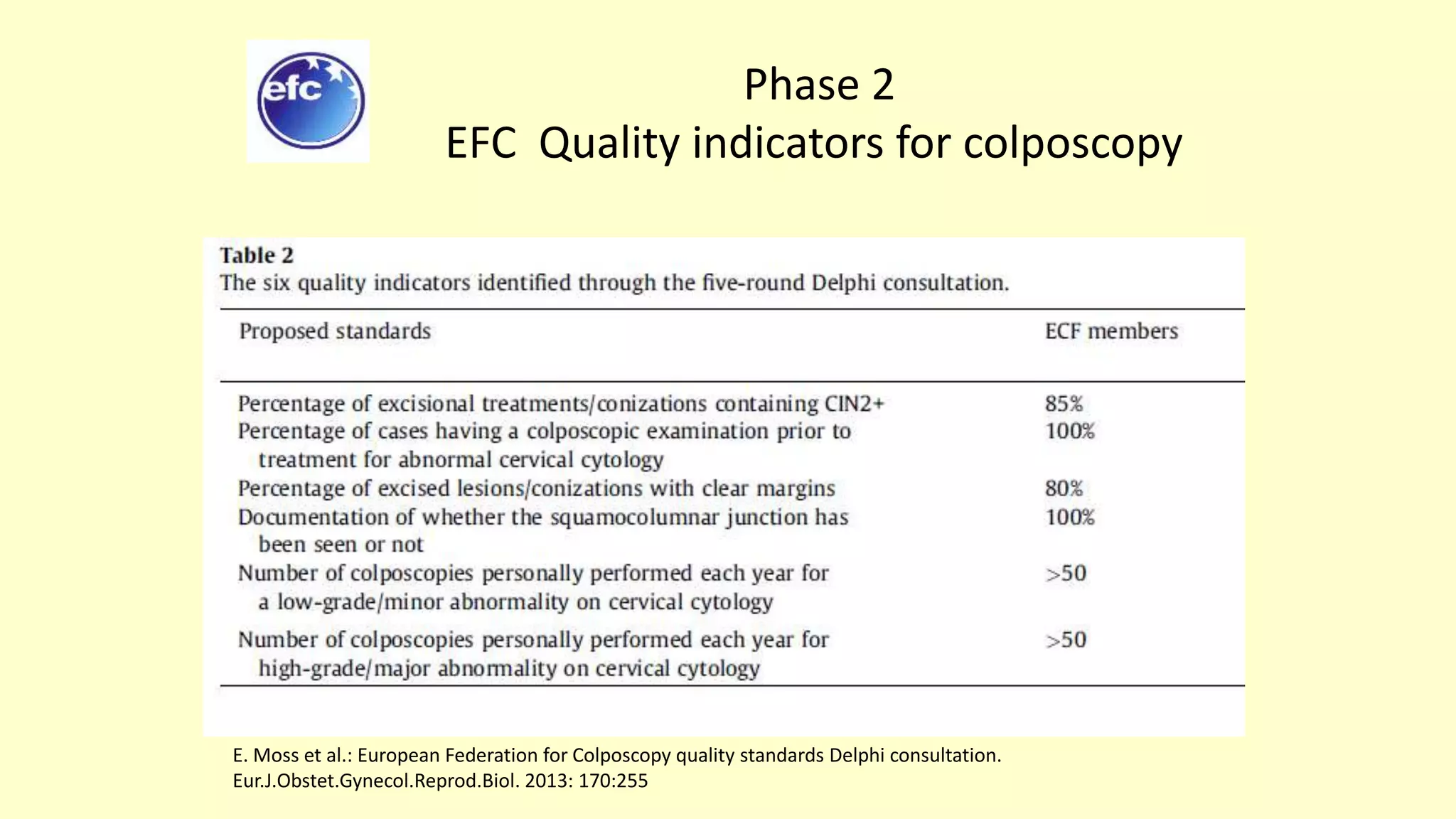
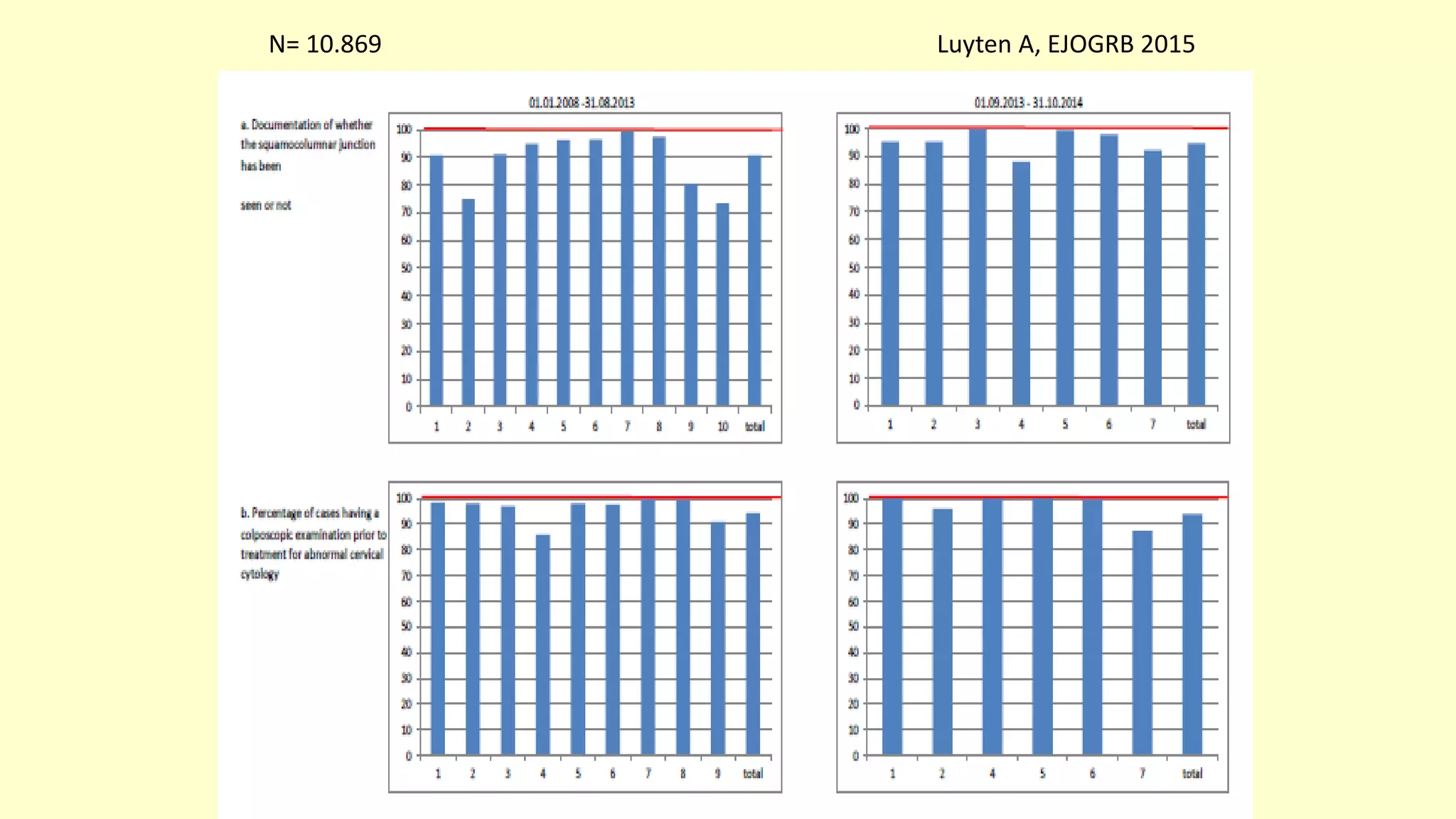
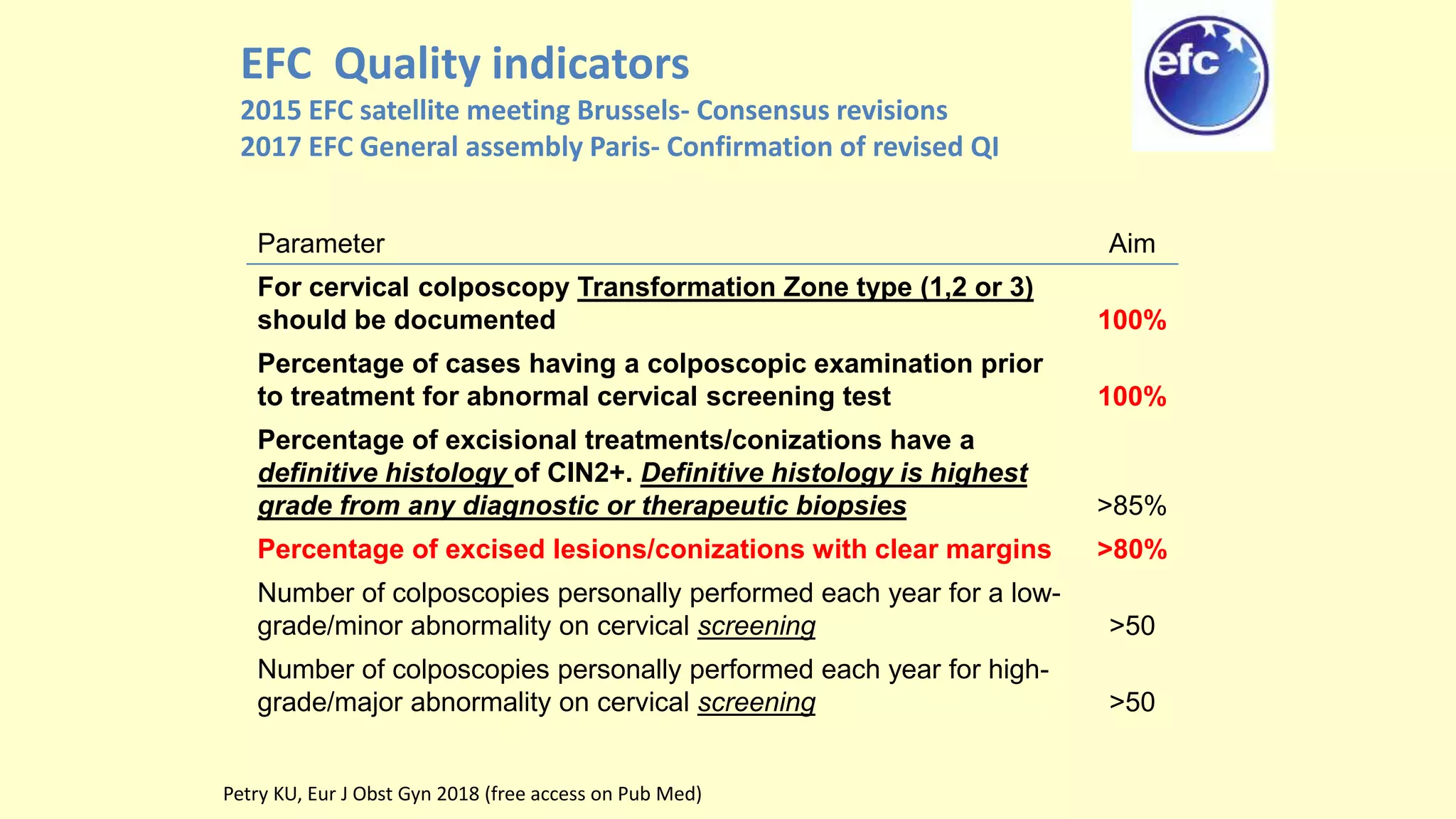
