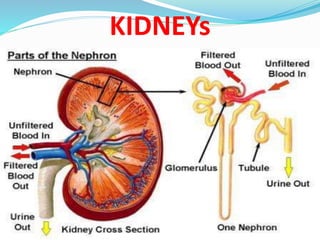
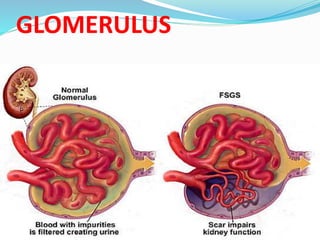
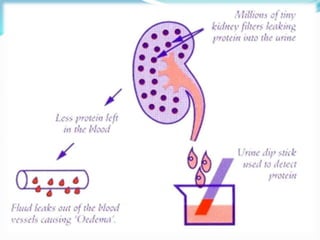
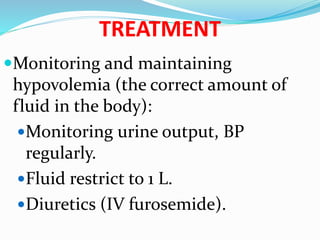
This document defines nephrotic syndrome as a condition characterized by proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia caused by damage to the glomeruli in the kidneys. It lists various primary and secondary causes of nephrotic syndrome including diseases like lupus, diabetes, and infections. The clinical manifestations are edema, hyperlipidemia, and proteinuria. Treatment involves monitoring fluid levels, treating underlying causes, and using diuretics, immunosuppressants, and in some cases anticoagulants.