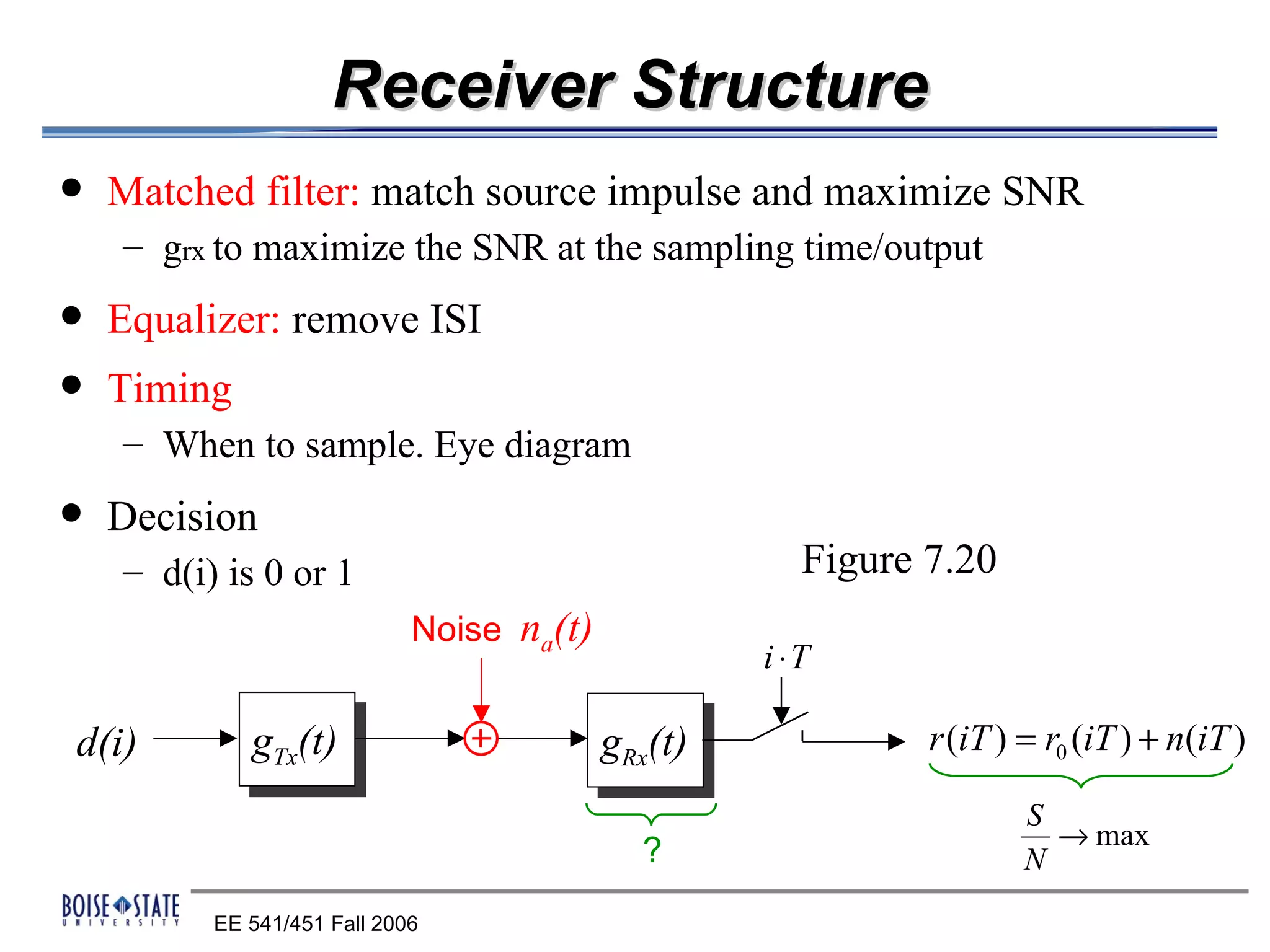
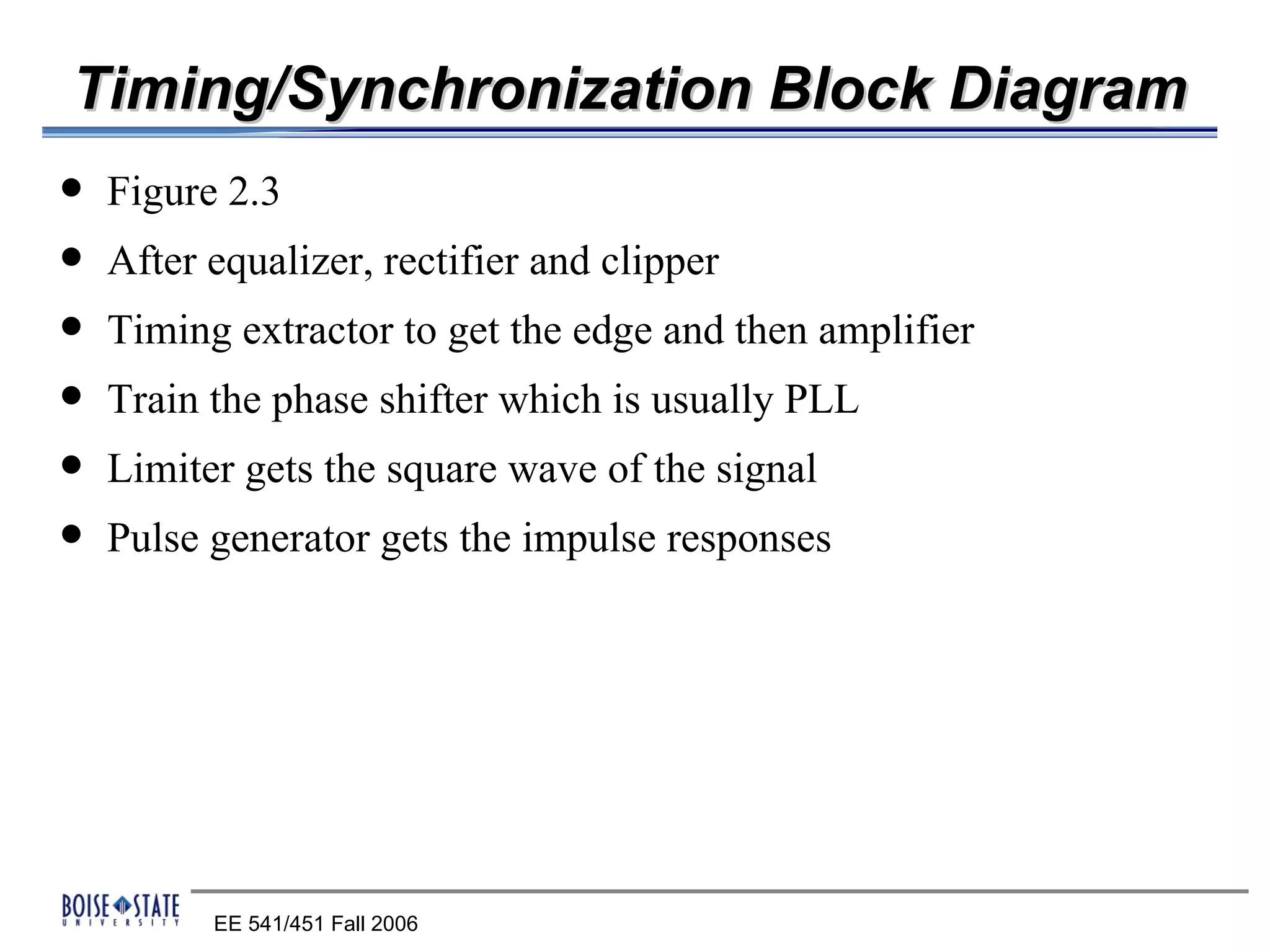
The receiver structure consists of four main components:
