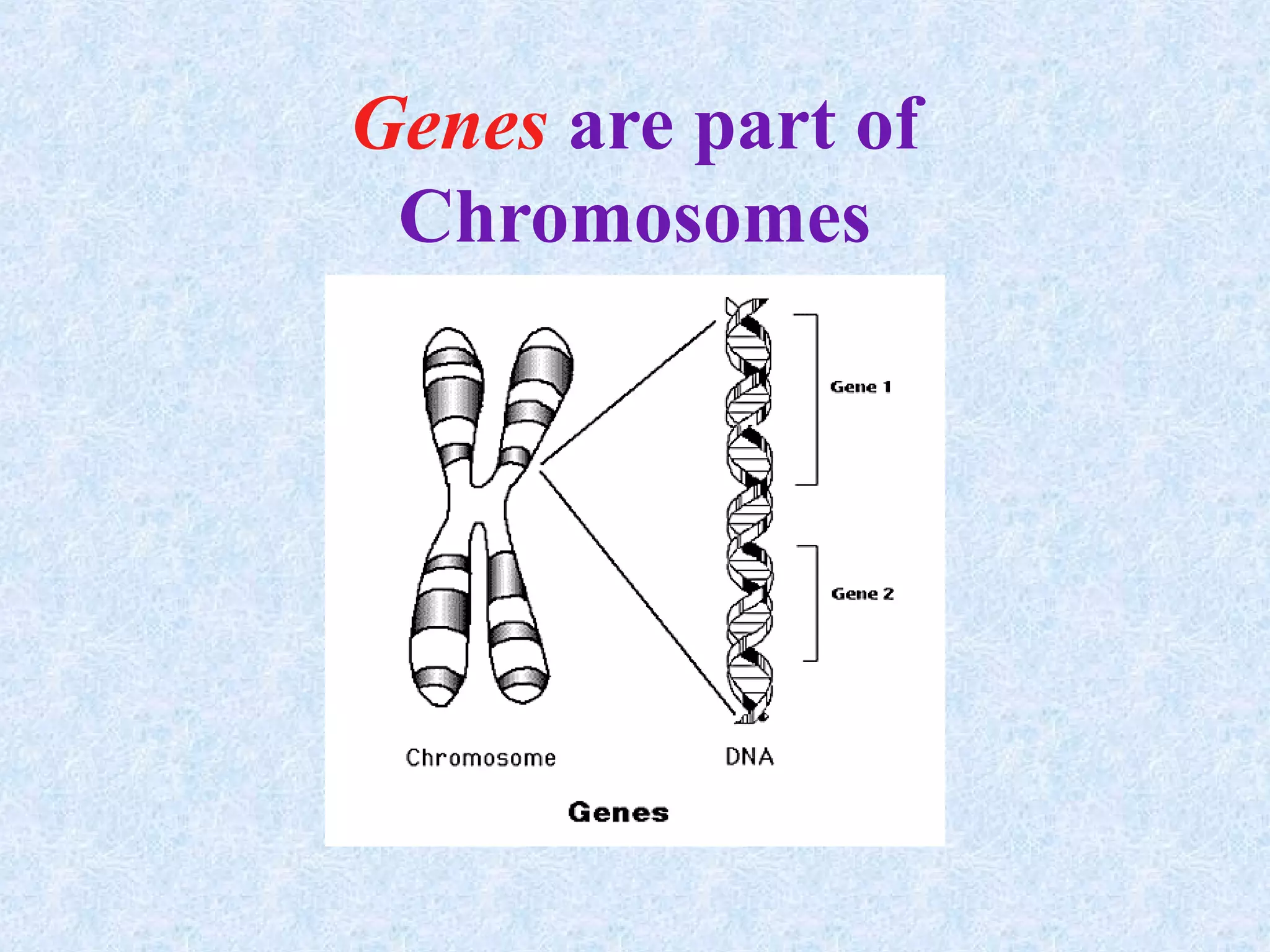
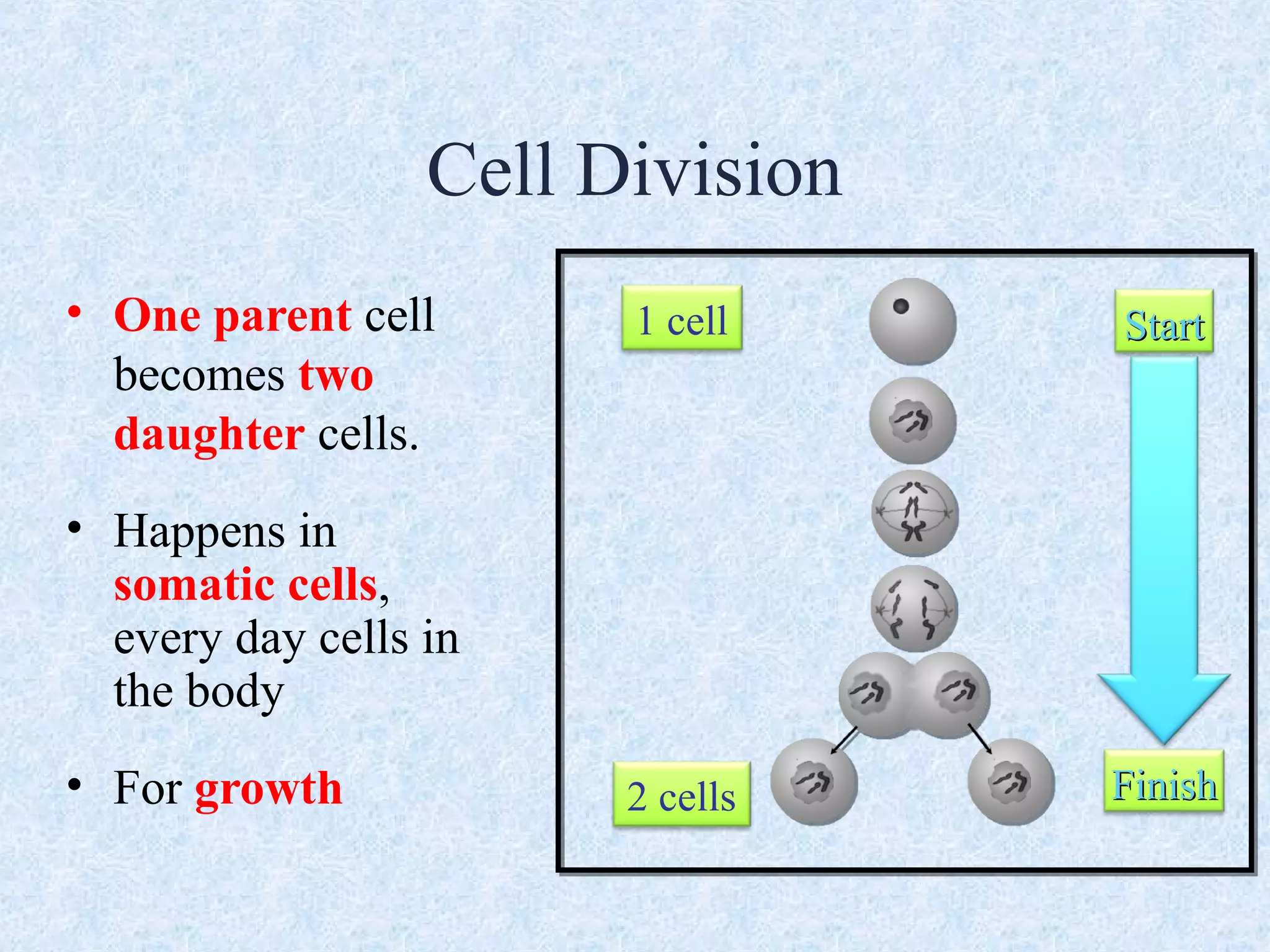
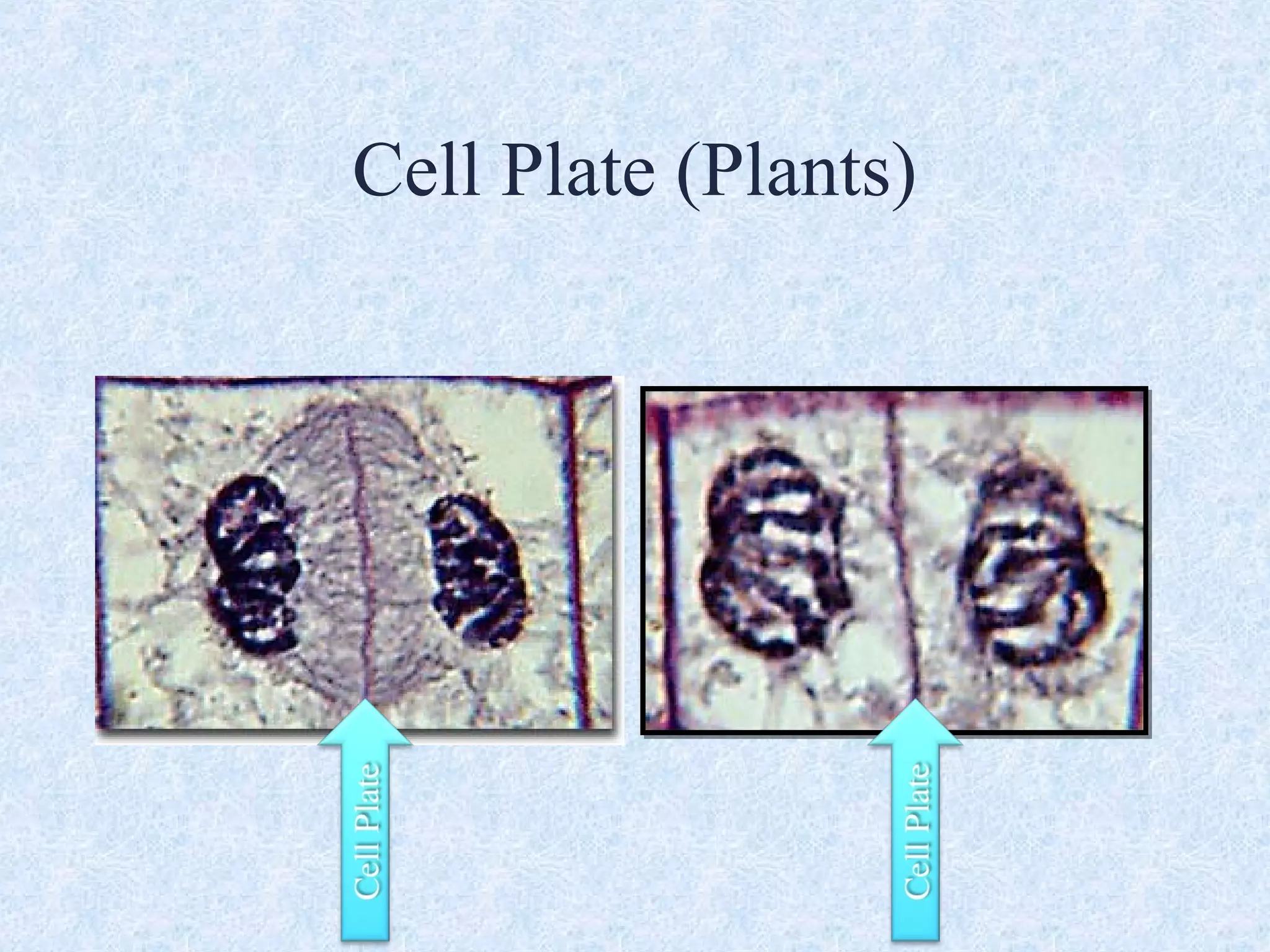
