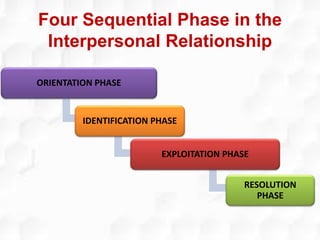
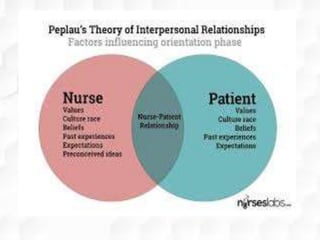
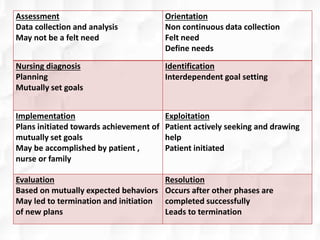
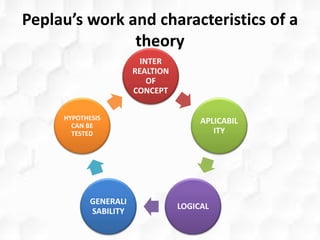
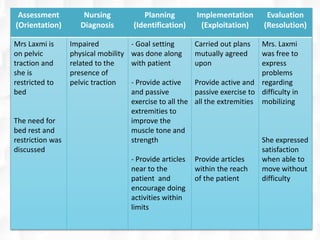
Hildegard Peplau developed the theory of interpersonal relations in nursing. The theory focuses on the nurse-patient relationship and involves four phases: orientation, identification, exploitation, and resolution. Peplau proposed that nursing is an interpersonal process where nurses fulfill various roles to help patients through therapeutic communication and goal-setting. The theory provides a framework for understanding the nurse-patient dynamic and is still widely applied in psychiatric nursing and the nursing process.