The document discusses several key factors in landing gear design:
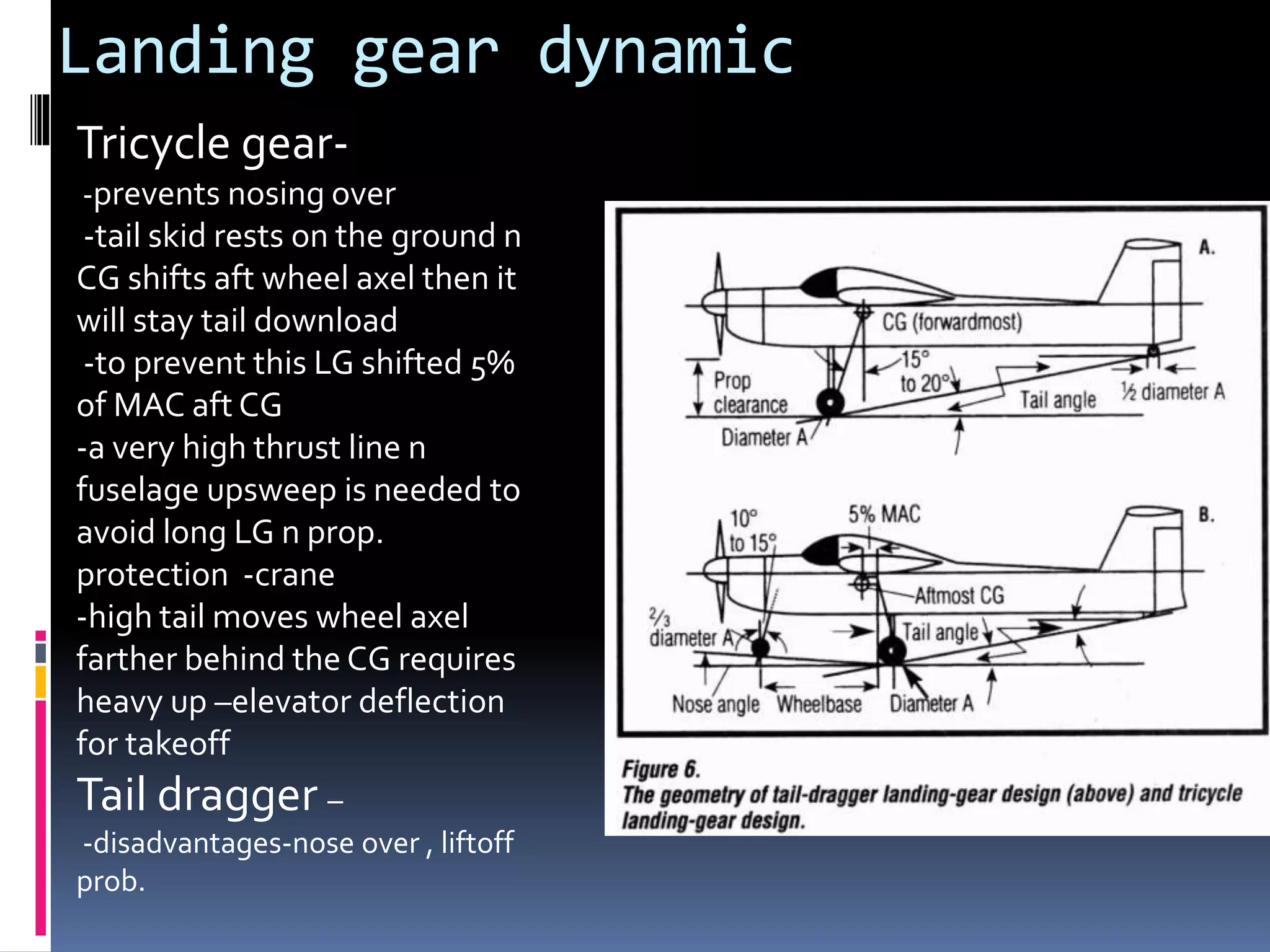
1. Landing gear must provide adequate ground clearance for the propeller tips and allow the plane to rotate on takeoff and landing to achieve the stalling angle of the airfoil.
