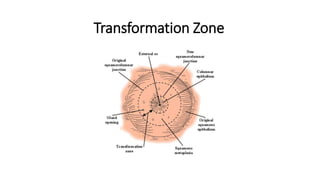
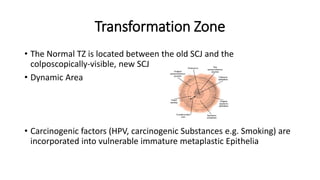
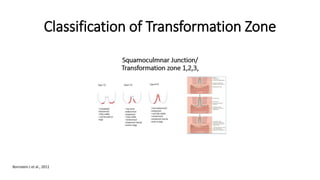
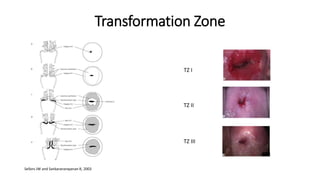
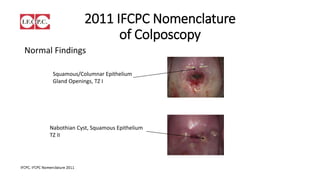
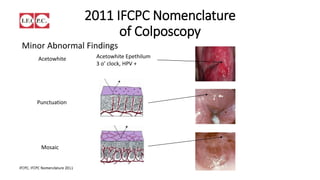
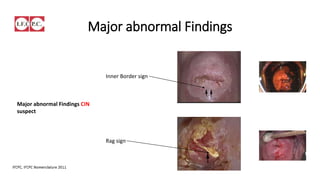
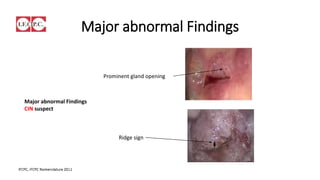
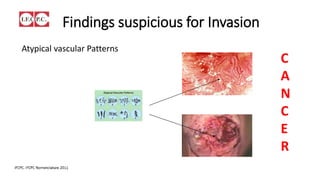
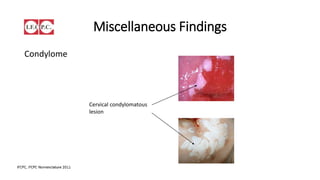
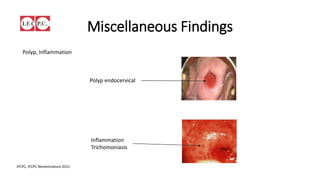
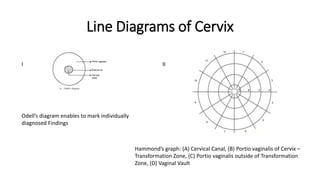
The document provides an overview of colposcopy as a secondary cervical cancer prevention method, detailing indications for the procedure, steps in conducting an examination, and classifications of transformation zones. It outlines the colposcopic signs, terminology, and the importance of teamwork in therapy following findings. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for standardized training in maternal health and gynecology services to enhance care for women.