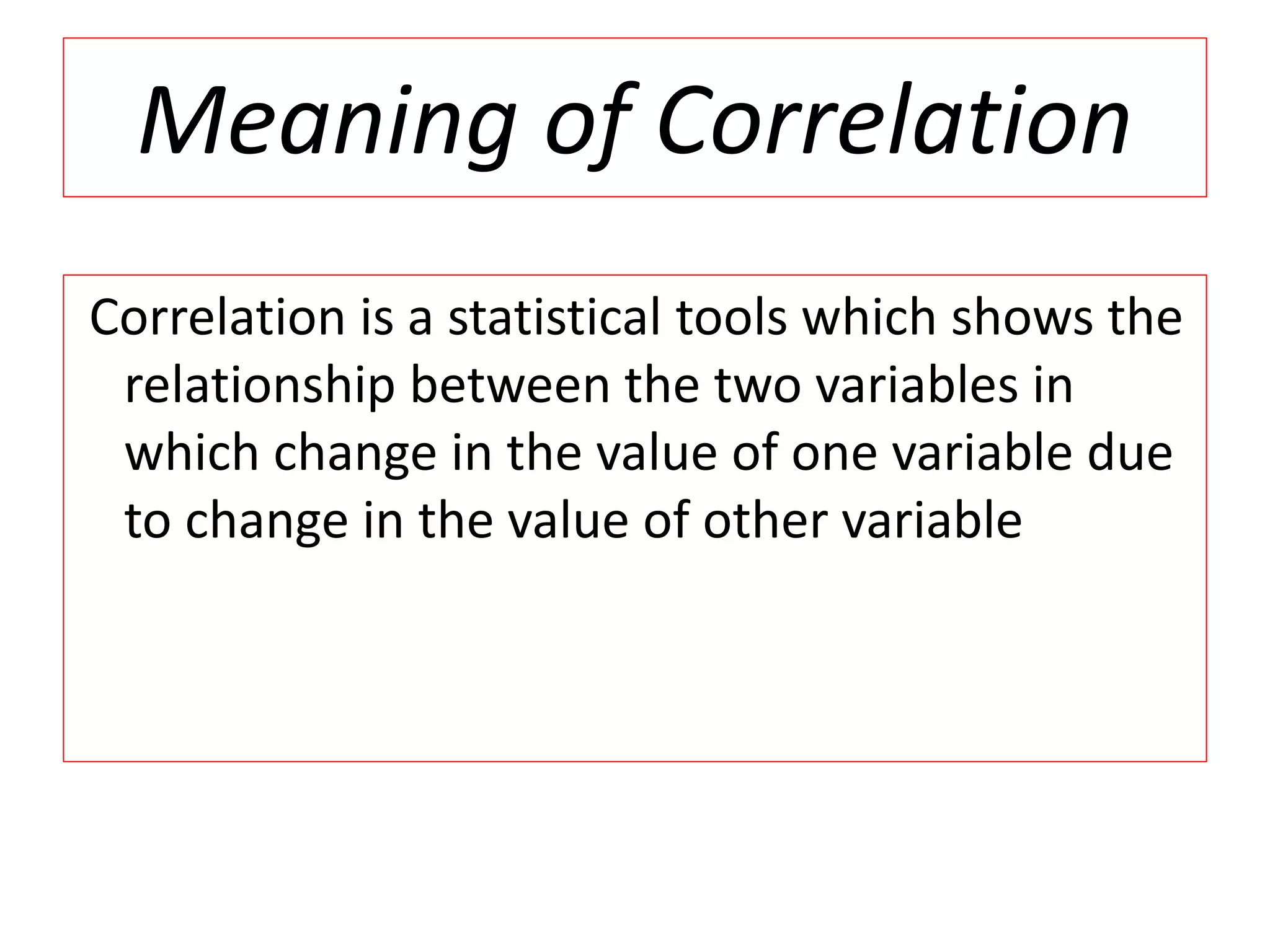
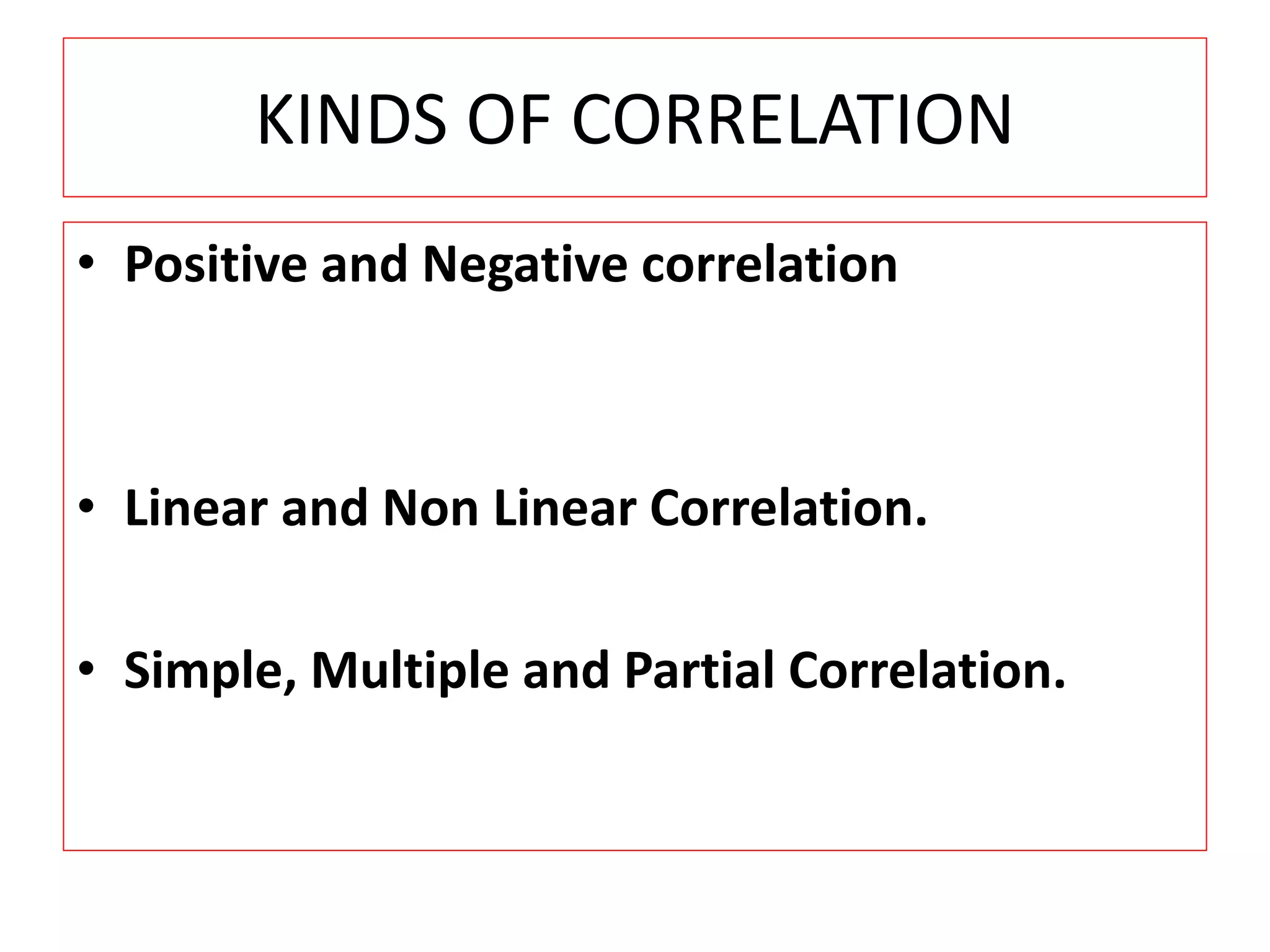
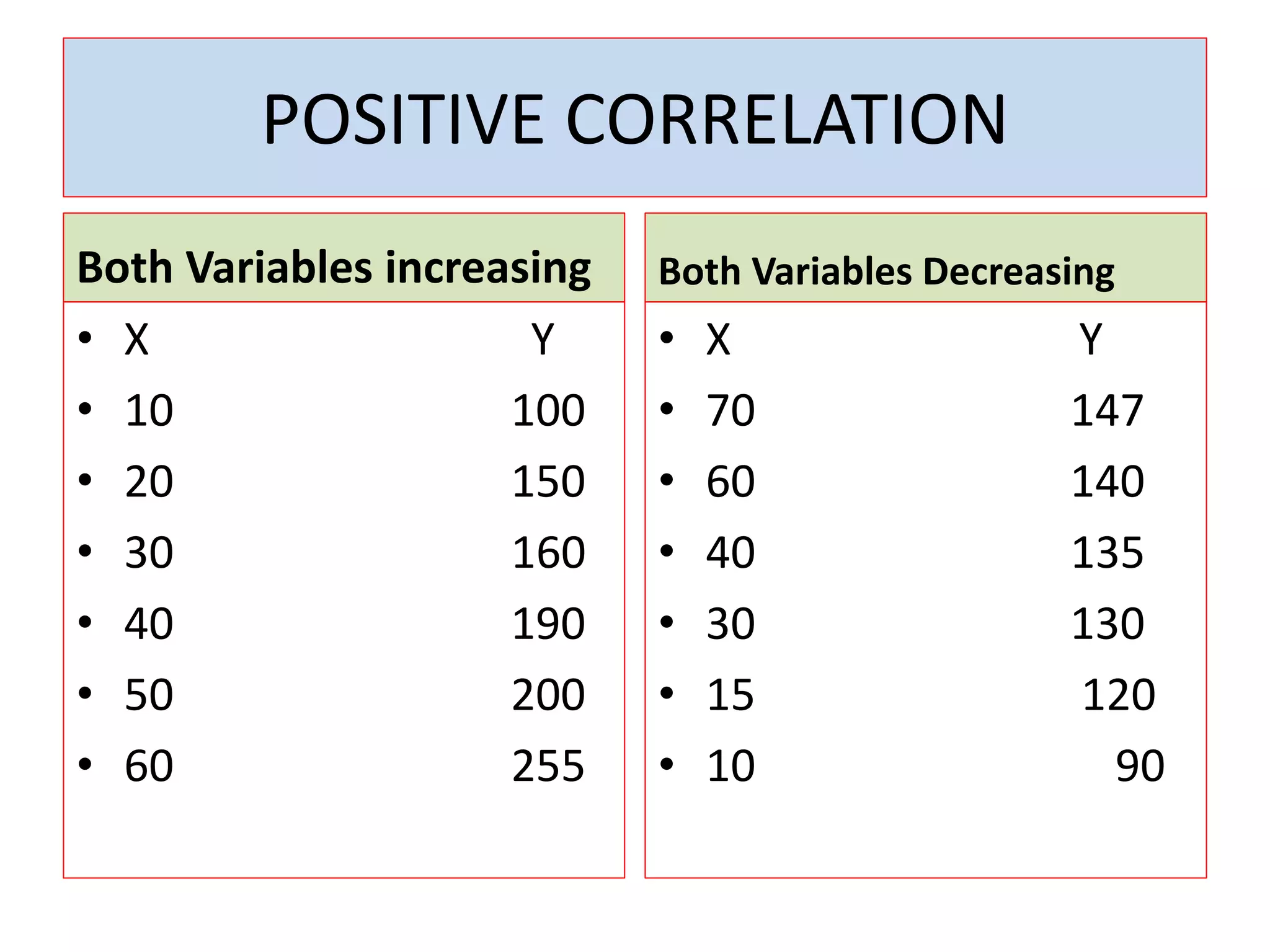
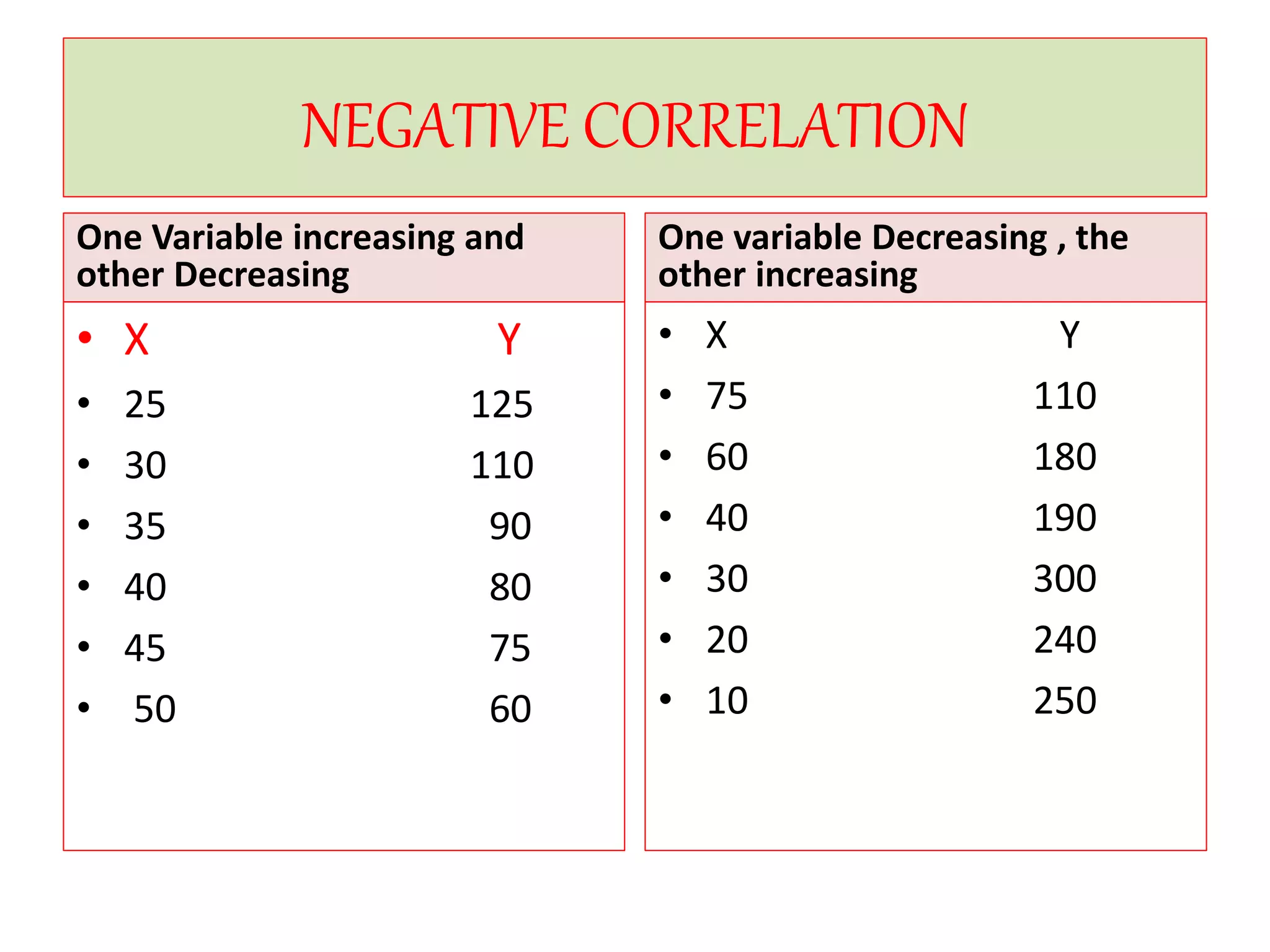