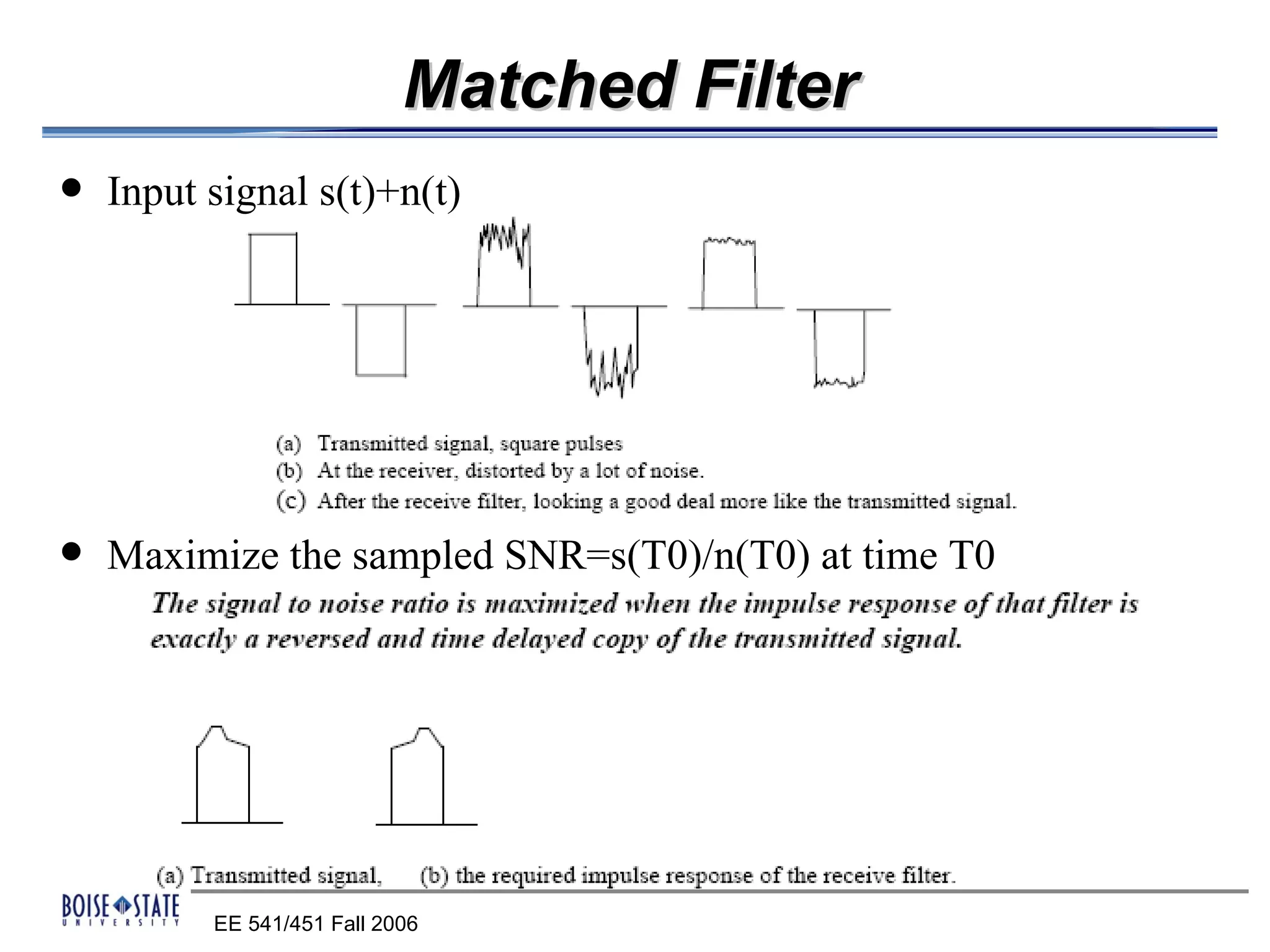
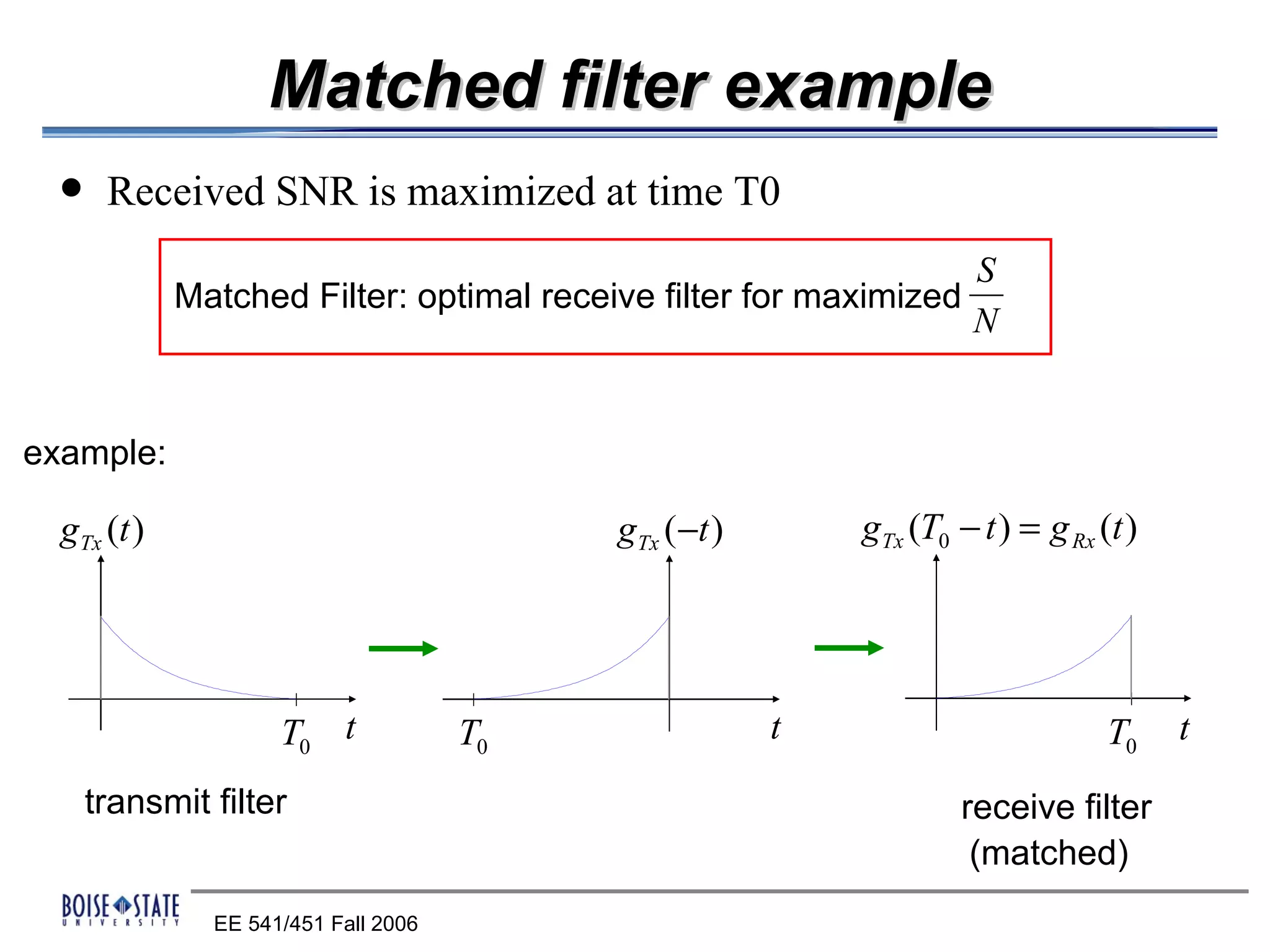
1. A matched filter that maximizes the SNR by matching the source impulse and channel.
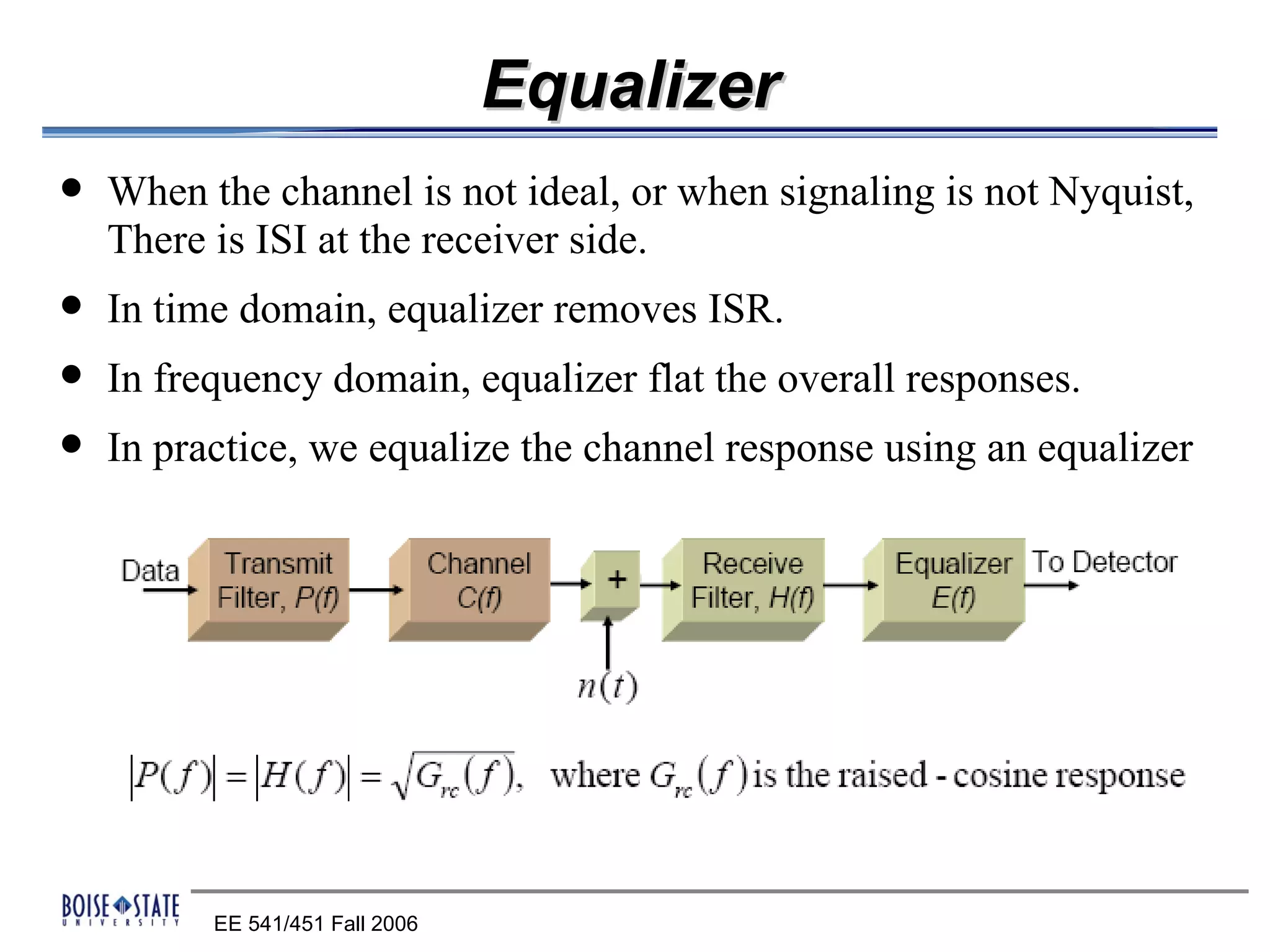
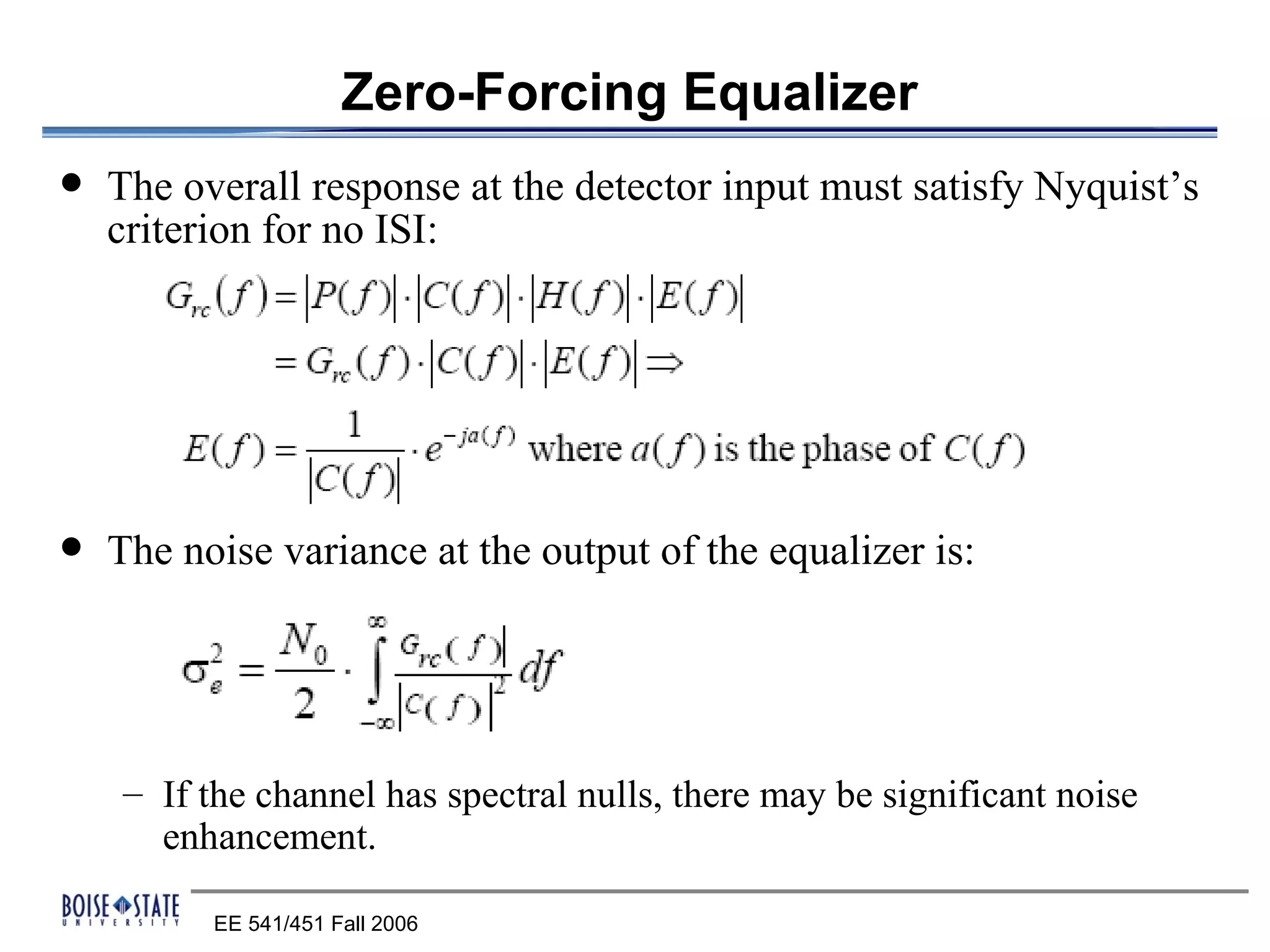
