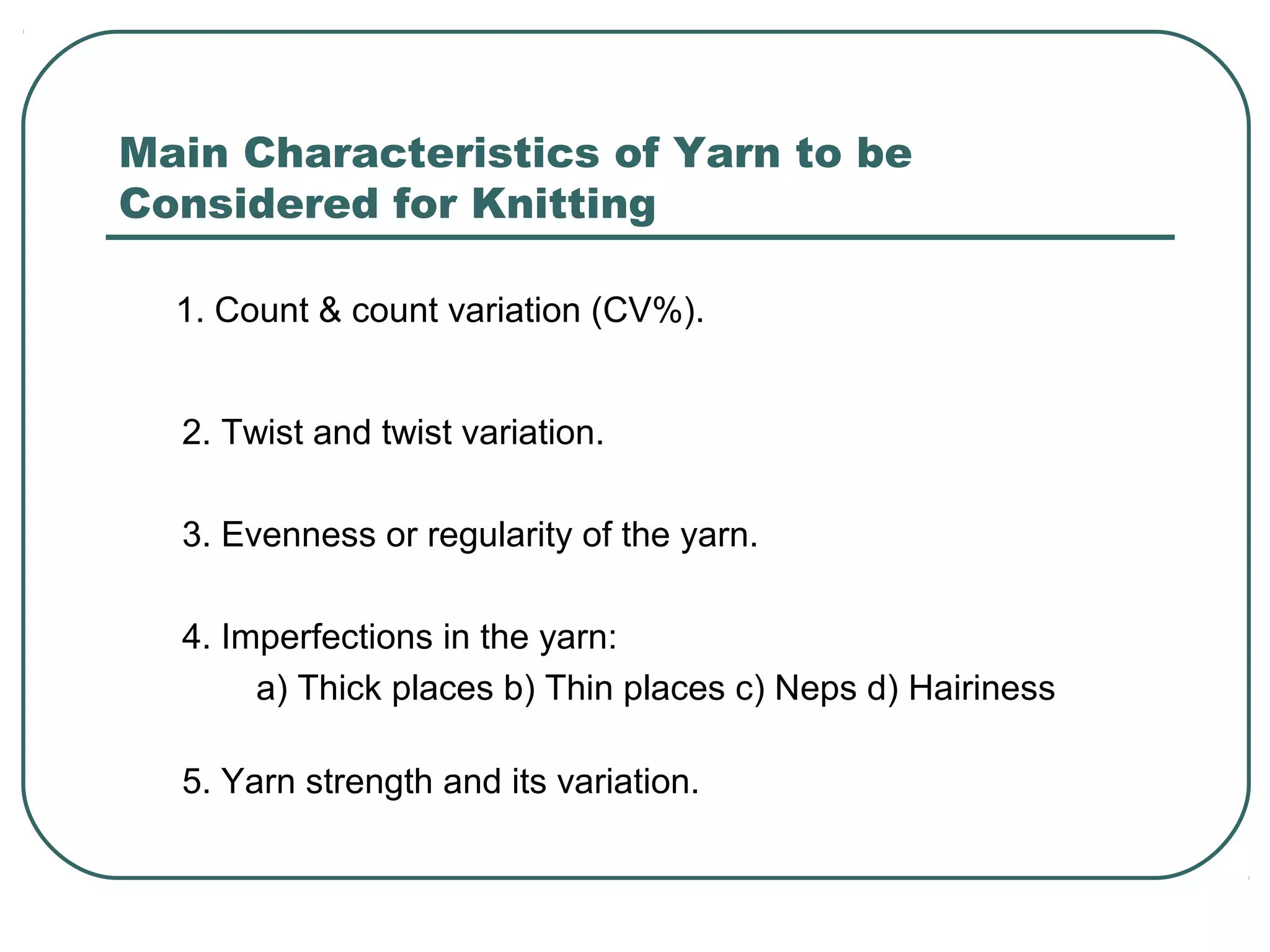
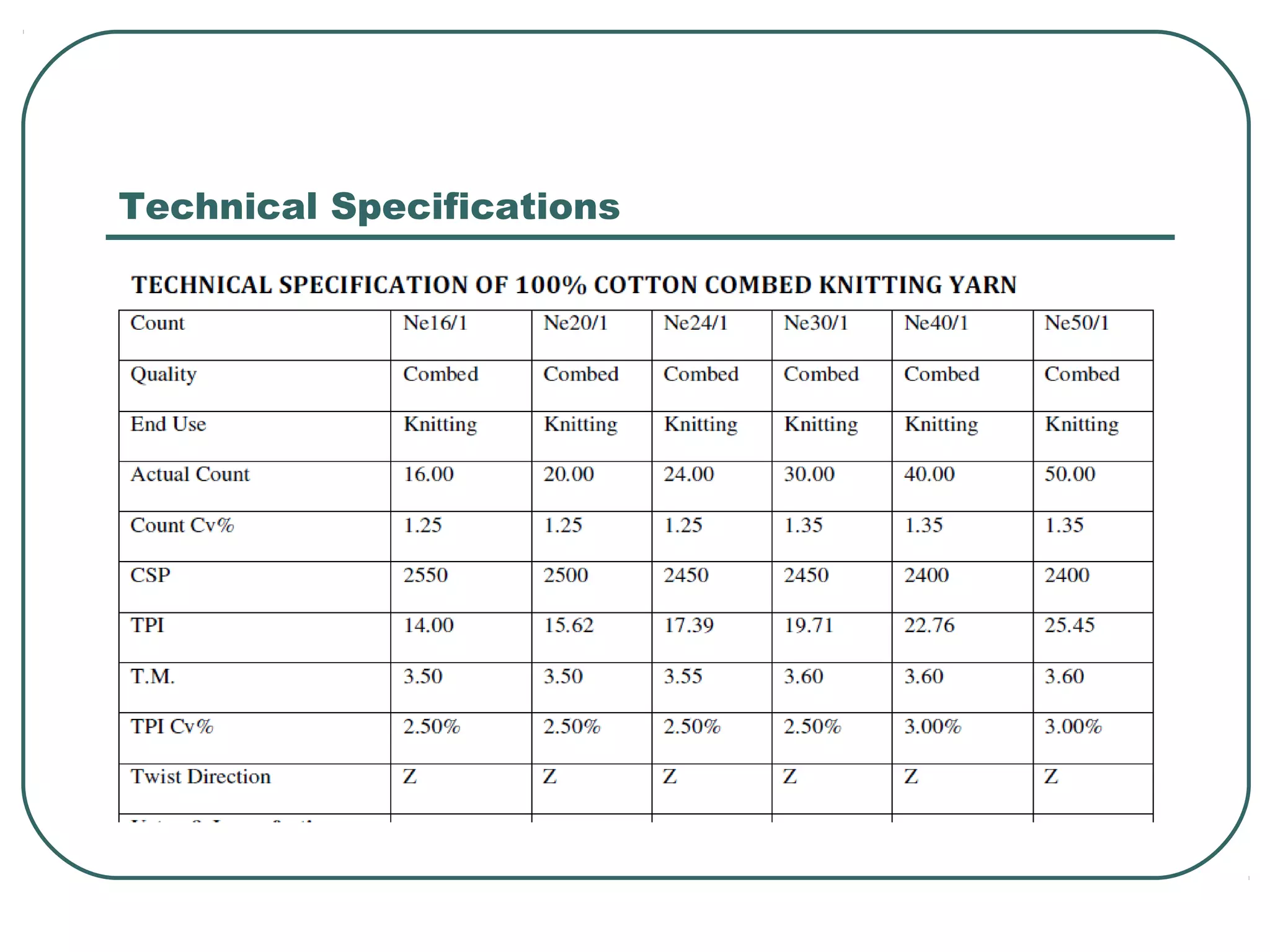
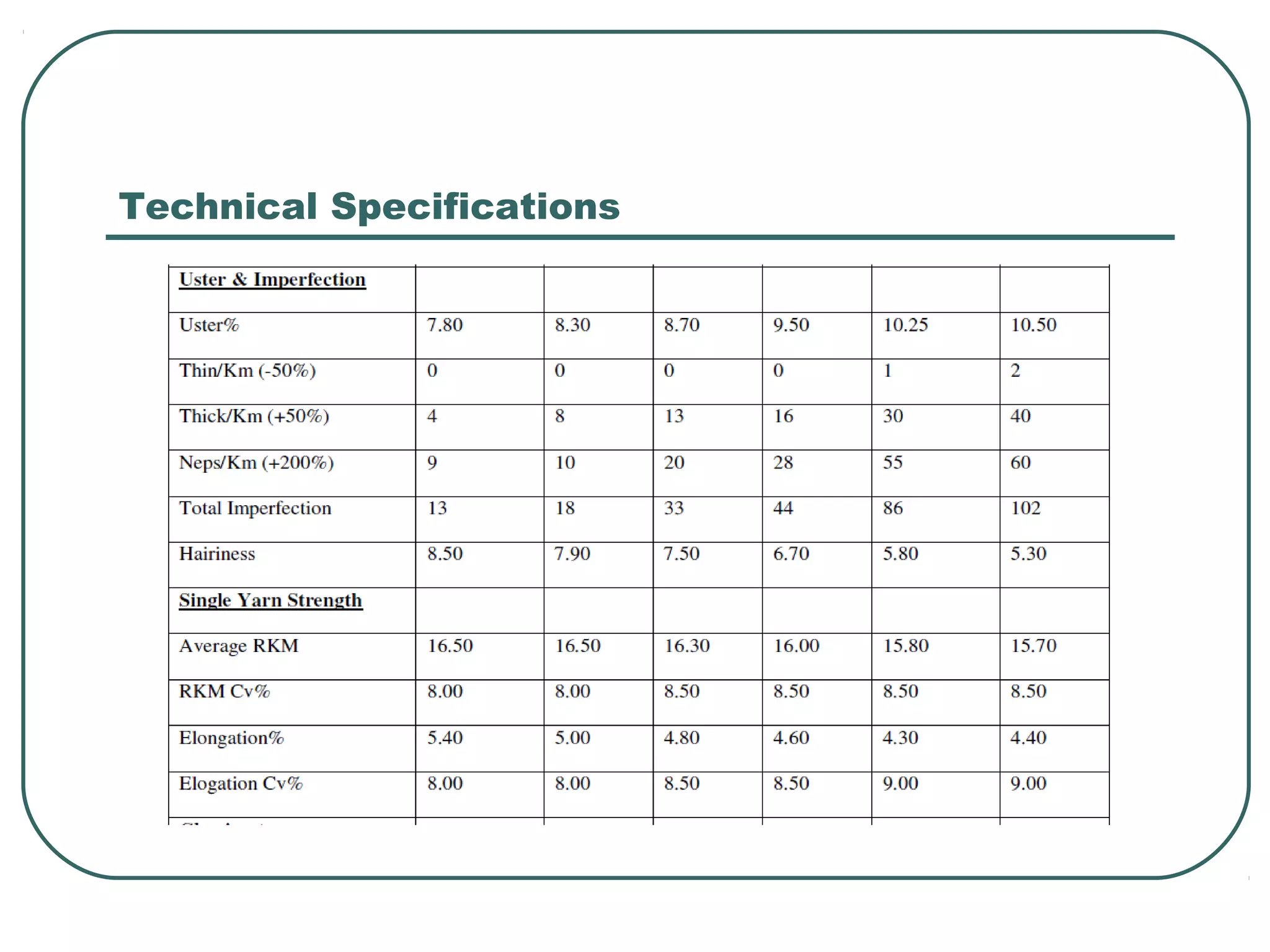
