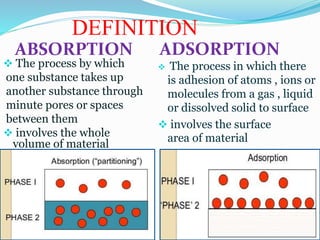
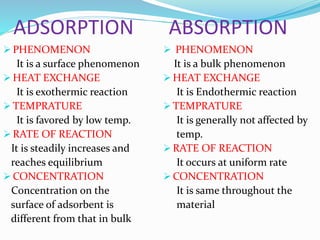
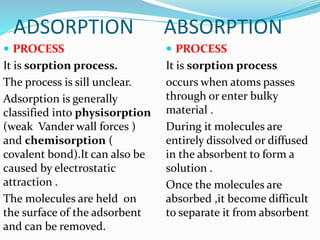
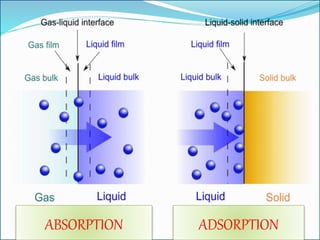
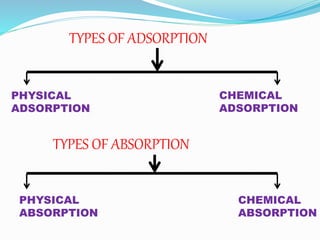
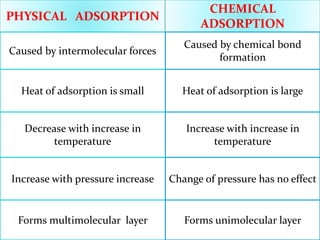
Adsorption involves the adhesion of atoms, ions, or molecules from a gas, liquid, or dissolved solid to a surface. It is a surface phenomenon that occurs more readily at low temperatures. Absorption involves one substance being taken up by another through its entire volume. It is a bulk phenomenon that generally occurs uniformly throughout the material regardless of temperature. Some common adsorbents include activated charcoal and alumina, while common absorbents include cotton and absorbent polymers. Adsorption and absorption both have various industrial and medical uses.