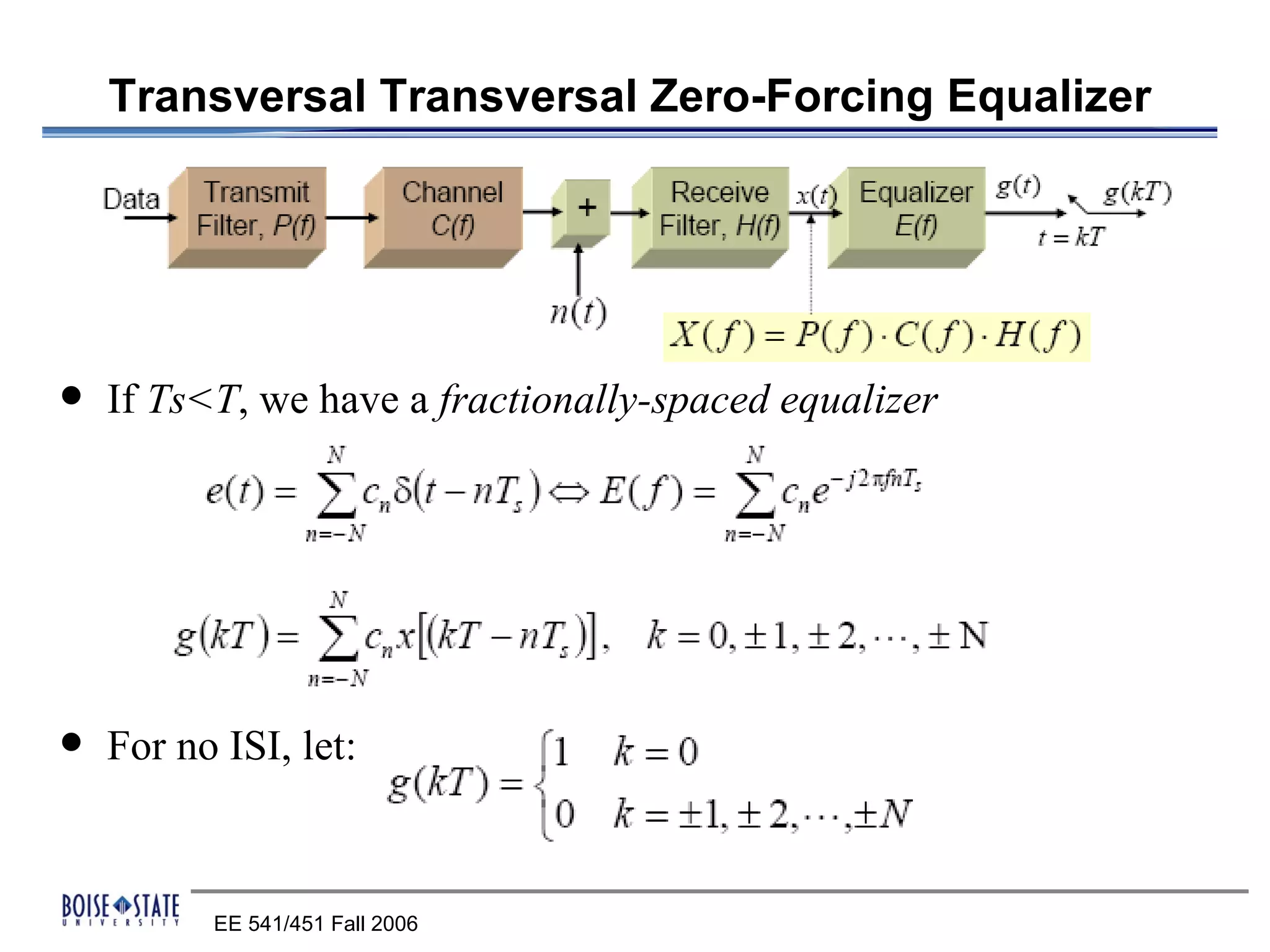
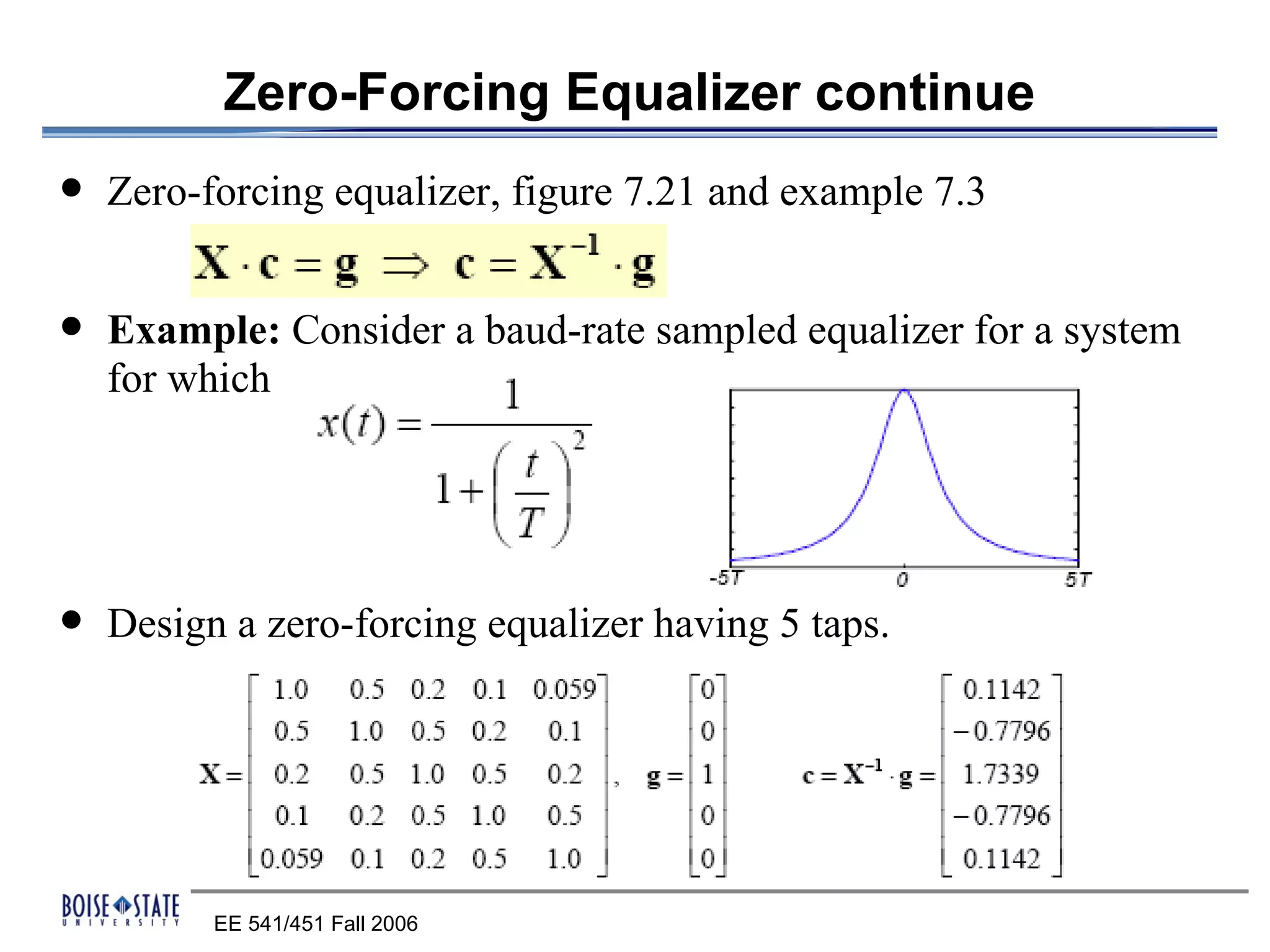
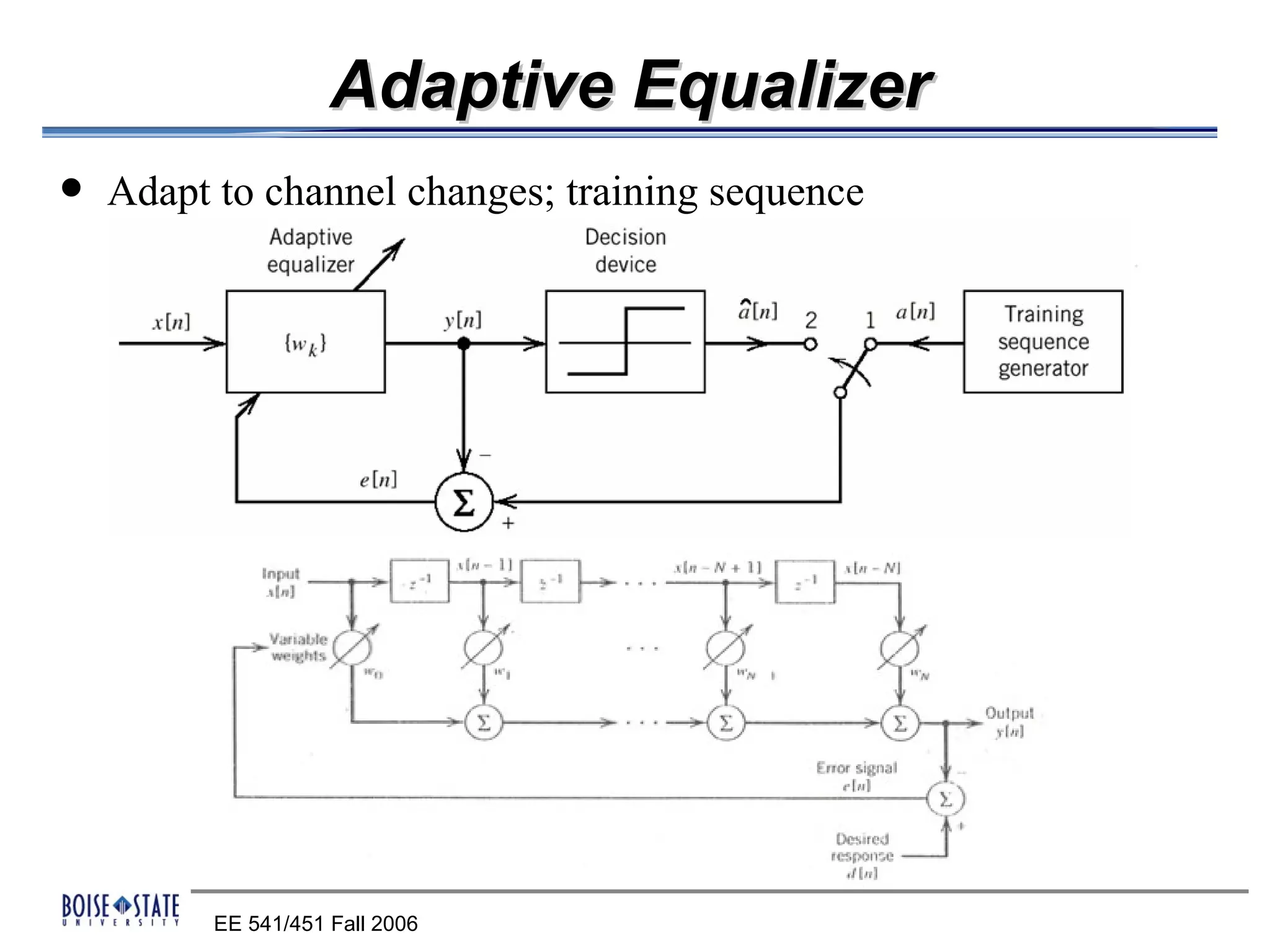
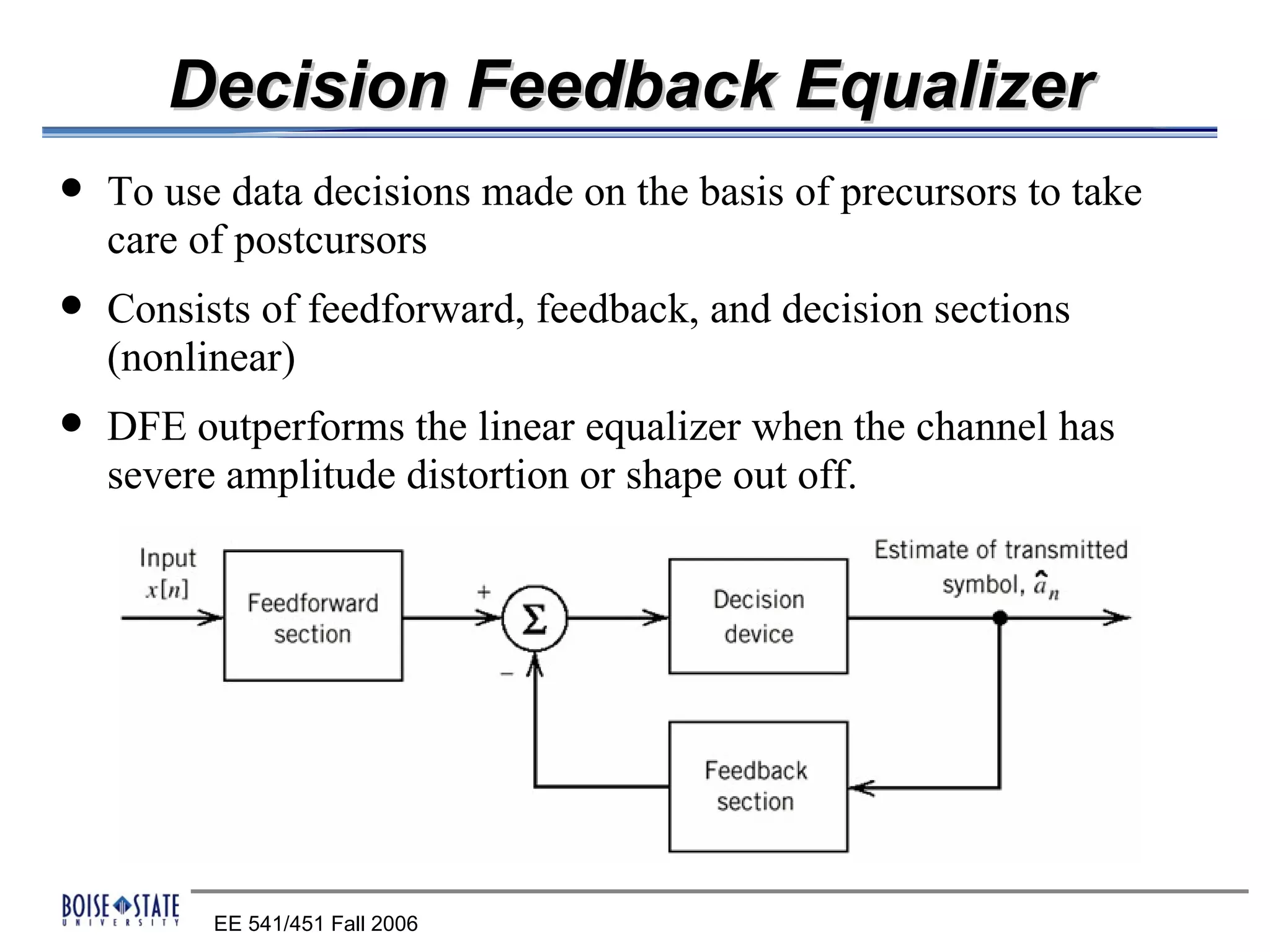
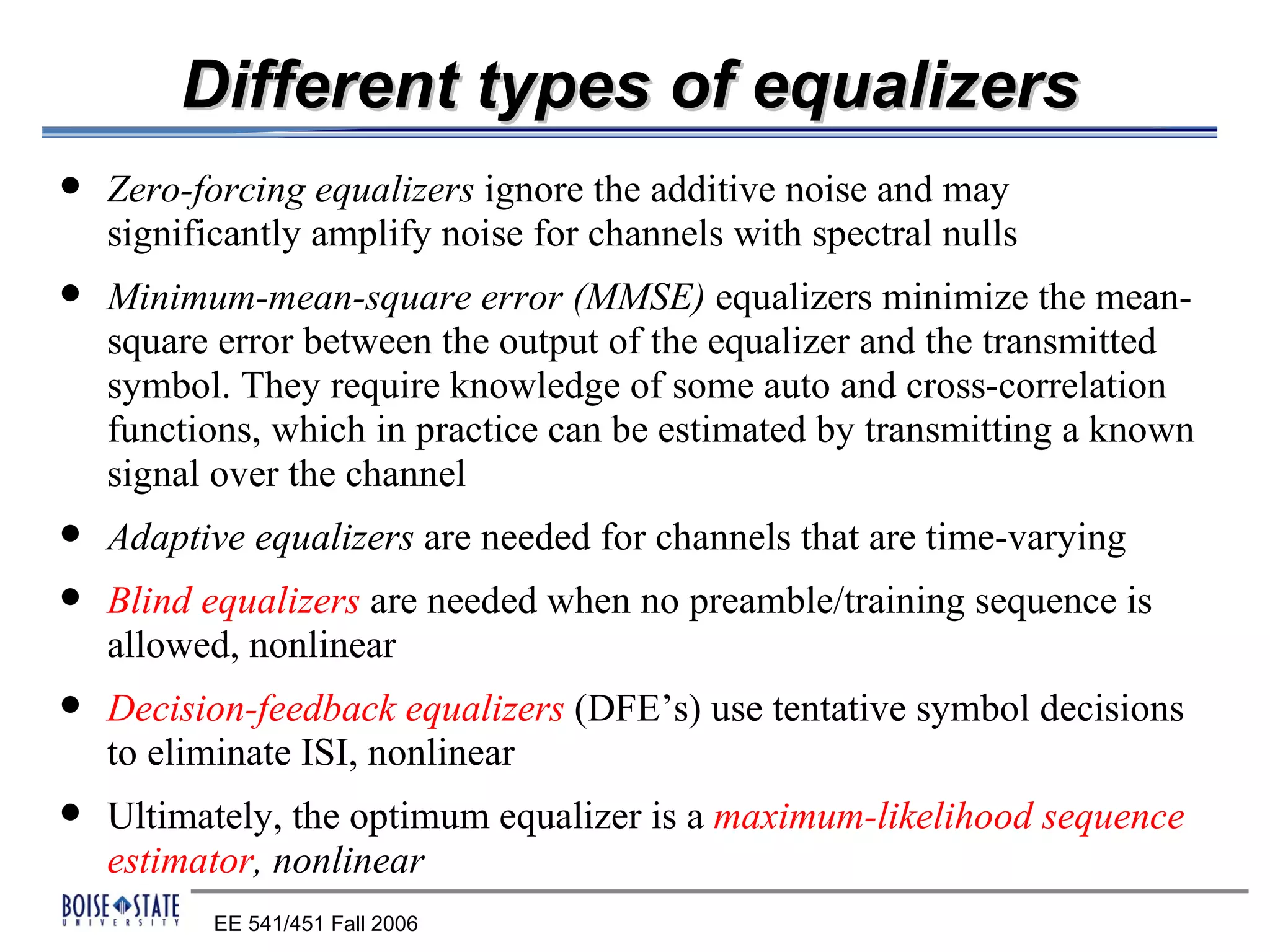
2. An equalizer that removes intersymbol interference.
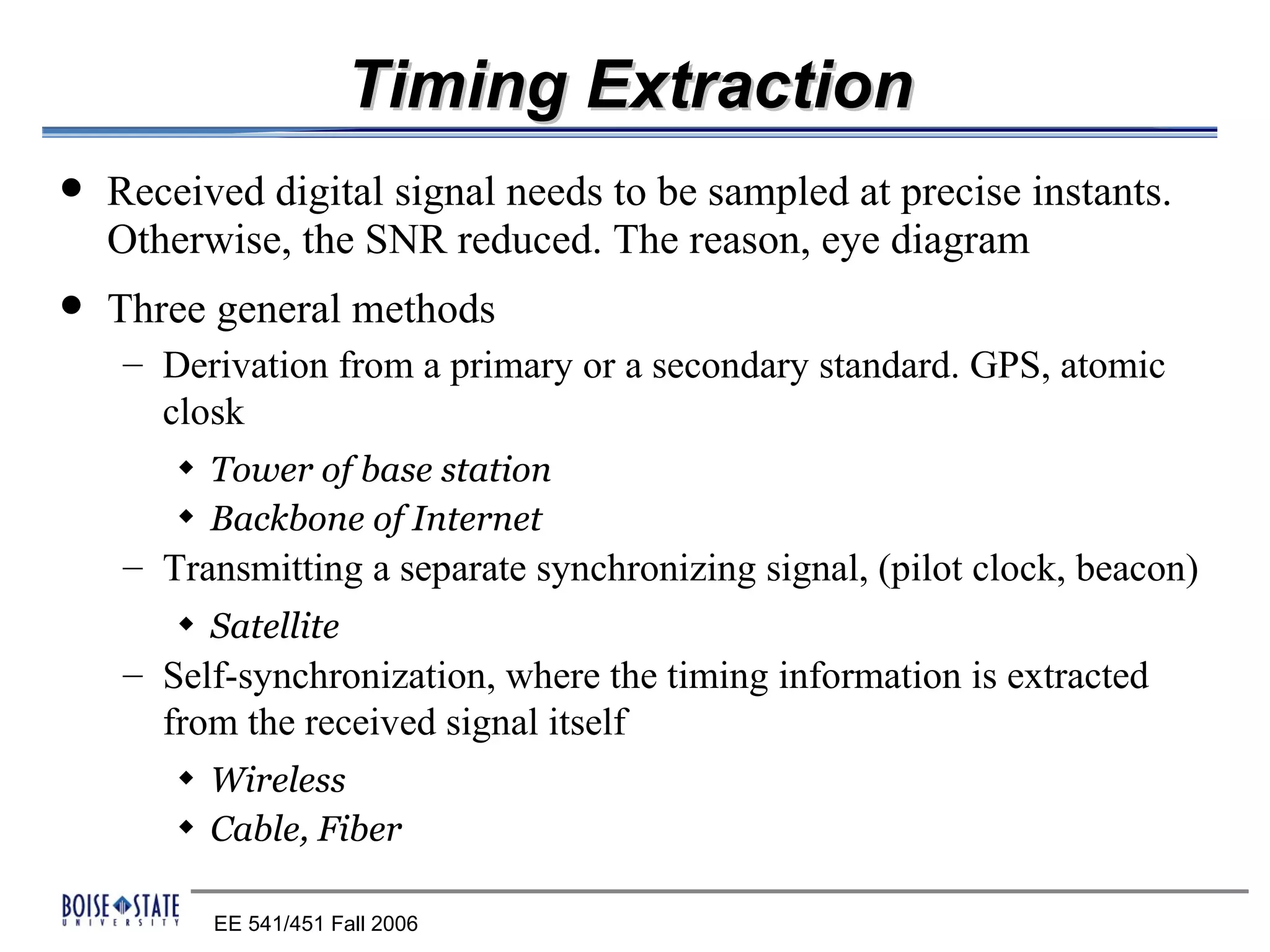
