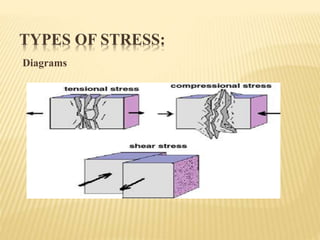
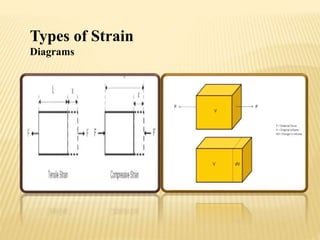
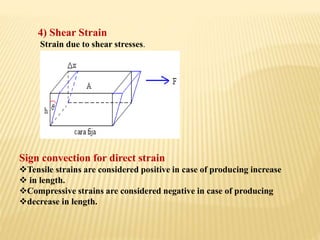
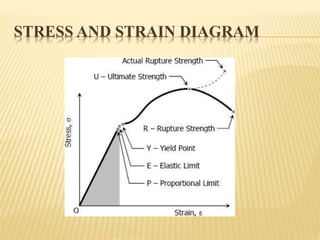
This document summarizes stress and strain concepts contributed by five authors from the Department of Geology at the University of Haripur. It defines stress and strain, related terminology, types of stress including normal and combined stresses, types of strain including tensile, compressive, shear and volumetric strains. It also describes Hooke's law which states that within the elastic limit, the ratio of stress to strain is constant, known as Young's modulus. Diagrams are included to illustrate different types of stresses and strains.