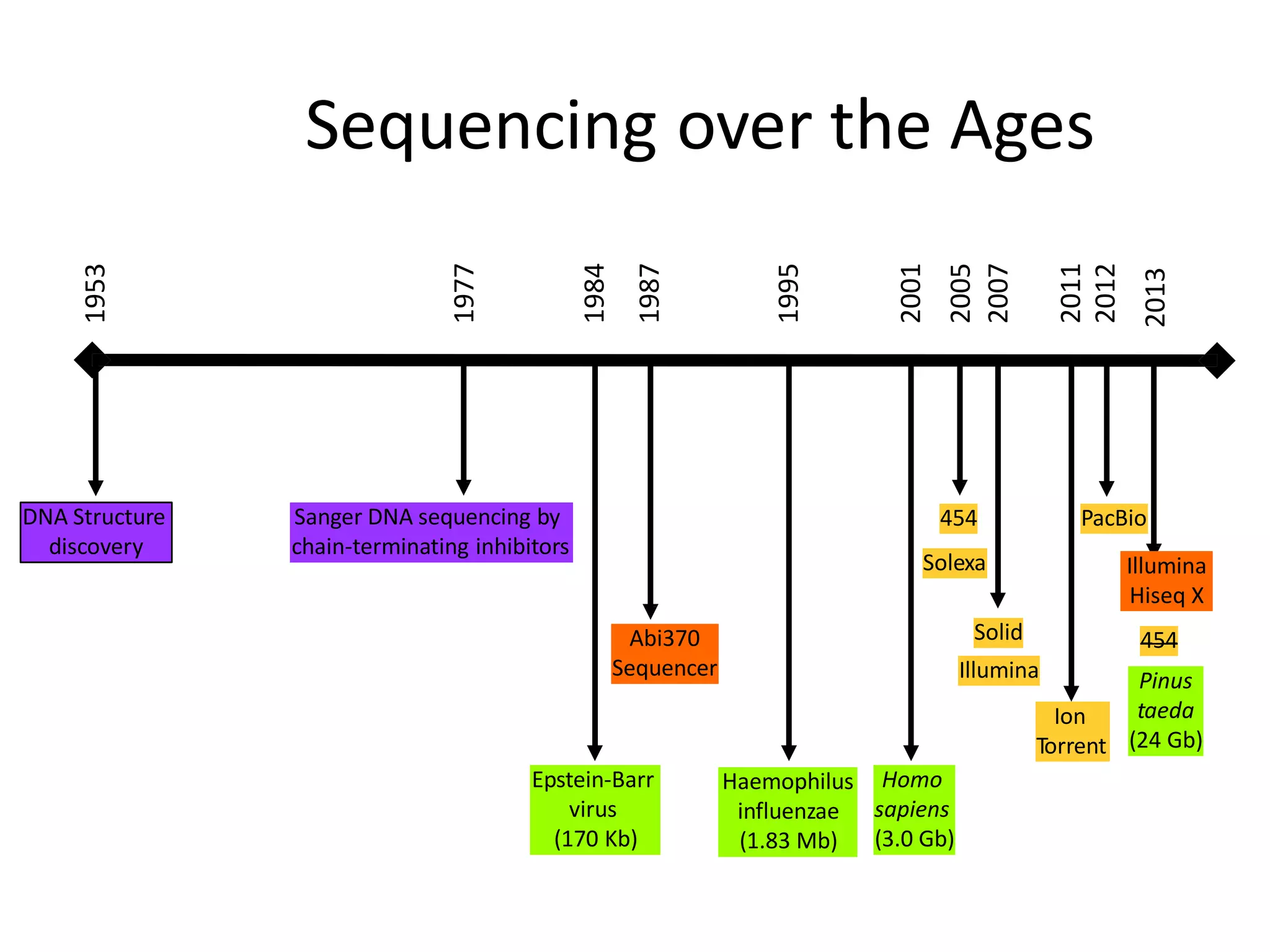
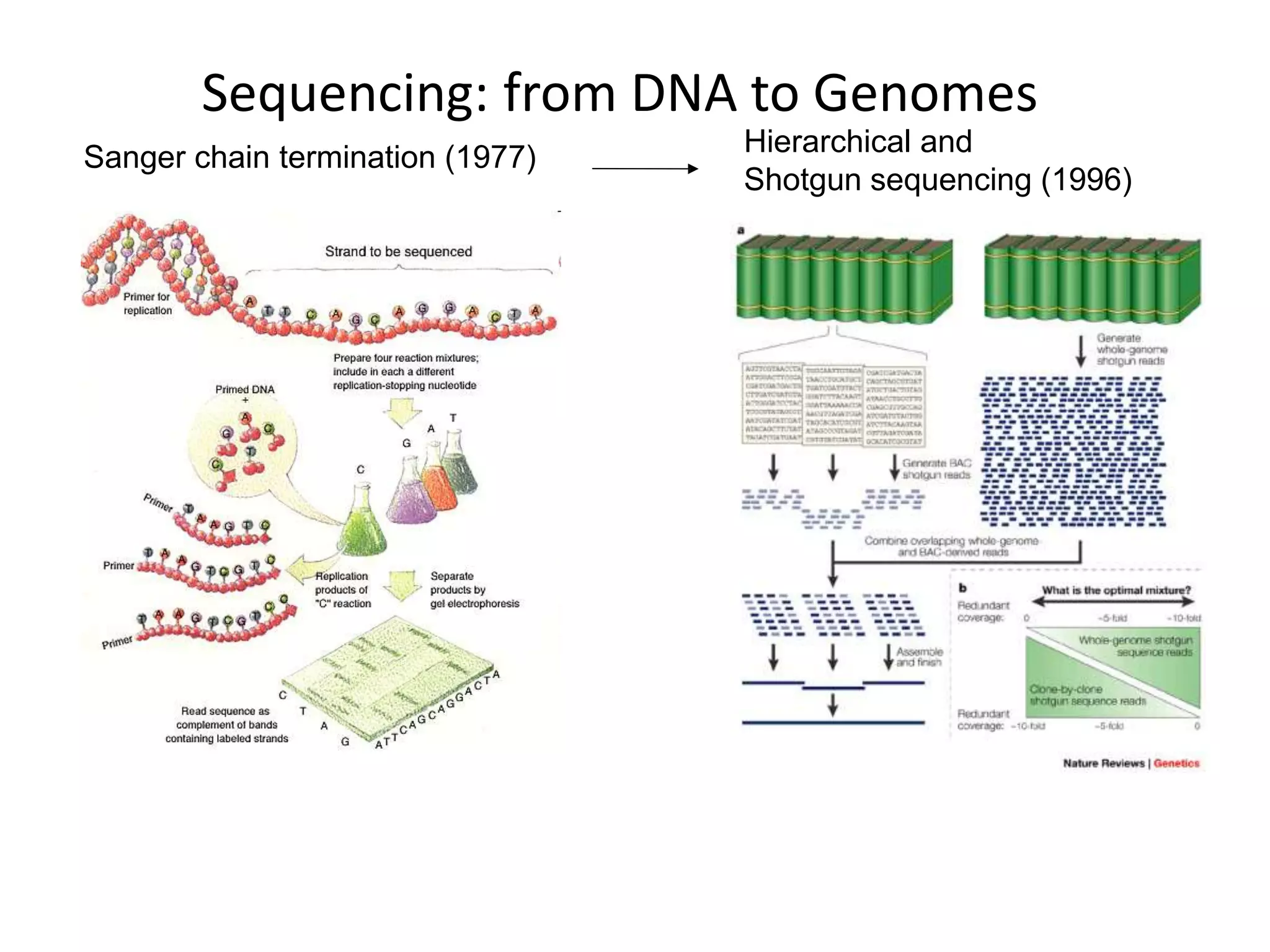
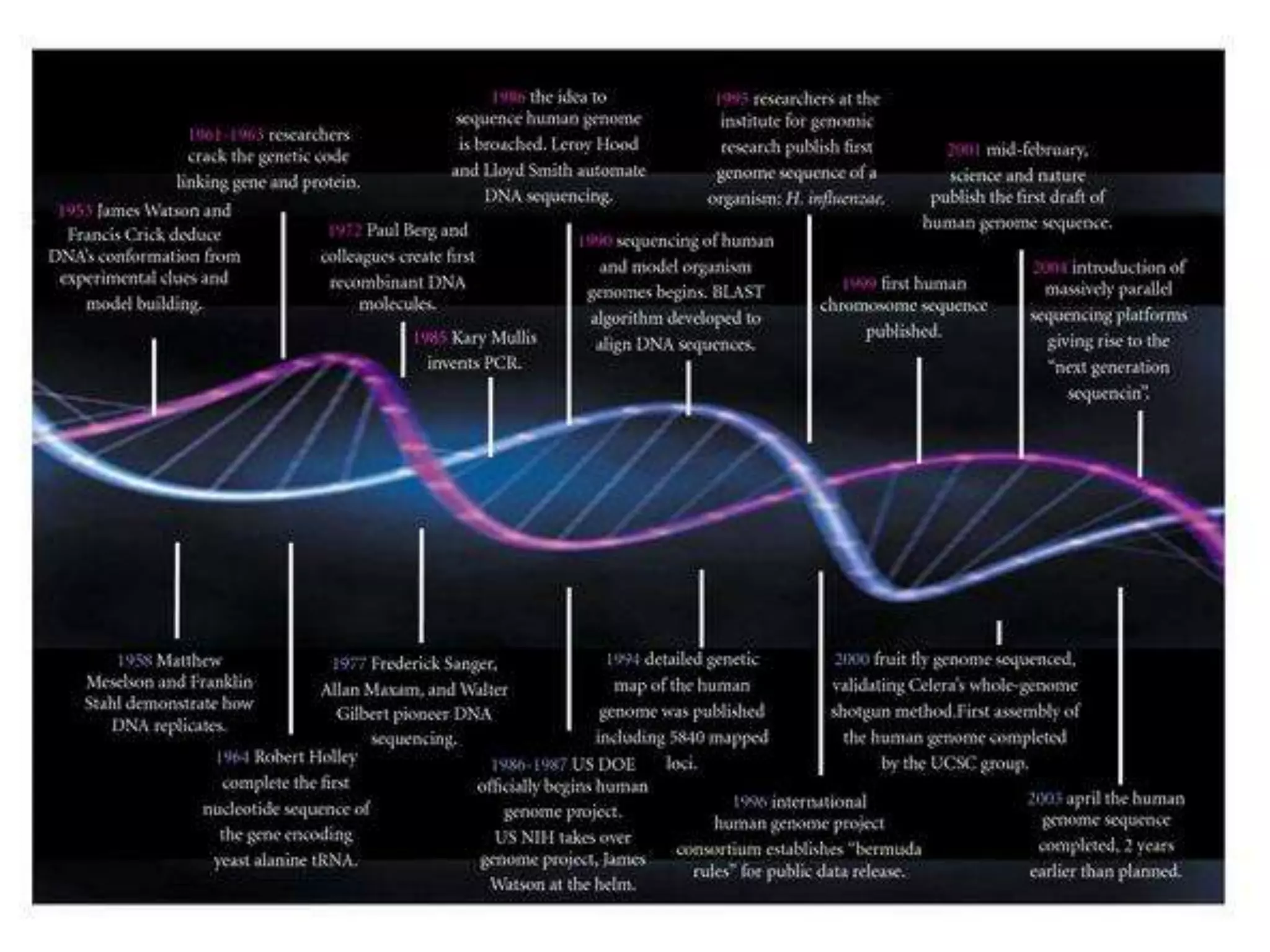
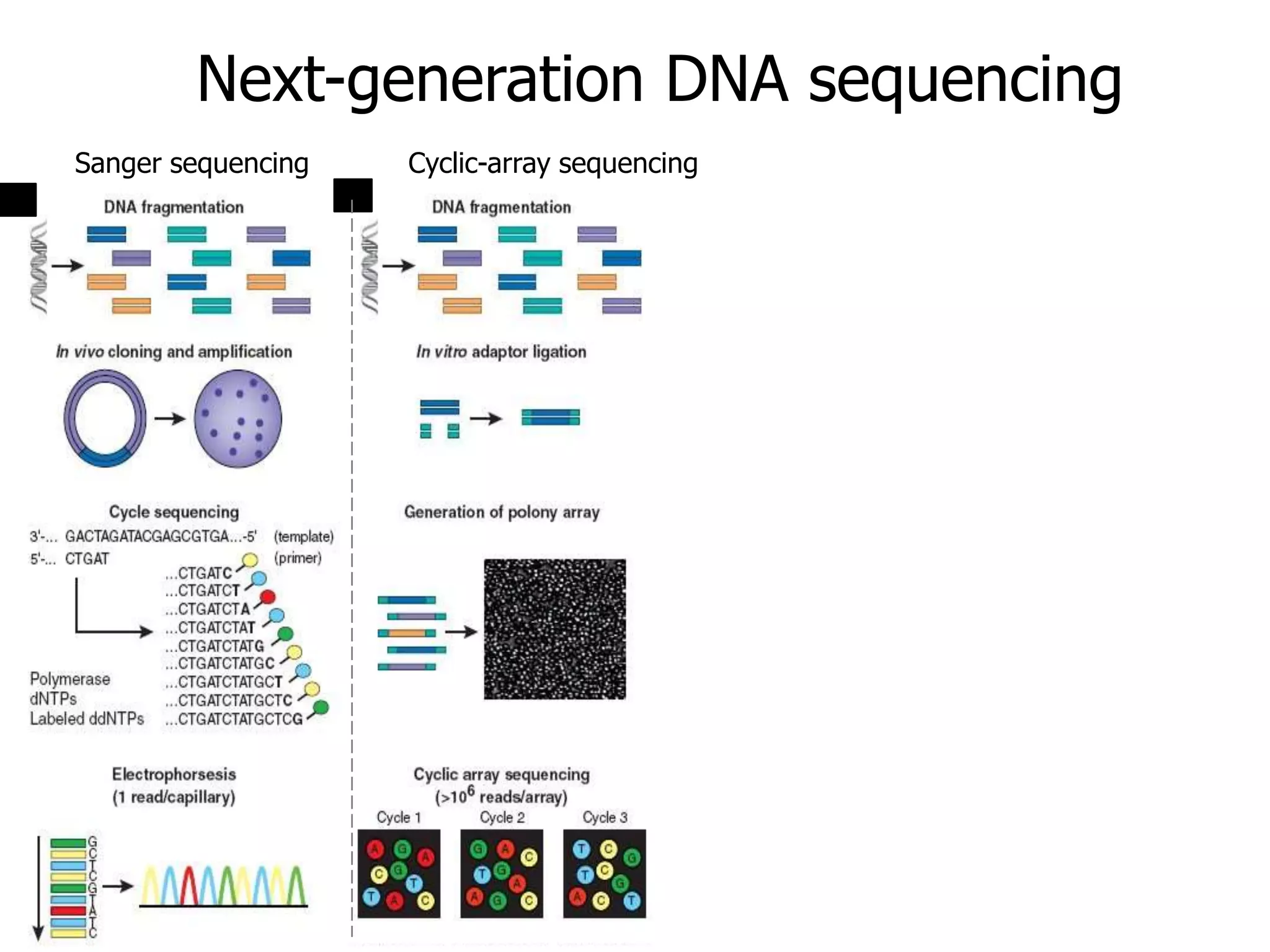
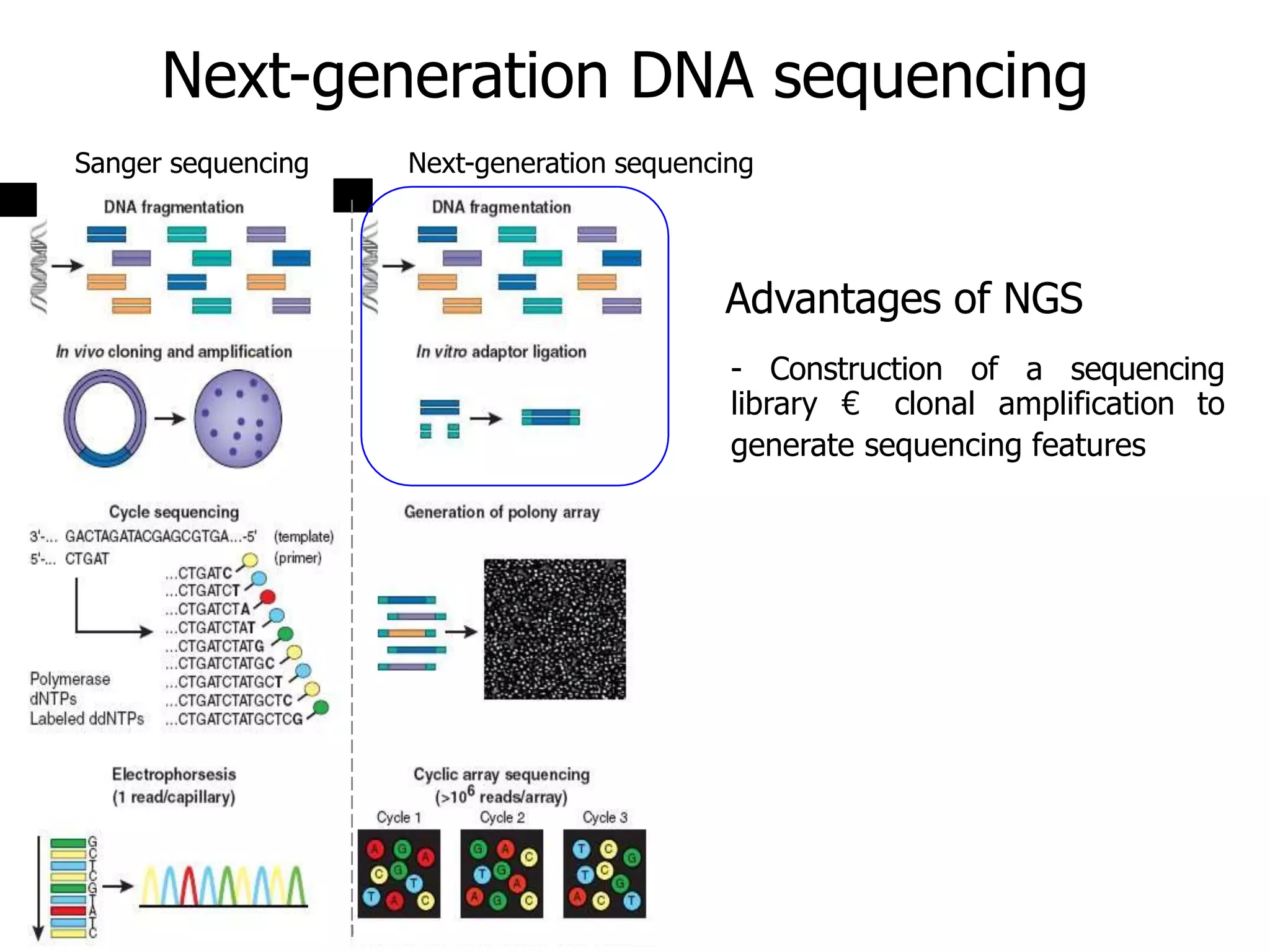
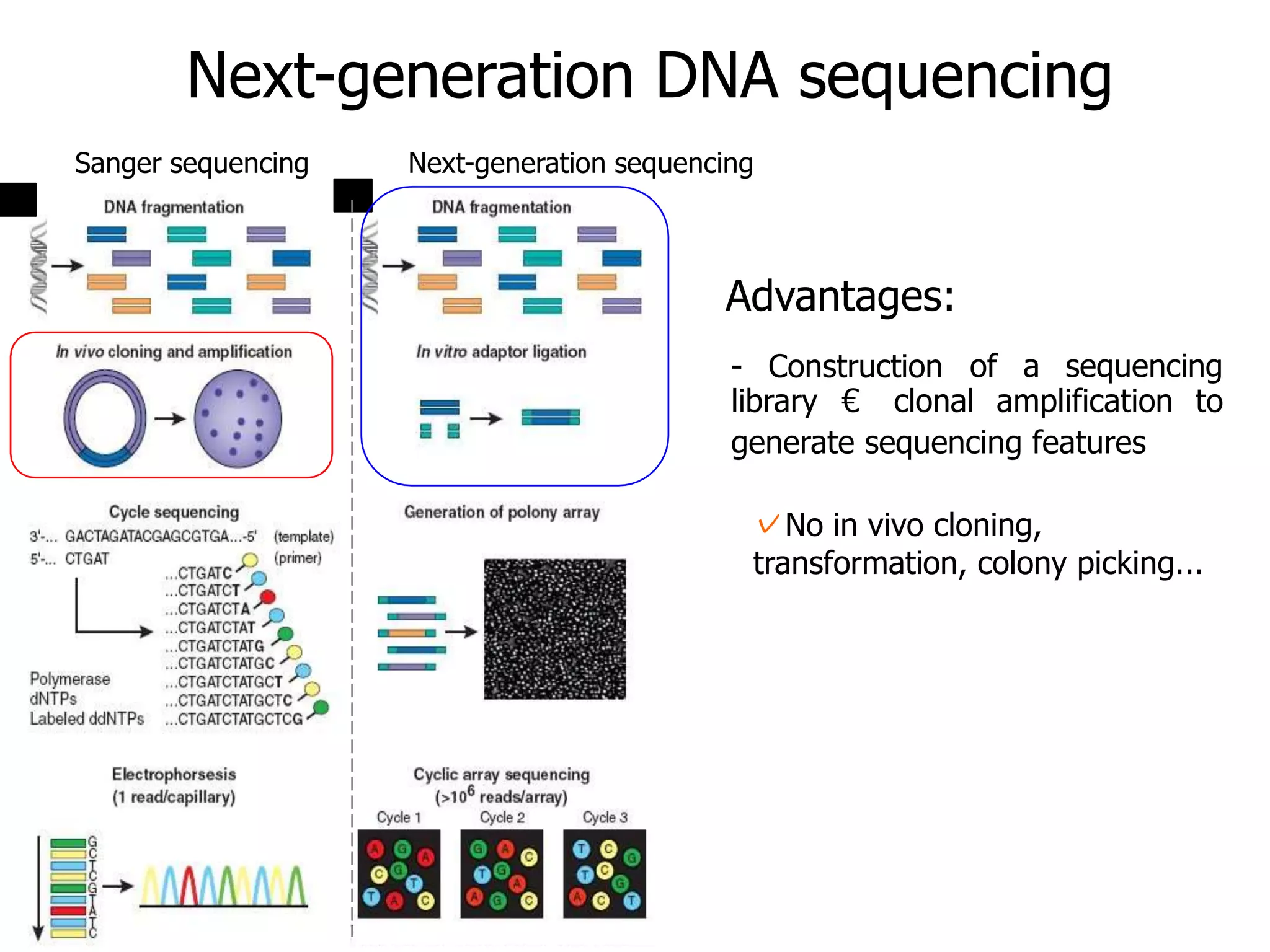
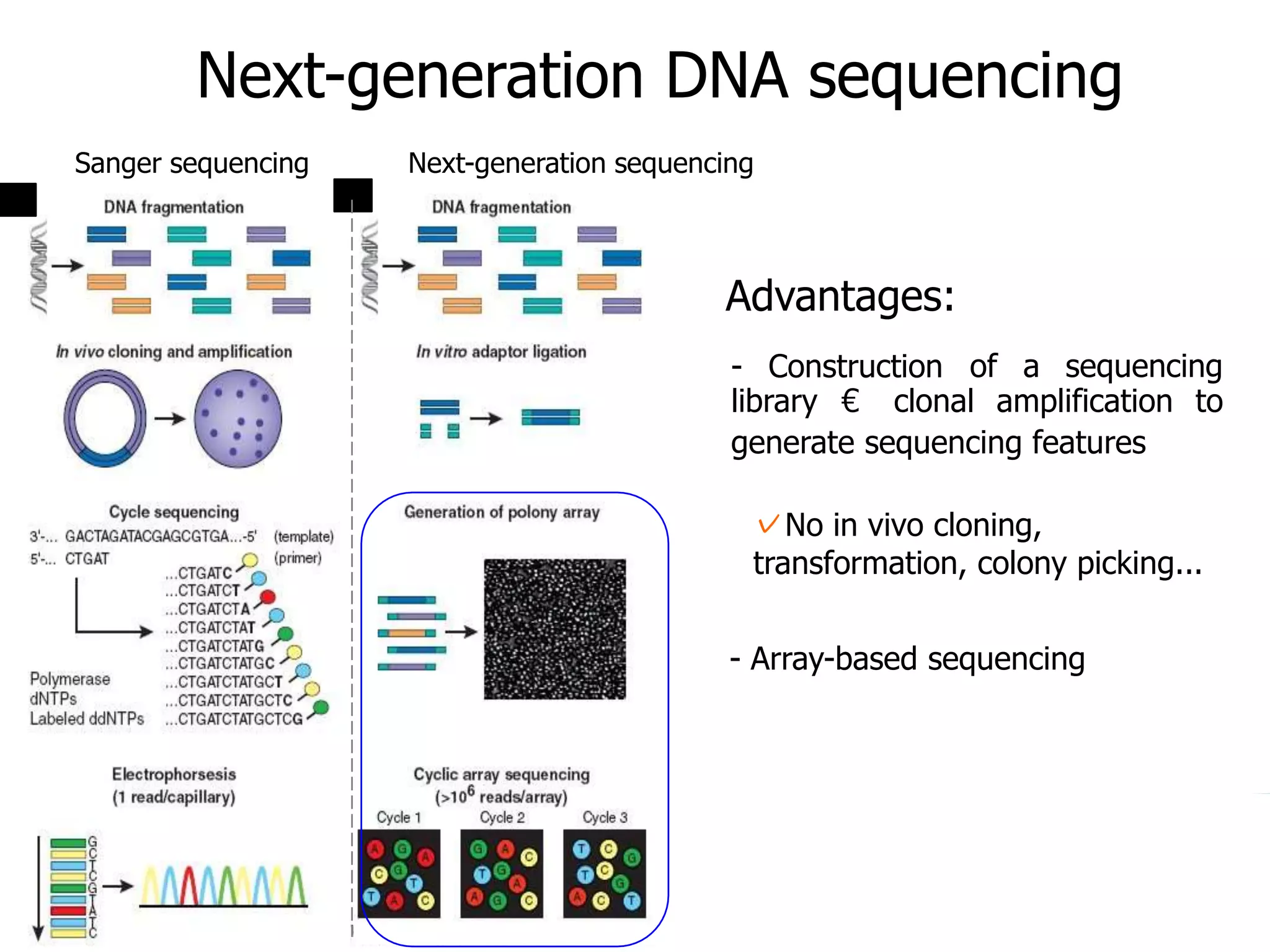
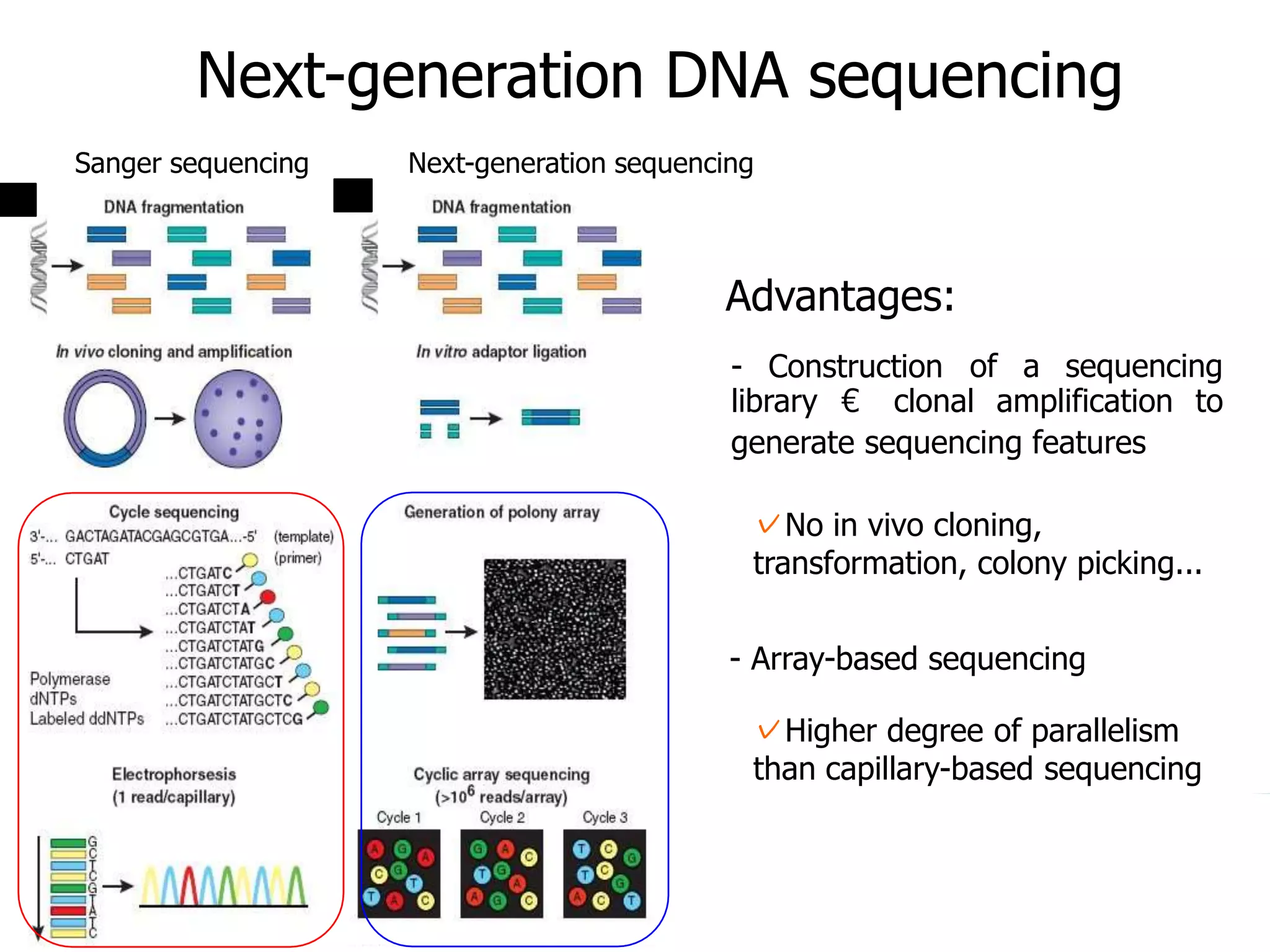
