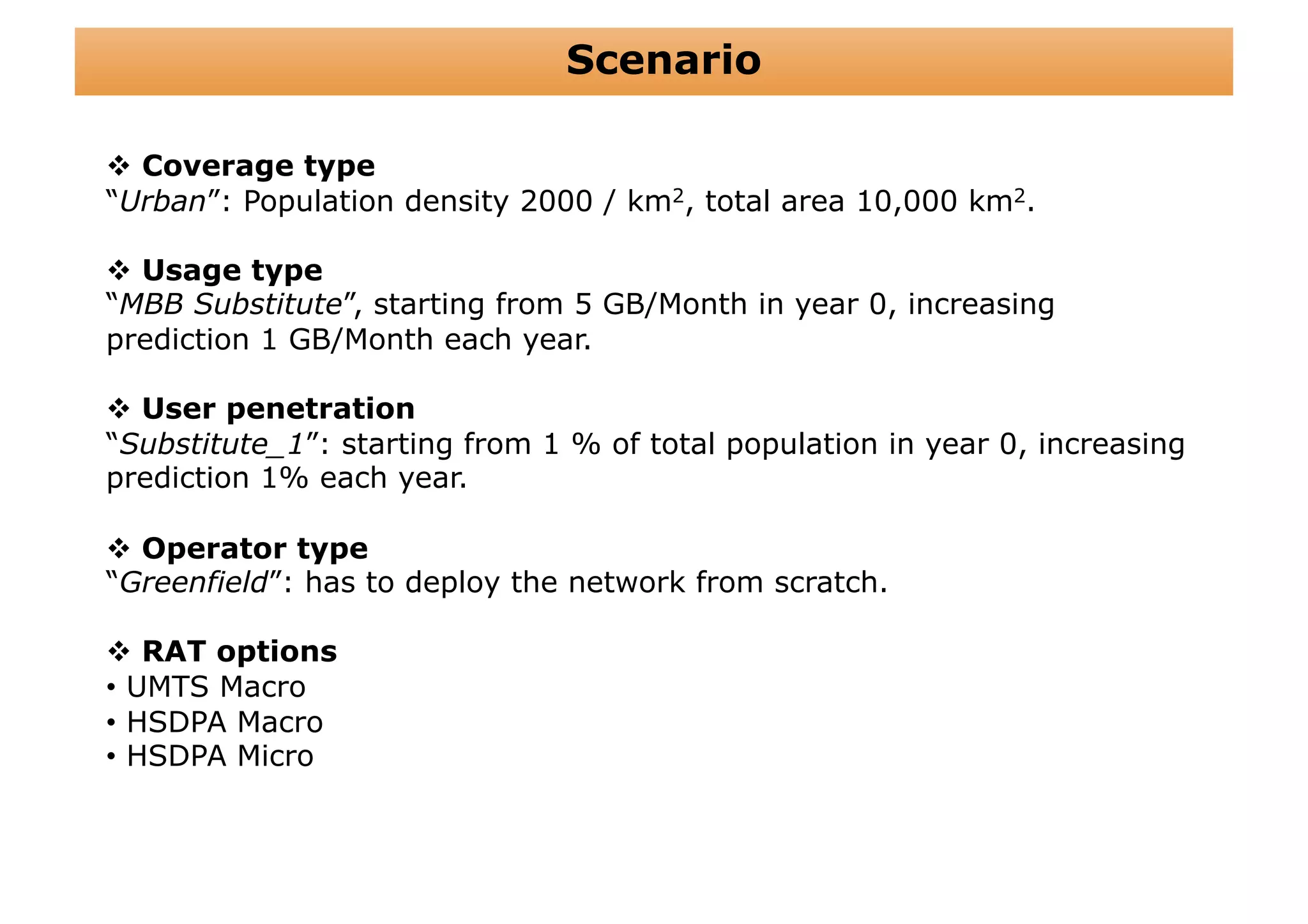
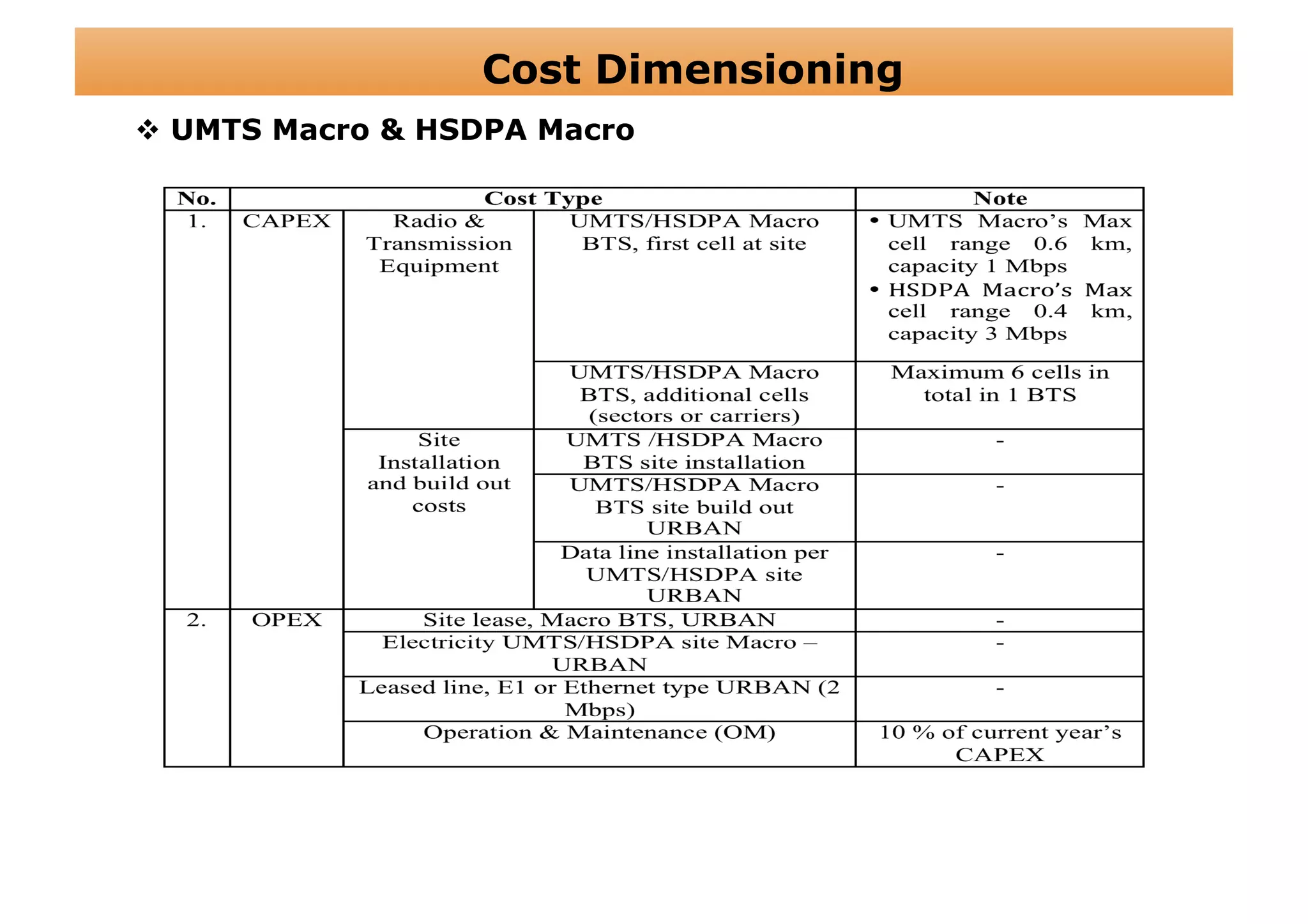
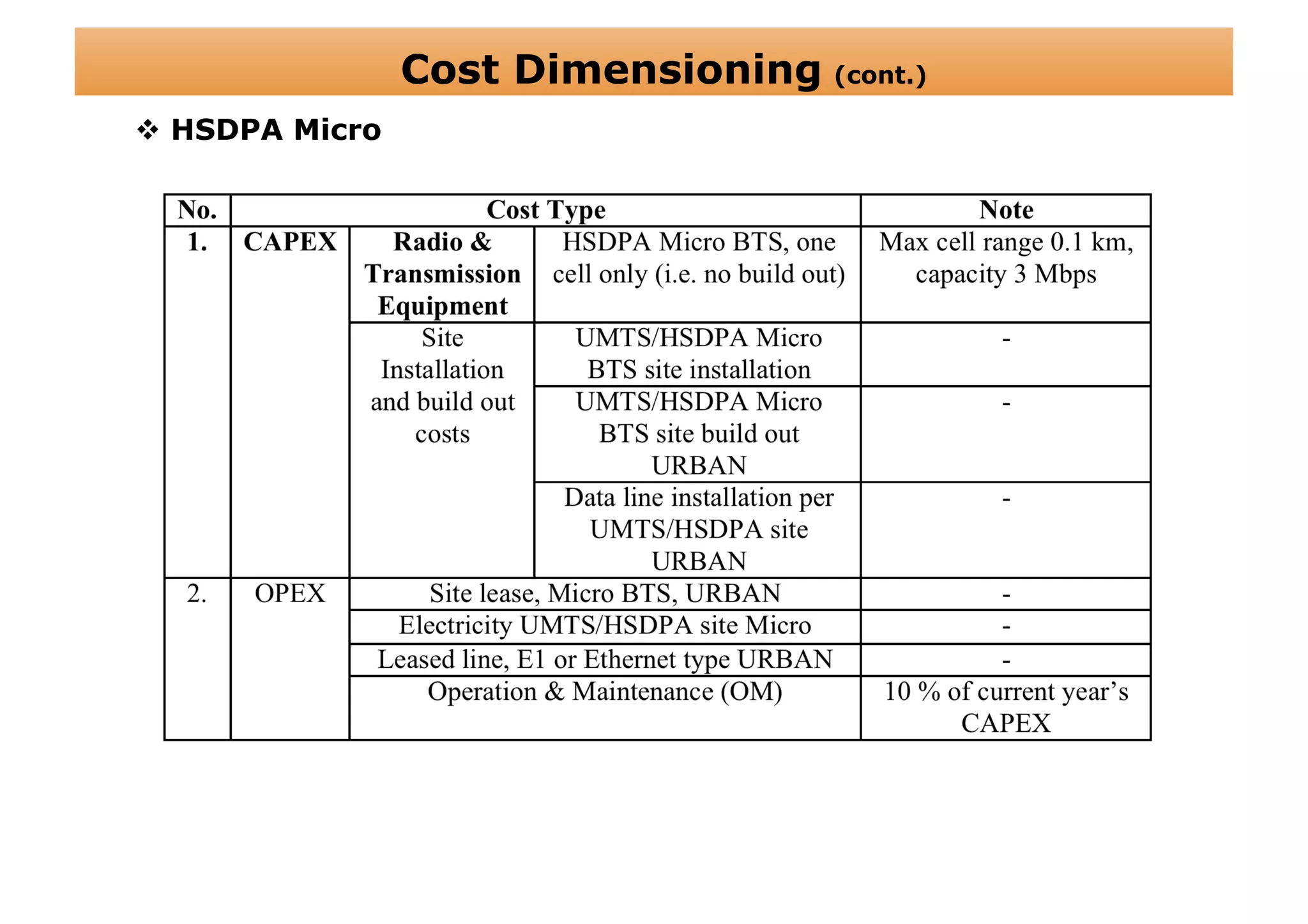