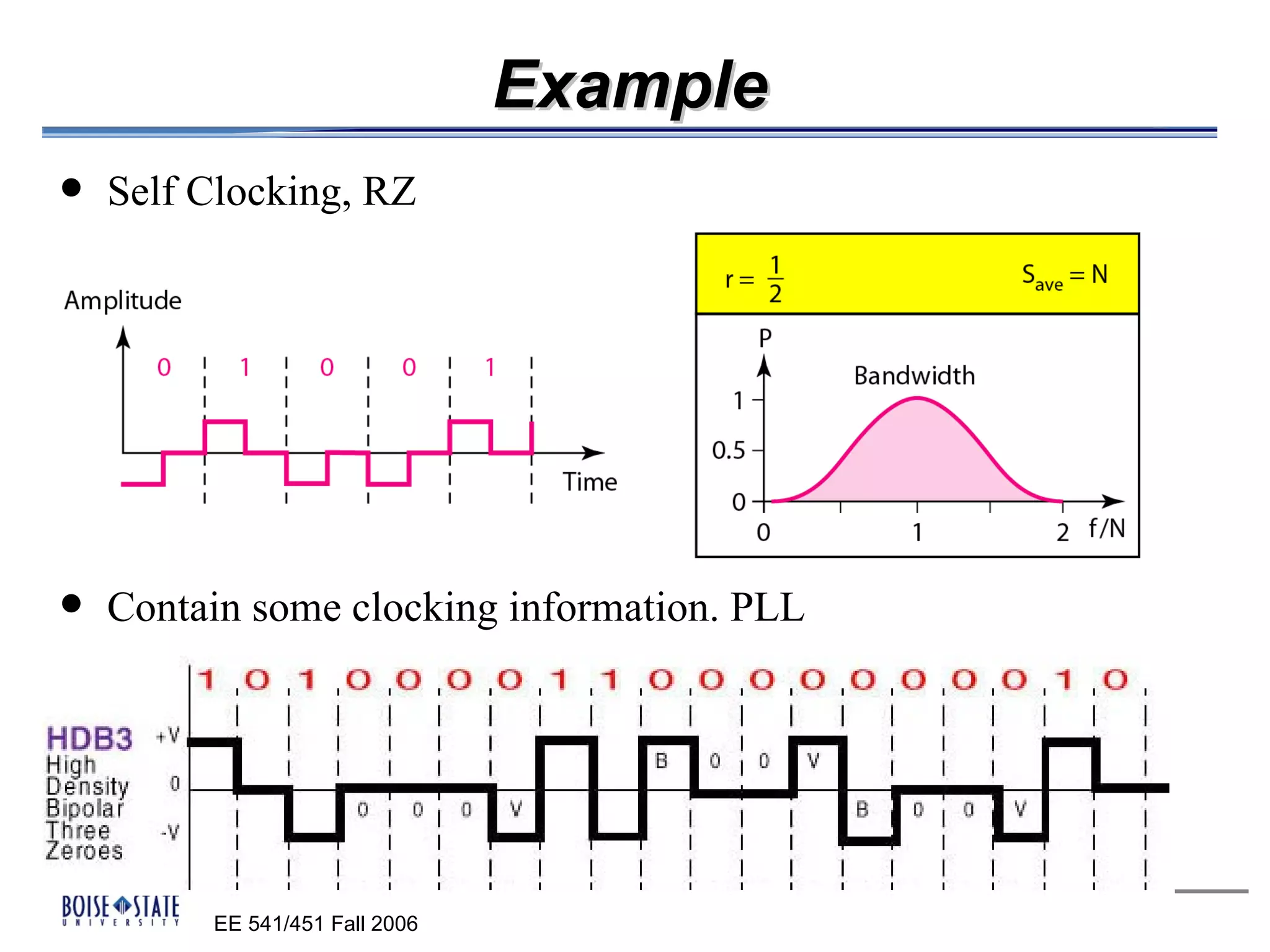
3. A timing component that determines the optimal sampling time using an eye diagram.
4. A decision component that determines whether the received bit is a 0 or 1 based on a threshold.
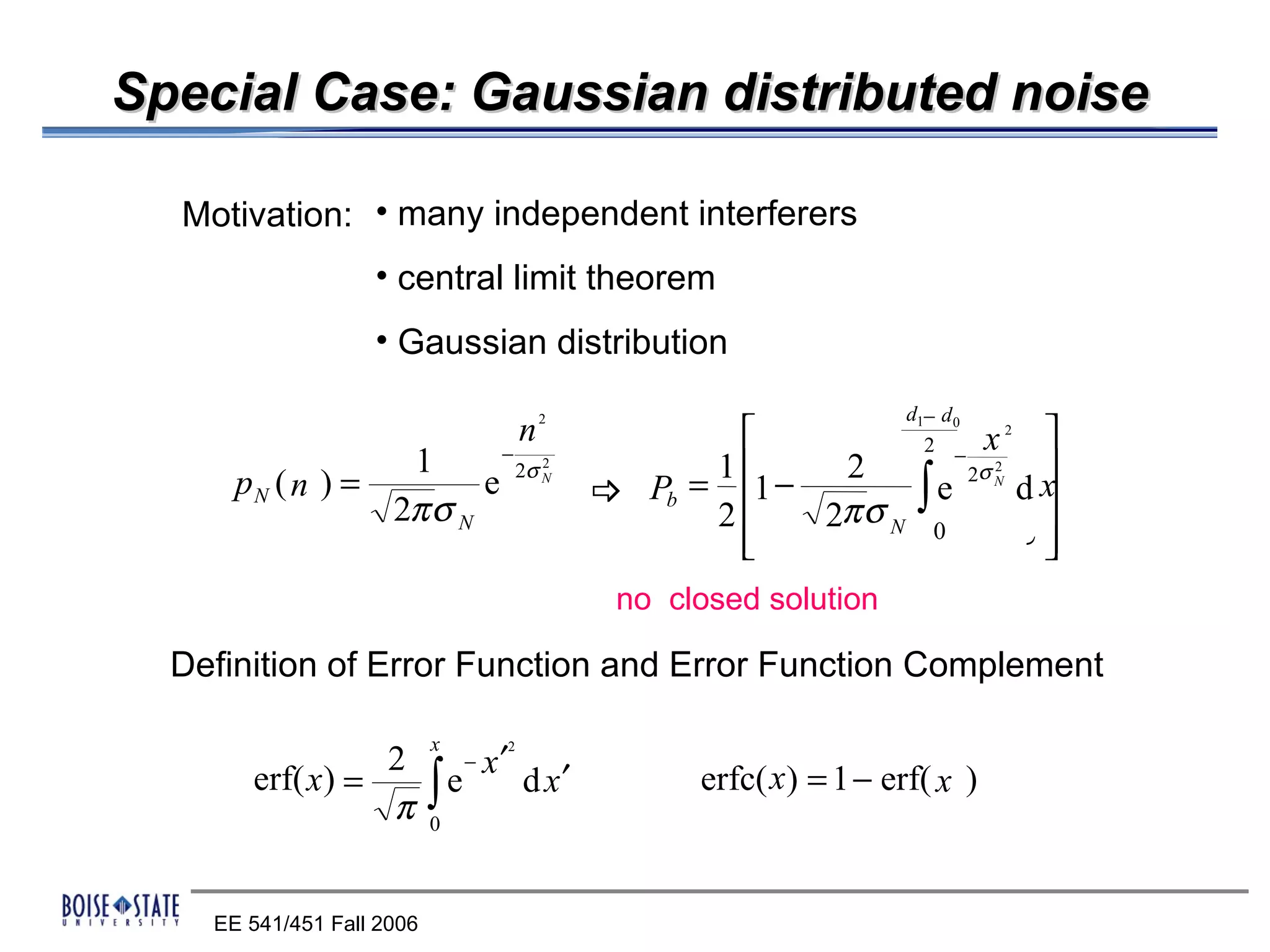
