This document discusses recommender systems, including:
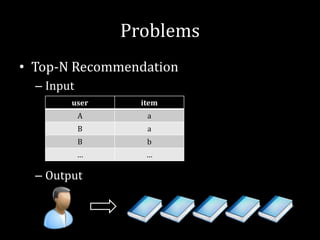
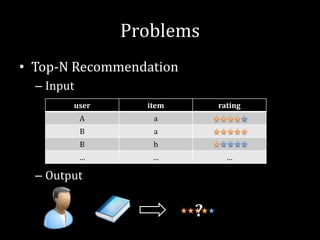
1. It provides an overview of recommender systems, their history, and common problems like top-N recommendation and rating prediction.
2. It then discusses what makes a good recommender system, including experiment methods like offline, user surveys, and online experiments, as well as evaluation metrics like prediction accuracy, diversity, novelty, and user satisfaction.
3. Key metrics that are important to evaluate recommender systems are discussed, such as user satisfaction, prediction accuracy, coverage, diversity, novelty, serendipity, trust, robustness, and response time. The document emphasizes selecting metrics based on business goals.







![History: Before 1992
• Content Filtering
– An architecture for large scale information
systems [1985] (Gifford, D.K)
– MAFIA: An active mail-filter agent for an
intelligent document processing support [1990]
(Lutz, E.)
– A rule-based message filtering system [1988]
(Pollock, S. )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-9-320.jpg)
![History: 1992-1998
• Tapestry by Xerox Palo Alto [1992]
– First system designed by collaborative filtering
• Grouplens [1994]
– First recommender system using rating data
• Movielens [1997]
– First movie recommender system
– Provide well-known dataset for researchers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-10-320.jpg)
![History: 1992-1998
• Fab : content-based collaborative
recommendation
– First unified recommender system
• Empirical Analysis of Predictive Algorithms
for Collaborative Filtering [1998] (John S.
Breese)
– Systematically evaluate user-based
collaborative filtering](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-11-320.jpg)
![History: 1999-2005
• Amazon proposed item-based collaborative
filtering (Patent is filed in 1998 and issued
in 2001) [link]
• Thomas Hofmann proposed pLSA [1999]
and apply similar method on collaborative
filtering [2004]
• Pandora began music genome project
[2000]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-12-320.jpg)
![History: 1999-2005
• Lastfm using Audioscrobbler to generate
user taste profile on musics.
• Evaluating collaborative filtering
recommender systems [2004] (Jonathan L.
Herlocker)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-13-320.jpg)
![History: 2005-2009
• Toward the Next Generation of
Recommender Systems: A Survey of the
State-of-the-Art and Possible Extensions.
[2005] (Alexander Tuzhilin)
• Netflix Prize [link]
– Latent Factor Model (SVD, RSVD, NSVD, SVD++)
– Temporal Dynamic Collaborative Filtering
– Yehuda Koren [link]’s team get prize](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-14-320.jpg)
![History: 2005-2009
• ACM Conference on Recommender System
[2007] (Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA)
• Digg, Youtube try recommender system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-15-320.jpg)

![History: 2010-now
• Facebook launches instant personalization
[2010]
– Clicker
– Bing
– Trip Advisor
– Rotten Tomatoes
– Pandora
– ……](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-17-320.jpg)












![Experiment Metrics
• Novelty
– Measure the ability of recommender system to
introduce long tail items to users.
– International Workshop on Novelty and
Diversity in Recommender Systems [link]
– Music Recommendation and Discovery in the
Long Tail [Oscar Celma]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystem-introduction-120415205114-phpapp02/85/Recommender-system-introduction-32-320.jpg)






