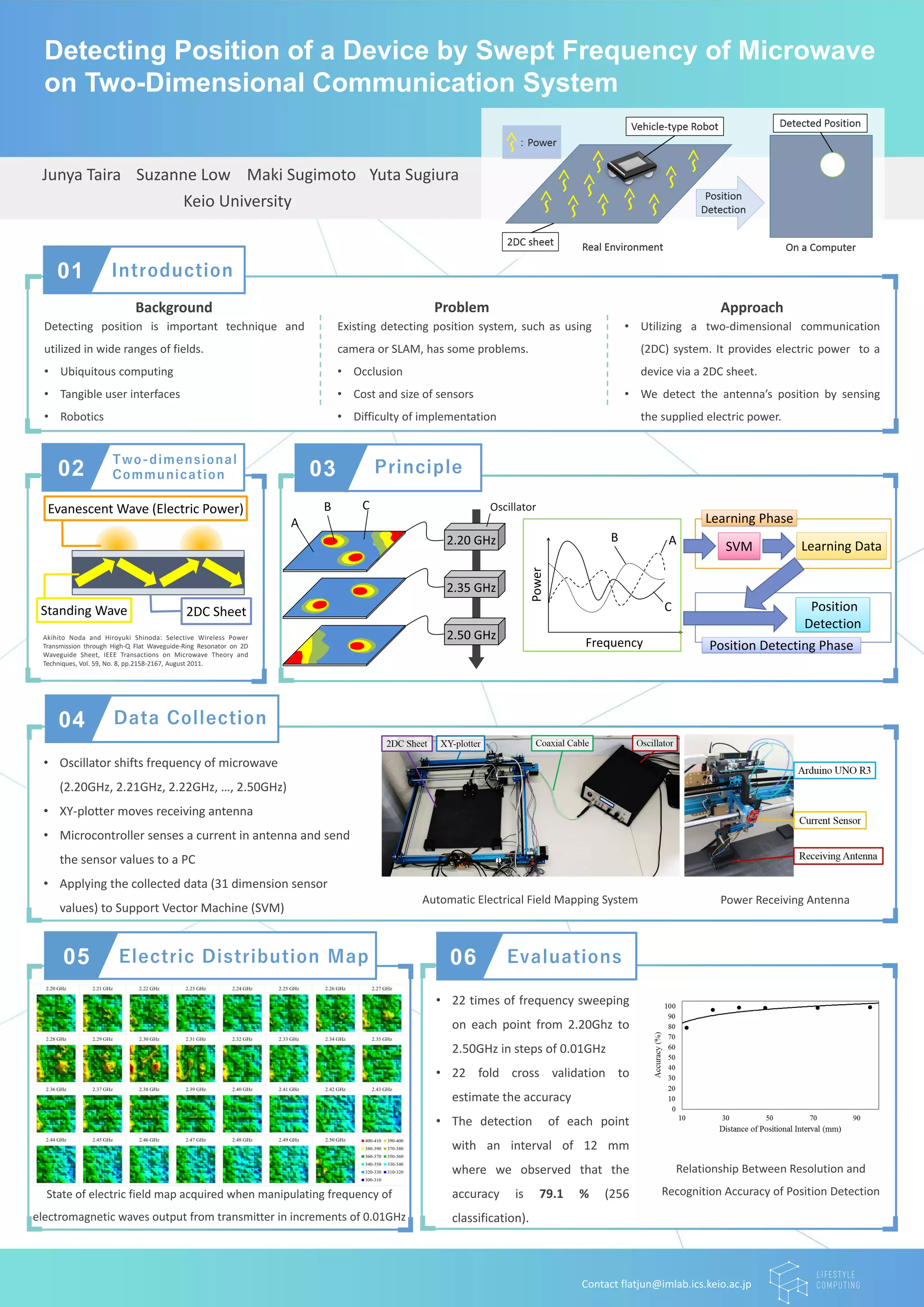
This document proposes detecting the position of a device using the swept frequency of microwaves on a two-dimensional communication system. It collects data on the current sensed by a receiving antenna as an oscillator shifts microwave frequencies and an XY-plotter moves the antenna. This data is applied to a support vector machine to generate an electric field distribution map and detect the antenna's position with 79.1% accuracy when the detection points have an interval of 12mm.