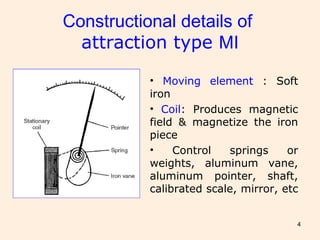
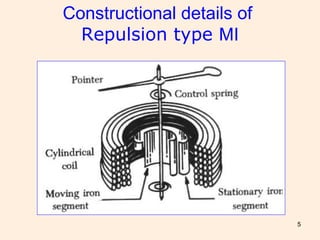
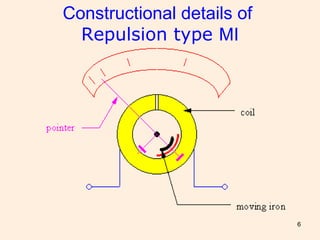
Moving iron instruments are used for measuring AC and DC current or voltage, with types classified into repulsion and attraction types. The working principle involves the movement of a pointer due to the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying coil, with torque provided by springs or weights. While offering high accuracy and low cost for AC measurements, they have limitations such as non-linear scales and sensitivity to frequency variations.