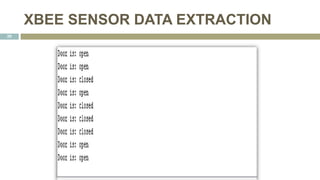
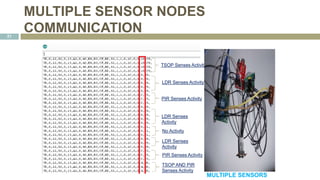
This document presents the design of a wireless sensor network using ZigBee technology for security and monitoring applications. It discusses the hardware and software components used, including ZigBee sensor nodes with various sensors, and a ZigBee coordinator node connected to a GSM modem. The sensor nodes send sensor data to the coordinator over the ZigBee network. If any sensor detects abnormal activity, the coordinator will send an alert message via GSM. The document outlines the modular design of the system and provides examples of sensor data transmission and extraction at the coordinator. It concludes with potential future applications of the wireless sensor network.



![Basic Terminology [2]
“A wireless sensor network (WSN) consist of spatially distributed
autonomous sensors to monitor physical or environmental
conditions, such as temperature, sound, pressure etc.to
cooperatively pass their data through the network to a main
location”
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zigbebasedwsn-181122152253/85/ZigBee-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Network-4-320.jpg)

![About ZigBee [3]
• ZigBee is a wireless protocol that works on RF Communication and
allows small, low-cost devices to quickly transmit small amounts of data.
• Dedicated for use in WPAN and WSN.
• Low cost and low power solution that can be used in various devices what
has been called Internet of Things (IOT).
• Unlike other wireless technologies, ZigBee supports and allows multiple
network topologies .
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zigbebasedwsn-181122152253/85/ZigBee-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Network-6-320.jpg)
![ZIGBEE DEVICE TYPE [5]
ZigBee Coordinator (ZC):
Root of the network tree
Acts as a bridge to other
networks.
ZigBee Router (ZR):
Acts as an intermediate
router.
ZigBee End Devices
(ZED):
functionality to talk to the
parent node.
cannot relay data from other
devices
allows the node to be asleep
ZigBee Coordinator
ZigBee Router/FFD
ZigBee RFD
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zigbebasedwsn-181122152253/85/ZigBee-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Network-7-320.jpg)
![WHY ZigBee ?? [4]
15 seconds
54 Mbps
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zigbebasedwsn-181122152253/85/ZigBee-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Network-9-320.jpg)

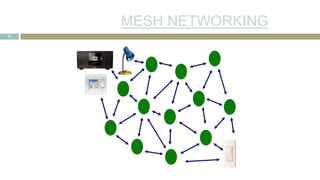
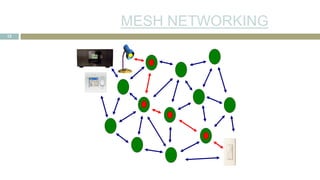
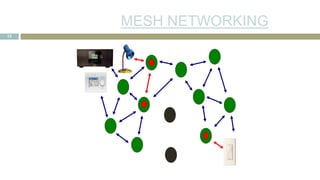
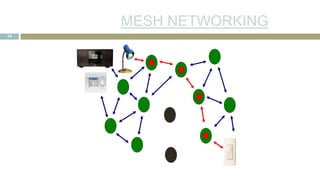
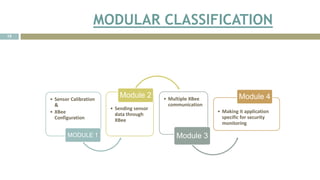


![SENSOR CHARACTERISTI
CS
PURPOSE EXAMPLE
PIR Sensitivity Range:
20feet
Motion Detecting motion in
secured (or unauthorized)
area.
LM35 Temperature
Range:
55 to 150 *C
Temperature Fire alarm.
TSOP 3 meters Object
Detection
Door opening/Closing
LDR Linear Resistance
with Light Intensity
Light Detection Automatic Lighting Control
Acceleromet
er
Sensitivity: 3g Position Prevent theft or tampering
with sensor node
About Sensors [6] [7] [8] [9] [10]
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zigbebasedwsn-181122152253/85/ZigBee-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Network-18-320.jpg)
![XBEE API Frame Received
[11]FRAME RECEIVED AT COORDINATOR CORRESPONDING TO VARIATION
DETECTED BY TSOP SENSOR CONNECTED TO SENSOR NODE
Start
delimiter
(Byte 1)
Length
(Byte 2-3)
Checksum
(Byte N)
0x7E MS
B
API Specific
Structure
1 ByteLS
B
SENSOR NODE WITH
TSOP
FRAME FORMAT
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zigbebasedwsn-181122152253/85/ZigBee-Based-Wireless-Sensor-Network-19-320.jpg)