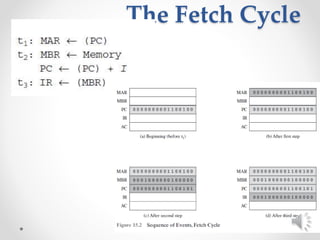
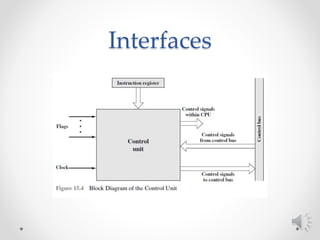
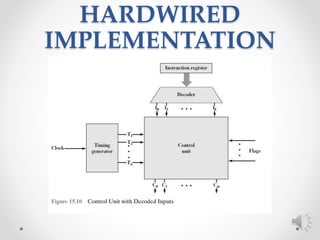
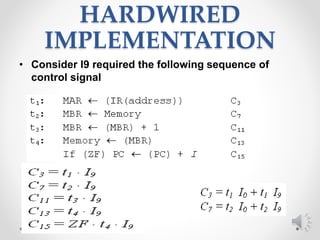
The control unit of a CPU performs two main tasks: 1) it sequences the processor through a series of micro-operations in the proper order based on the program being executed, and 2) it generates control signals to execute each micro-operation. Micro-operations include transferring data between registers, transferring data between a register and external bus, and arithmetic logic unit operations. The control unit uses control signals to open and close logic gates to transfer data and operate the ALU.