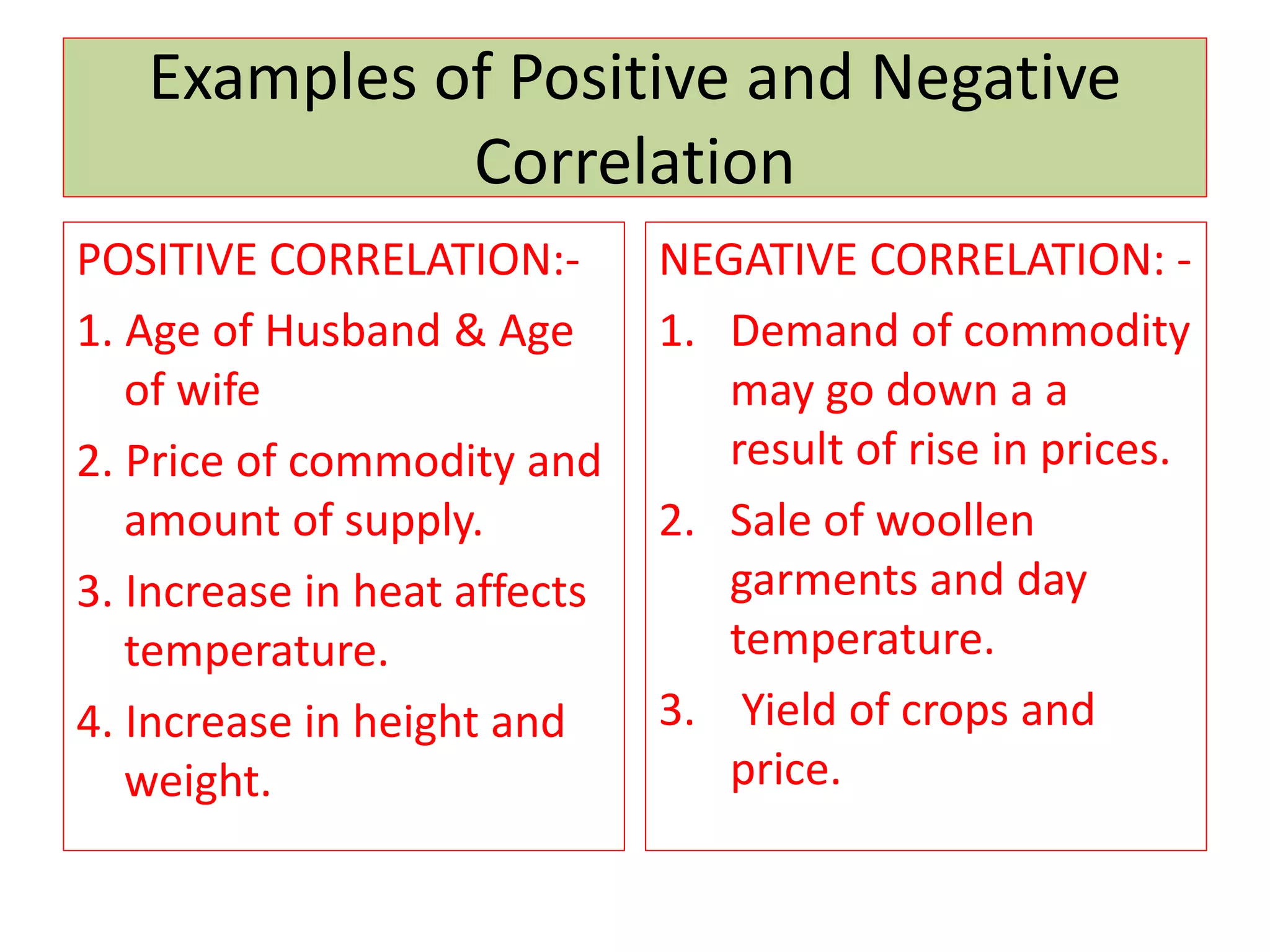
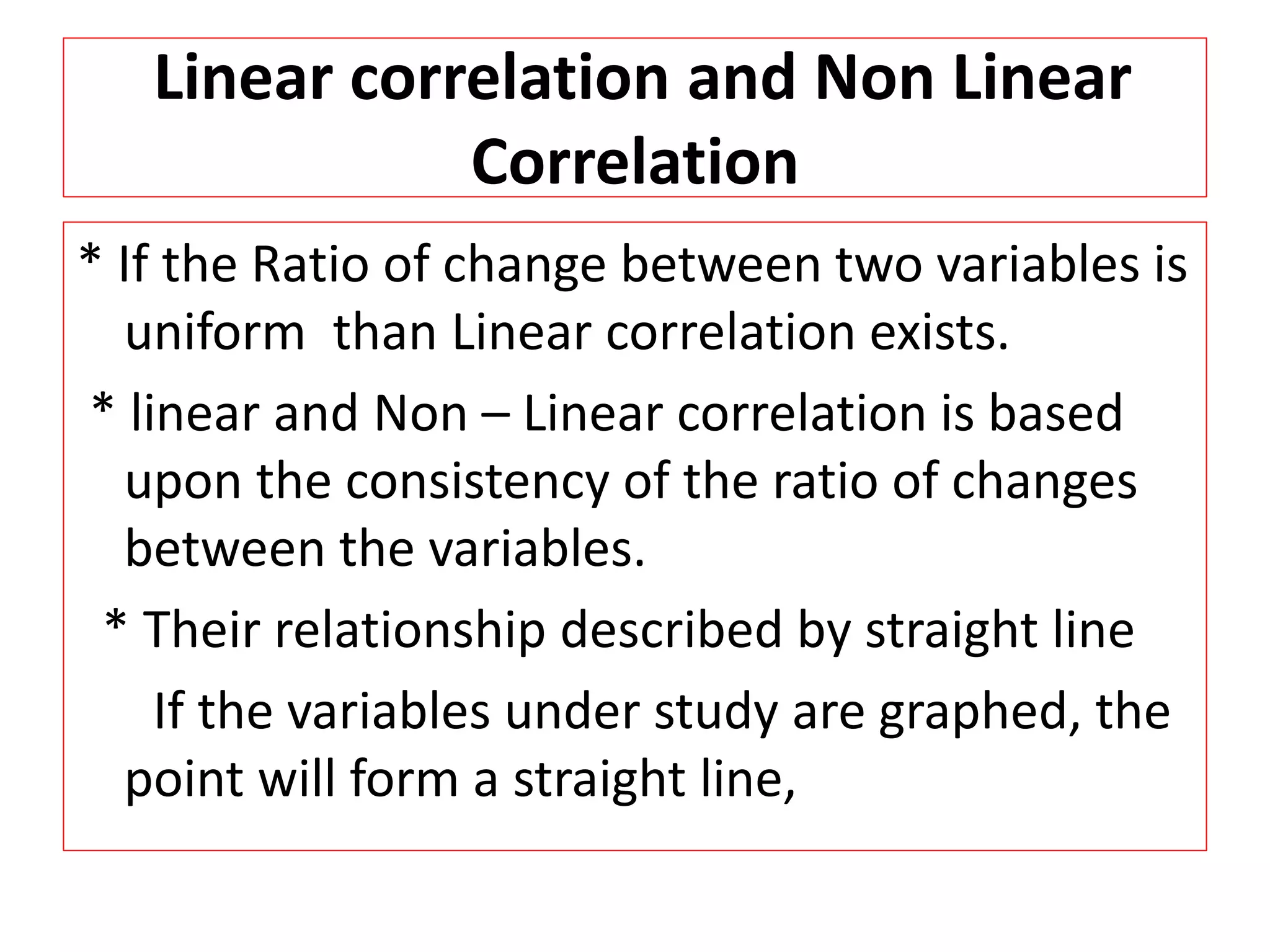
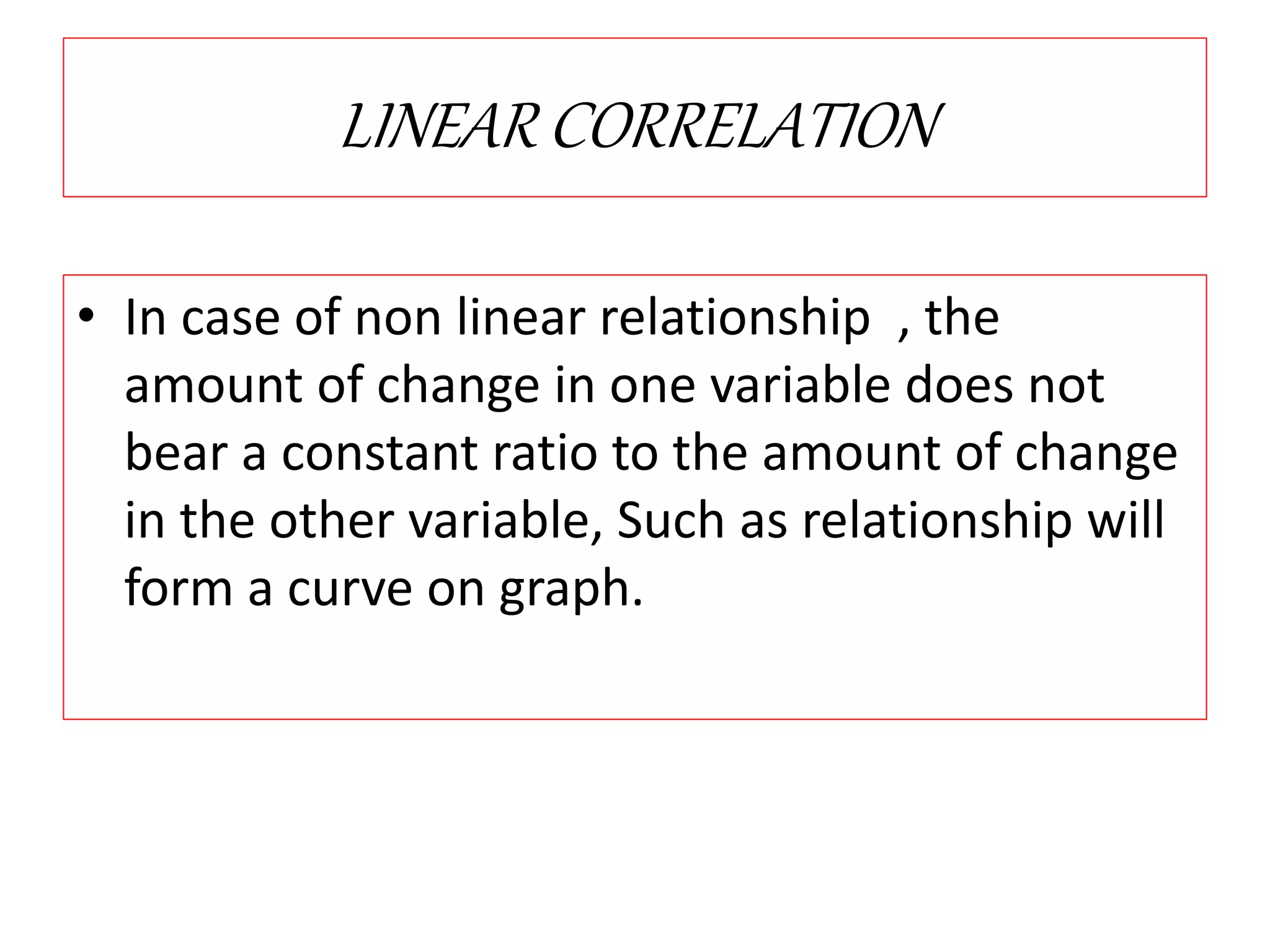
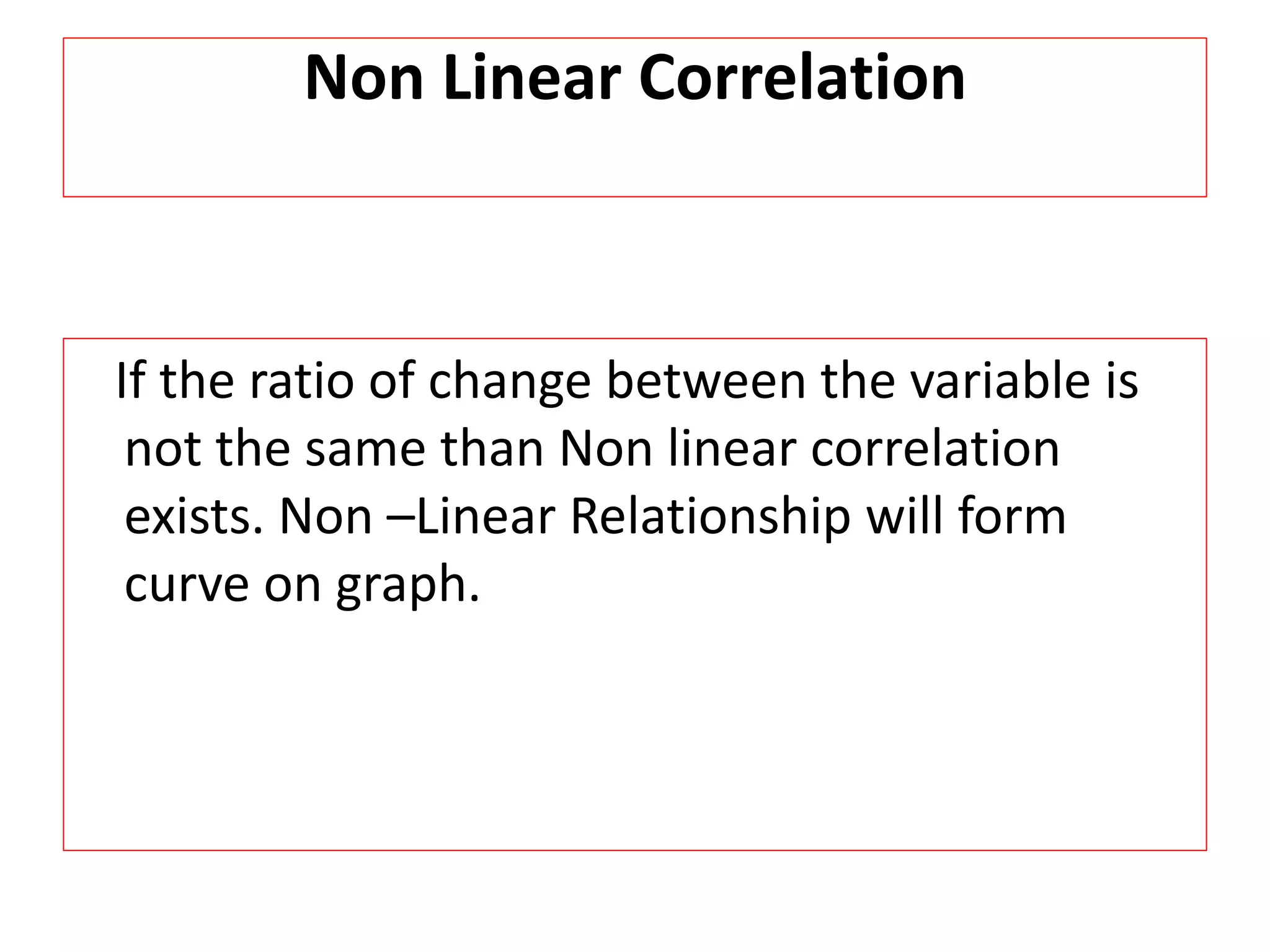