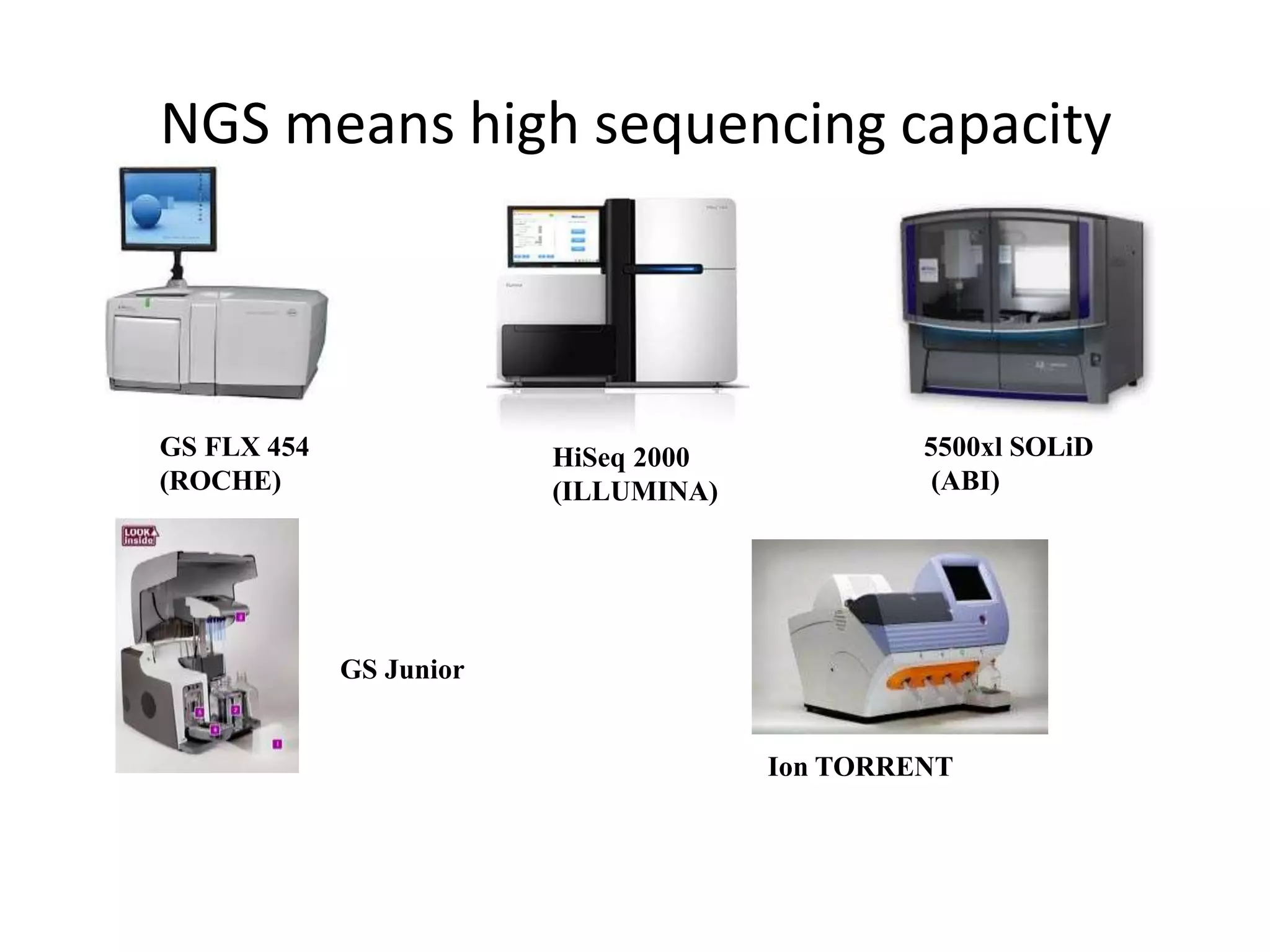
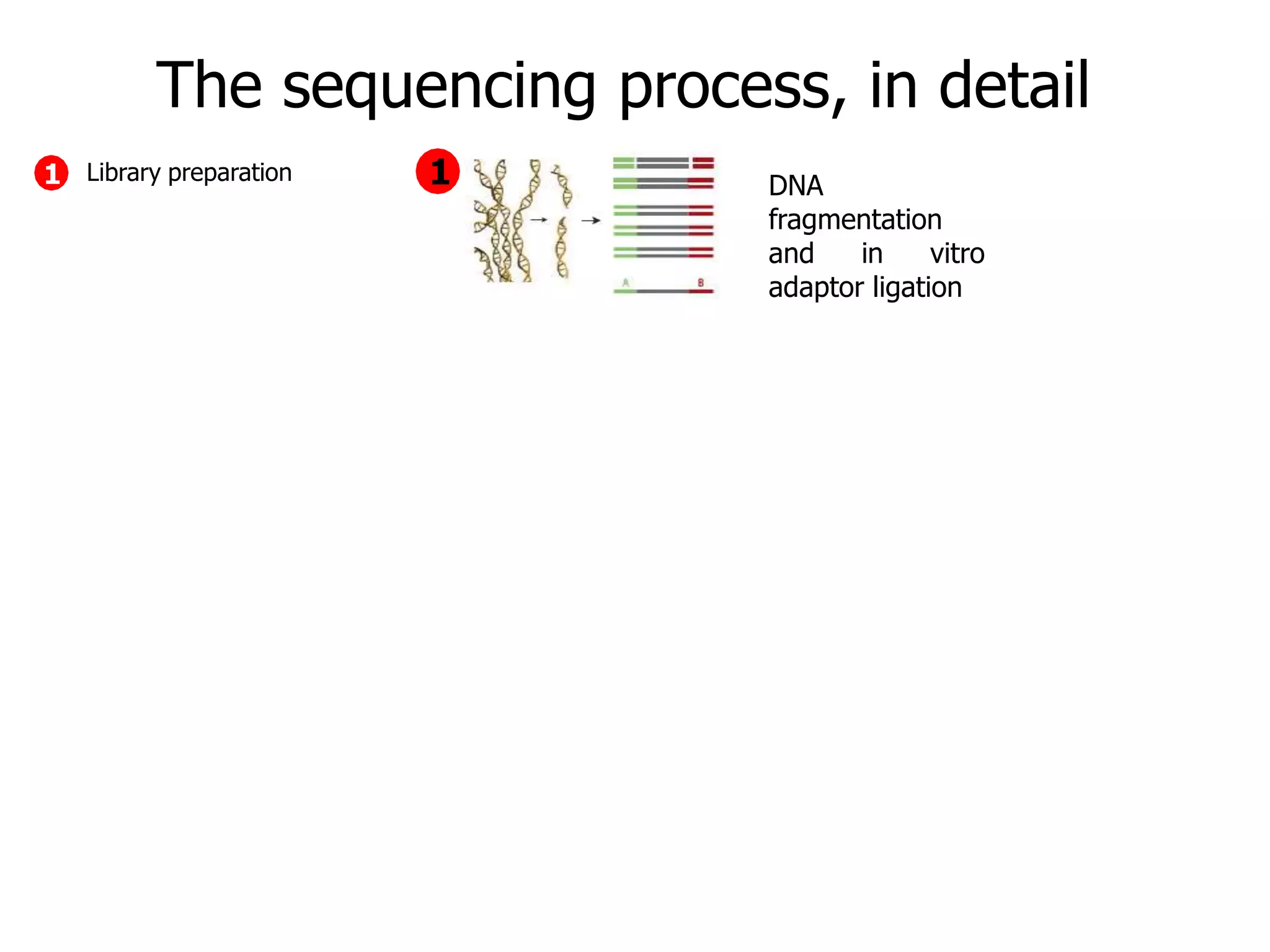
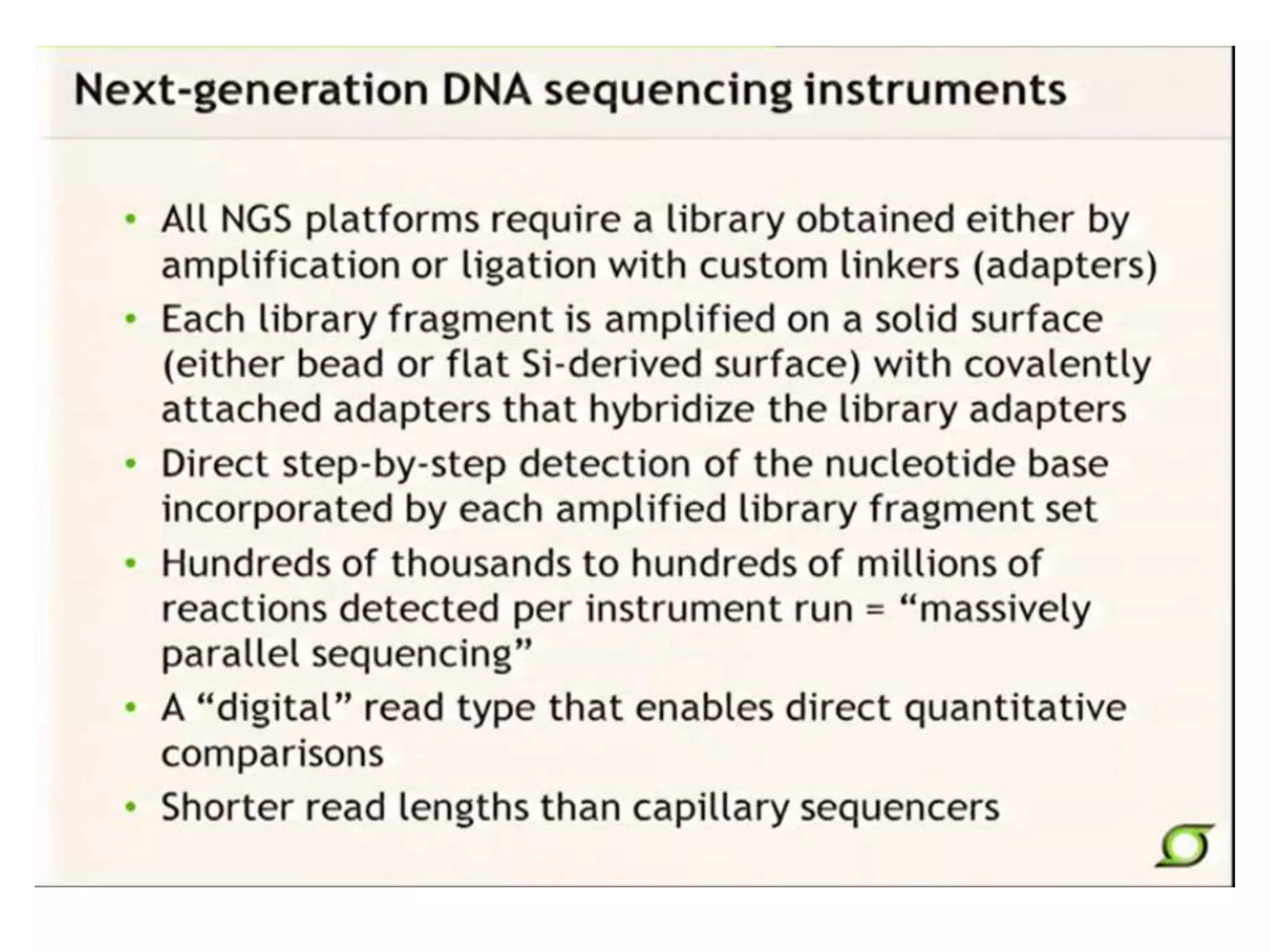
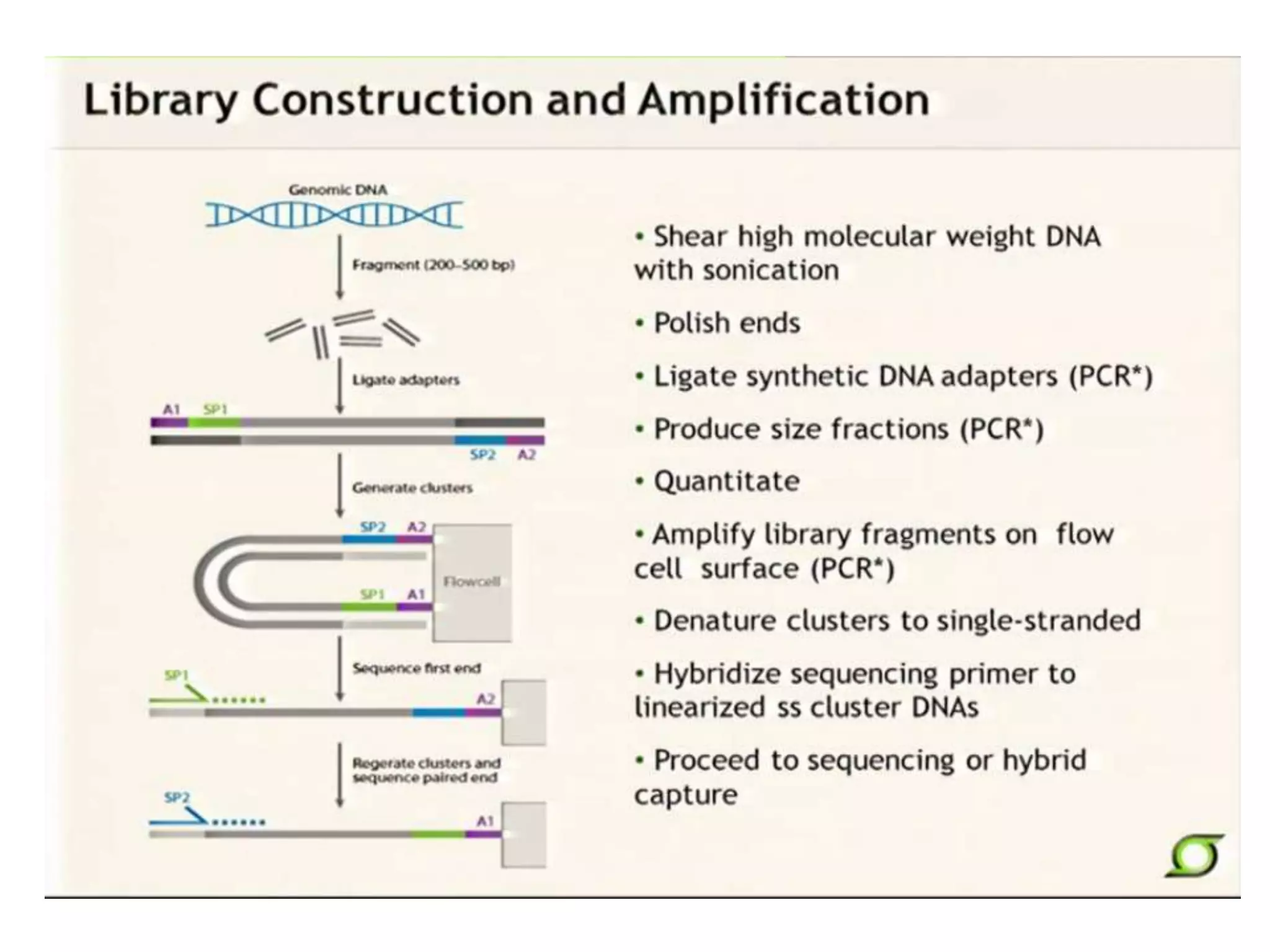
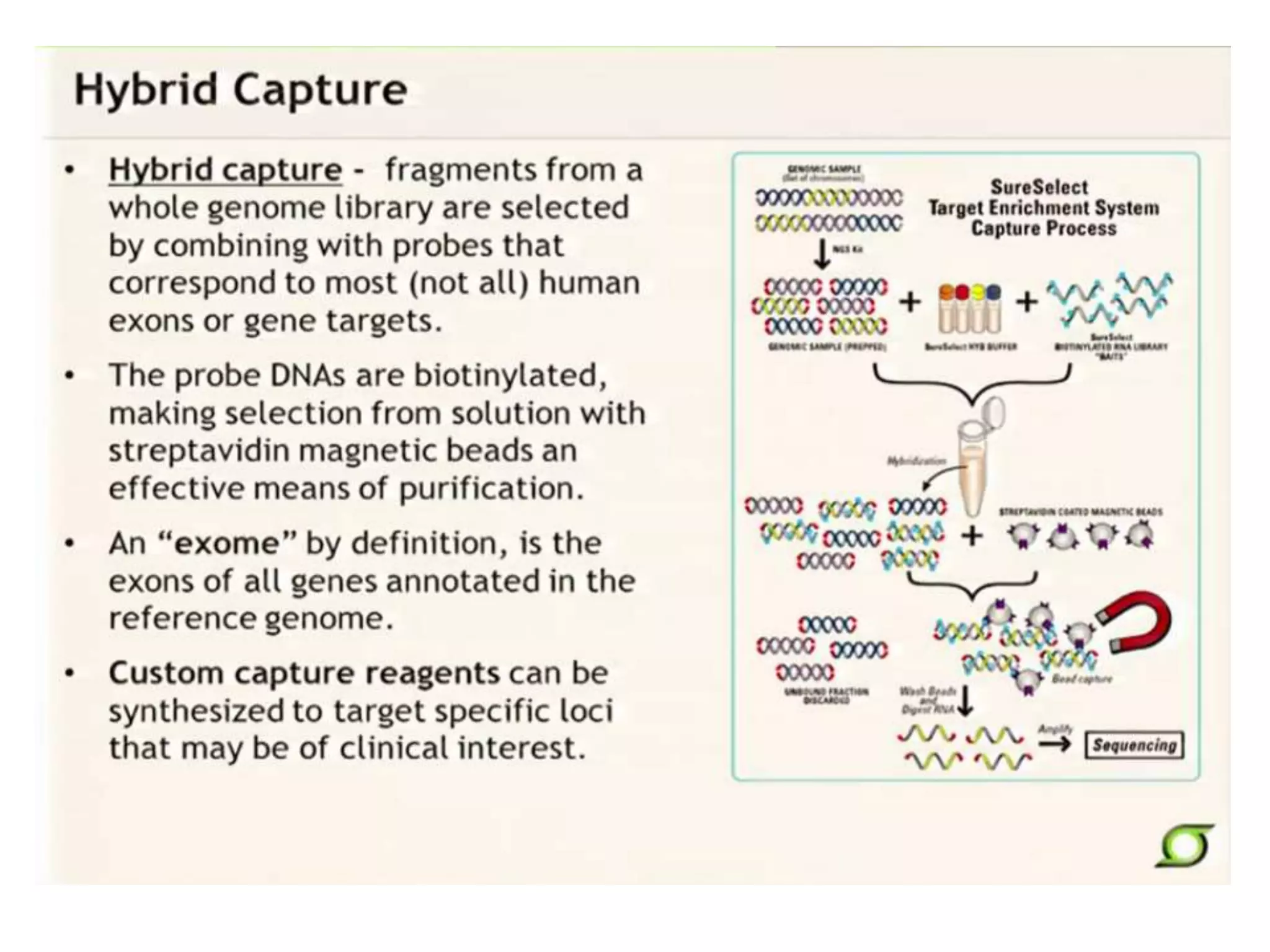
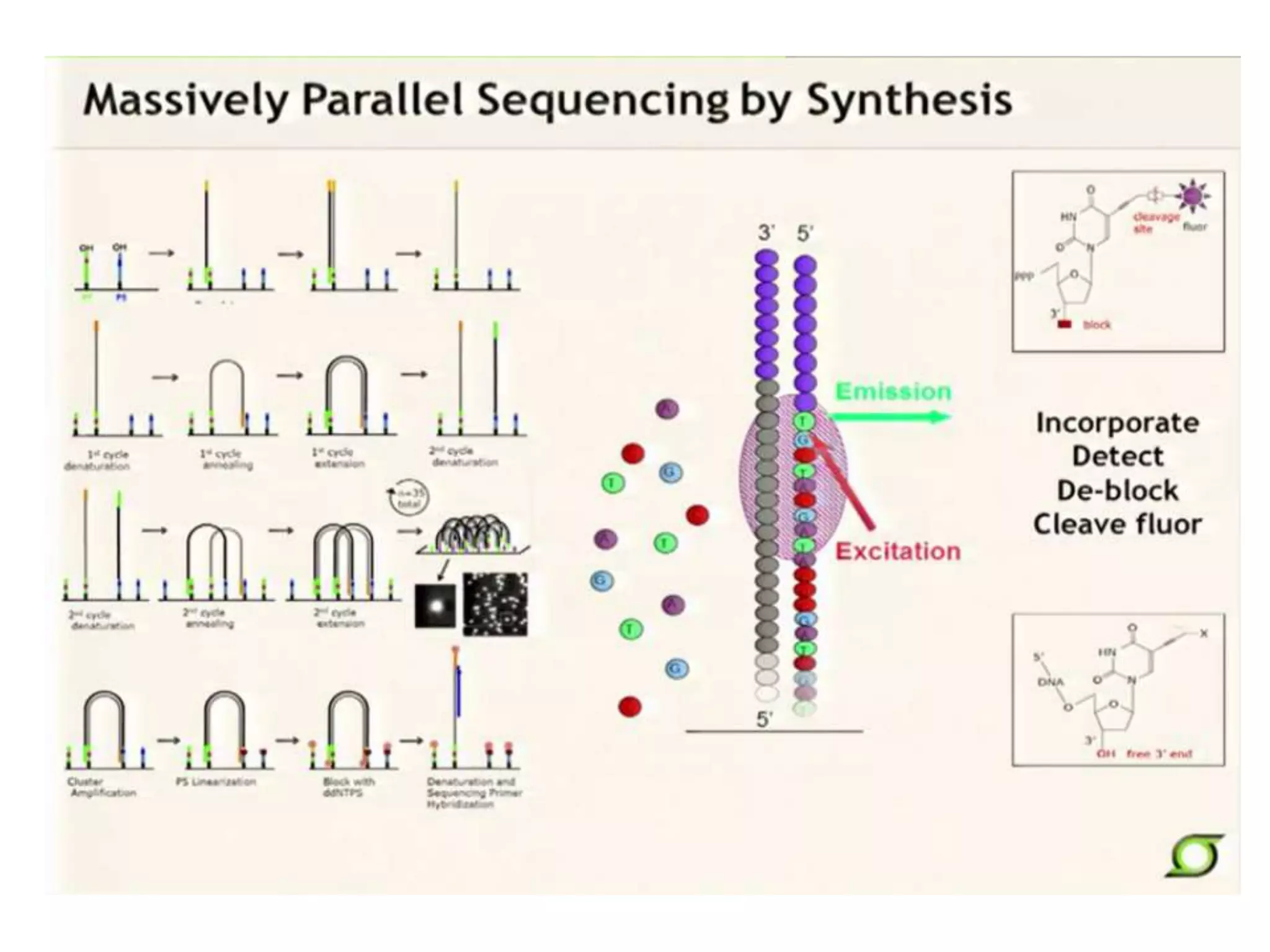
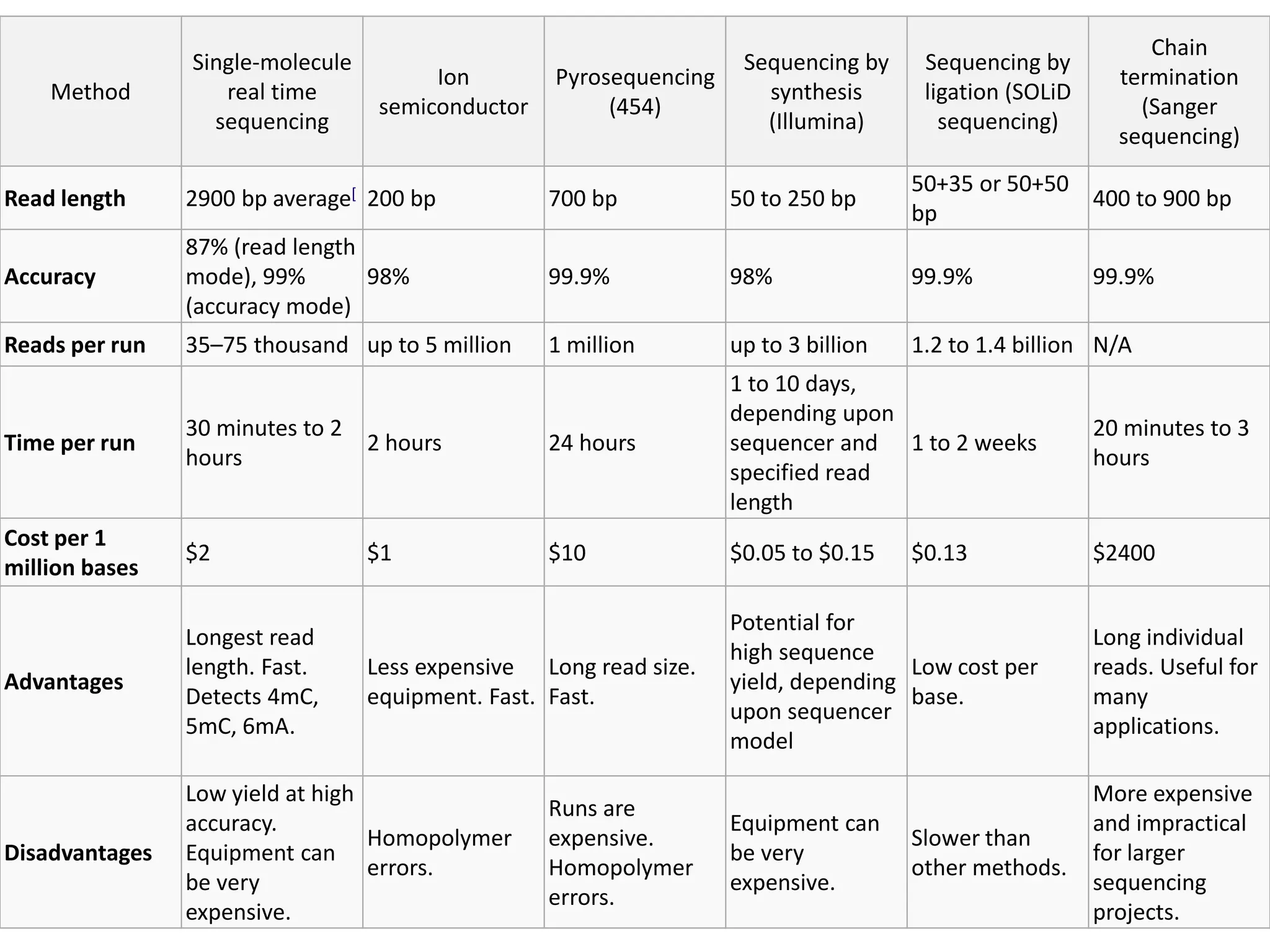
This document discusses the history and evolution of DNA sequencing technologies. It