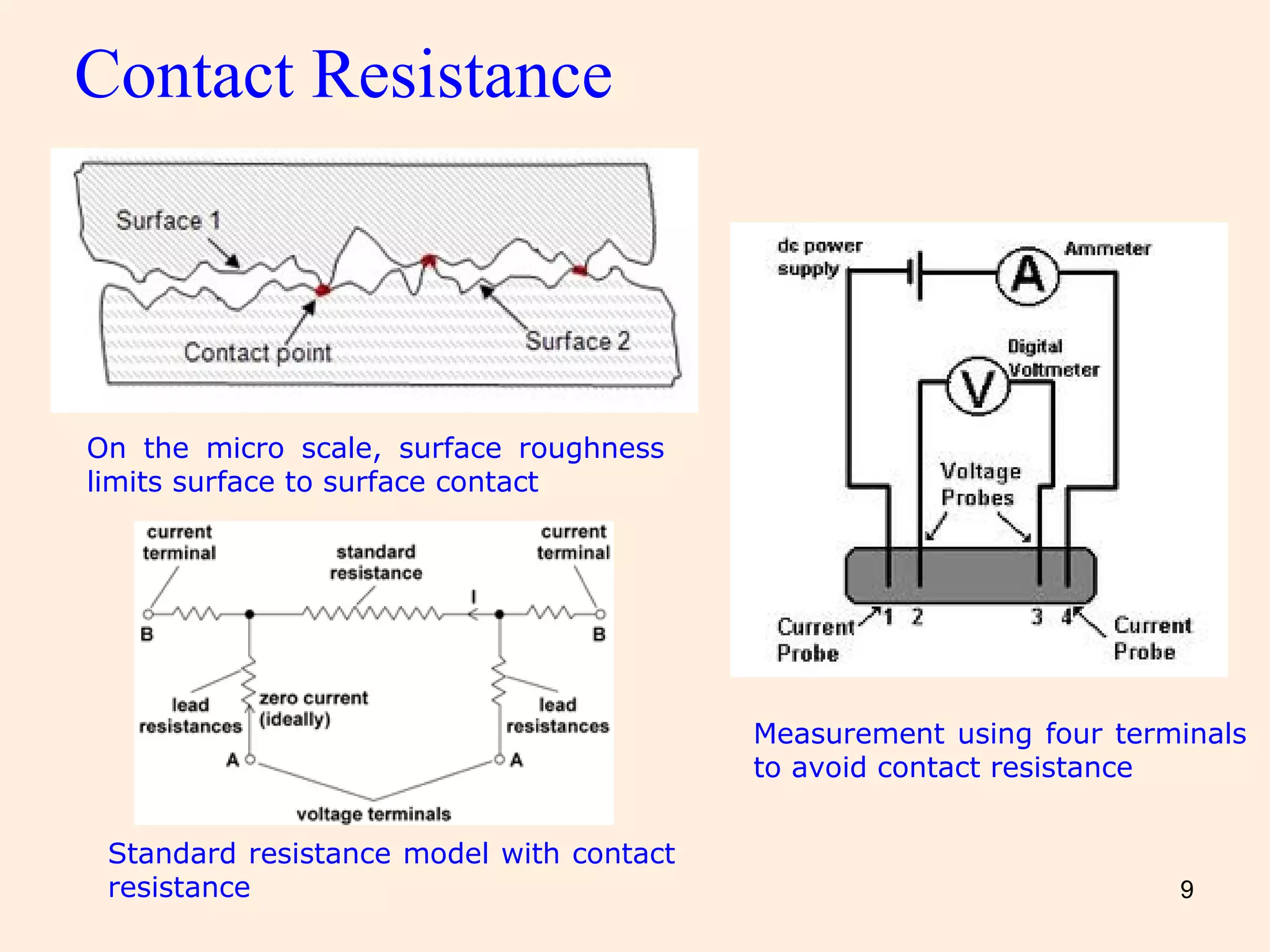
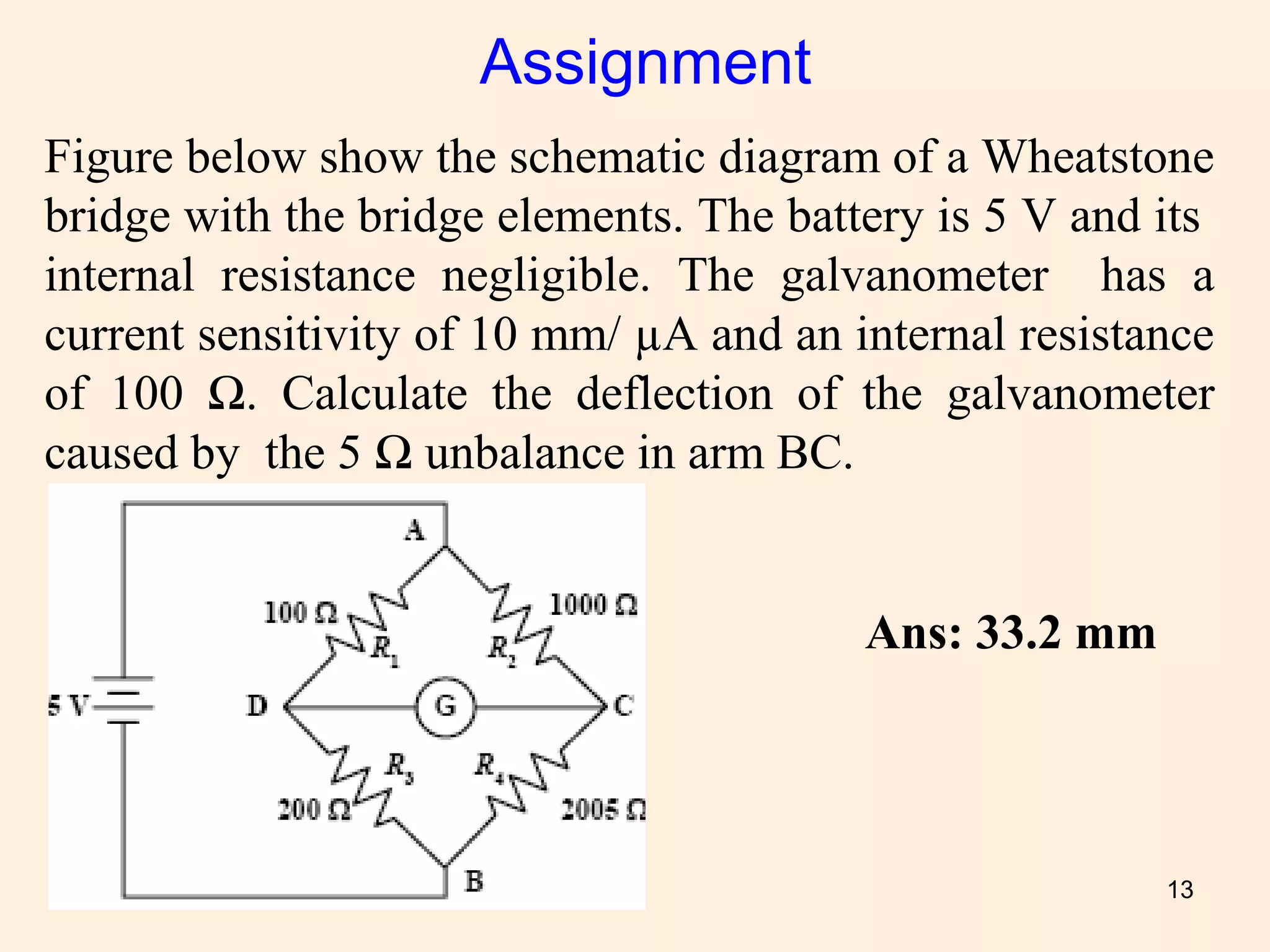
The document discusses various resistance measurement methods, including voltmeter-ammeter, substitution, ohmmeter, and bridge methods, highlighting their advantages and limitations. It details the Wheatstone bridge's operation, measurement errors due to thermal EMF and contact resistance, and provides schematics and calculations related to galvanometer deflection. The document also includes assignments and answers for further understanding of resistance measurements.