2. Factors that affect landing and takeoff speeds and angles include the airfoil characteristics, planform, effect of flaps, and ground effect.
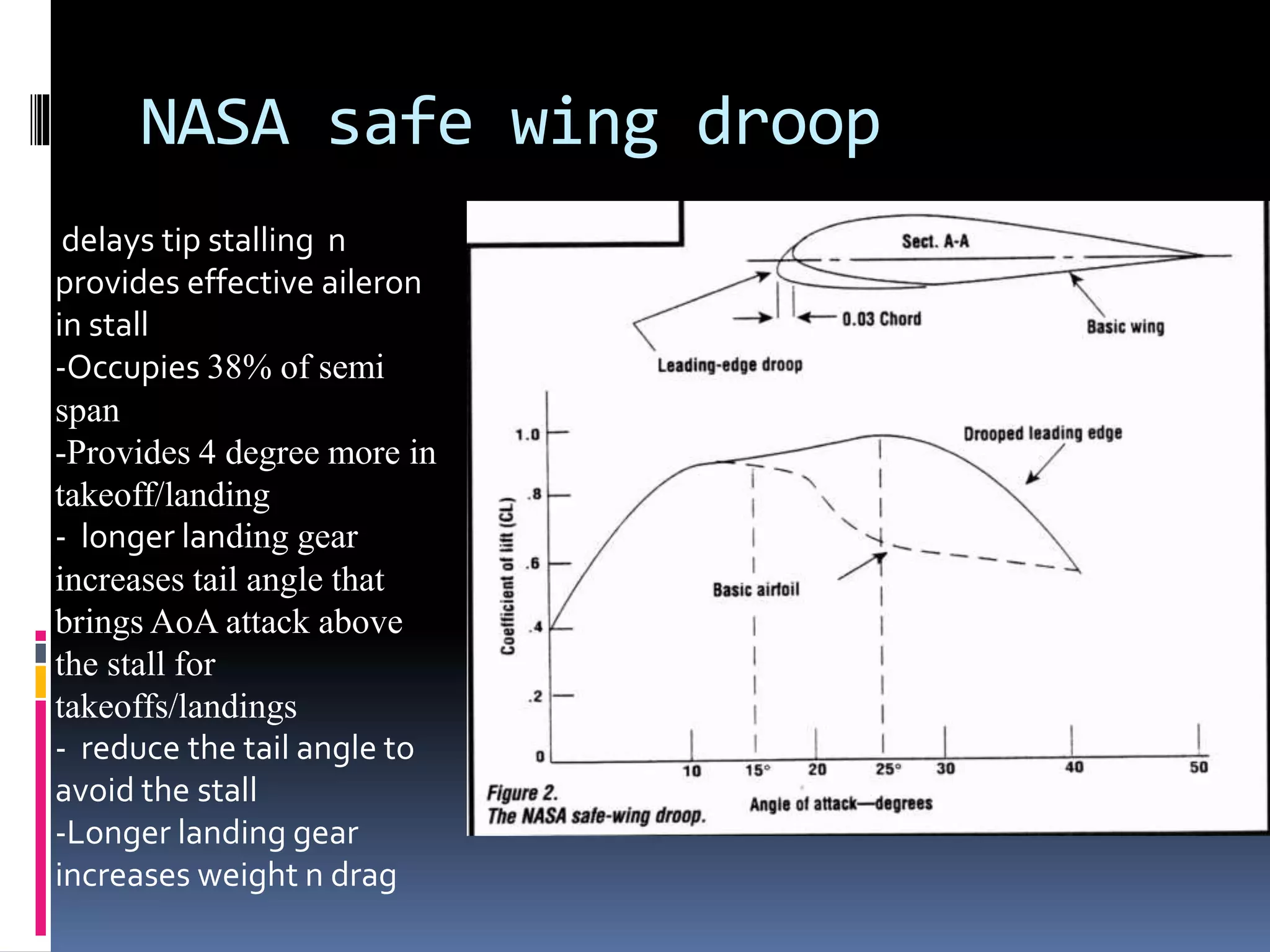
3. NASA's droop wing design increases takeoff and landing angles by delaying wing tip stalling and providing effective aileron control in a stall.