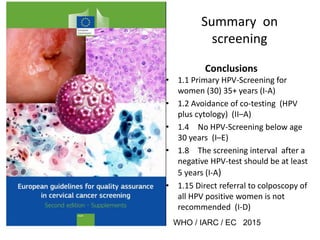
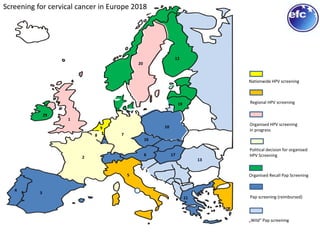
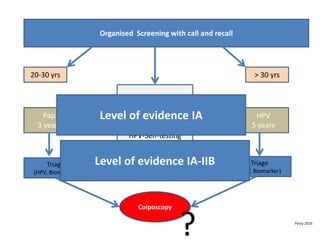
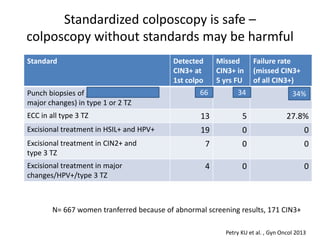
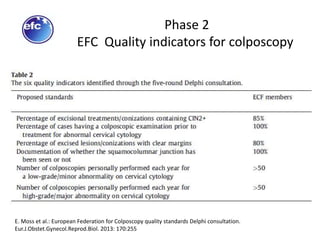
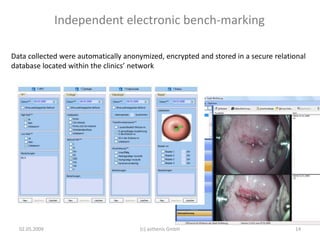
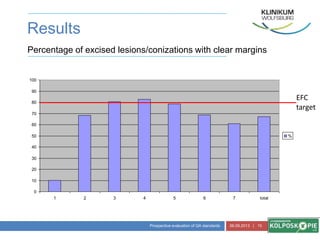
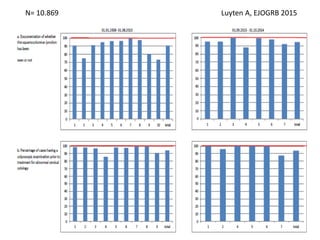
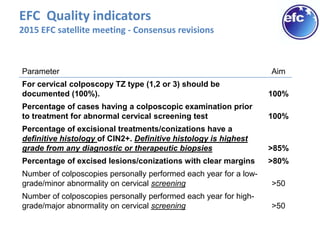
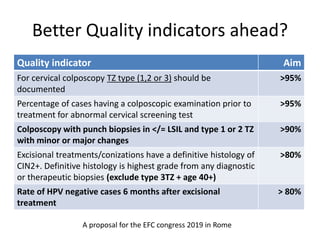
This document discusses quality standards for colposcopy. It proposes that the European Federation for Colposcopy (EFC) approve national quality assurance concepts for colposcopy. This would include evaluating colposcopists' case loads and performance on key quality indicators. The document also reviews different quality indicators for colposcopy, such as rates of clear margins after treatment and detection of high-grade lesions. It suggests these indicators could be improved and should allow flexibility for national standards. Overall it argues continuous quality assurance of colposcopy education, training and practice is needed, and this can be delivered across different healthcare settings with EFC harmonization.