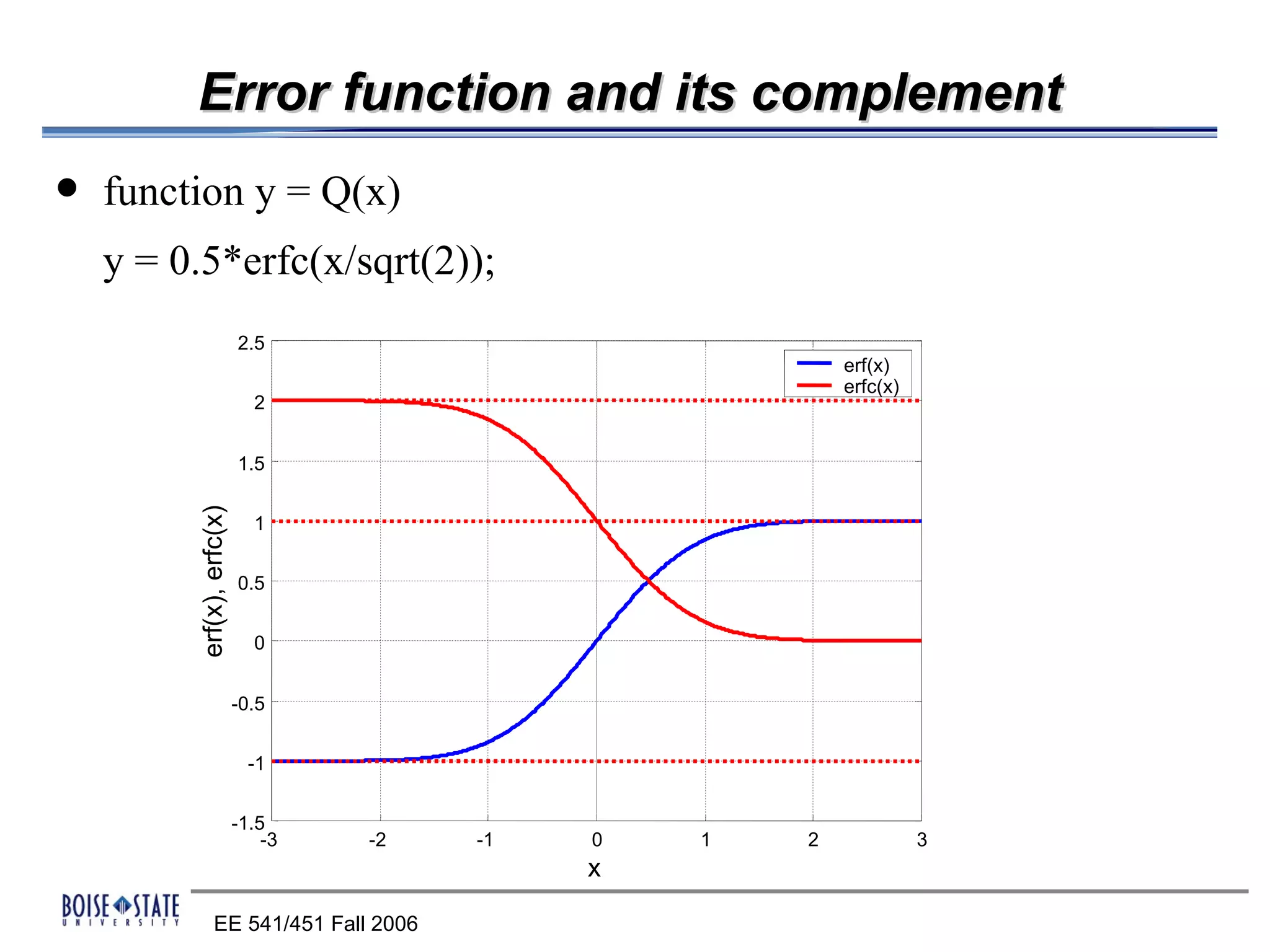
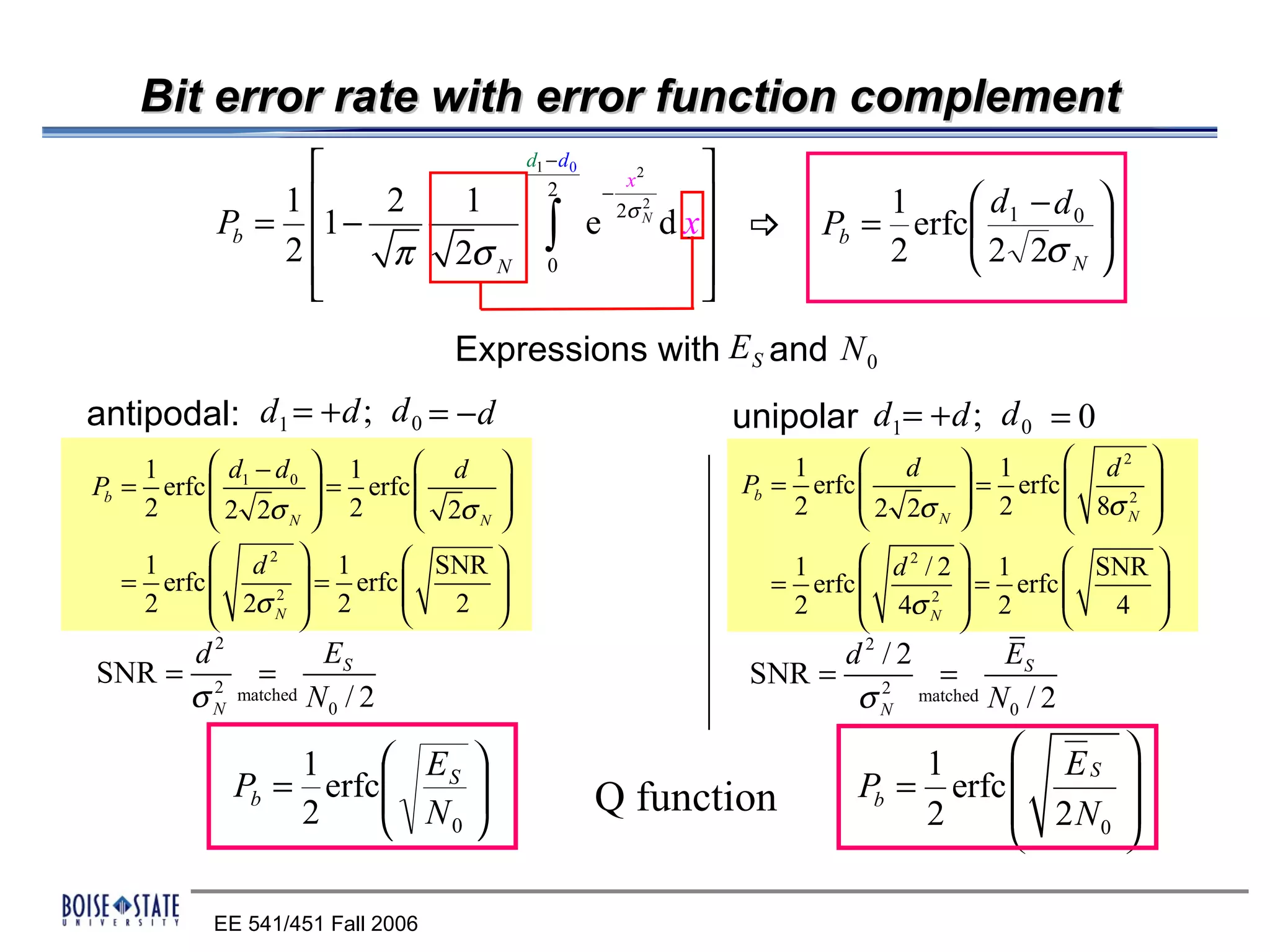
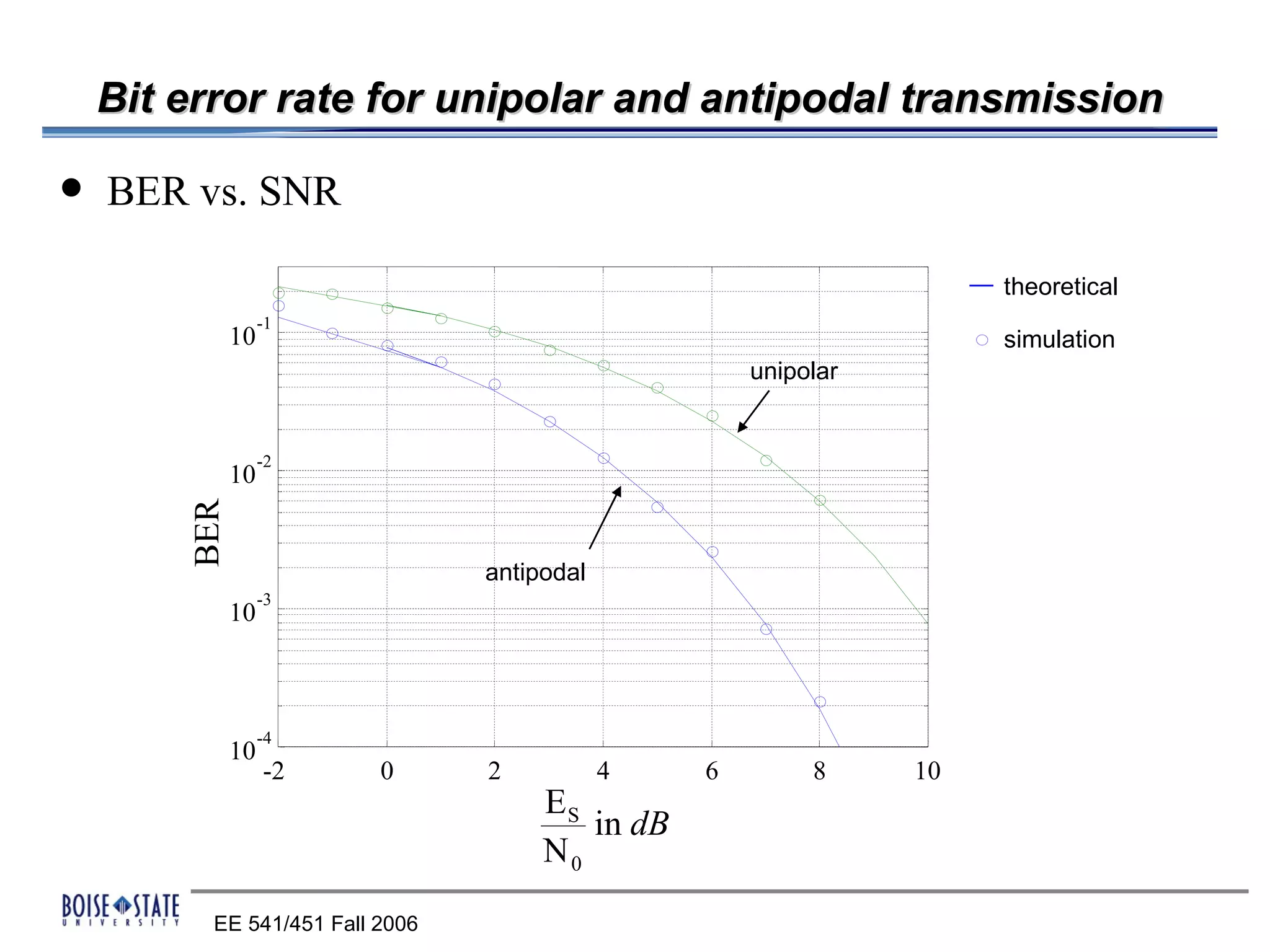
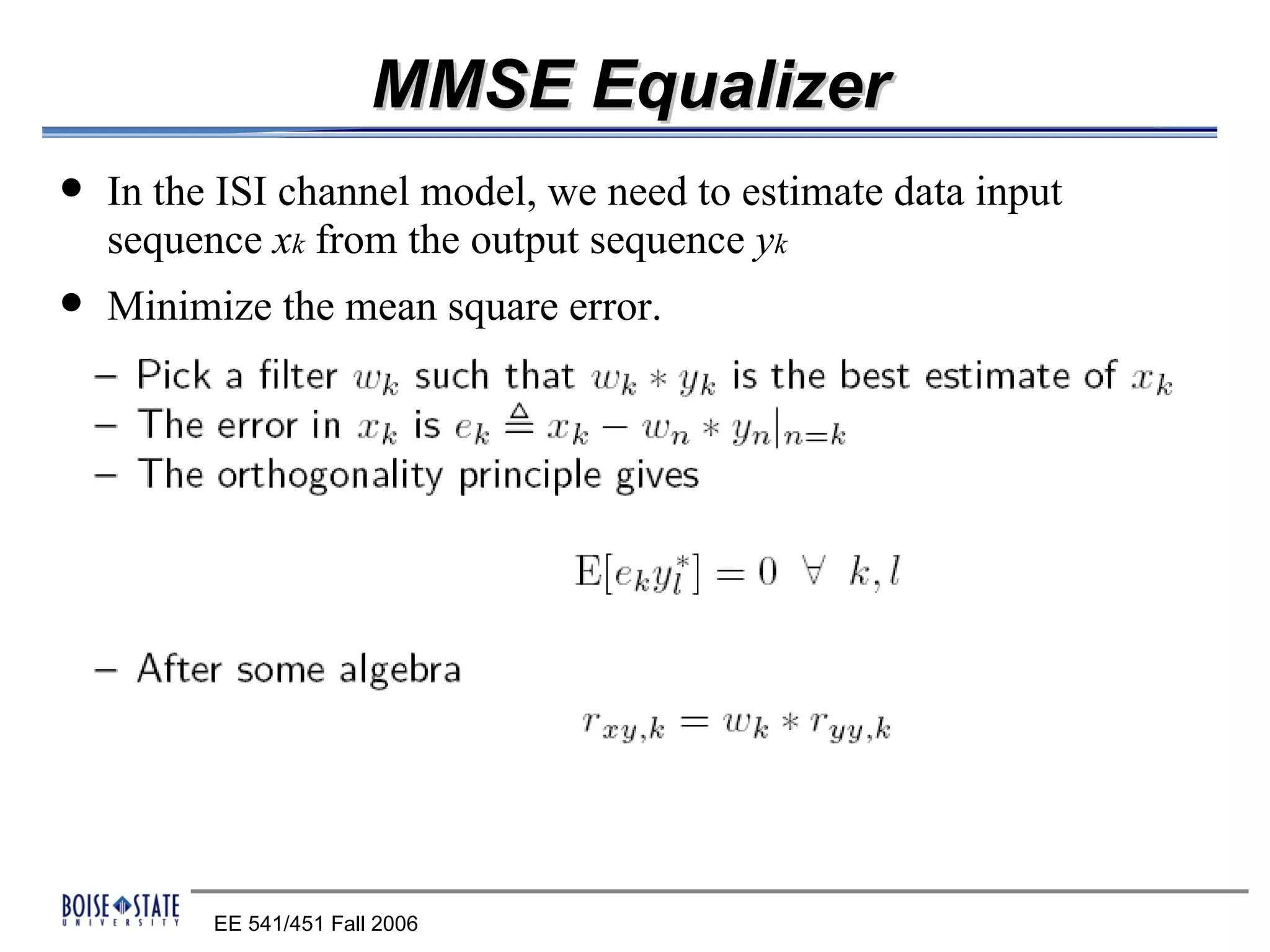
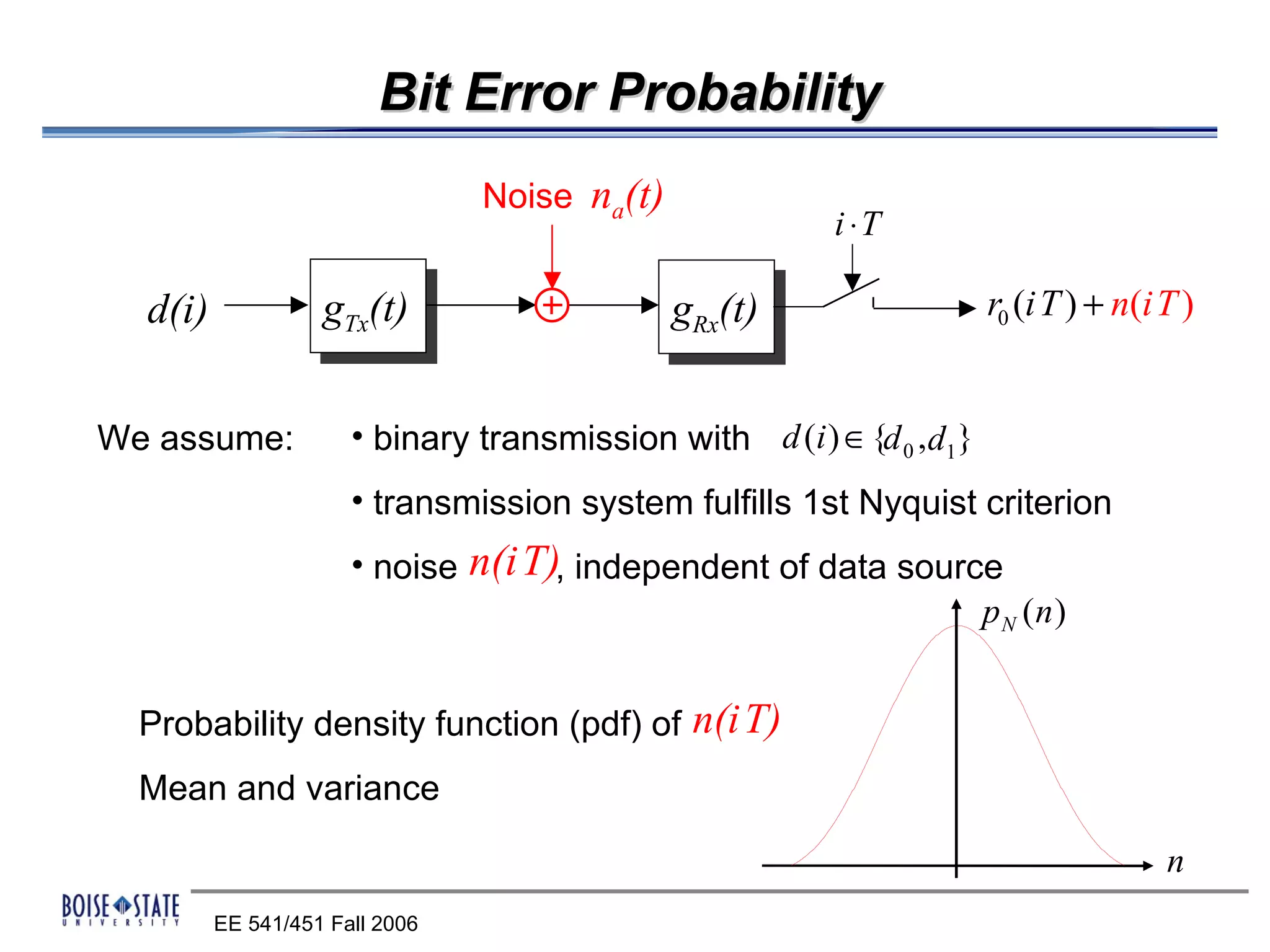
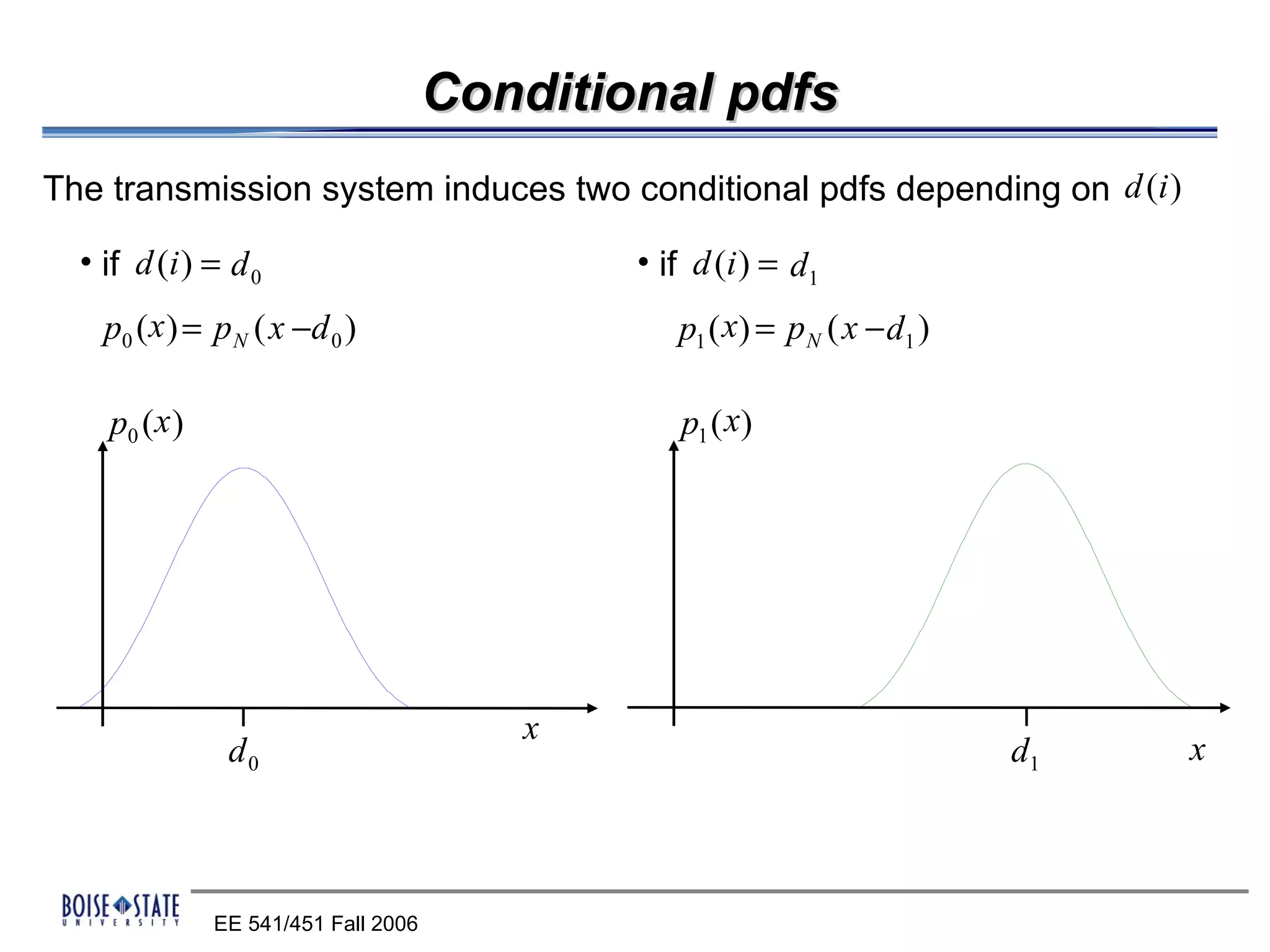