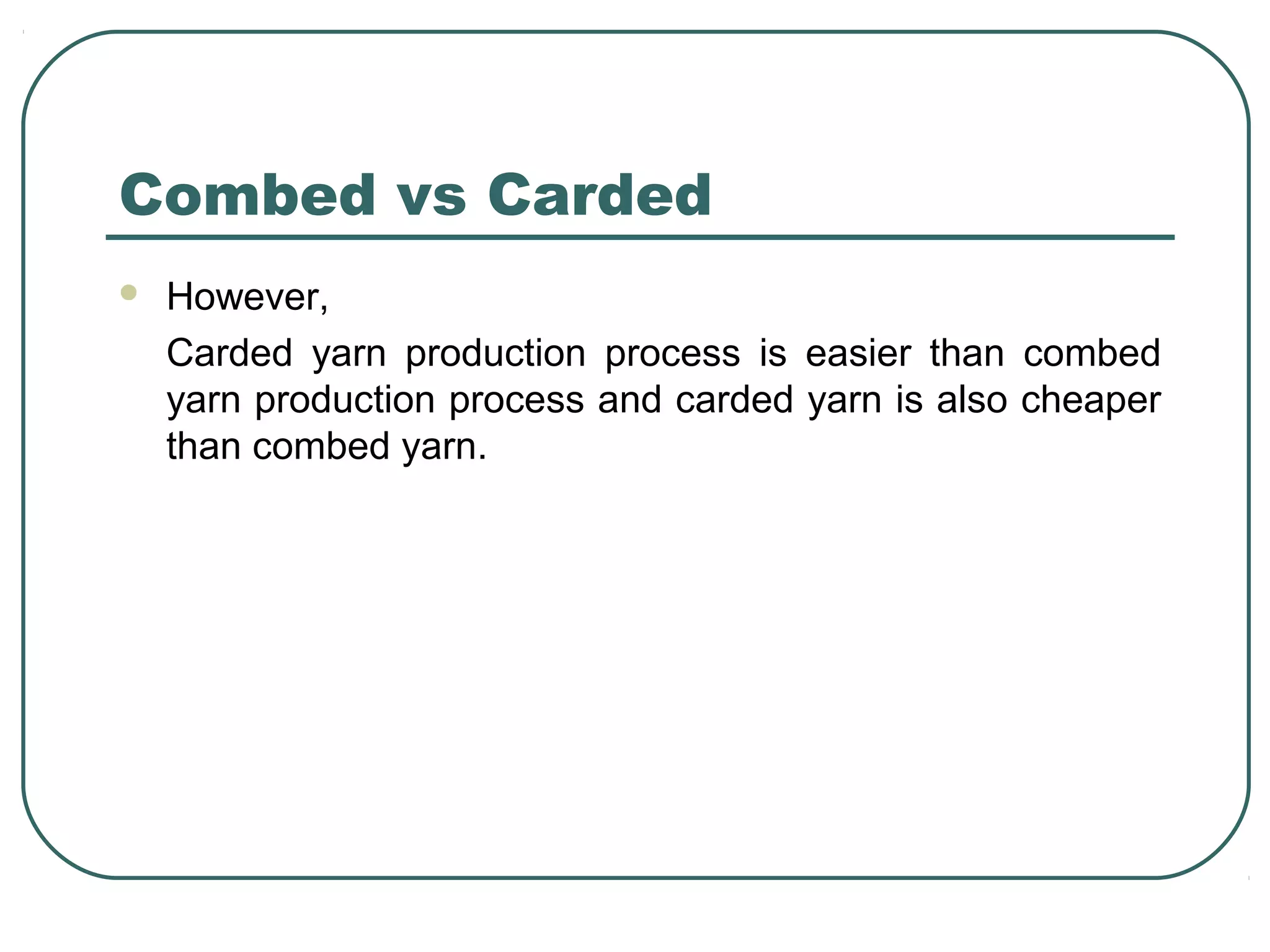
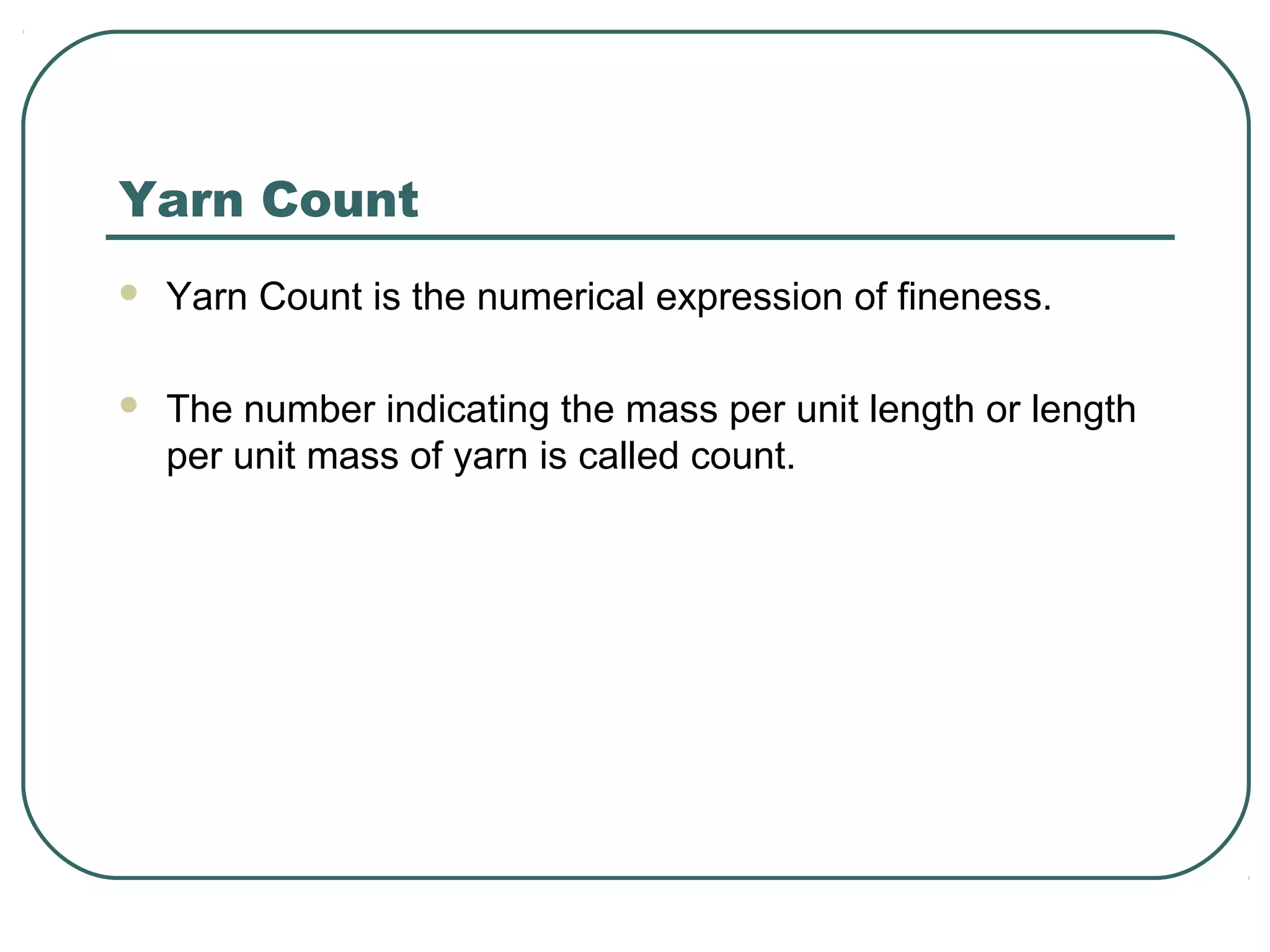
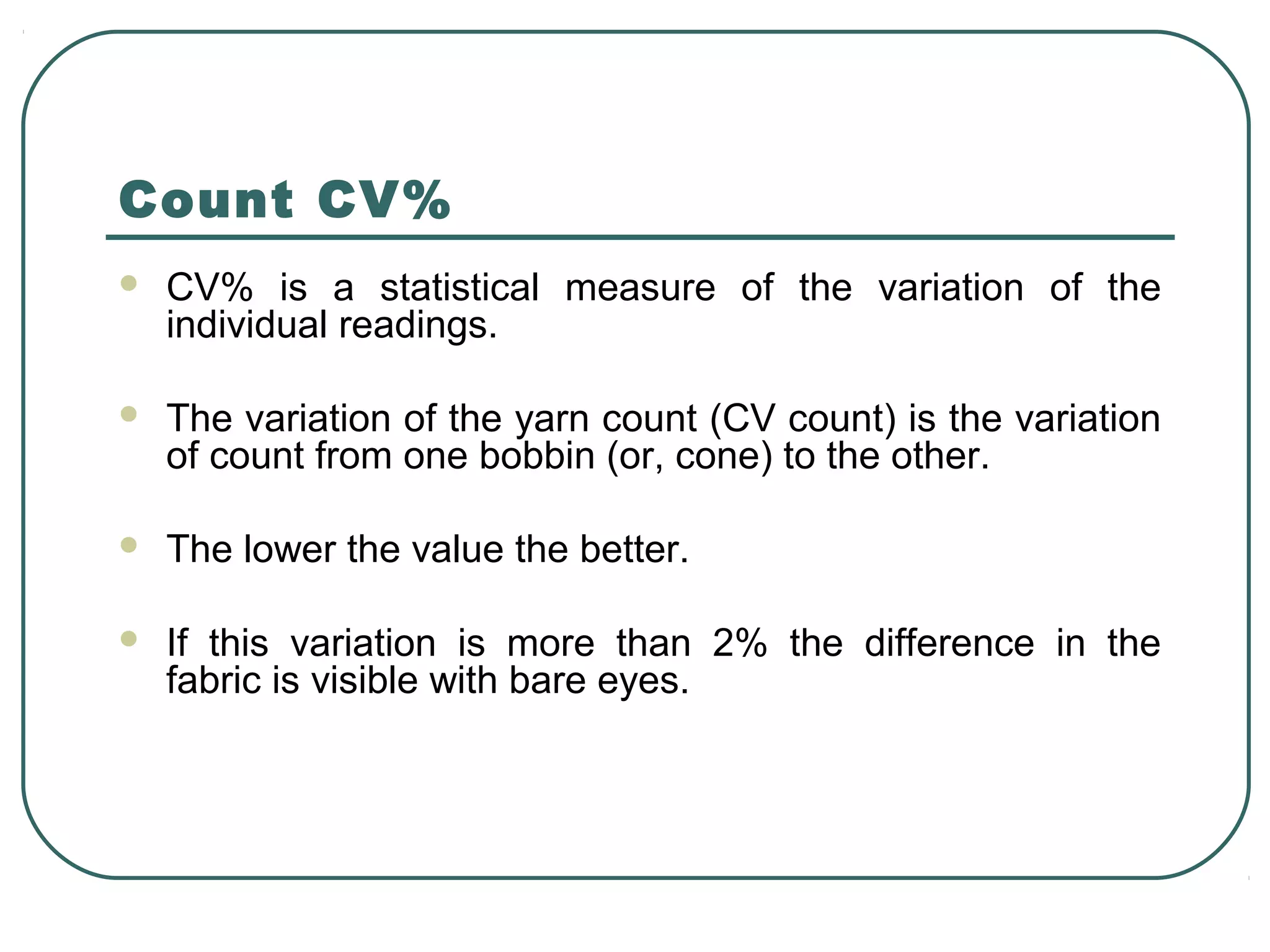
