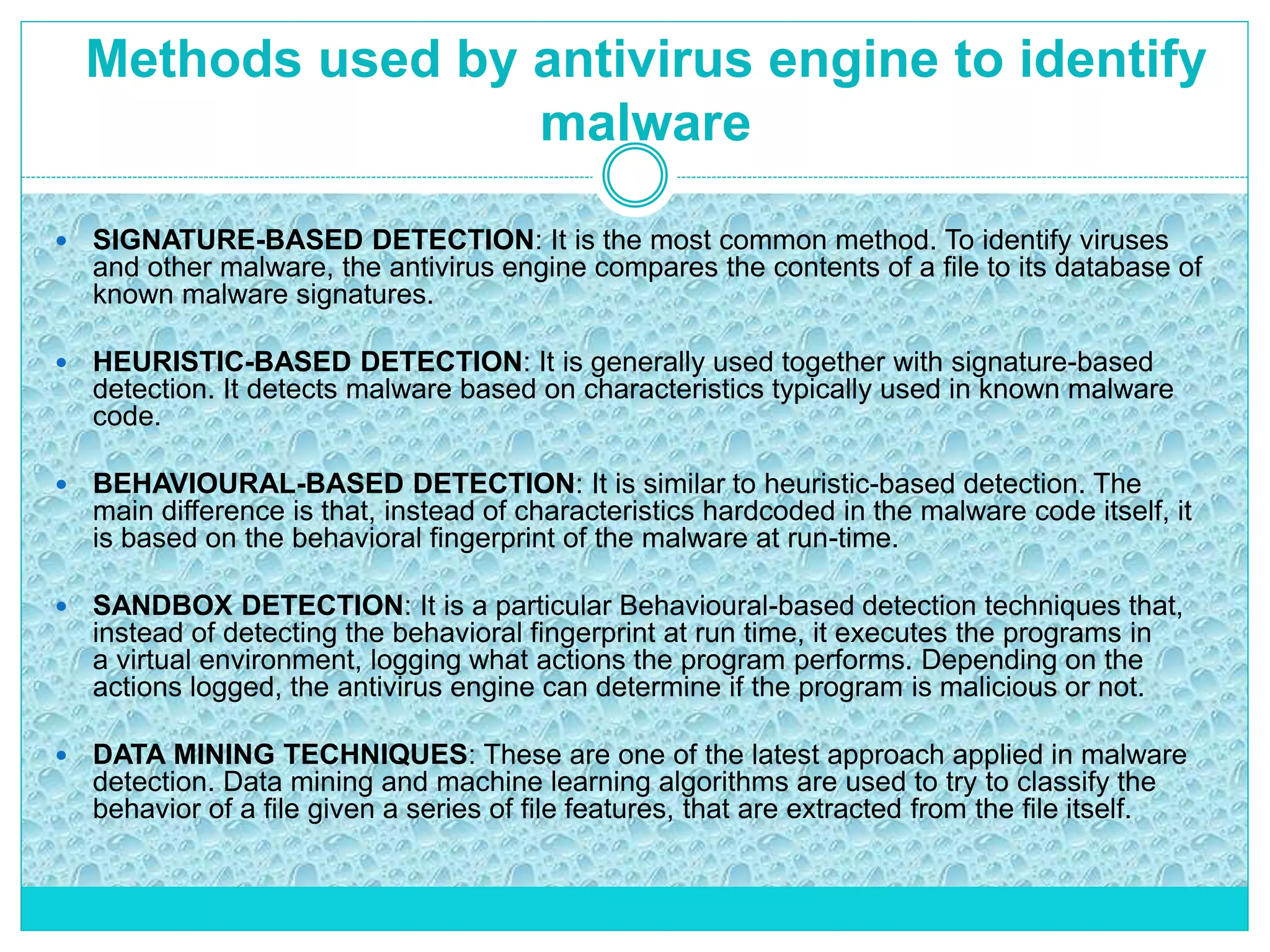
The document extensively discusses computer viruses, including their definitions, types, and methods of operation and spread. It highlights the increasing prevalence of viruses due to internet usage and provides insights into common entry points and symptoms of virus attacks. Additionally, it details various techniques used by viruses and antivirus software methods to combat them, alongside preventive measures for users.