The performance of the receiver depends on factors like noise, equalization technique used, and timing accuracy. The bit error rate can be estimated using tools like error functions.

![Probability of wrong decisions
Placing a threshold S
p0 ( x ) p1 ( x)
Probability of
wrong decision
x x
d0 S S d1
∞ S
Q0 = ∫ p0 ( x) dx Q1 =
∫ p ( x)dx
1
S −∞
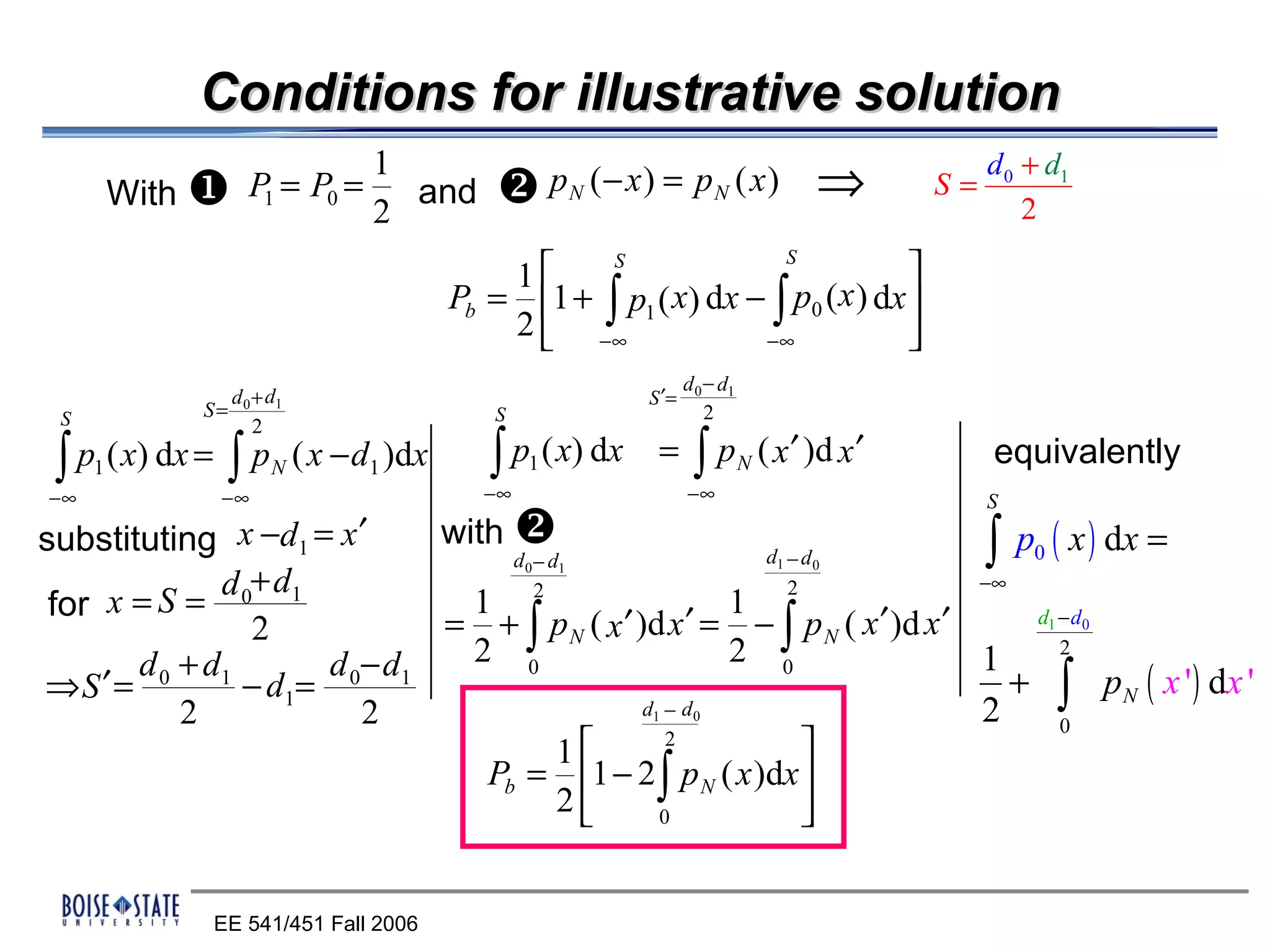
When we define P0 and P1 as equal a-priori probabilities of d 0 and d1
(P0 = P = 1 )
we will get the bit error probability 1 2
∞ S S
Pb = P0Q0 + P Q1 =
1
1
2 ∫s p ( x)dx + ∫ p ( x)dx =
S
0
1
2
−∞
1
1
2 + ∫[
−∞
1
2 p1 ( x) − 1 p0 ( x ) ] dx
2
1 24
4 3
S
1− ∫ p0 ( x ) dx
−∞
EE 541/451 Fall 2006](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matchedfilter-120429100514-phpapp02/75/Matched-filter-18-2048.jpg)