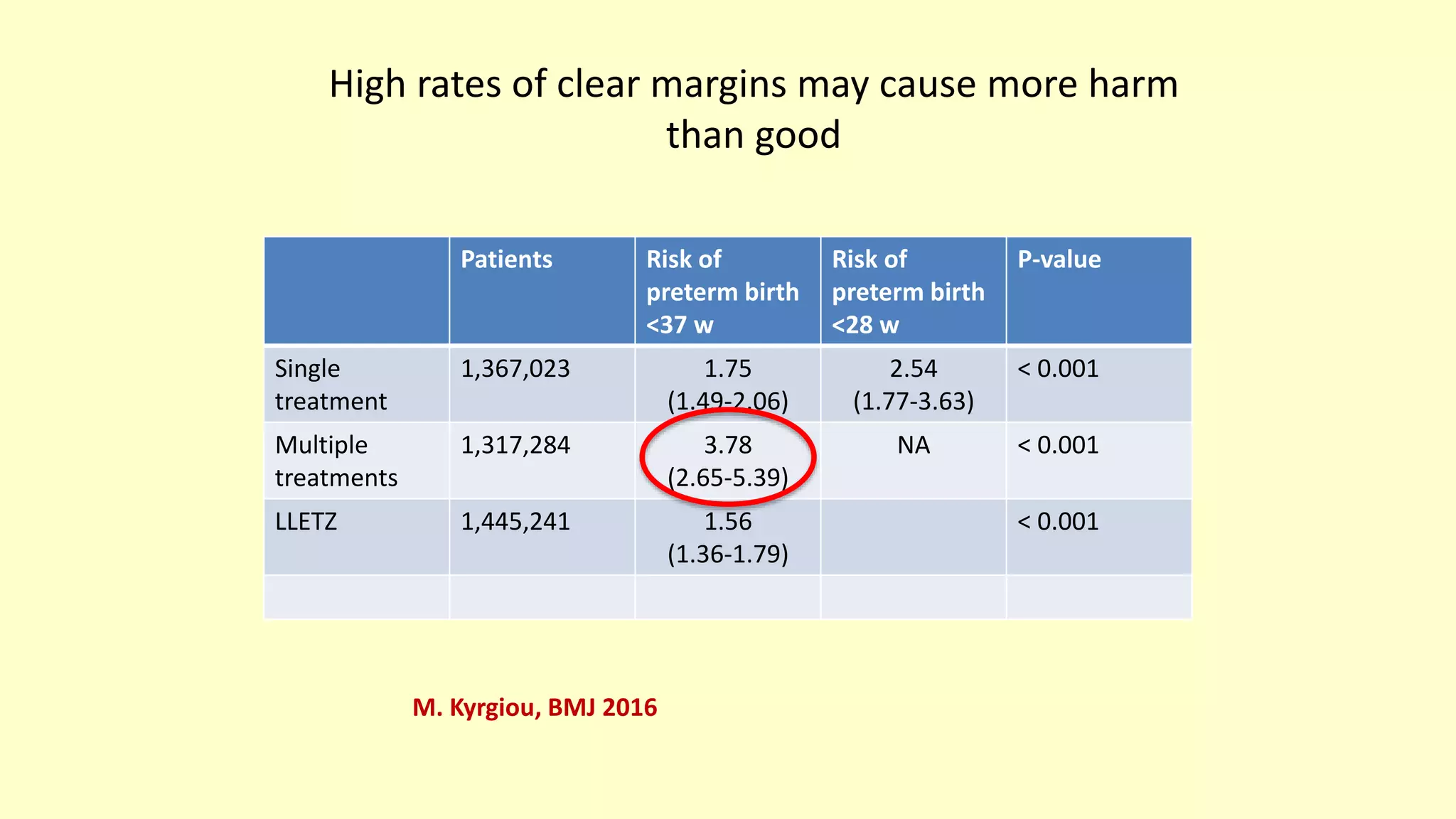
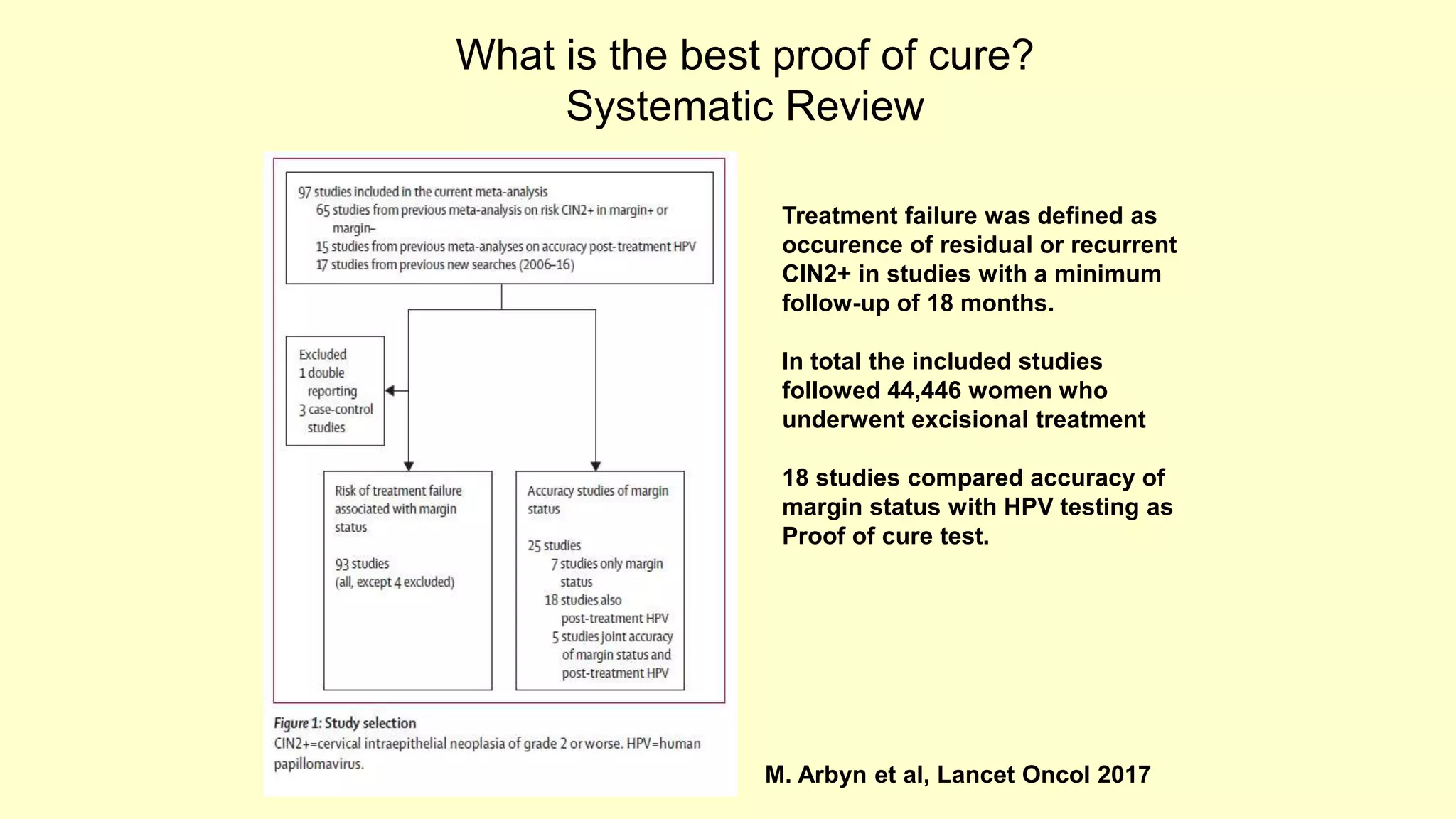
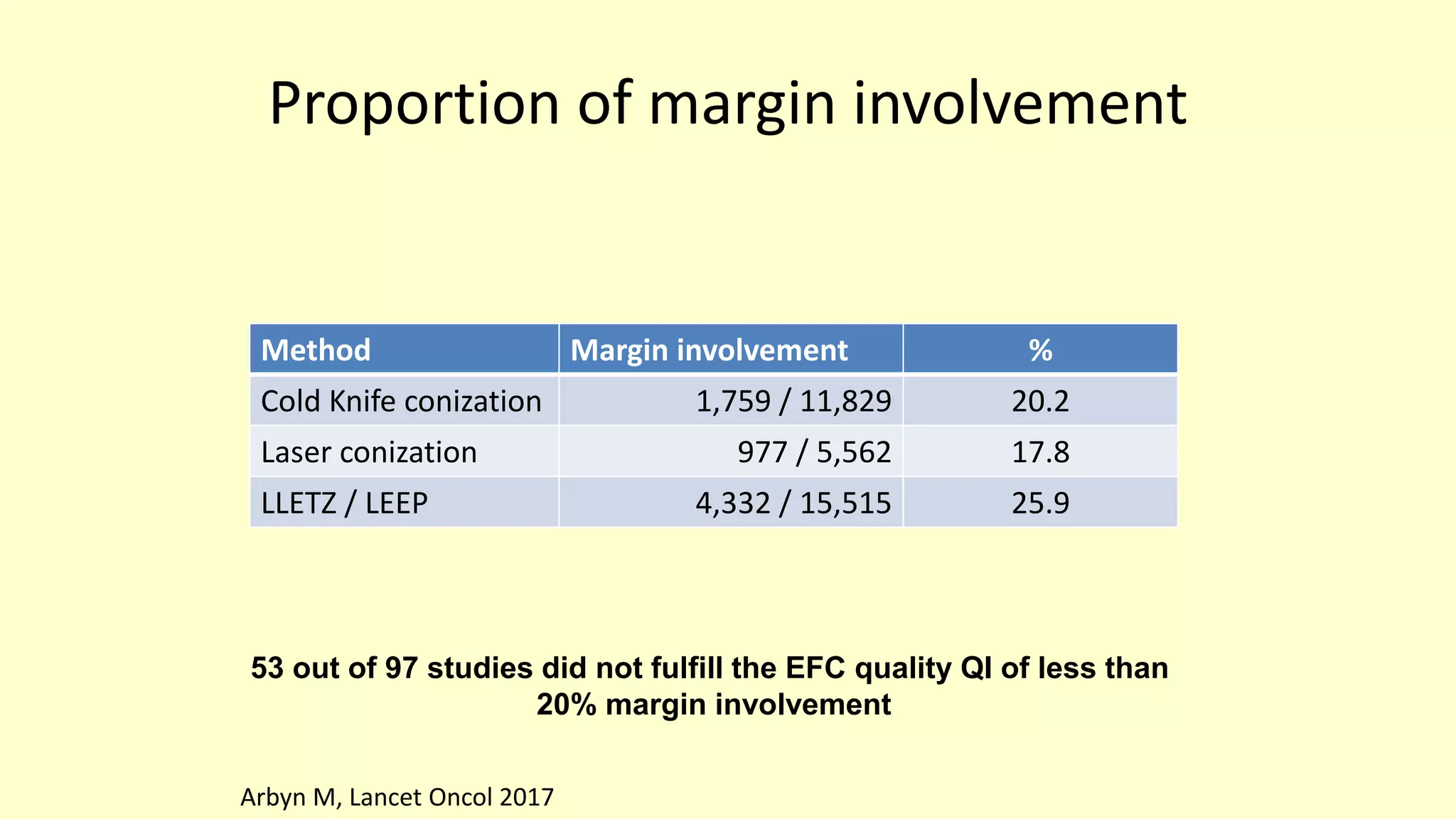
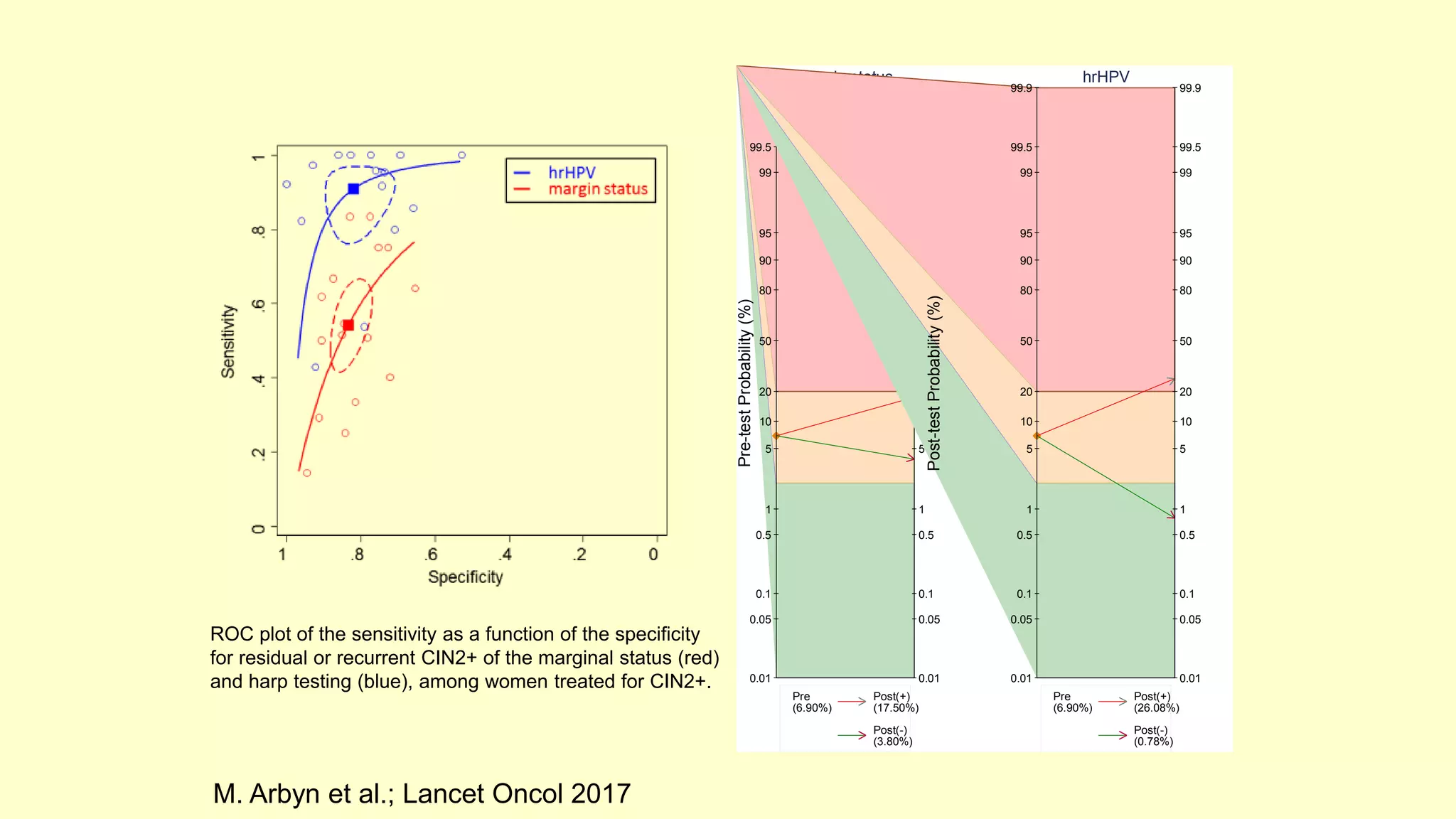
