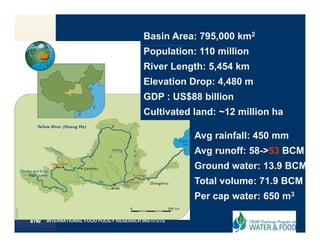
The document summarizes a project focused on addressing key water and food challenges in the Yellow River Basin in China. The project involves 6 work packages to study water poverty, availability, productivity, and institutions in the basin to identify high-priority interventions. Challenges include data limitations, negotiating water allocations between provinces, and balancing demands between sectors. The goal is to increase water and food security while maintaining environmental sustainability.






![PROJECT PARTNERS
• Yellow River Conservancy Commission
y
[WP2/WP5]
• Beijing Normal University [WP2]
• China Center for Agricultural Policy
[WP4]
• University of Illinois [WP3]
• Int. Food Policy Research Institute
[WP1/WP6]
INTERNATIONAL FOOD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yellowriverbfpstartup2-090618094505-phpapp02/85/Yellow-River-Basin-Focal-Project-8-320.jpg)

![Basin Diagnostic Tour [lower
basin]
Water scarcity considered the largest problem
for irrigation
g
Water fees and water quality are also important
Increased competition with urban-industrial and
environmental water uses
Zero tillage as one strategy to save water and
labor, adoption for maize and wheat
Most f
M t farmers are part-time [
t ti [small l d area,
ll land
many non-farm employment opportunities]
Climate change potential future threat –
experience of more extreme cold events during
i f t ld t d i
winter and reduced runoff despite stable rainfall
Relatively low poverty in Henan and Shandong
provinces [d
i [downstream b i ]
t basin]
INTERNATIONAL FOOD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yellowriverbfpstartup2-090618094505-phpapp02/85/Yellow-River-Basin-Focal-Project-10-320.jpg)



![WP1 Methodology: Poverty Map
et odo ogy o e ty ap
Use statistical, small area estimation
statistical small-area
(SAE), techniques
• Produces readily interpretable estimates
• Statistical precision can be gauged
• Encouraging results to date
g g
• But, extensive data requirements
[combination of household-level data of
Population Census and household
expenditure data]
INTERNATIONAL FOOD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yellowriverbfpstartup2-090618094505-phpapp02/85/Yellow-River-Basin-Focal-Project-15-320.jpg)
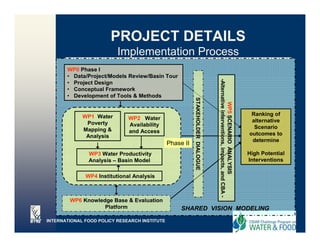
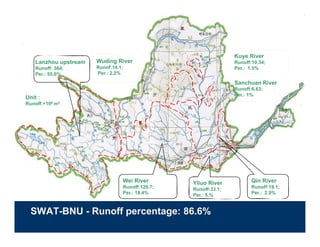
![WP2 - Methodologies
g
Large body of information on
[spatial/temporal] distribution of water
availability and water h
il bilit d t hazards d
Use SWAT-BNU to estimate rainfall-runoff
[sediment and human interactions]
Will feed into aggregated existing Yellow
River Hydrologic Model
INTERNATIONAL FOOD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yellowriverbfpstartup2-090618094505-phpapp02/85/Yellow-River-Basin-Focal-Project-16-320.jpg)
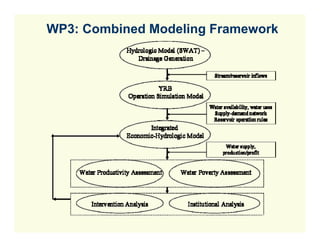



![WP5: Intervention Analysis
L a n d u s e / c ro p p in g
p a tte rn s
YRCC & SW AT
W a te r
A c c o u n tin g W a te r
E n v iro n m e n ta l flo w s p r o d u c tiv it y S C E N A R IO
W a te r [e c o n o m ic &
p h y s ic a l] A N A L Y S IS
a c c o u n tin g &
Institution & Policy Dialogue
A g ric u ltu ra l
Irrig a tio n w a te r L iv e s to c k
d e v e lo p m e n t a v a ila b ility & Irrig a te d c ro p s
access R a in fe d c ro p s
(F is h )
N o n a g ric u ltu ra l
w a te r d e m a n d
E c o n o m ic -
ns
In s titu tio n a l- W a te r
In s titu tio n a l a n a ly s is p o v e rty H IG H
A g r o n o m ic -
Im p a c ts P R IO R IT Y
M a c ro /S e c to ra l a n d E q u a tio n
d is trib u te d IN T E R -
T ra d e p o lic ie s s y s te m s by gender and
V E N T IO N S
in c o m e g ro u p
P o v e rty M a p p in g
K n o w le d g e b a s e
S H A R E D V IS IO N M O D E L IN G / IN F O R M A T IO N
S H A R IN G – / R E S U L T D IS S E M IN A T IO N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yellowriverbfpstartup2-090618094505-phpapp02/85/Yellow-River-Basin-Focal-Project-24-320.jpg)

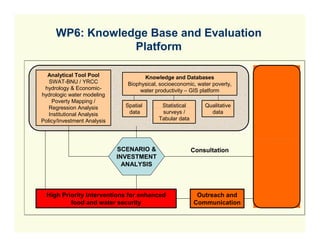





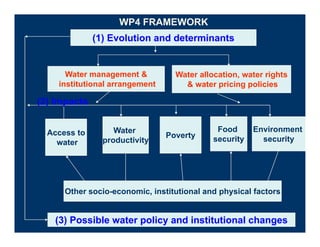
![On the Positive Challenges Side
Need to re-negotiate provincial water allocation –
but no information on provincial water use benefits
Large demand for knowledge on pro-poor water
savings and willingness to experiment with water
rights trading
Large interest in outcomes of tradeoff analysis
among water-using sectors
Several Chinese Government policy changes
[trade,
[trade ag policies] that allow for useful scenario
analysis
Need for information on climate change impacts
g p
INTERNATIONAL FOOD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yellowriverbfpstartup2-090618094505-phpapp02/85/Yellow-River-Basin-Focal-Project-35-320.jpg)