ABSTRACT: Artificial intelligence is no longer confined to the cloud. Thanks to Edge AI, we can now run AI models directly on embedded devices with limited power and resources. This session will explore the full pipeline of developing a Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML) model, from data collection to deployment, addressing key challenges such as dataset preparation, model training, quantization, and optimization for embedded systems. We’ll explore real-world use cases where AI-powered embedded systems enable smart decision-making in applications like predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and voice recognition. The talk will include a live hands-on demonstration on how to train and deploy a model using popular tools like Google Colab and TensorFlow, and then run real-time inference on an Arduino board.
BIO: Leonardo Cavagnis is an experienced embedded software engineer, interested in IoT and AI applications. At Arduino, he works as a firmware engineer, developing libraries and core functionalities for boards while also focusing on communication and engaging with the community.







![13
Neural Network: The basics
An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) consists of layers of neurons that process information
- Each neuron is a unit that performs calculations
Neuron
Input
tensor
x
Weights
W ∑
Bias
b
Activation
function
f(z)
Output
tensor
y
x[] y[]
z = W⋅x + b
y = f(z)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-13-320.jpg)




![24
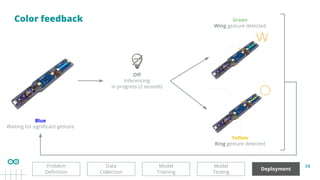
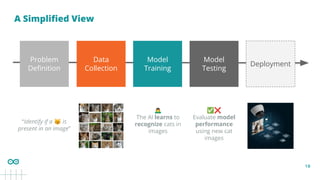
Classification problem
Deployment
Model
Testing
Data
Collection
Problem
Definition
Model
Training
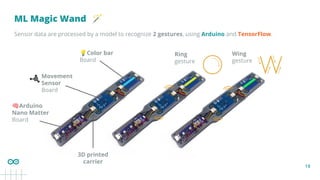
The problem involves gesture recognition using
accelerometer data from an IMU sensor.
The goal is to classify 2+1 gestures:
1. Wing (W)
2. Ring (O)
3. No Gesture (idle or unrecognized movements)
👀 This is a Supervised Learning classification problem.
TinyML Model
Probabilities
[Wing, Ring, No Gesture]
Accelerometer data
[P1,P2,P3]
[ax, ay, az]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-24-320.jpg)
![25
Define model input
Deployment
Model
Testing
Data
Collection
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
TinyML Model
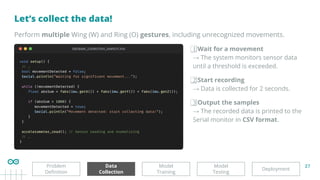
IMU sensor readings frequency = 100 Hz
Sample duration = 2 secs approx.
2s * 100 Hz = 200
200 tuples of accelerometer [aX,aY,aZ] sensor data
for each sample
→ a total of 600 (200 * 3) data points/sample
Accelerometer data
recorded for 2 secs
200 * [aX, aY, aZ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-25-320.jpg)
![26
Data preprocessing
Deployment
Model
Testing
Data
Collection
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
Collected raw data is processed to make it suitable for model training:
- Normalization
- Noise filtering
- Interpolation
- Feature Extraction
- …
normalized_value = (raw_value_acc + 2000) / 4000
Normalization
Scaling data to specific range, typically [0,1] → preventing large values and improve stability
Accelerometer data is expressed in milliG (mG) in in a range [-2000, +2000]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-26-320.jpg)
![28
Dataset splitting
Deployment
Model
Testing
Data
Collection
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
Dataset is divided into 3 subsets:
1. Training [60%]
Train the machine learning model.
2. Validation [20%]
Monitor its performance during training.
3. Test [20%]
Evaluate the model's performance after training.
Validation Test
Training](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-28-320.jpg)
![30
Model Architecture with TensorFlow
Deployment
Model
Testing
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
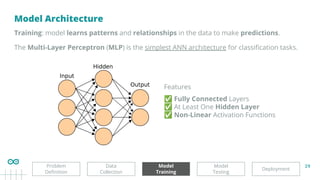
A Multi-Layer ANN can be defined using:
import tensorflow as tf
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
Data
Collection
For our problem, we can design a network with:
● 256 neurons in the hidden layer
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'))
● 3 neurons in the output layer, each representing one of the 3 gestures to classify
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation='softmax'))
…
Wing
Ring
None
600 = 200 * [aX,aY,aZ]
256
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-30-320.jpg)
![31
Model Architecture with TensorFlow
Deployment
Model
Testing
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
A typical Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) architecture consists of two hidden layers.
import tensorflow as tf
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
Data
Collection
For our problem, we can design a network with:
● 256 neurons in the first hidden layer
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'))
● 128 neurons in the second hidden layer
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'))
● 3 neurons in the output layer, each representing one of the 3 gestures to classify
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation='softmax'))
…
…
Wing
Ring
None
600 = 200 * [aX,aY,aZ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-31-320.jpg)
![32
Model Training with TensorFlow
Deployment
Model
Testing
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
Set training parameters:
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
…Let’s start the training!
model.fit(inputs_train, outputs_train,
epochs=100, batch_size=8,
validation_data=(inputs_validate, outputs_validate))
Validation Test
Training
Data
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-32-320.jpg)
![33
Monitoring Training Results
Deployment
Model
Testing
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
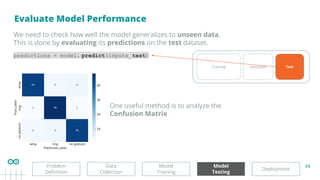
Monitor the loss and accuracy curves for both the training and validation data:
Epoch 3/100
32/32 [==============================] -
0s 8ms/step - loss: 1.0856 - accuracy: 0.4233 - val_loss: 1.0800 - val_accuracy:
0.4200
If the loss decreases while
the accuracy increases
→ the model is learning well ✅
Data
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-33-320.jpg)
![35
From “Big” to Tiny
Deployment
Model
Testing
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
Data
Collection
To run the model on a microcontroller, we need to convert it to a TinyML model
using TensorFlow Lite.
converter = tf.lite. TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model)
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize. DEFAULT]
converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet. TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8]
tflite_model = converter. convert()
Integer Quantization
Converting float to nearest
8-bit fixed-point numbers
⚡Optimizations:
- LATENCY
- SIZE
- DEFAULT (trade-off)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-35-320.jpg)
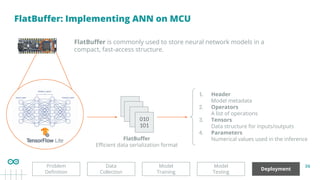
![37
Let’s code!
Deployment
Model
Testing
Model
Training
Problem
Definition
Data
Collection
TinyML Model
Probabilities
[Wing, Ring, No Gesture]
Accelerometer data
200 * [ax, ay, az]
The gesture with the highest
probability could be
considered the detected one](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/specktech-20250409edgeaibringingintelligencetoembeddeddevices-250411195748-906dc888/85/Edge-AI-Bringing-Intelligence-to-Embedded-Devices-37-320.jpg)