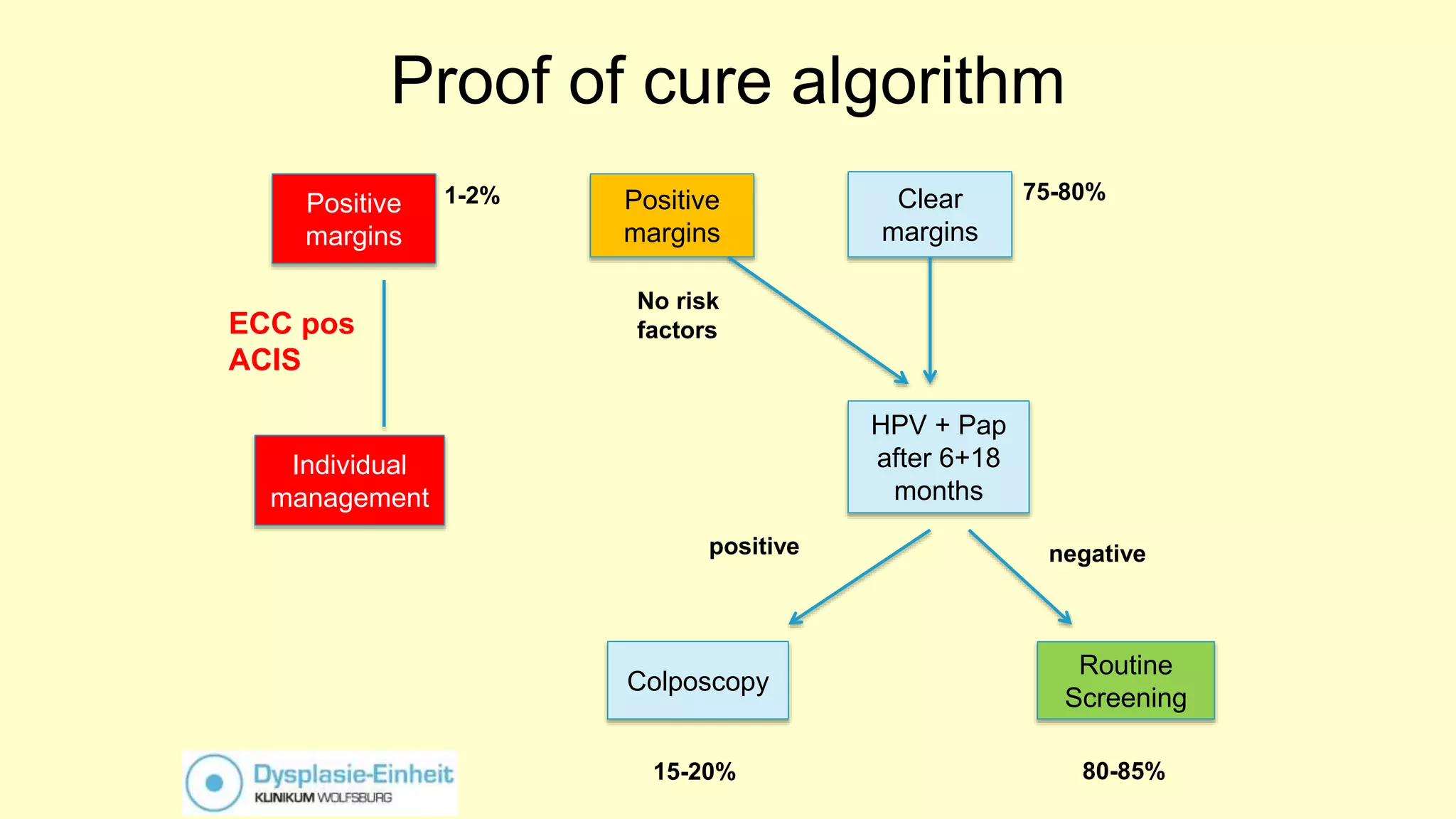
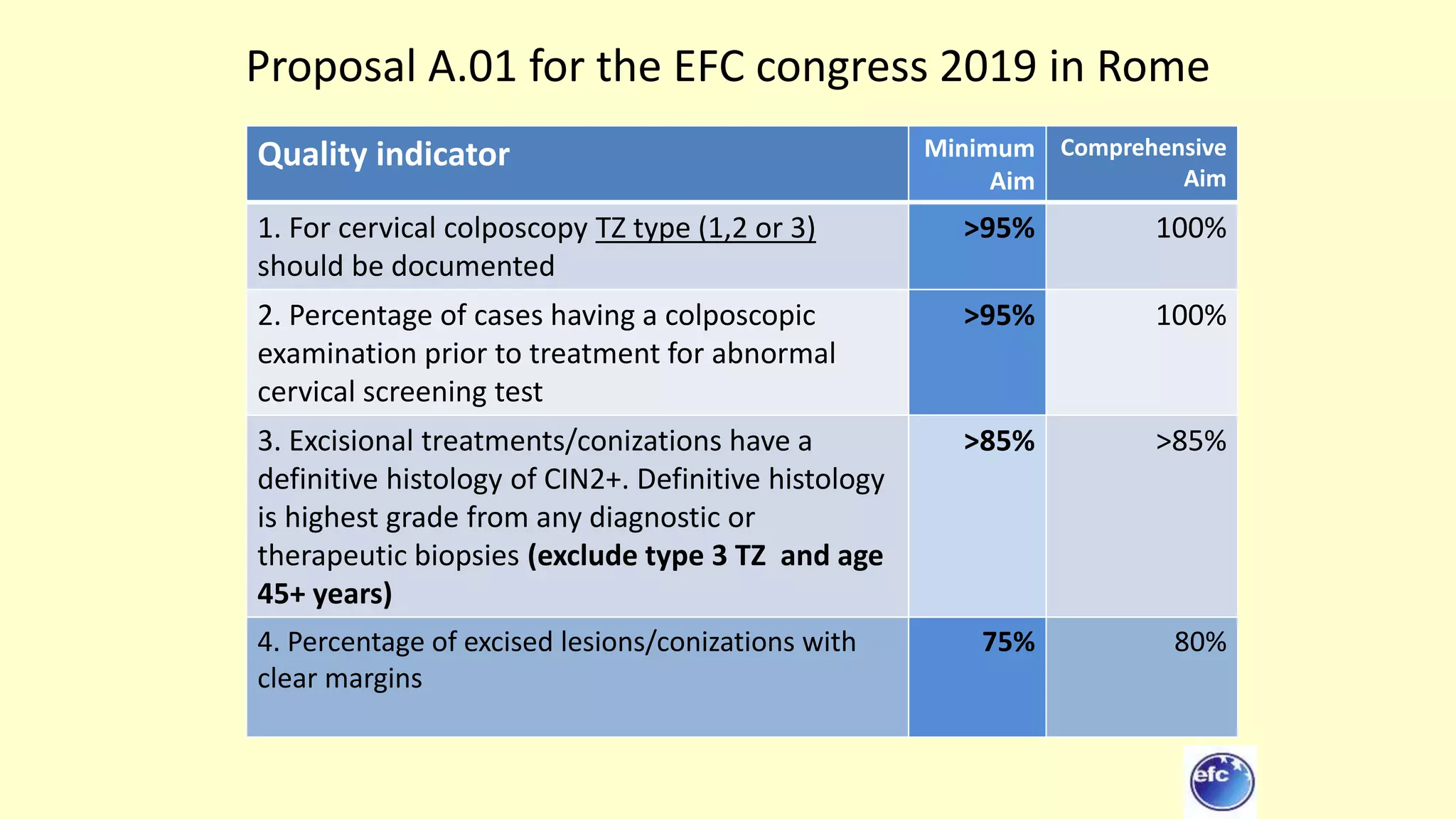
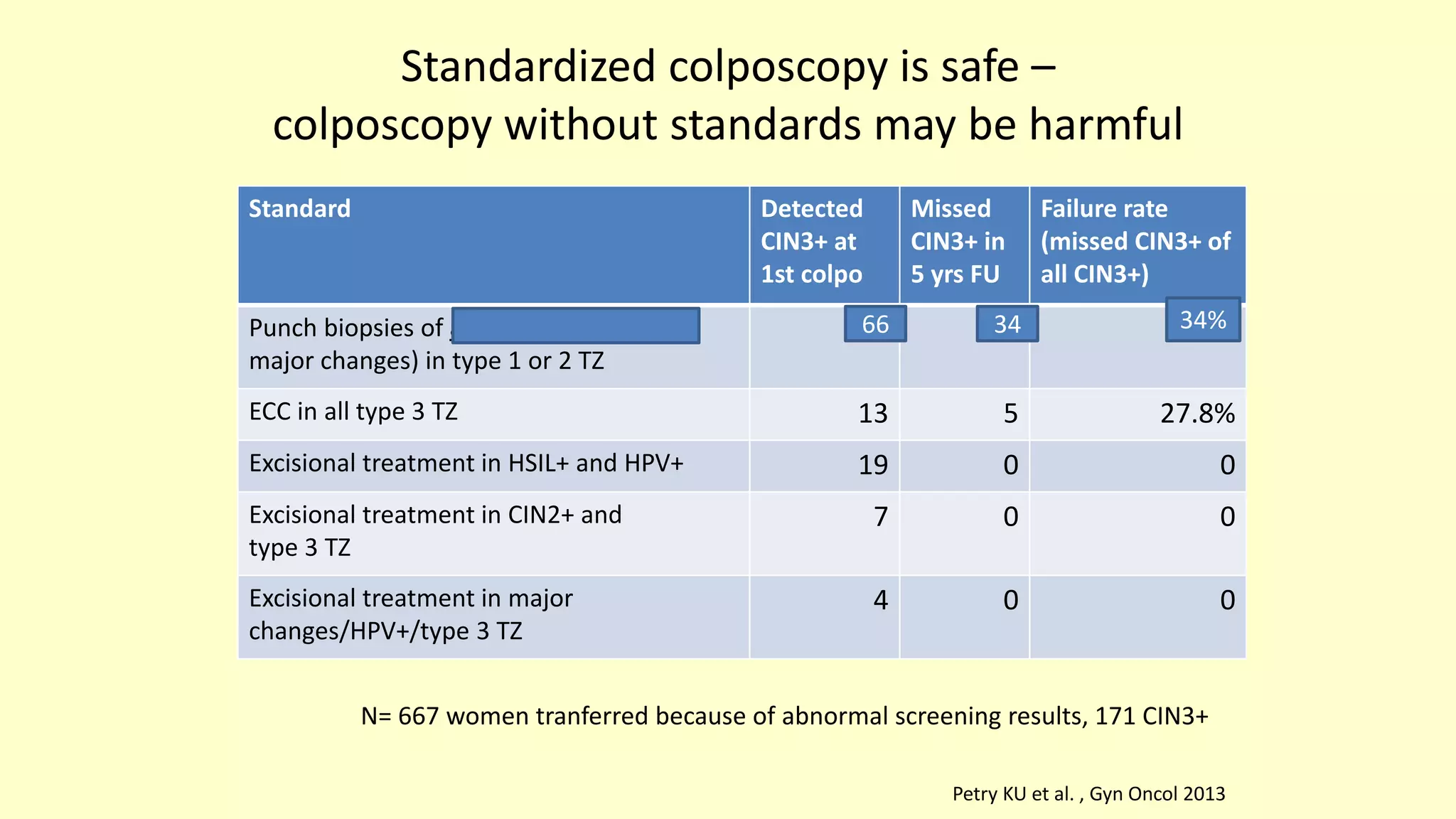