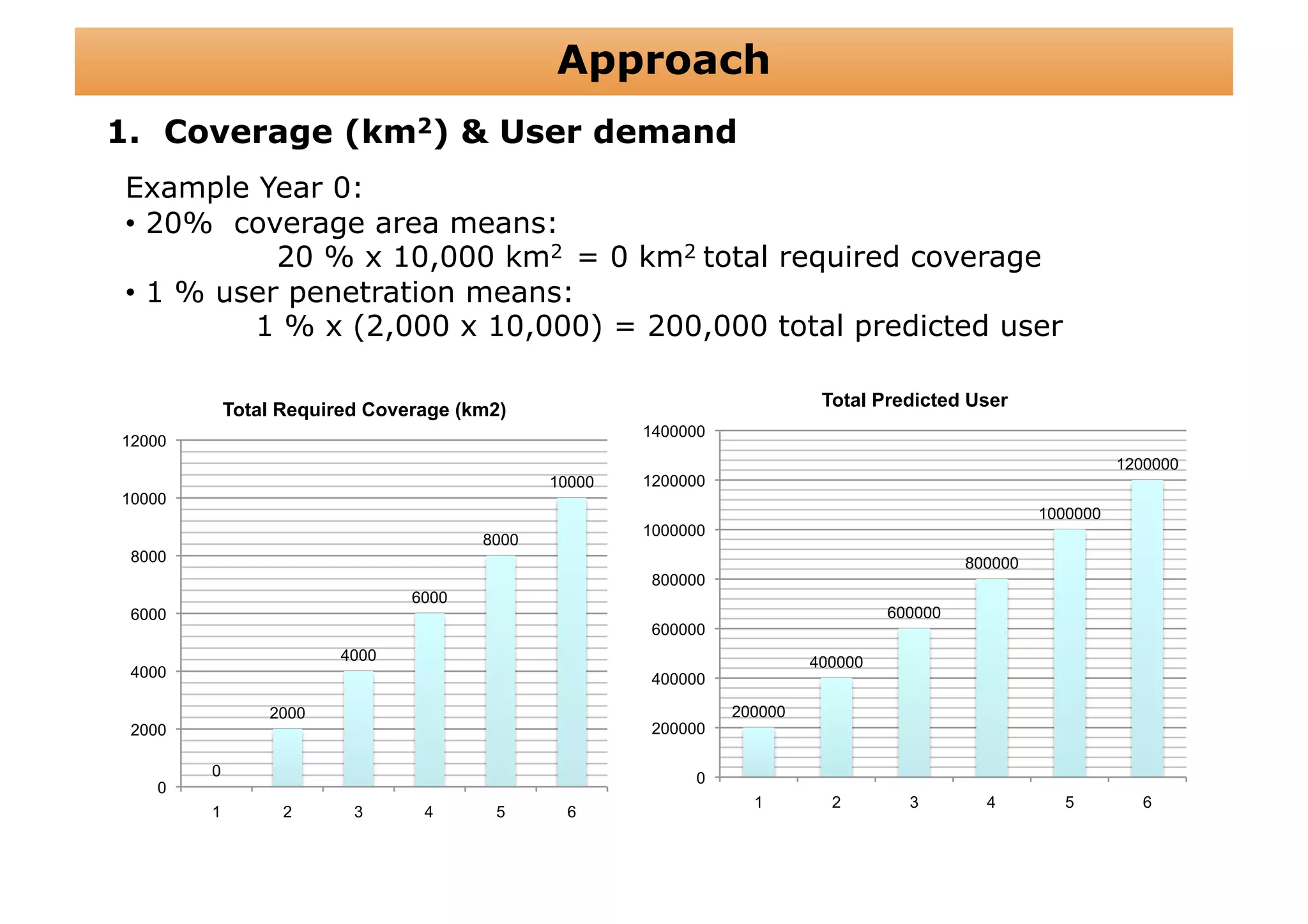
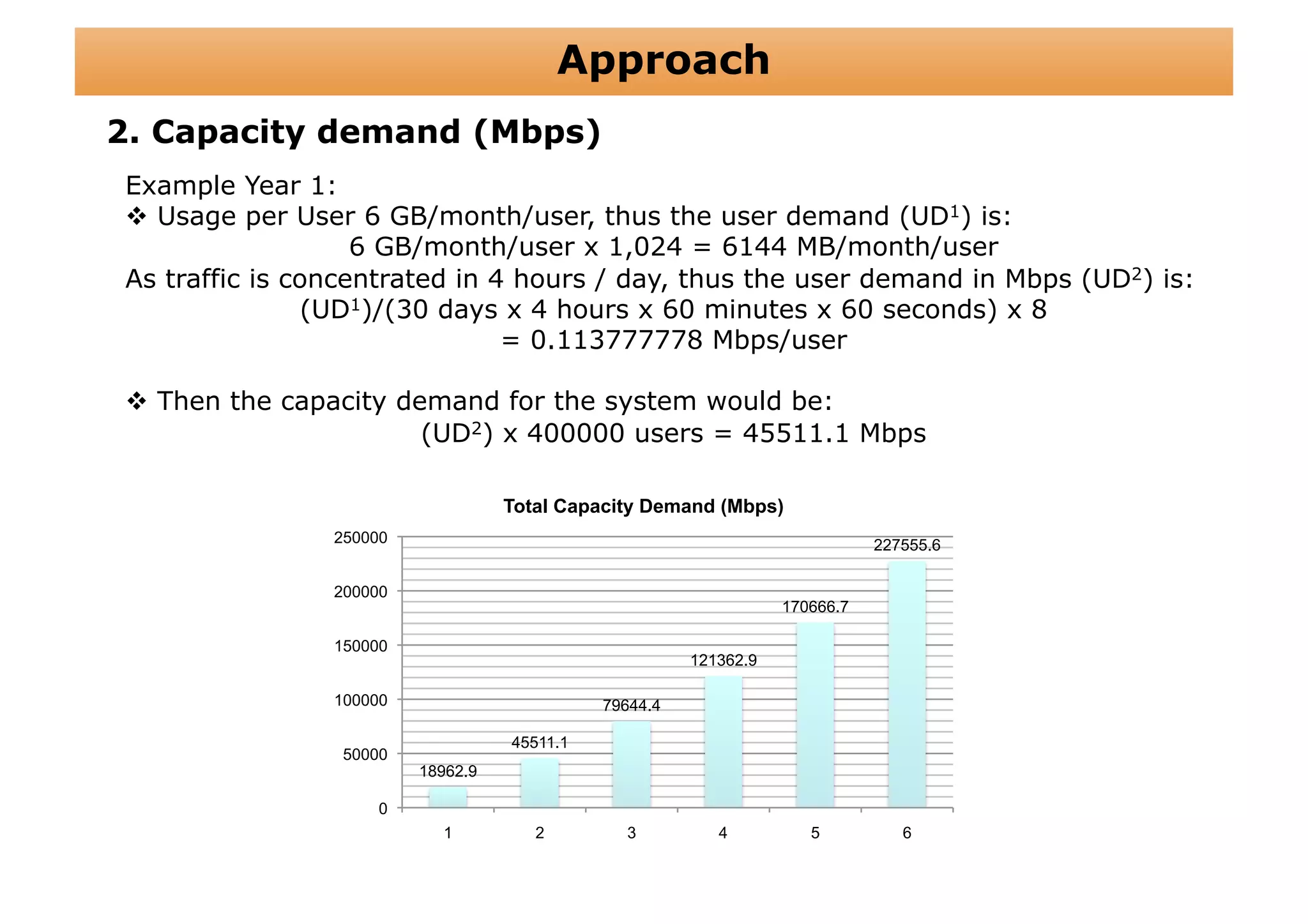
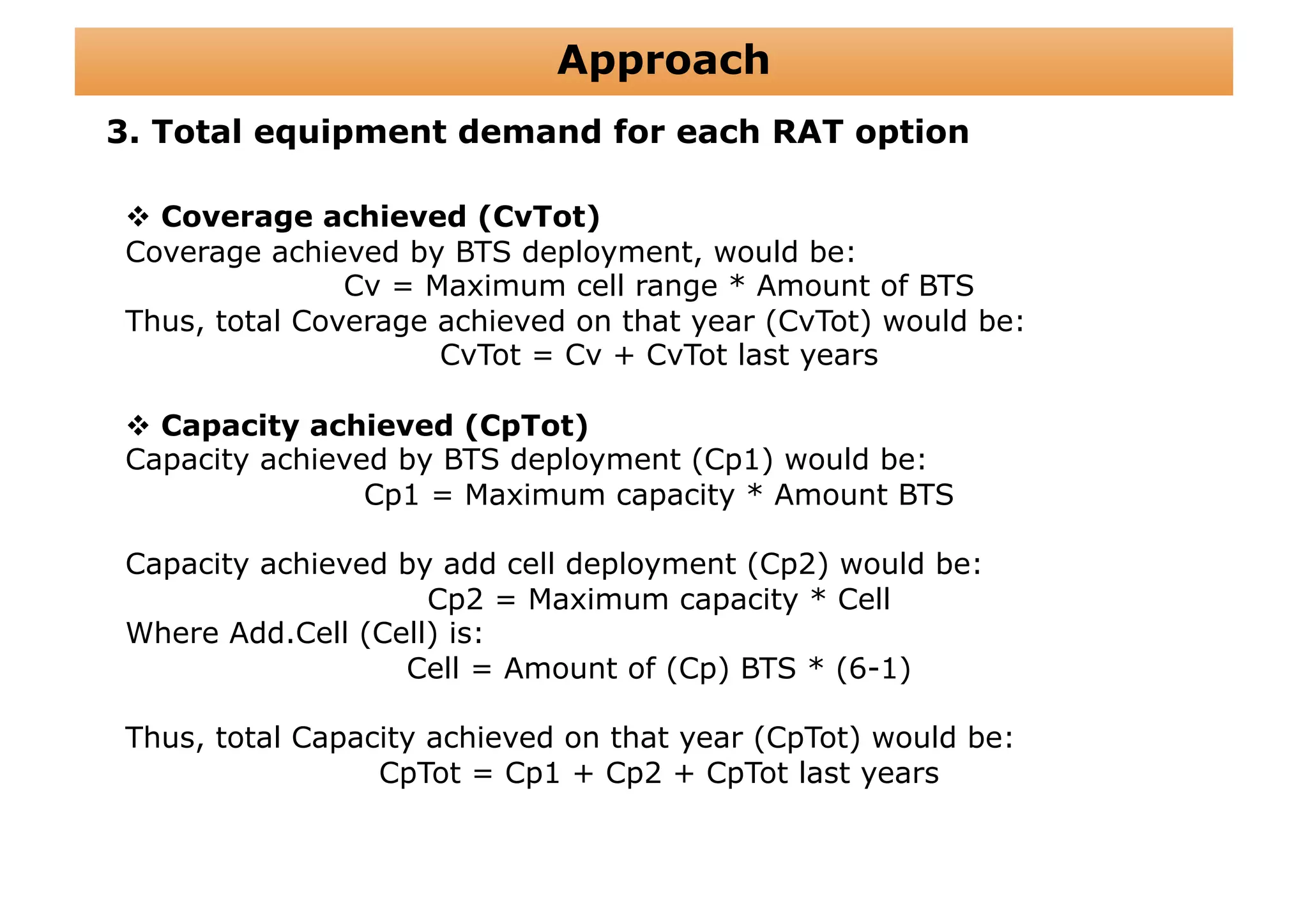
