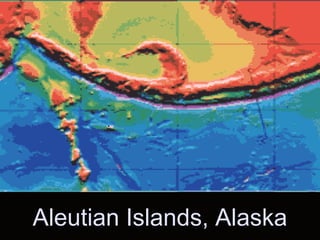
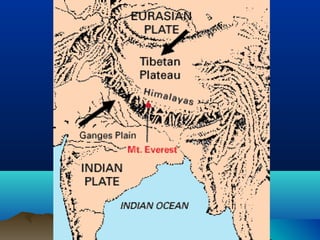
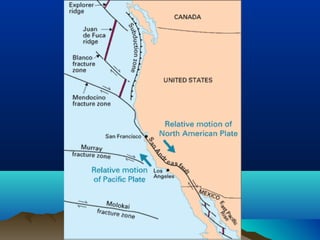
Plate tectonics describes how the Earth's crust is broken into plates that move around on the mantle. There are two types of plates - ocean plates under the oceans and continental plates under the continents. Plates meet at boundaries where they either move apart, collide together, or slide past one another. The movement of convection currents in the mantle is the driving force behind plate tectonics.