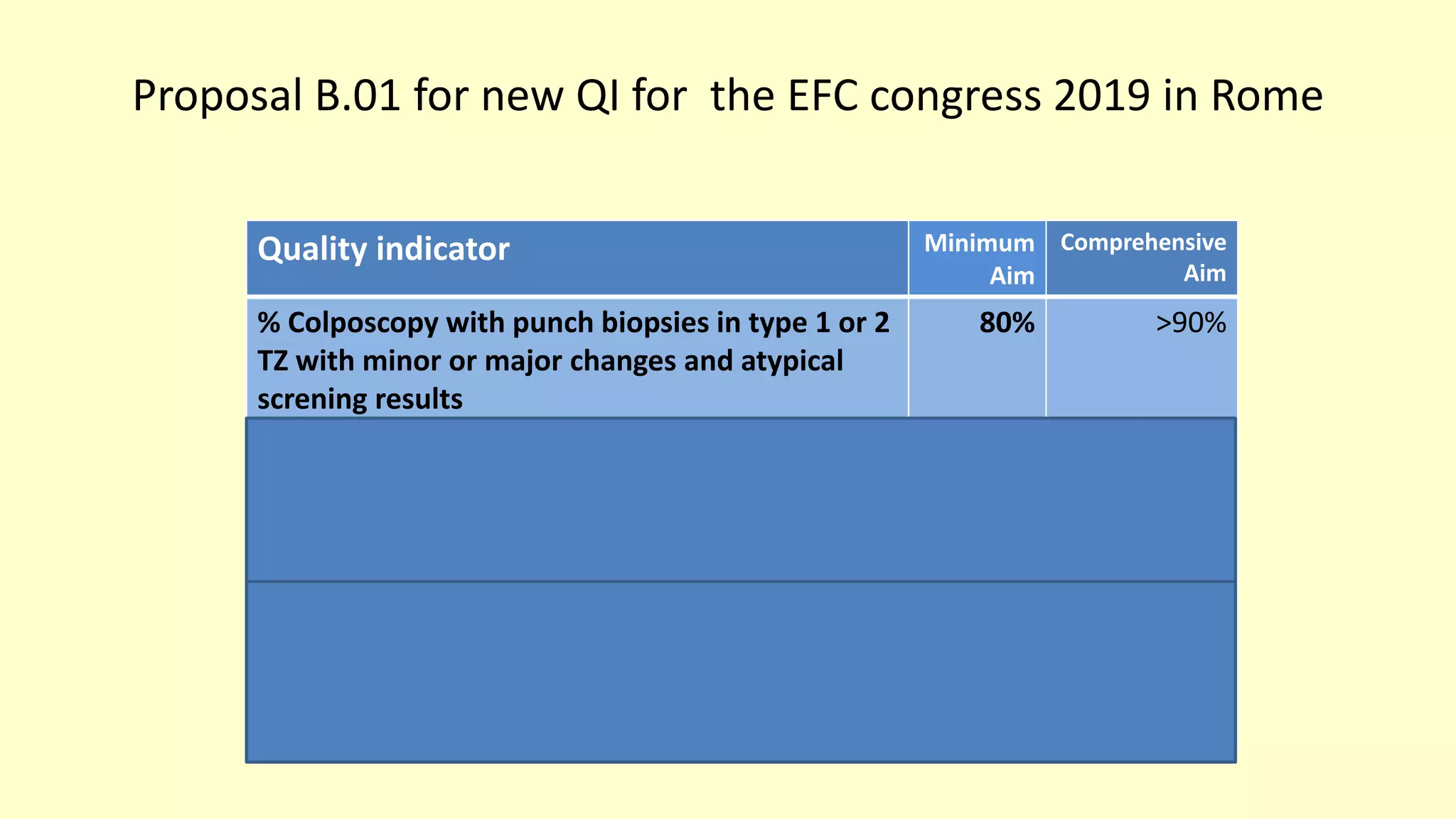
This document discusses quality indicators for colposcopy and proposes updates. It summarizes recent studies on margin status and HPV testing as proof of cure after treatment. It finds that the current quality indicator of 80% clear margins is not useful as margin status is a poor predictor of treatment failure. HPV testing 3-12 months after treatment is a better predictor of cure. It proposes revising the quality indicators to focus on comprehensive colposcopy examinations and HPV-negative proof of cure after treatment. It also discusses the importance of standardized colposcopy to safely manage pre-cancer and avoid unnecessary procedures.