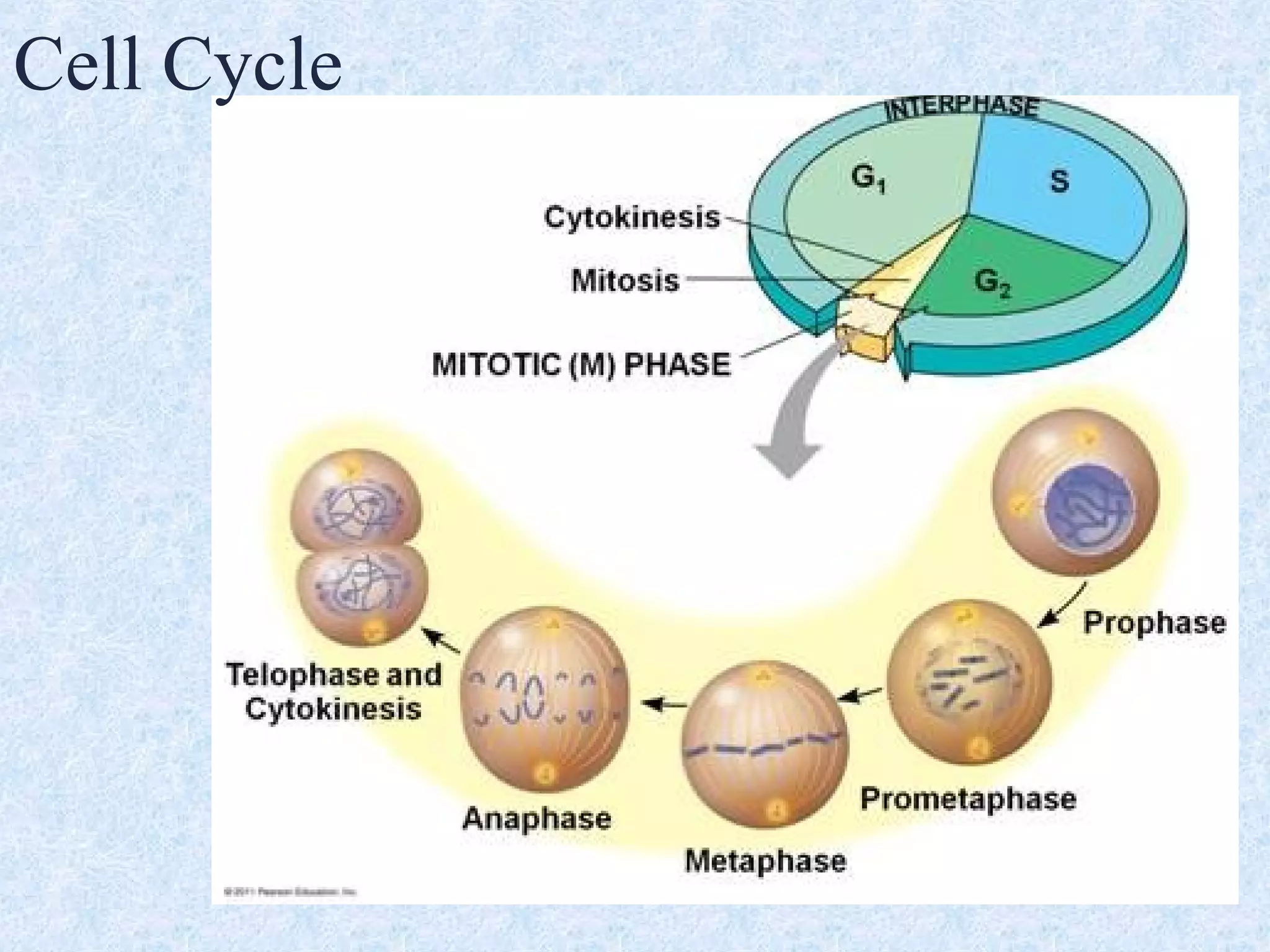
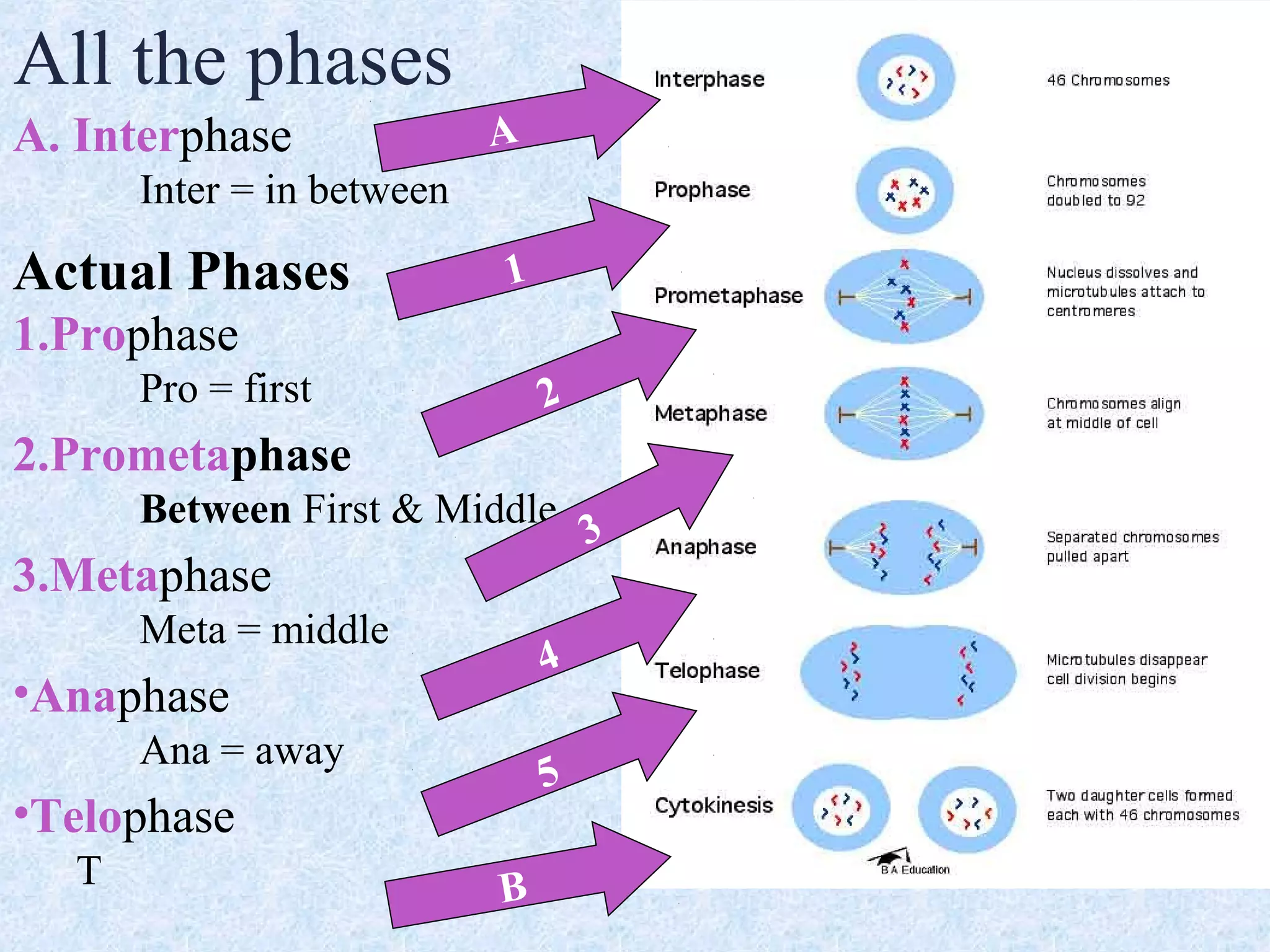
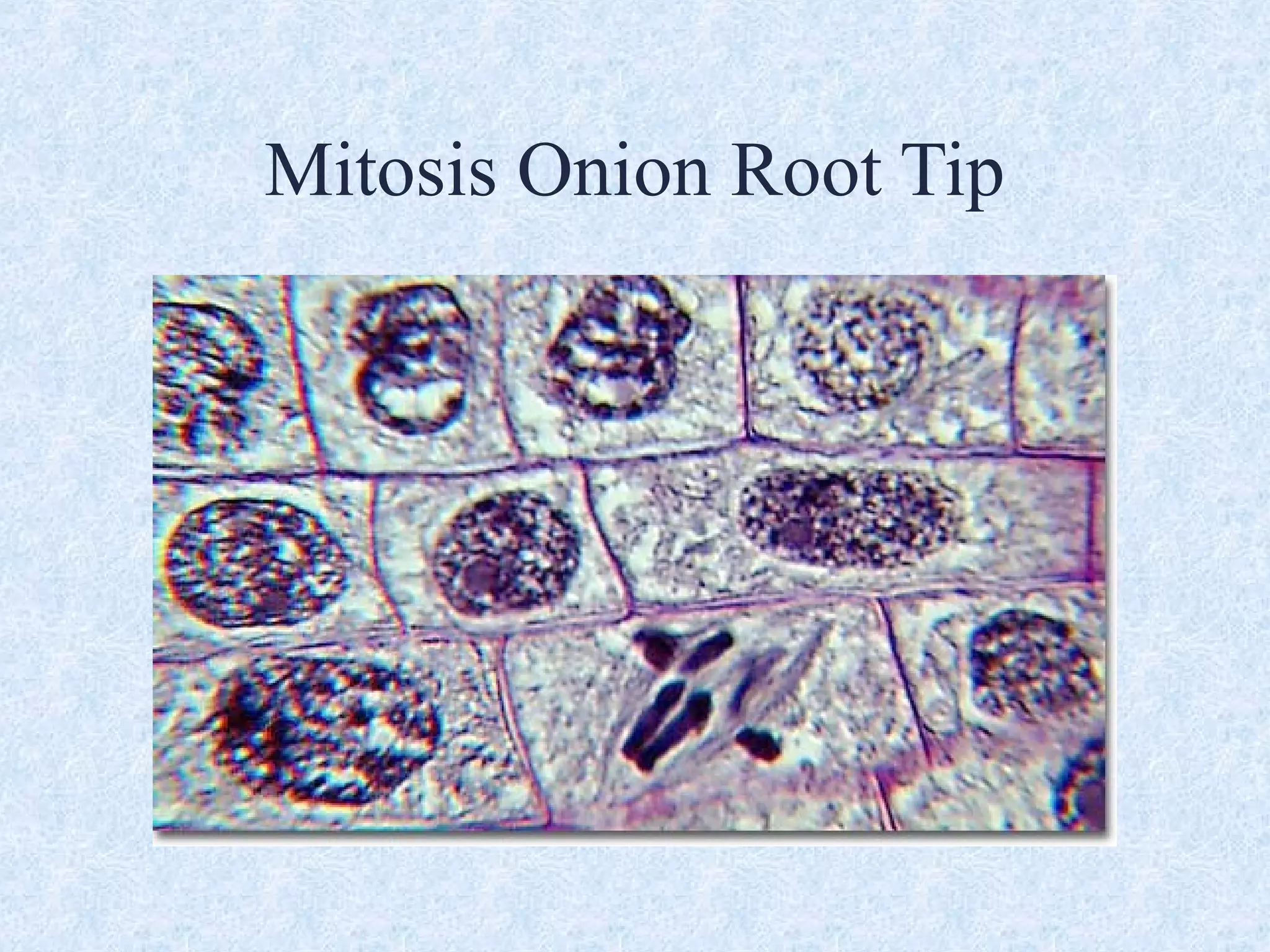
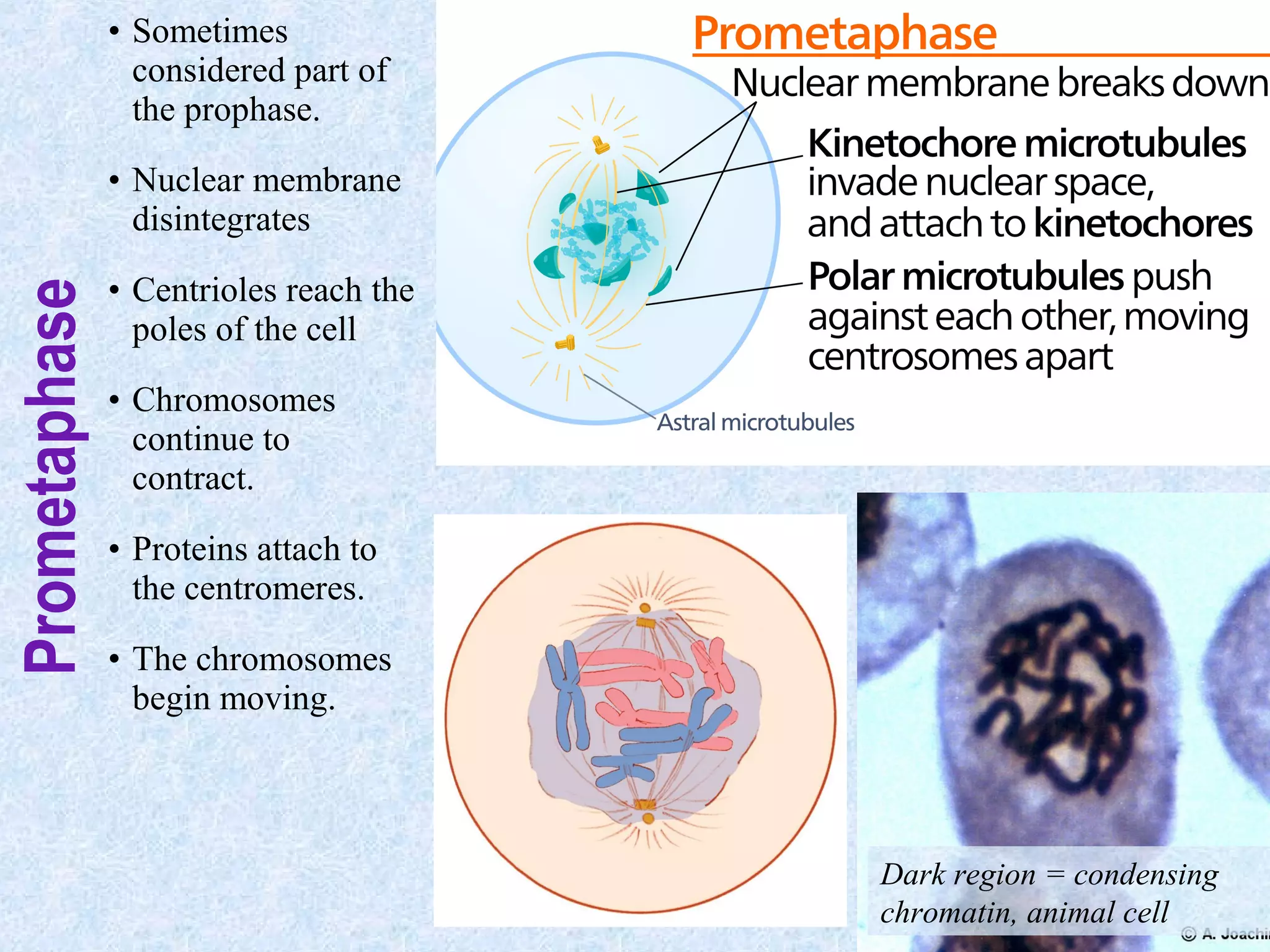
