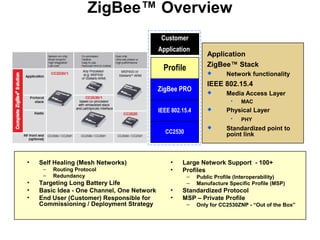
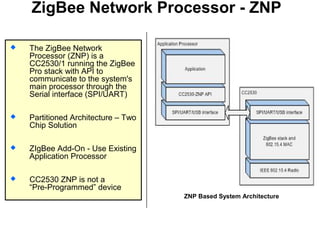
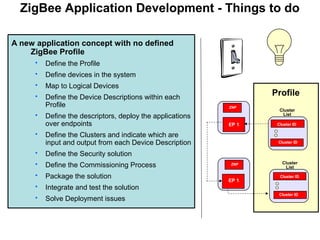
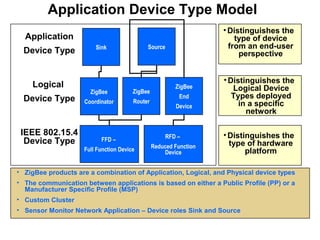
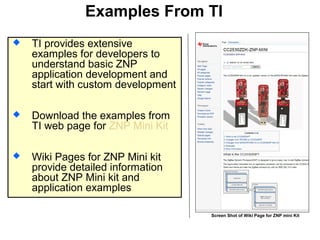
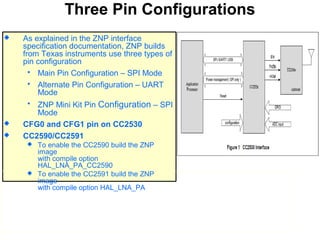
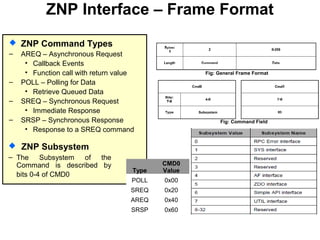
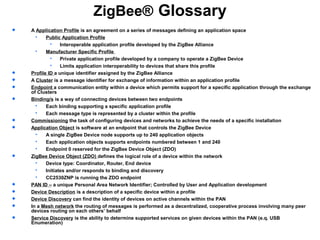
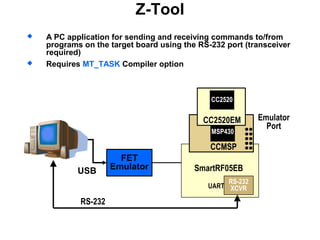
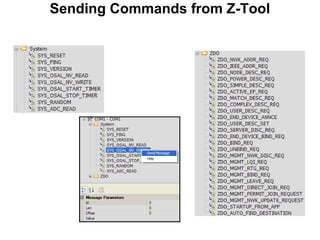
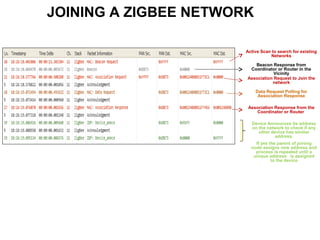
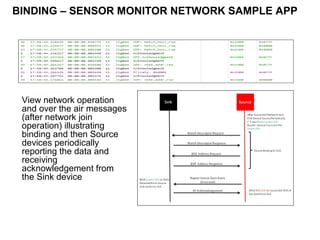
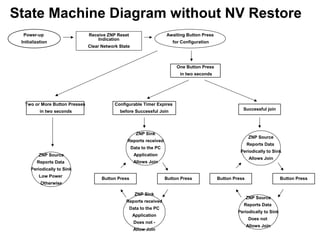
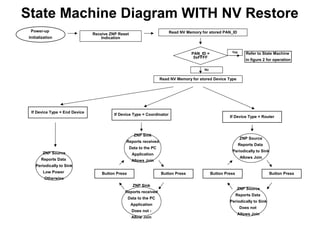
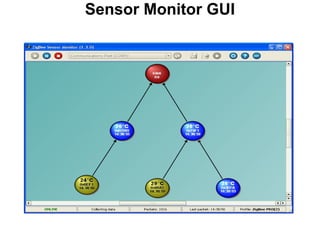
This 3-hour workshop introduces participants to ZigBee and how to build ZigBee applications using the CC2530ZNP Mini Kit. Participants will learn about ZigBee networks and protocols, understand the CC2530ZNP interface, and complete three labs to build small and large ZigBee networks and develop ZigBee applications. The workshop covers ZigBee concepts like mesh routing, commissioning, and personal area networks.