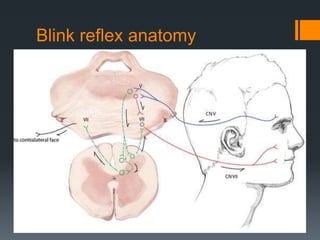
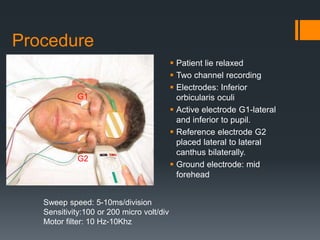
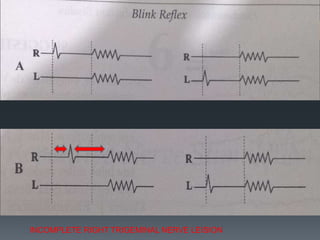
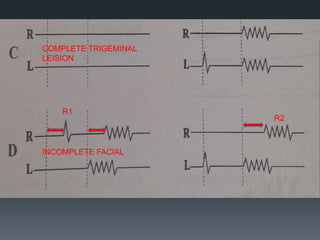
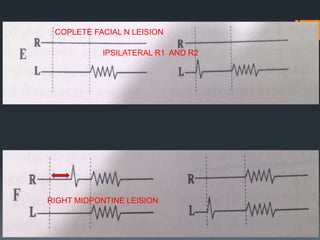
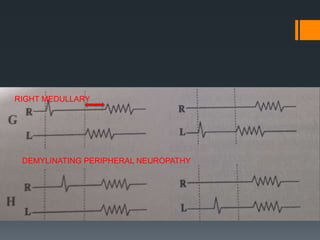
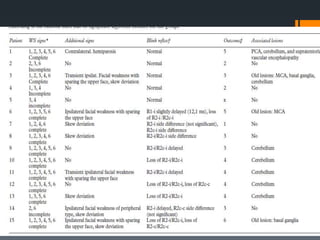
The blink reflex is a disynaptic or multisynaptic reflex that involves the trigeminal and facial nerves. It has two responses - an early ipsilateral R1 response and a late bilateral R2 response. The blink reflex test stimulates the supraorbital nerve branch to evaluate conduction along the trigeminal and facial nerve pathways. Abnormalities in the R1 and R2 responses can localize lesions in different parts of the brainstem or peripheral nerves. The test involves recording electromyography of the orbicularis oculi muscle in response to supraorbital nerve stimulation.