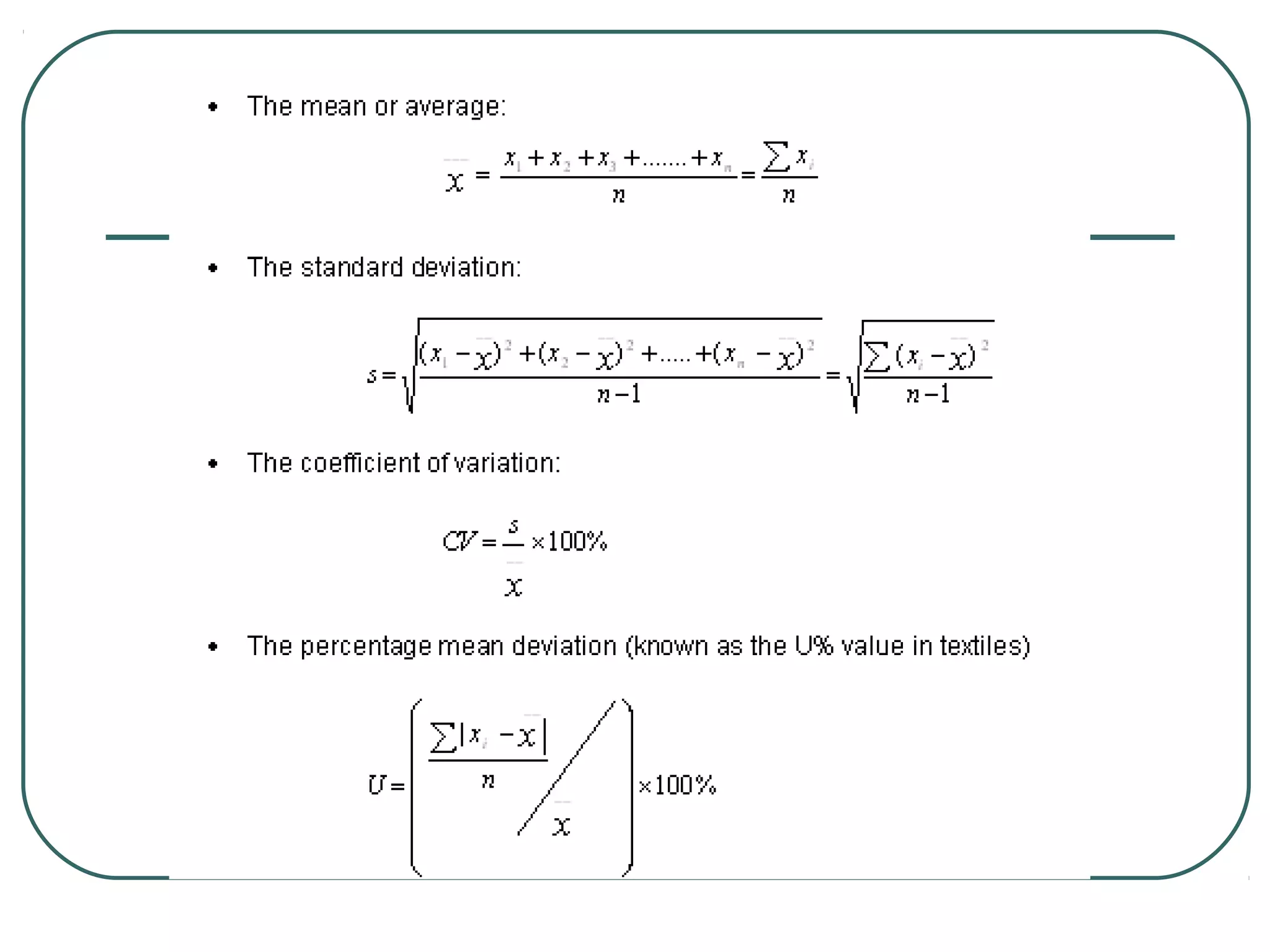
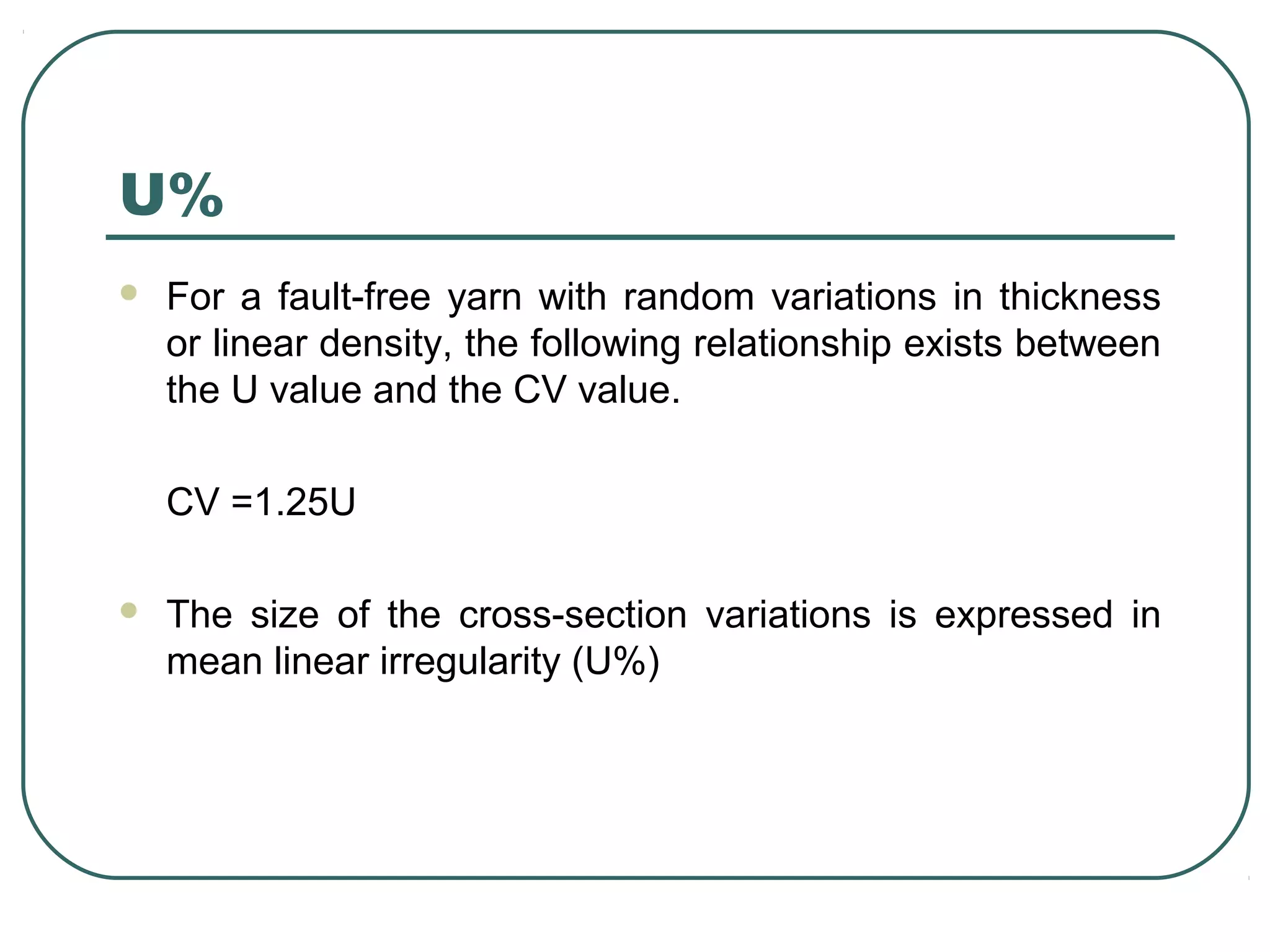