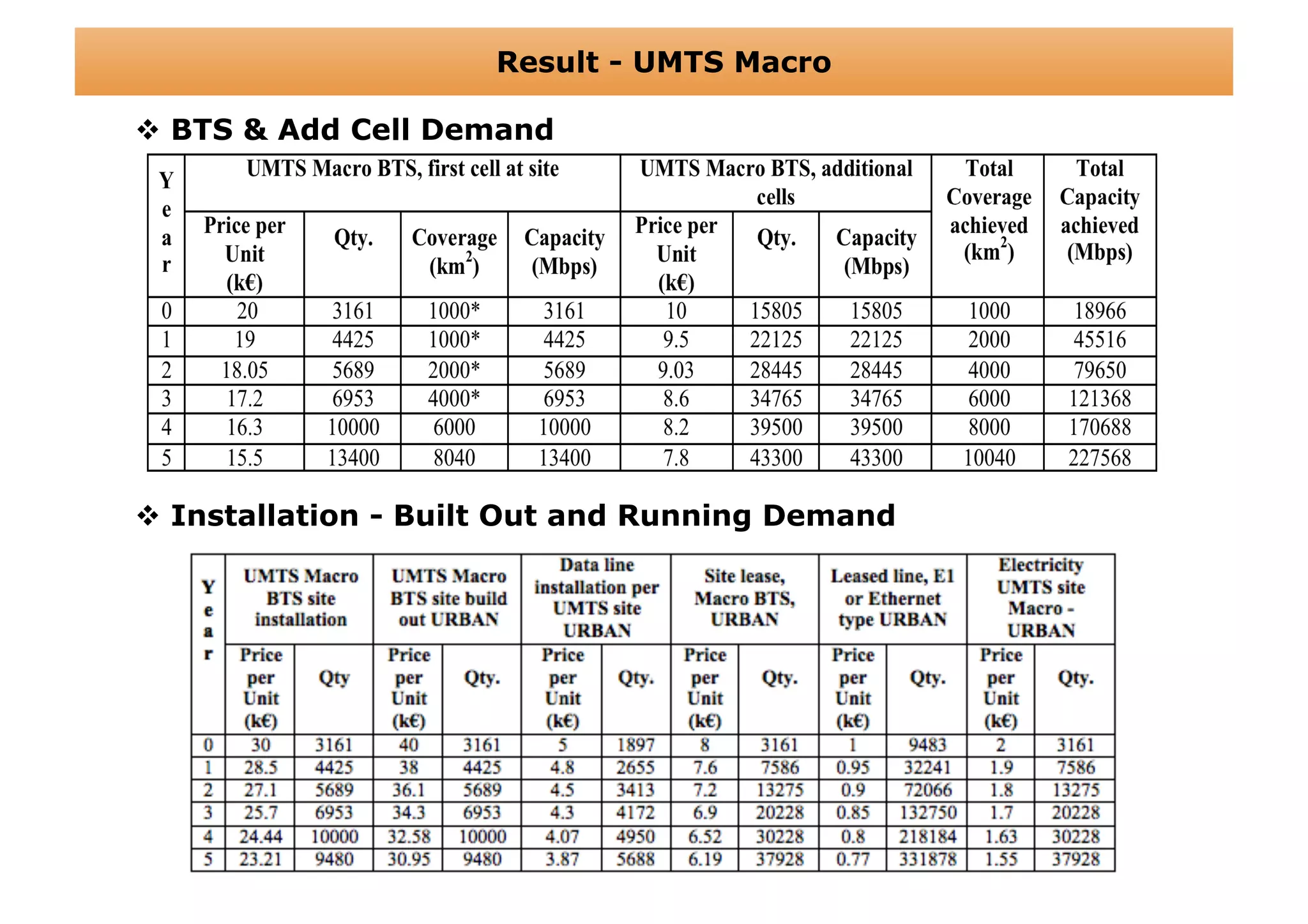
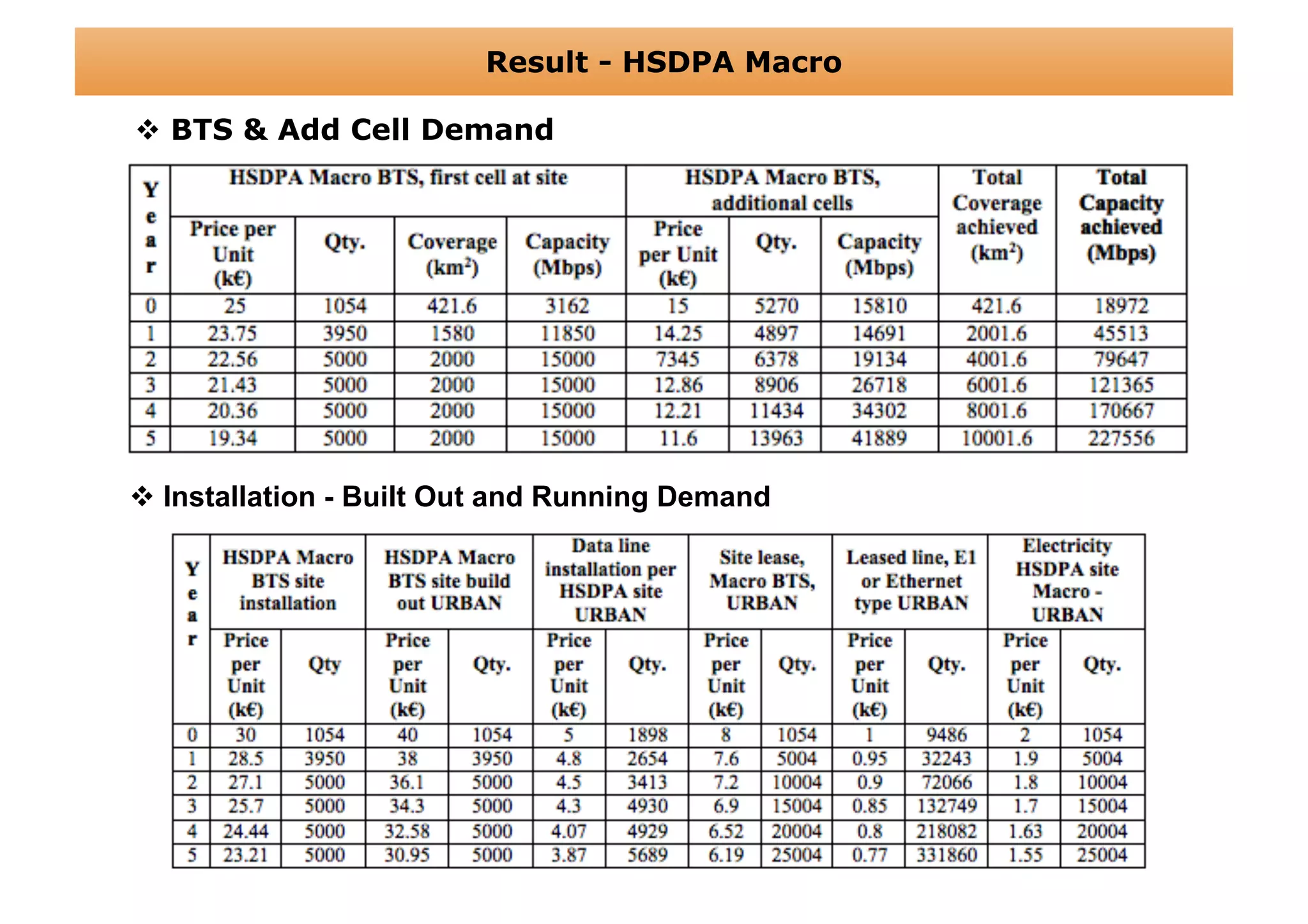
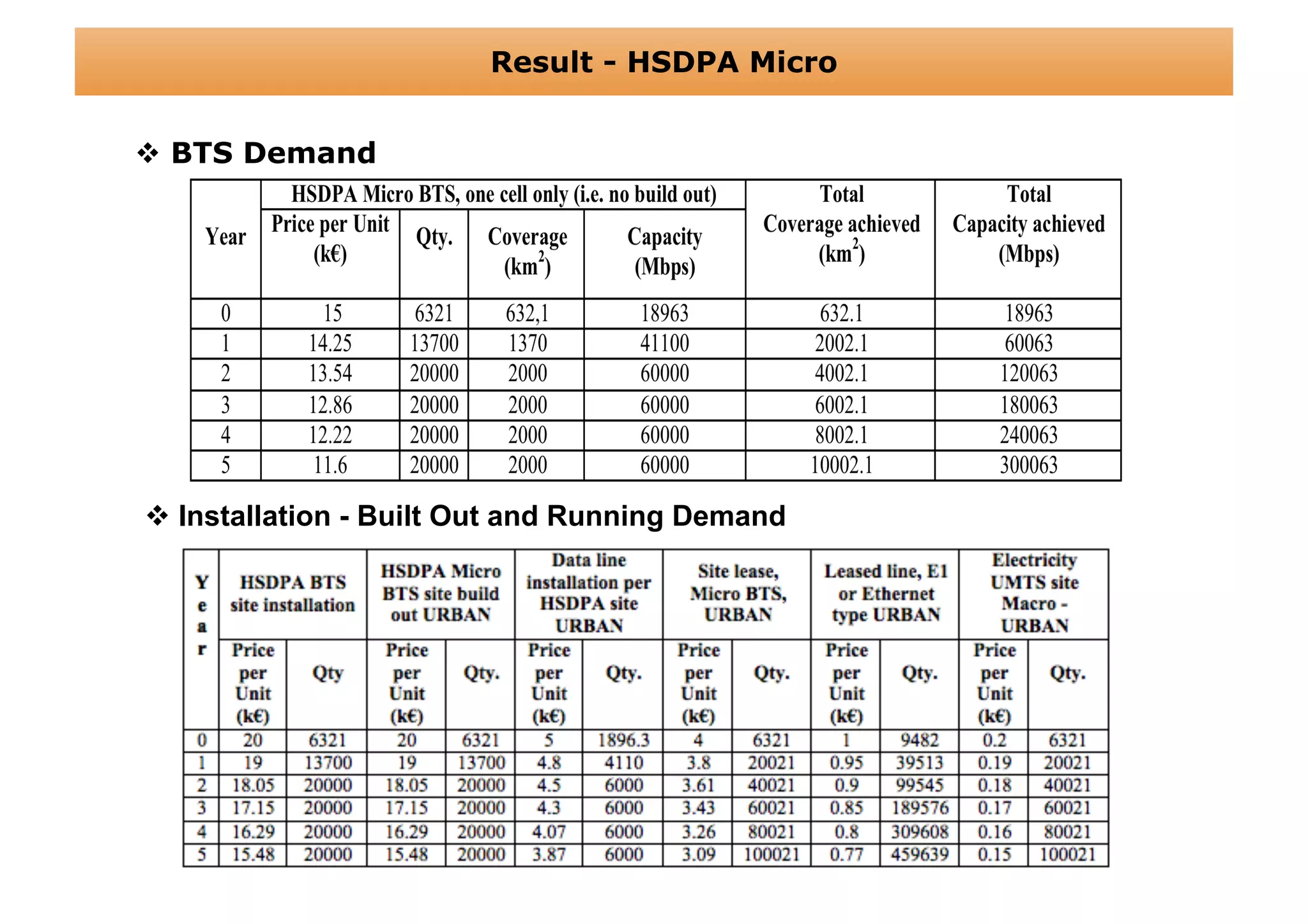