begins with early manual sequencing methods developed in the 1970s by Sanger and others. Automated Sanger sequencing and the sequencing of larger genomes followed in the 1980s-1990s. Next generation sequencing (NGS) methods were developed starting in 1996 and became commercially available in 2005, enabling massively parallel sequencing. NGS platforms such as 454, Illumina, and SOLiD are discussed. Third generation real-time sequencing methods such as PacBio and nanopore sequencing are also introduced, providing longer read lengths. The document compares key parameters of different sequencing methods such as read length, accuracy, throughput, cost and advantages/disadvantages.




![References
• Sequences, sequences, and sequences. Sanger, F. s.l. : Annu Rev Biochem, 1988,
Vol. 57, pp. 1-28.
• Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Sanger, F, Air, GM and
Barrell, BG.1977, Nature, Vol. 265, pp. 687-695.
• DNA Sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Snager, F, Nicklen, S and
Coulson, AR. s.l. : Proc NatI Acad Sci USA, Vol. 74, pp. 5463-5467.
• Overview of DNA sequencing strategies. Shendure, JA, Porreca, GJ and Church,
GM.Chapter 7, s.l. : John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
• Energy transfer primers: a new fluoresence labeling paradigm for DNA sequencing
and analysis. Ju, J, Glazer, AN and Mathies, RA. 2, s.l. : Nat Med, 1996, pp. 998-999.
• 454 Sequencing. [Online] 2015. [Cited: 6 2, 2015.] http://www.454.com/.
• illumina. [Online] 2015. [Cited: 6 2, 2015.] http://www.illumina.com/.
• SOLiD. Applied Biosystems. [Online] 2015. [Cited: 6 2, 2015.]
http://www.appliedbiosystems.com/absite/us/en/home/applications-
technologies/solid-next-generation-sequencing.html.
• Ion Torrent. Applied Biosystems. [Online] 2015. [Cited: 6 2, 2015.]
http://www.lifetechnologies.com/ca/en/home/brands/ion-torrent.html.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g8fkxysjtg22agbwalra-signature-10c61403fb80237547b1b76ac0fb1c6a029769e31fed509ff4f97c29df7057e2-poli-150812202403-lva1-app6891/75/Ngs-introduction-30-2048.jpg)
