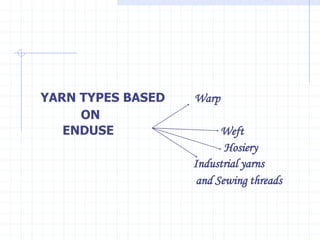
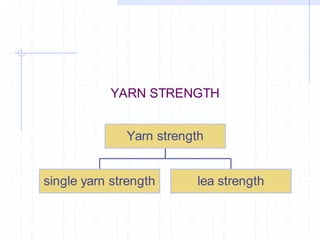
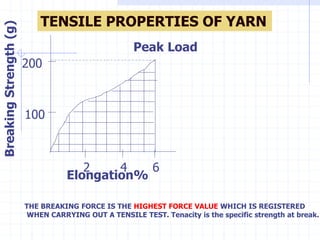
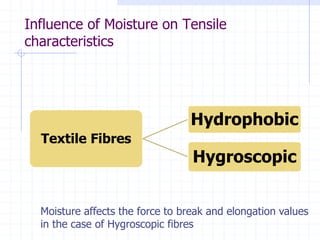
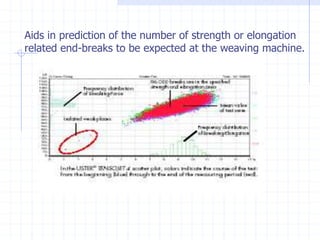
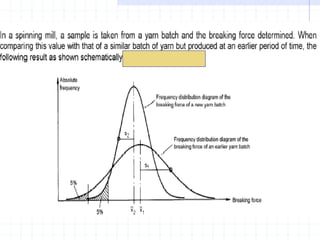
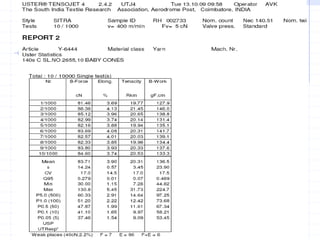
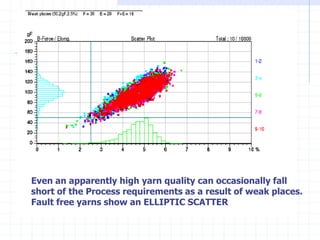
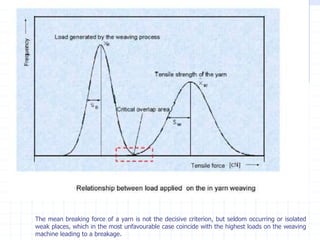
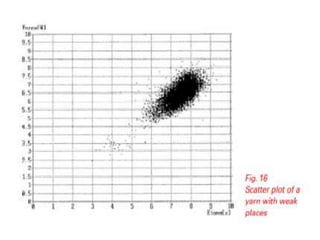
This document discusses yarn strength testing. Yarn strength is an important indicator of quality and ability to withstand loads during weaving and knitting without breaking. There are different machines that can test single yarn strength at varying speeds, from 300 tests per hour to over 30,000 tests per hour. Key properties measured include breaking force, elongation, and variation within samples. Understanding yarn strength helps predict performance and end breaks during processing.