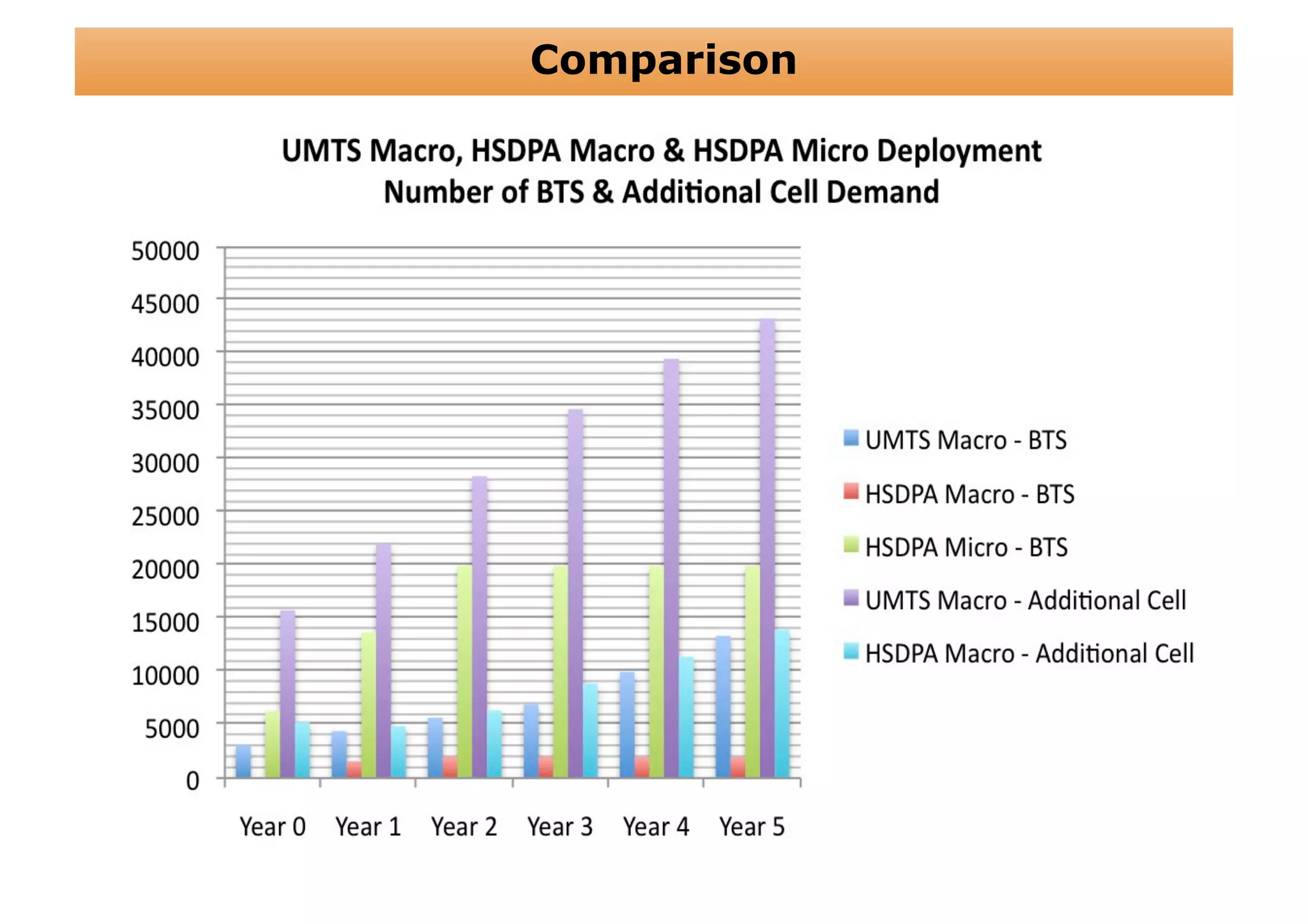
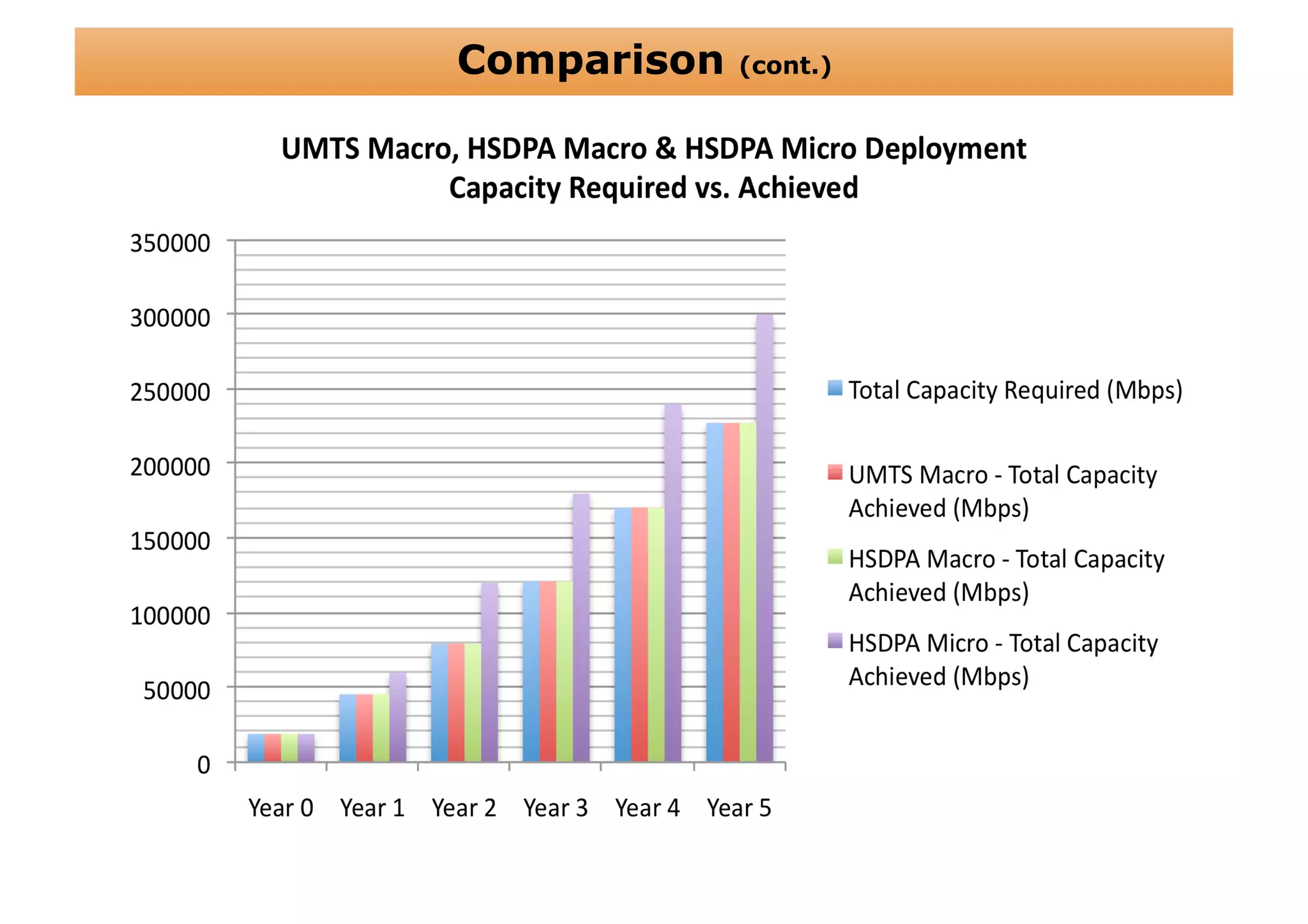
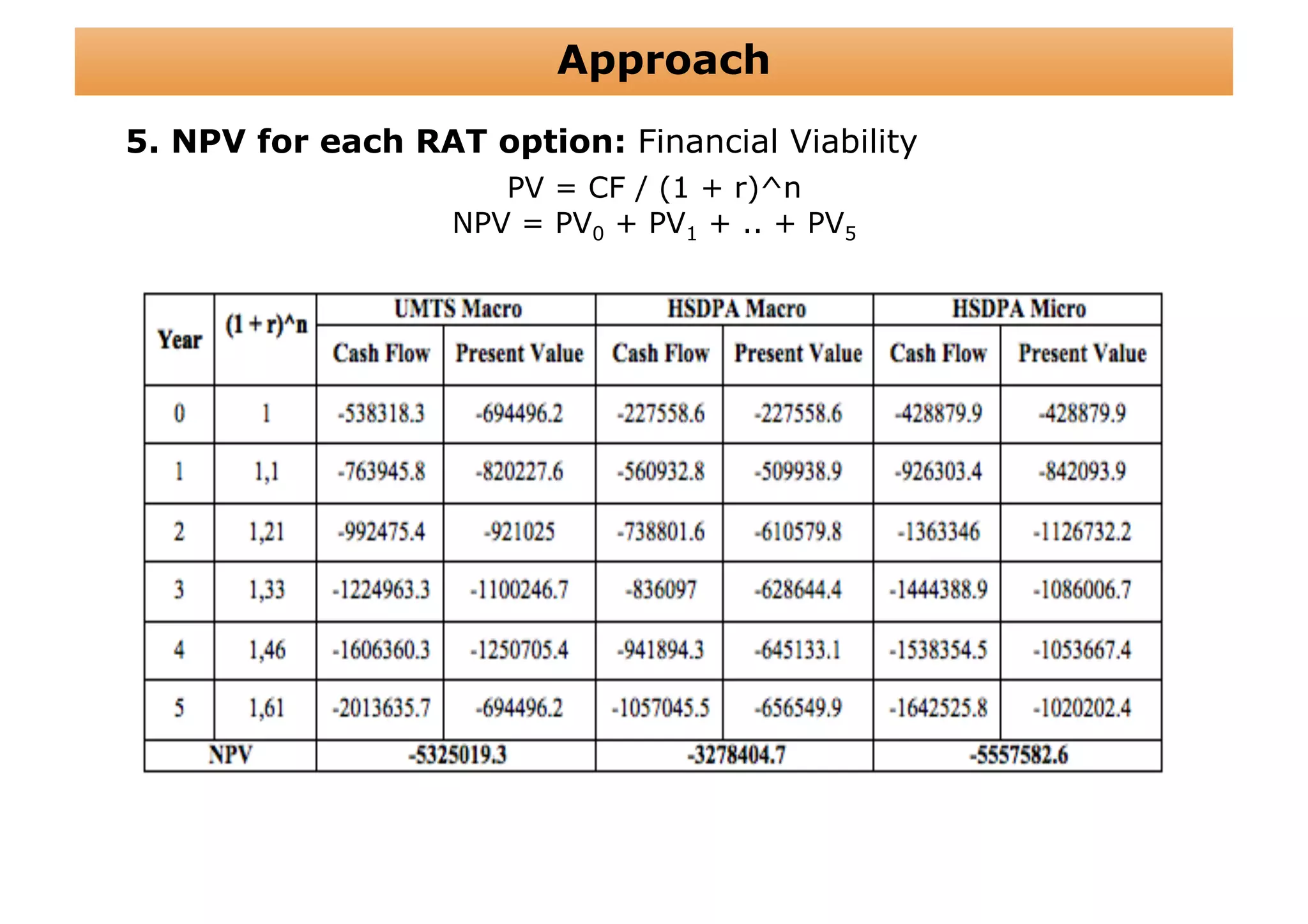
The document outlines a cost structure analysis for deploying a wide area data service network in an urban environment, focusing on user demand forecasts and required coverage. It discusses different radio access technology (RAT) options, including UMTS and HSDPA, and provides calculations for capacity demand, total equipment demand, and overall costs (CAPEX and OPEX). The conclusion recommends HSDPA macro due to its lower deployment needs and better financial viability compared to UMTS and HSDPA micro.