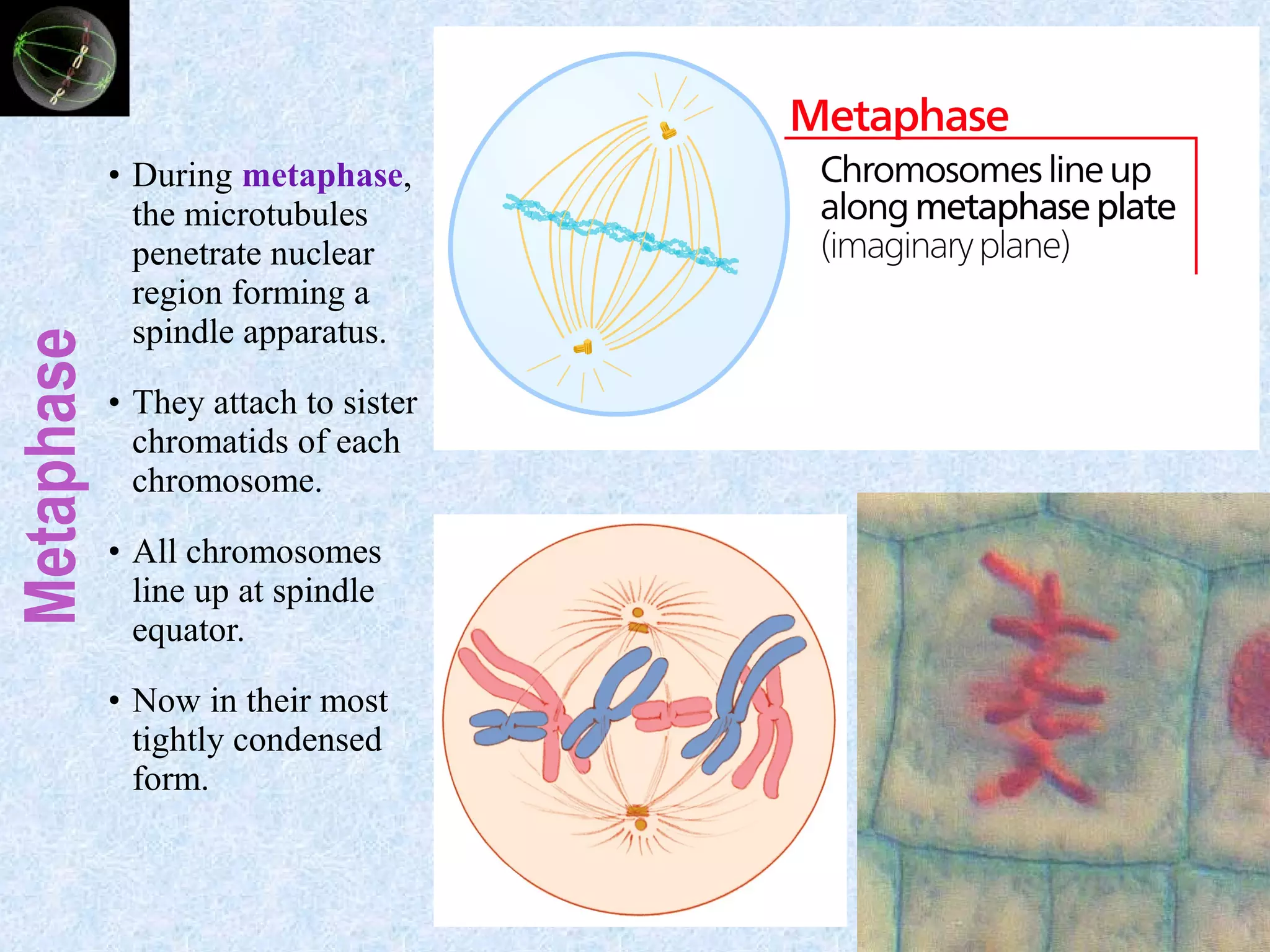
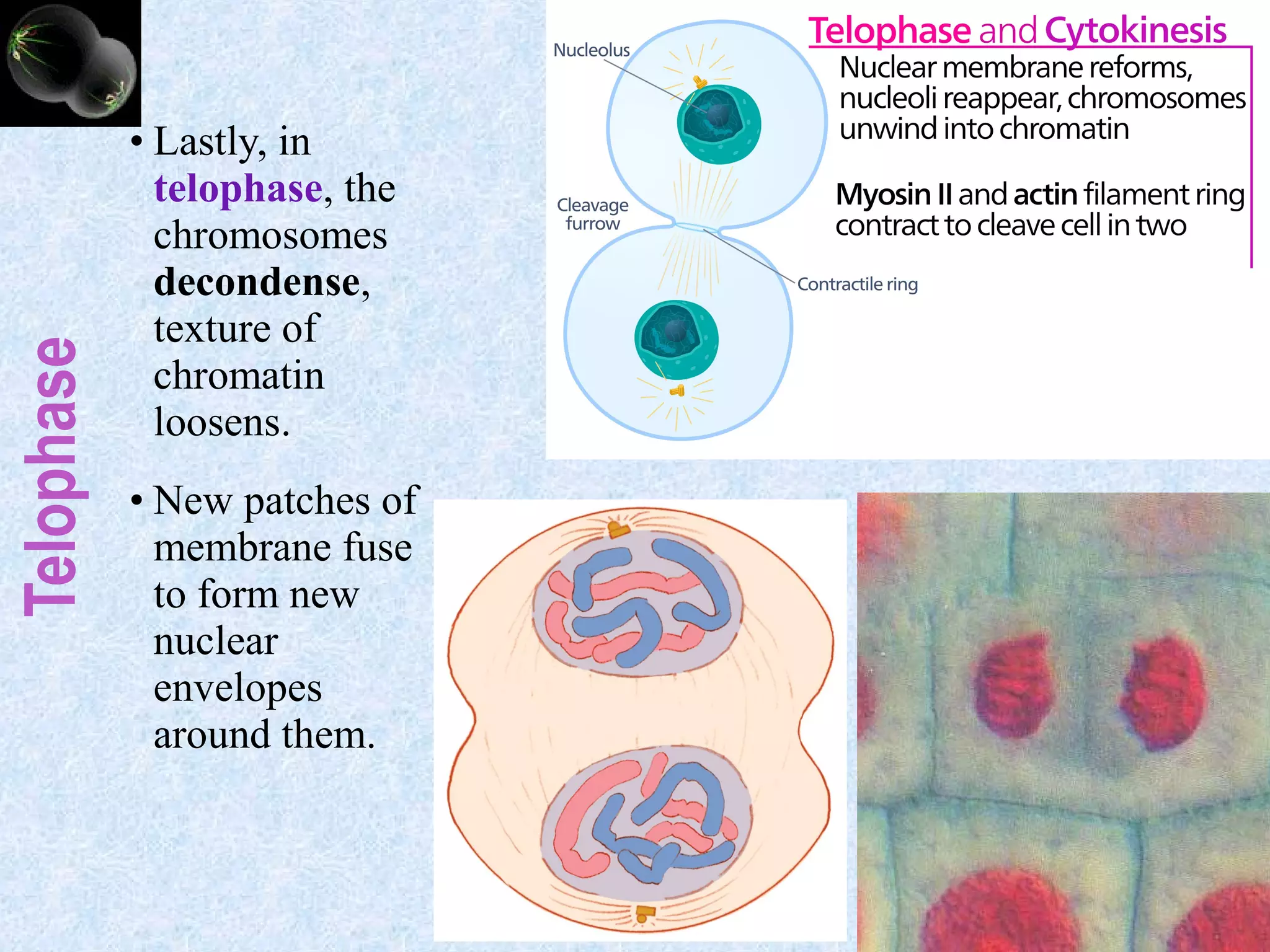
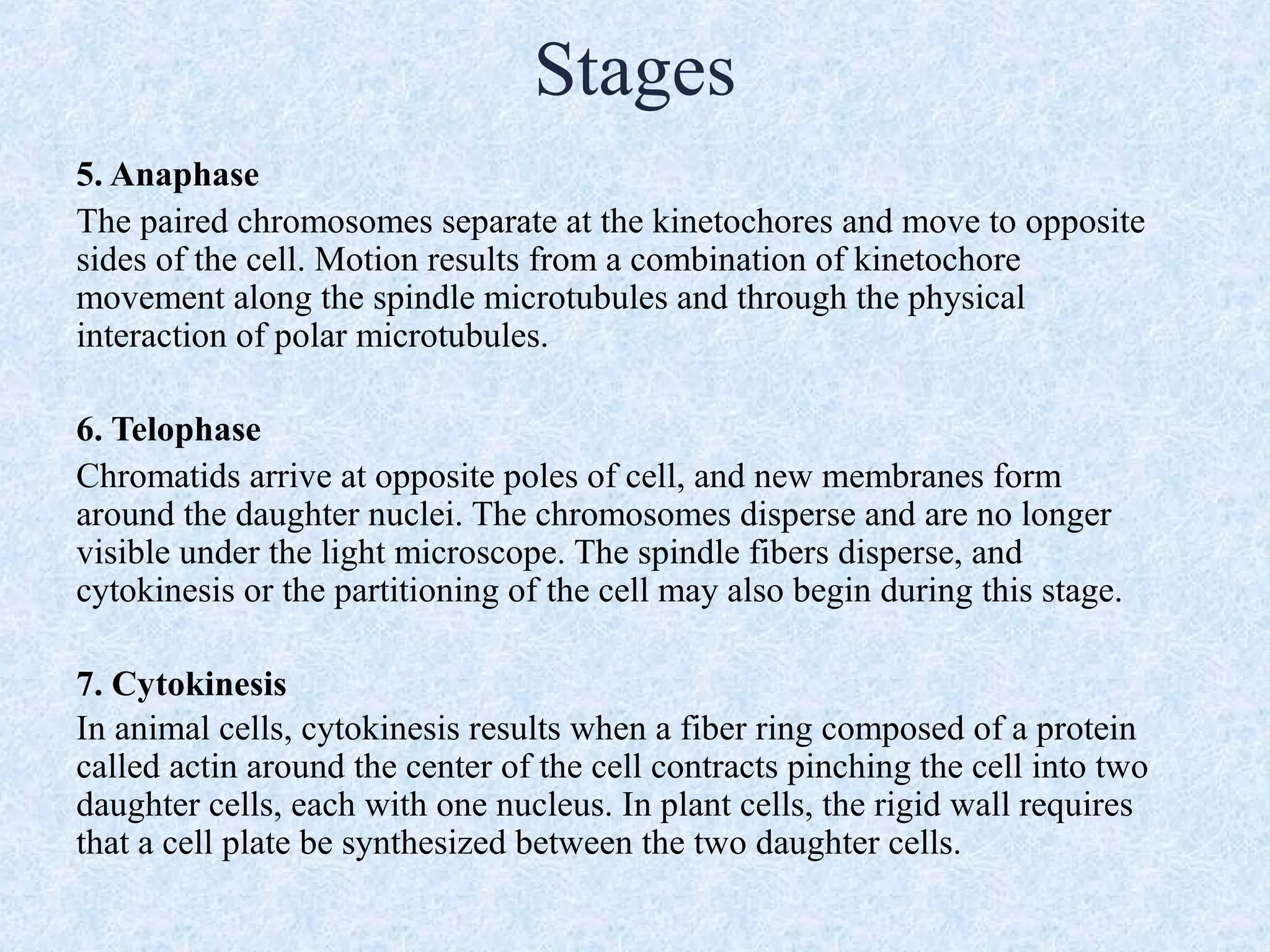