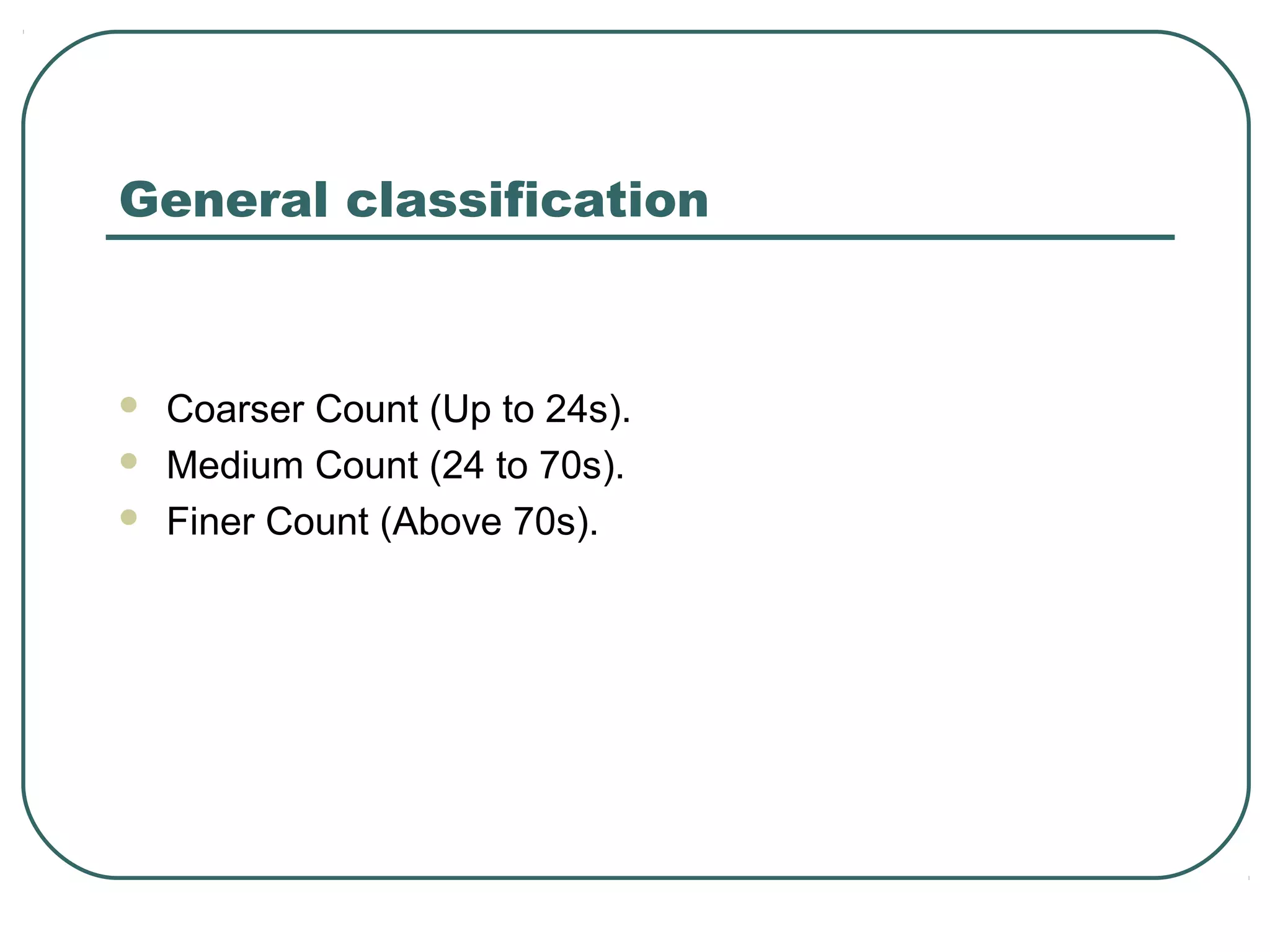
This document discusses yarn properties that are important for knitting, including count, twist, evenness, and imperfections. It compares combed and carded yarns, noting that combed yarn is of higher quality with fewer imperfections. Combed yarn produces knit fabrics with less pilling, shrinkage, and higher grammage. While more expensive to produce, combed yarn results in fabrics with better properties for knitting. The document also discusses yarn count, count variation, unevenness percentage, and classifications of yarn fineness.