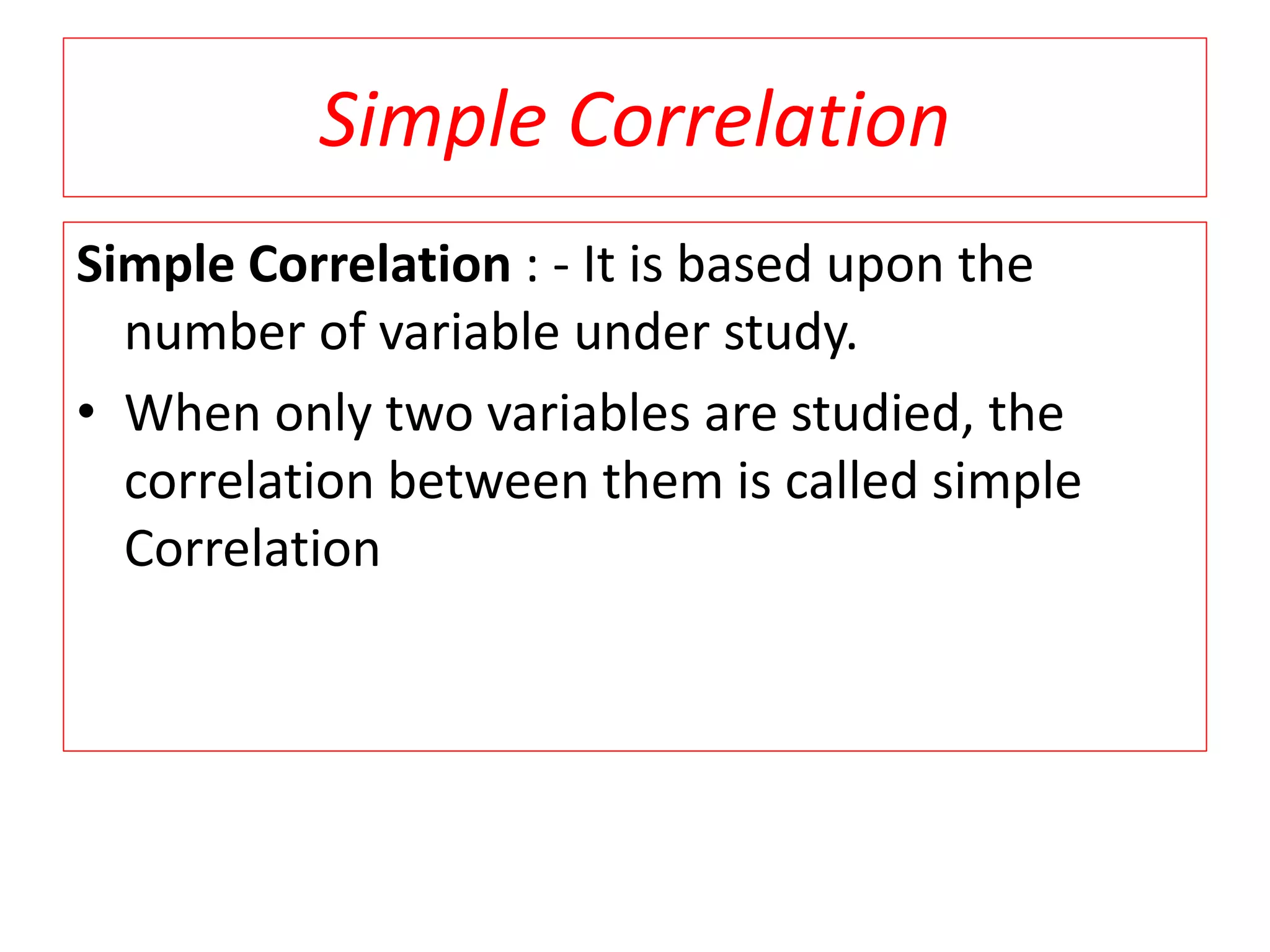
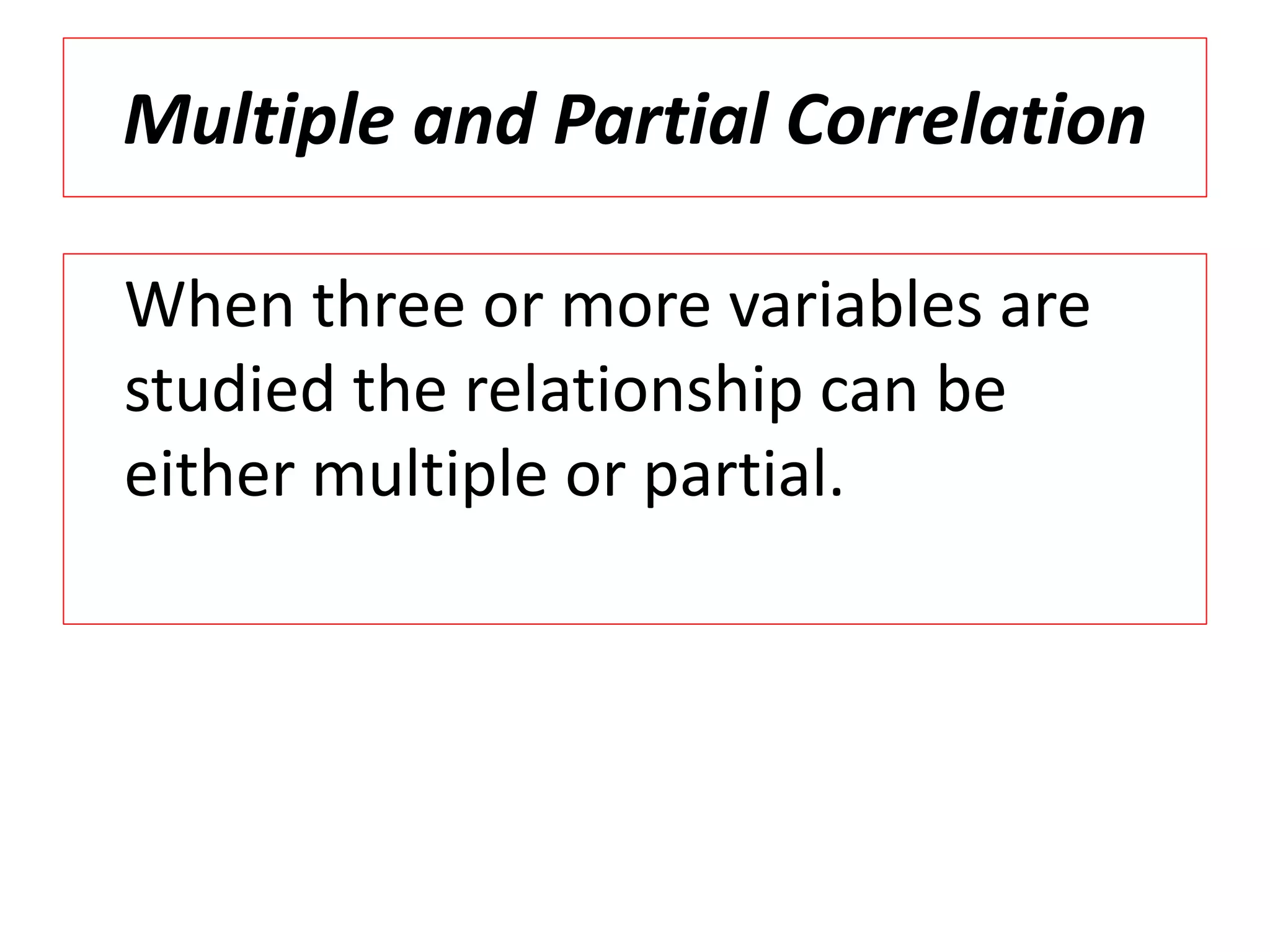
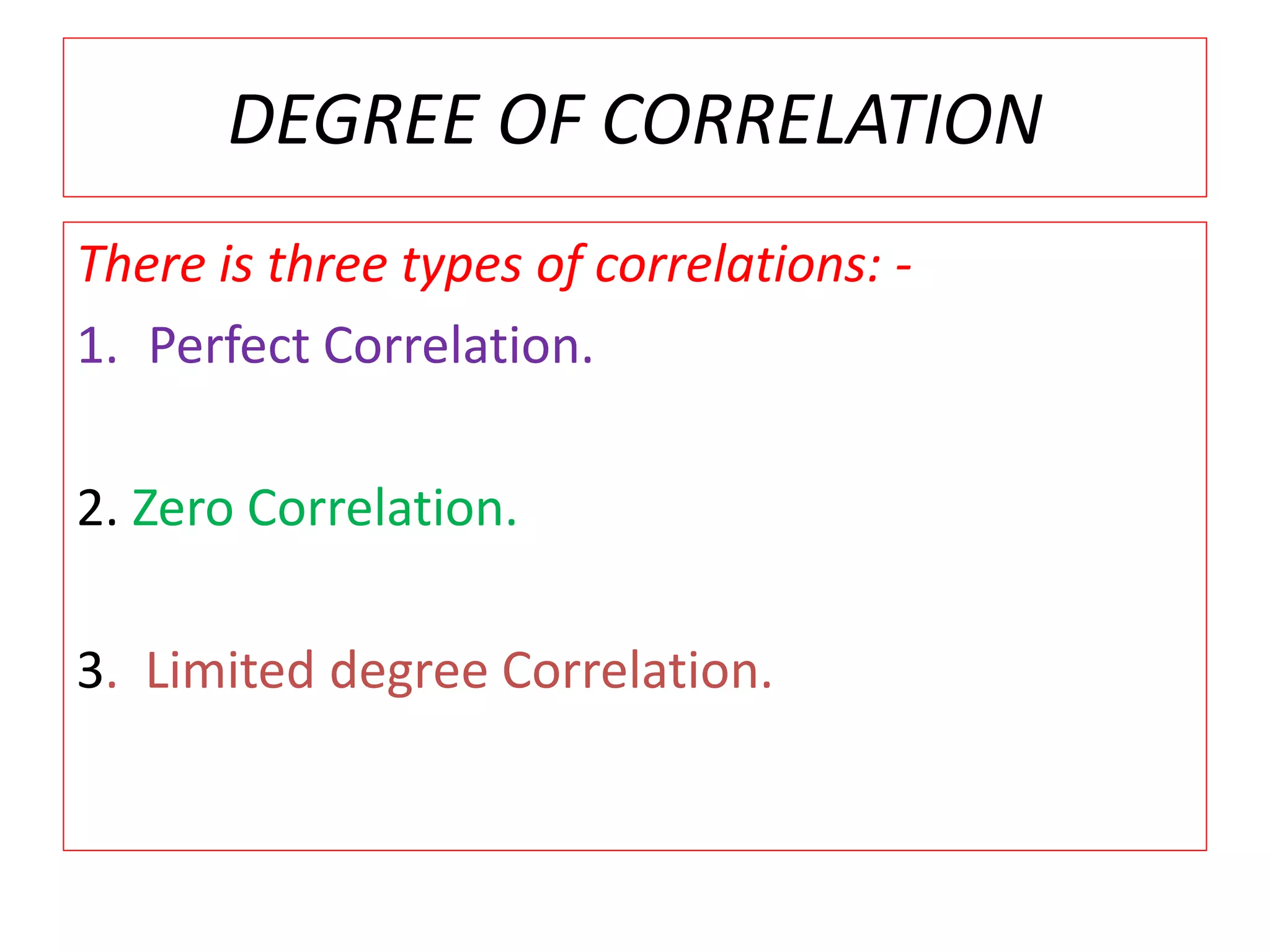