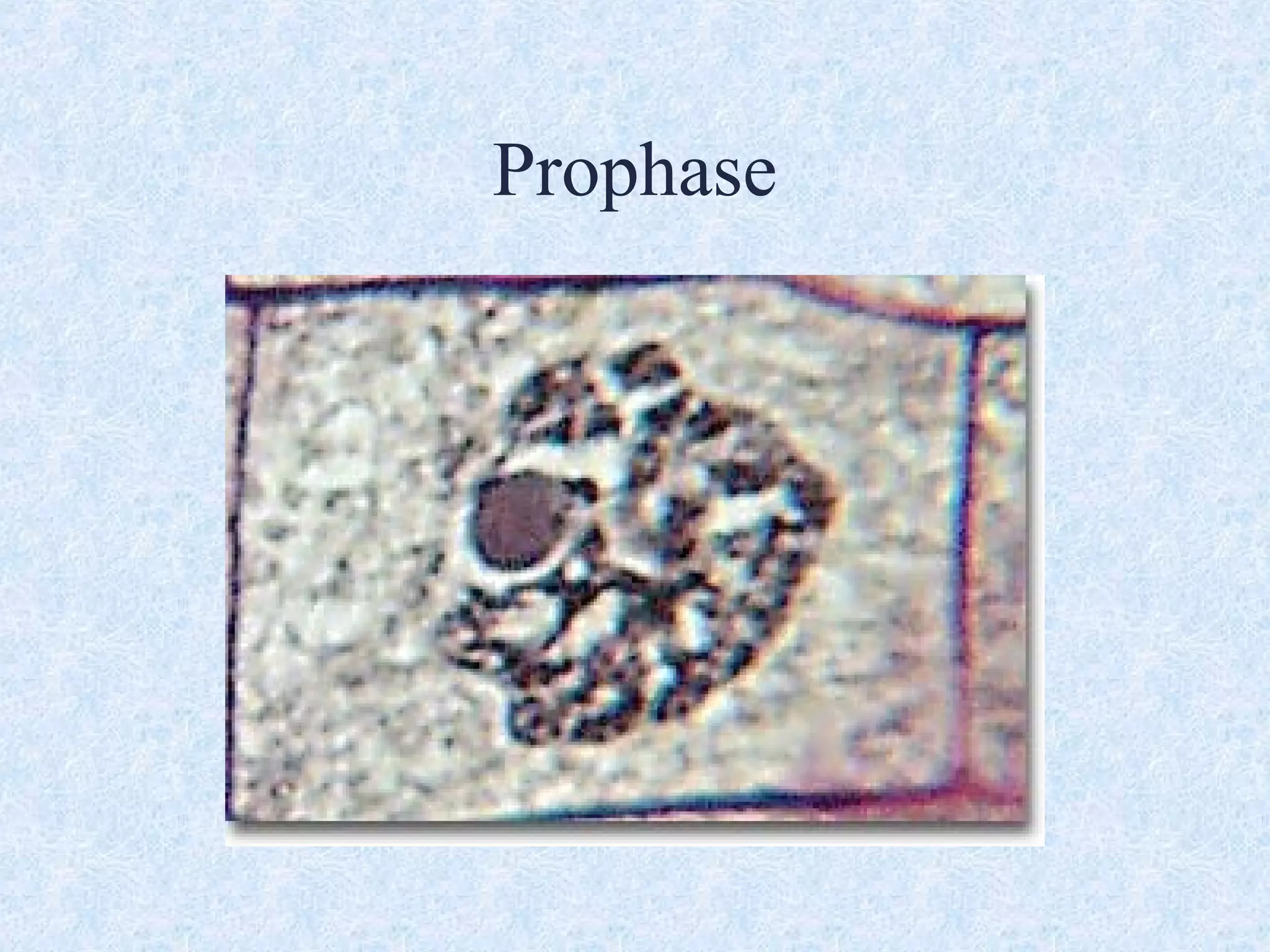
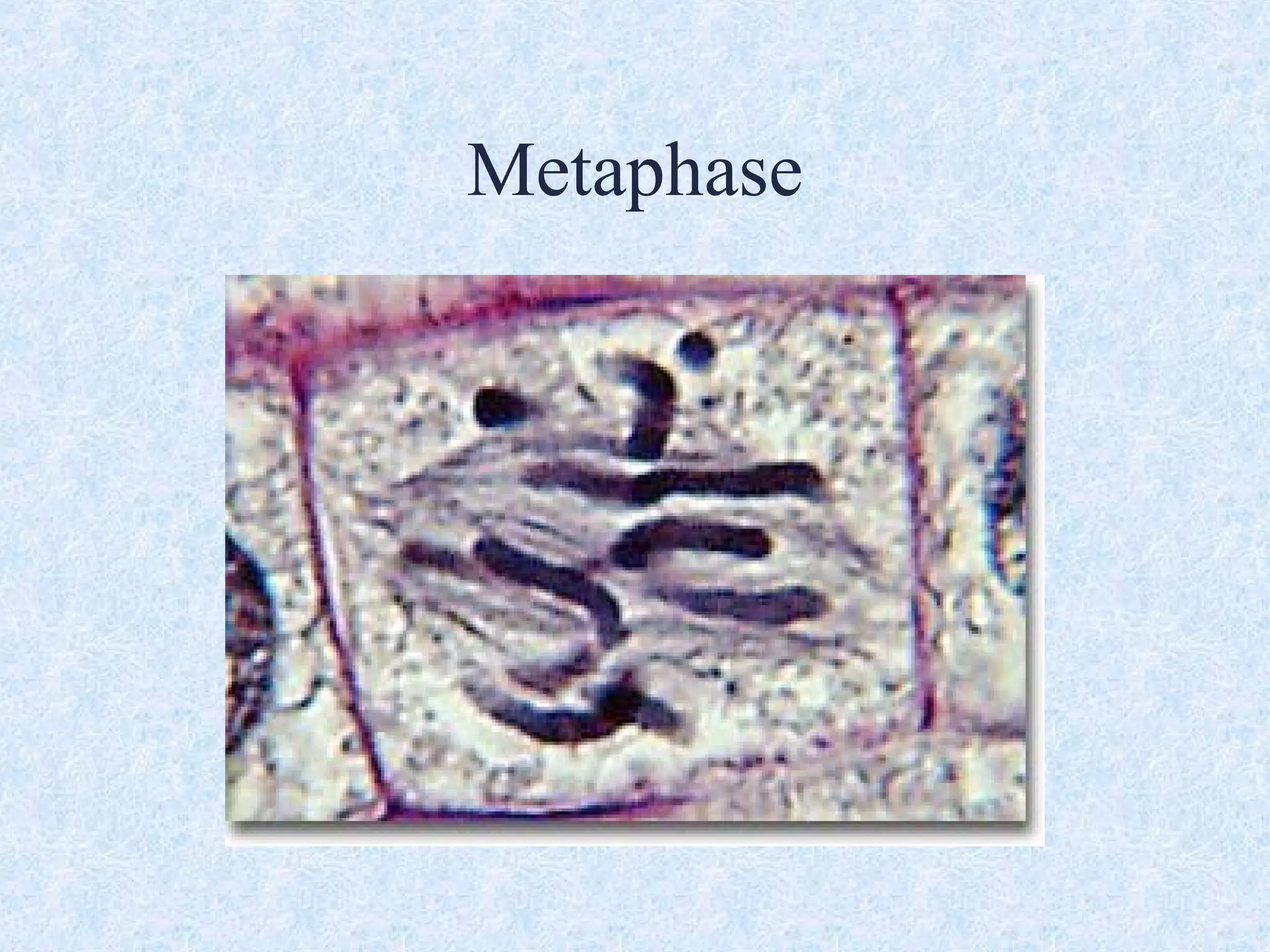
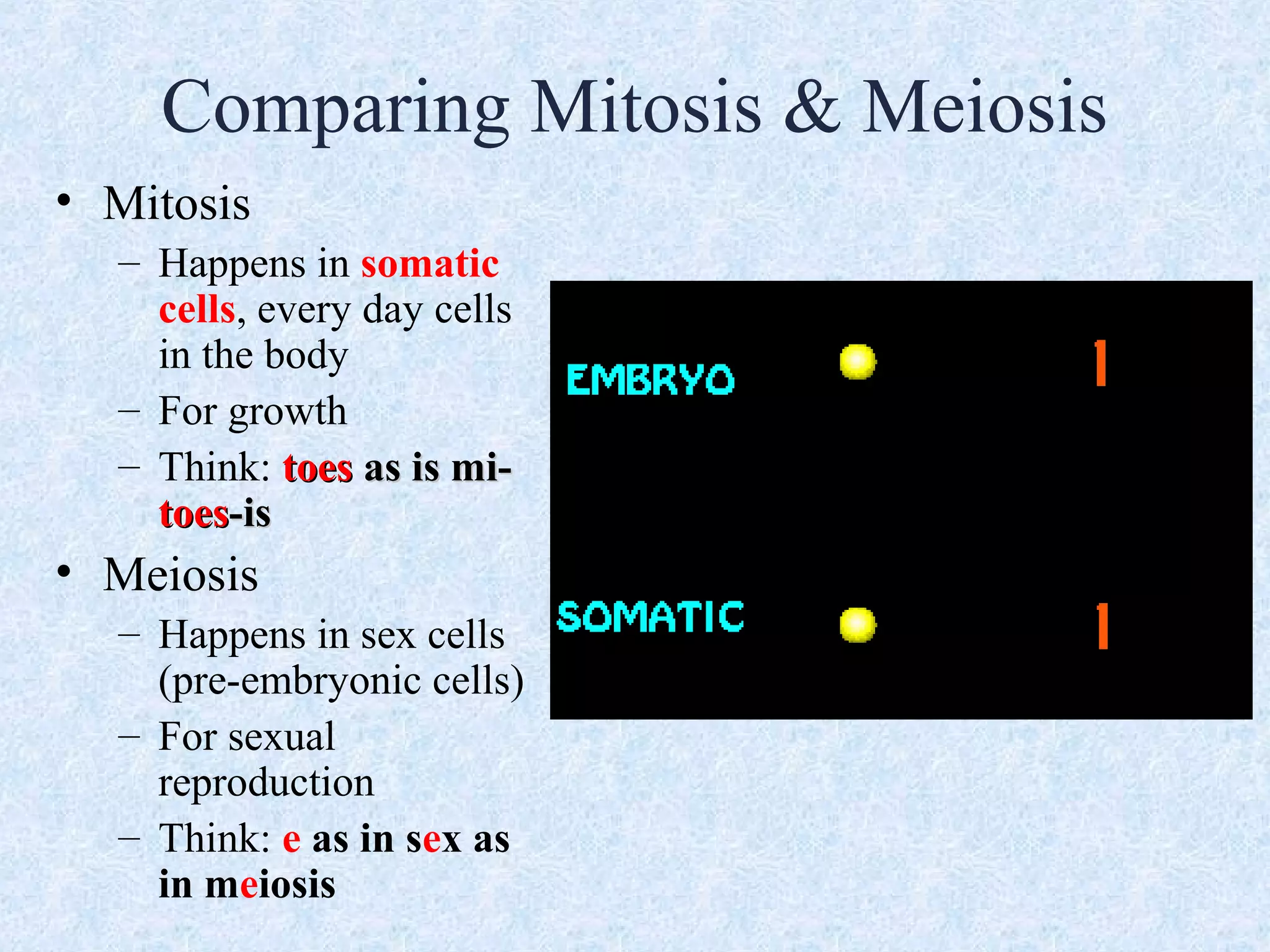
Cell division occurs through the process of mitosis in somatic cells. Mitosis involves five phases - interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is duplicated in preparation for division. In prophase, chromosomes condense and the mitotic spindle begins to form. Metaphase sees chromosomes aligned at the center. Anaphase involves the separation of sister chromatids to opposite sides. Finally, in telophase, division is complete and two identical daughter cells have formed, each with the full complement of chromosomes. Mitosis results in the reproduction of body cells for growth and tissue repair.