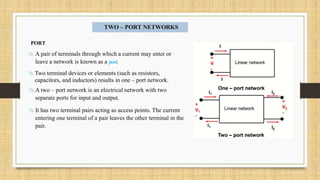
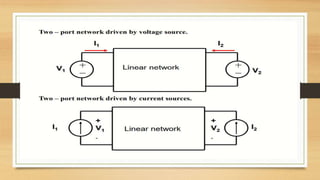
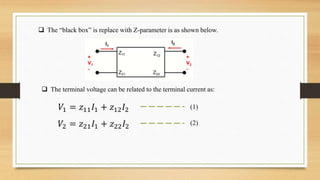
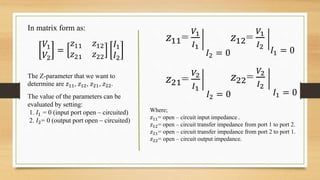
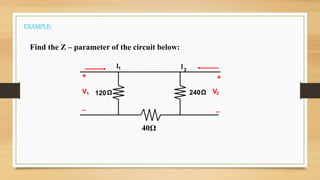
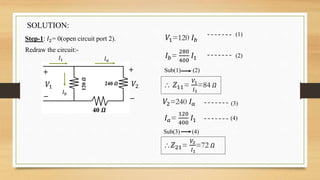
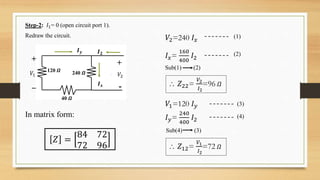
This document discusses two-port networks and Z-parameters. It defines a two-port network as an electrical network with two ports for input and output. The document explains that Z-parameters relate the terminal voltages and currents, where z11 is the input impedance, z12 is the transfer impedance from port 1 to port 2, z21 is the transfer impedance from port 2 to port 1, and z22 is the output impedance. An example circuit is then used to calculate the Z-parameters of the network by setting the ports to open circuit conditions.