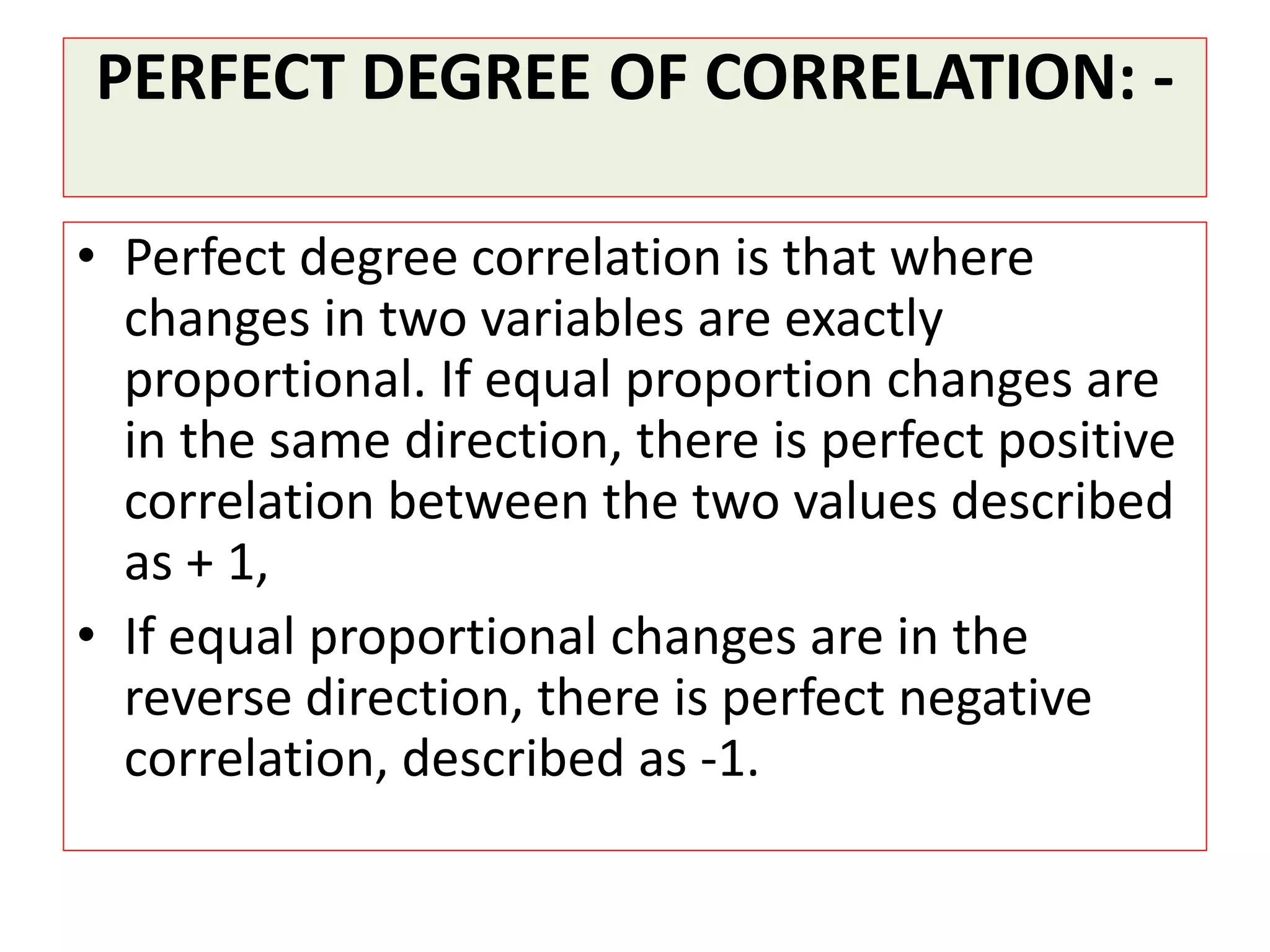
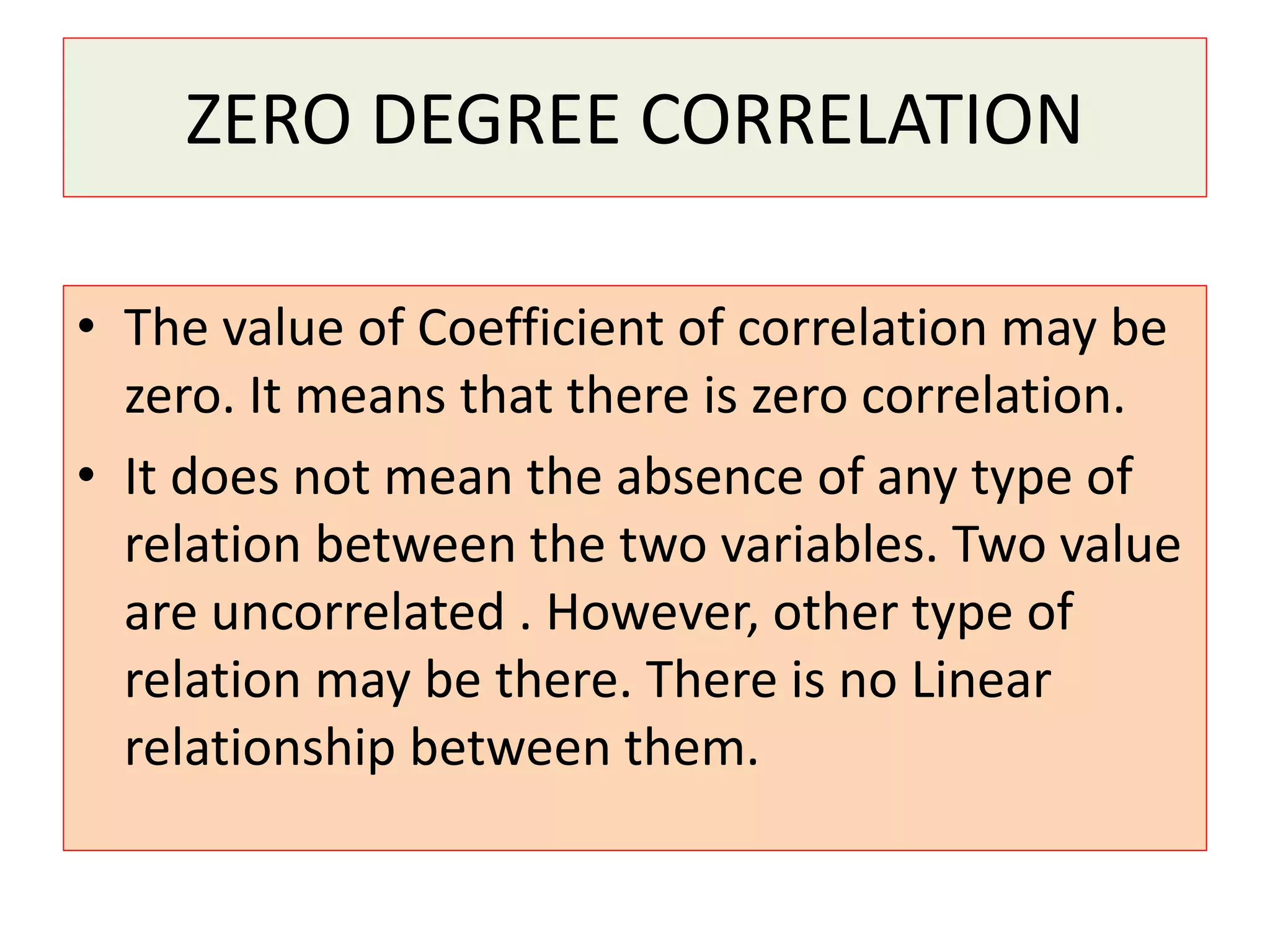
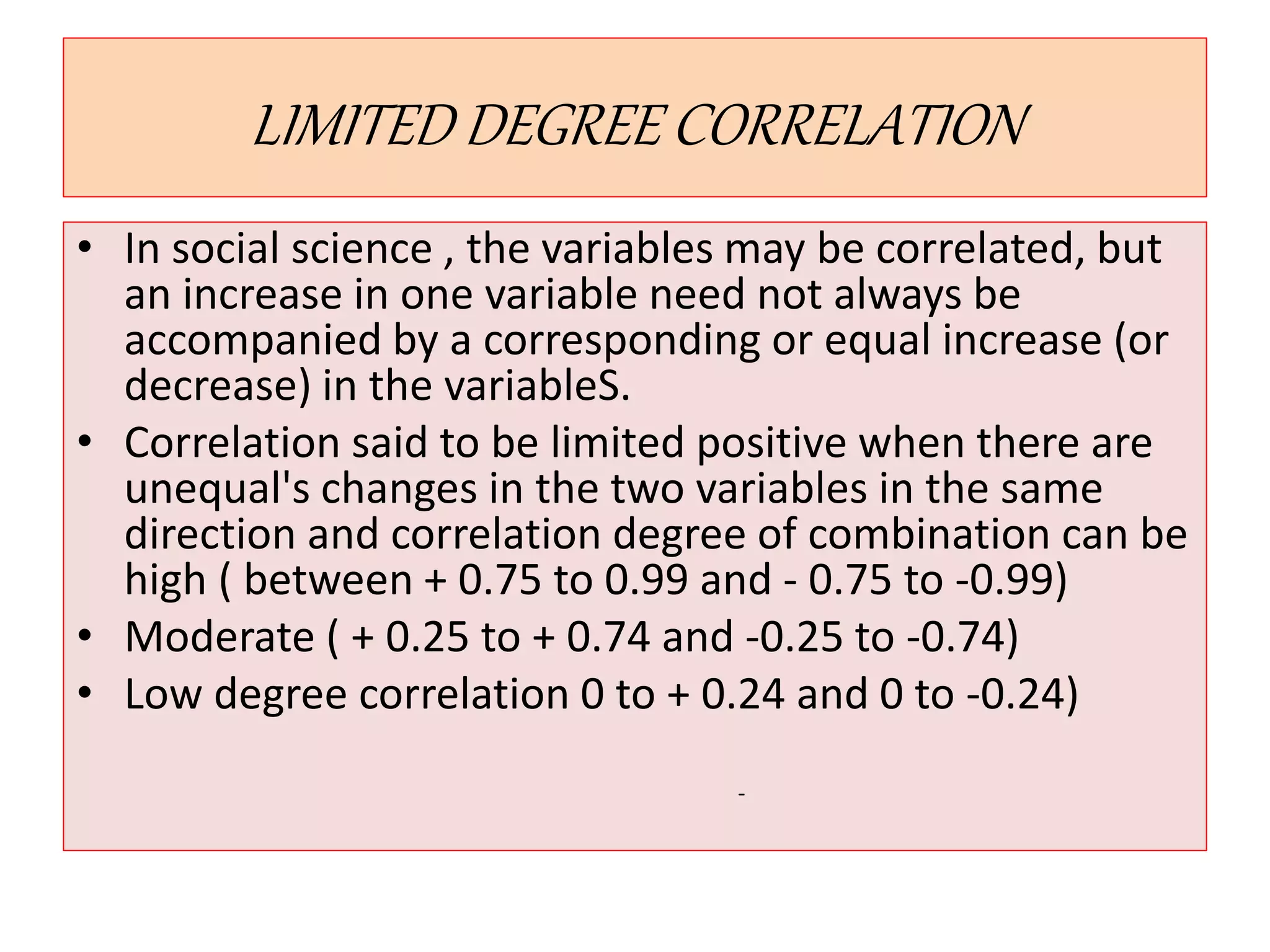
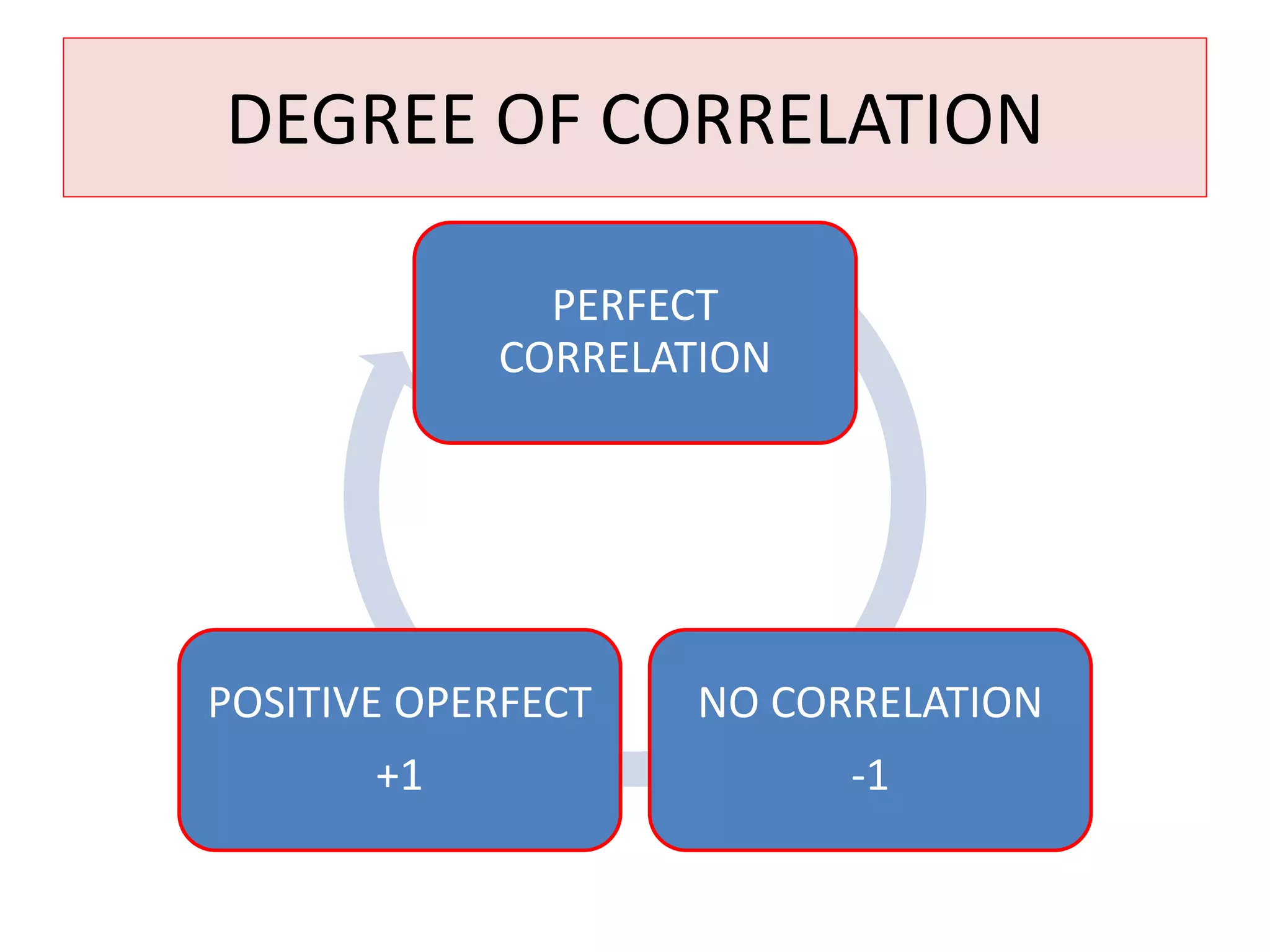
