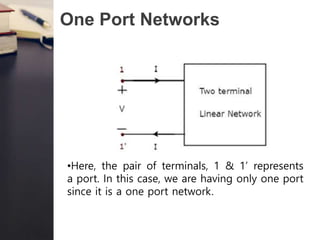
- Two port networks contain two ports, with one used as an input and the other as an output.
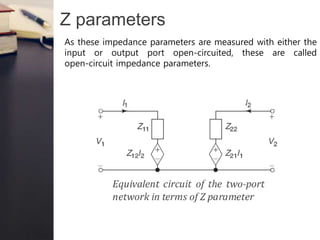
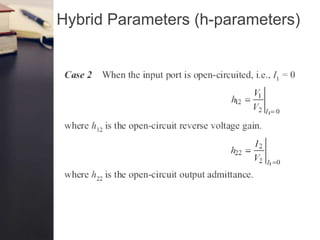
- There are four key parameters used to characterize two port networks: Z parameters (open circuit impedance), Y parameters, h parameters, and ABCD parameters.
- The Z parameters express the voltages at each port in terms of the currents, while the h parameters express the voltage at one port and current at the other in terms of the current and voltage at the other port.