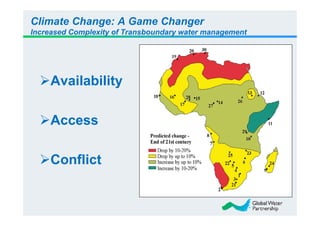
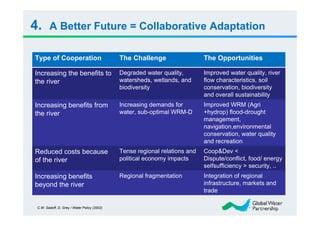
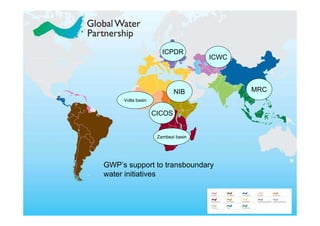
The document discusses the significant challenges posed by climate change to transboundary river water resources management, emphasizing that water security is a global concern closely linked to climate issues. It highlights the need for collaborative adaptation strategies among countries sharing water resources, focusing on integrated water resource management (IWRM) and strong intersectoral cooperation. Ultimately, achieving water security relies on fostering mutual benefits and shared responsibilities among riparian nations.





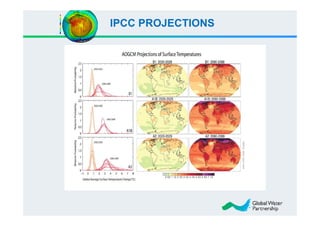

![Model-Projected Runoff Change (%)
[(2041-2060)-(1900-1970)]
(Milly et al., 2005)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aitkadi-mrc2x-100414020700-phpapp01/85/Climate-Change-Challenges-in-Transboundary-River-Water-Resources-Management-presented-by-Dr-Mohamed-AIT-KADI-GWP-Technical-Committee-Chair-MRC-at-International-Conference-2-3-April-2010-Hua-Hin-Thailand-9-320.jpg)