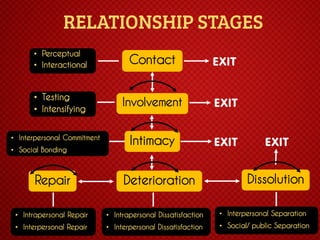
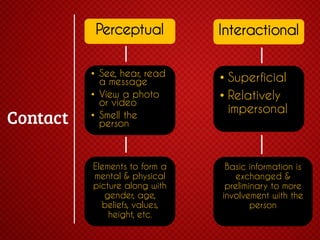
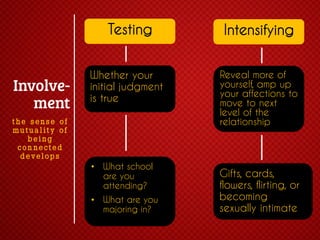
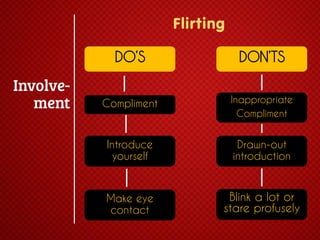
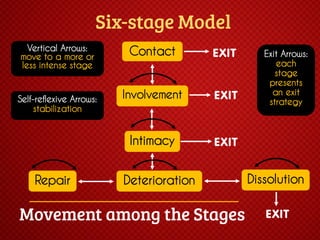
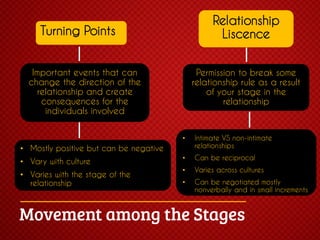
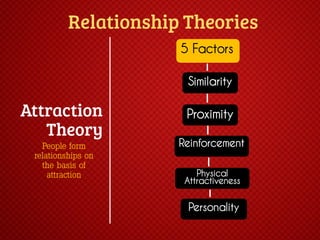
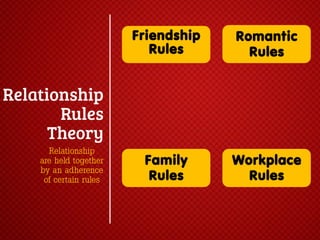
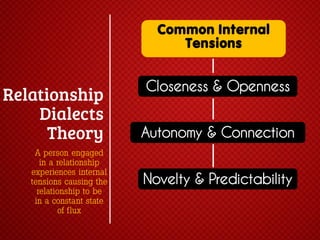
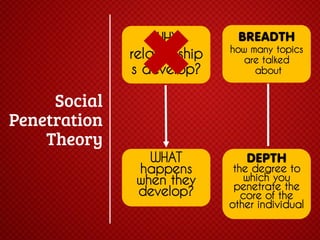
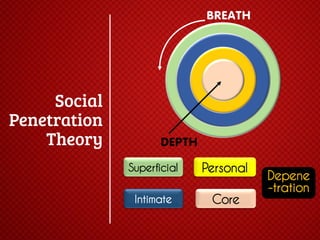
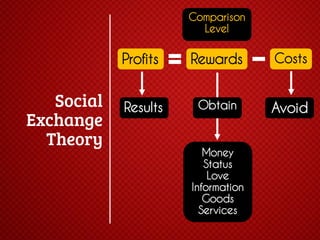
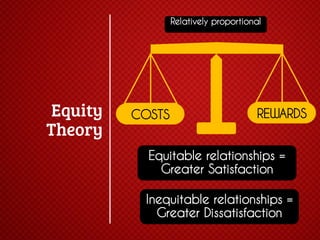
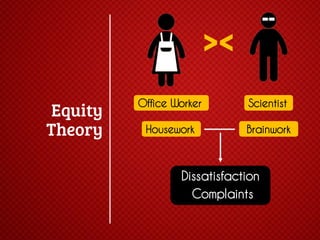
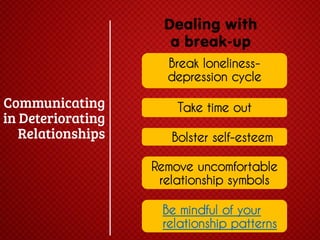
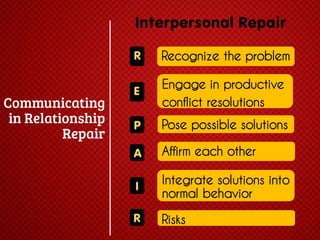
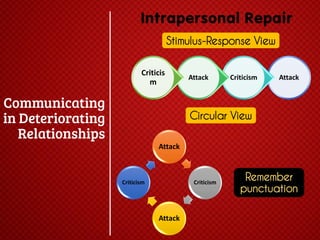
The document discusses various stages of relationships from initial contact through intensifying involvement, commitment, bonding, deterioration, and dissolution. It examines relationship theories including turning points, relationship rules and licenses, comparison levels, and strategies for repairing and disengaging from relationships. Communication patterns and tensions within relationships are also analyzed at different stages.