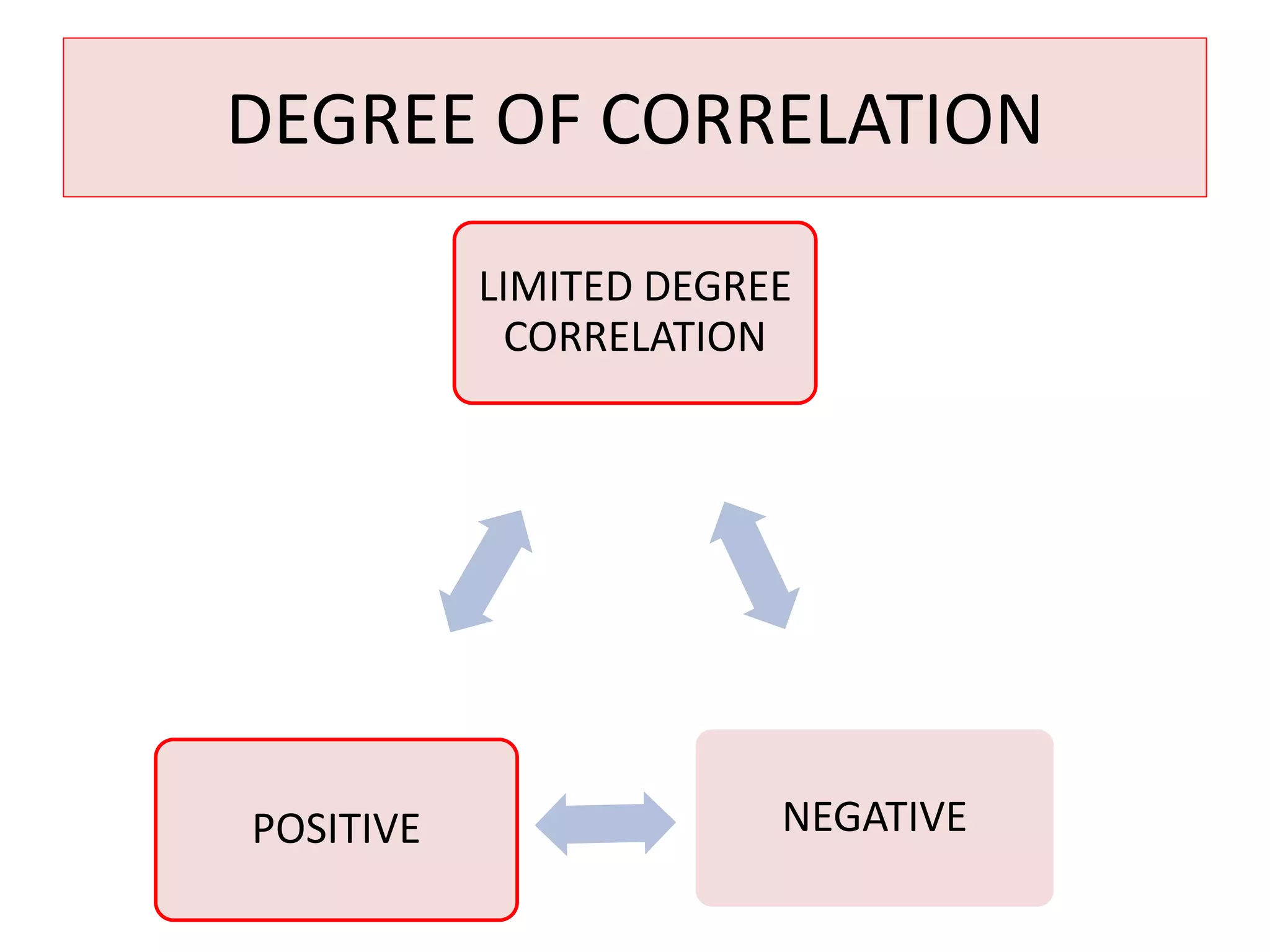
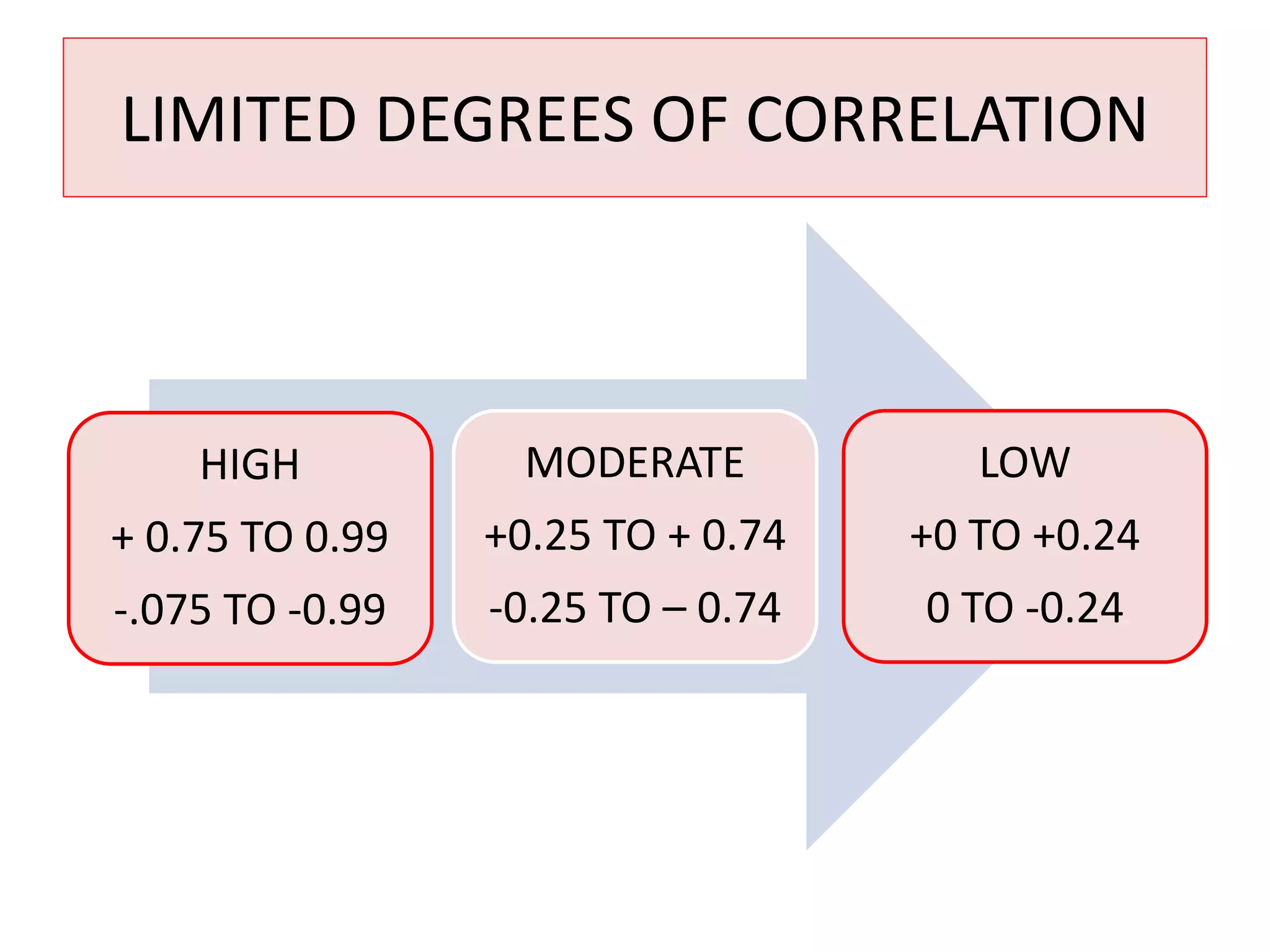
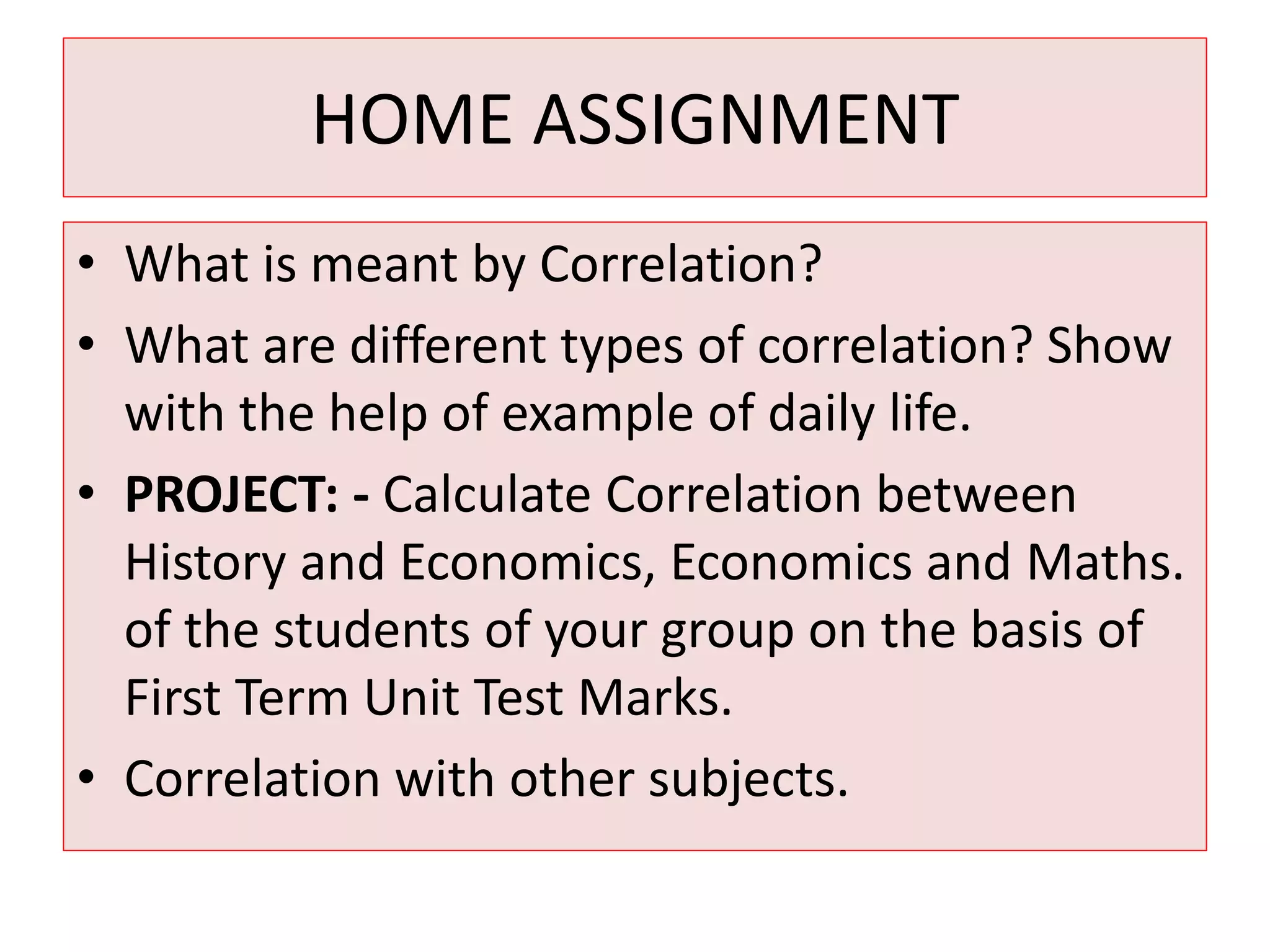
The document introduces the concept of correlation in statistics, detailing the relationships between variables, including positive, negative, linear, and non-linear correlations. It outlines various types of correlations such as simple, multiple, and partial correlations, and explains the degrees of correlation, including perfect, zero, and limited degrees. The document also includes activities for students to identify examples of correlations and suggests home assignments related to the topic.