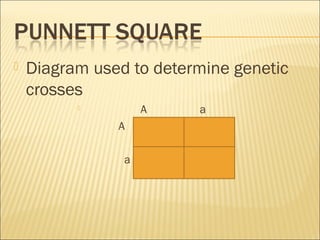
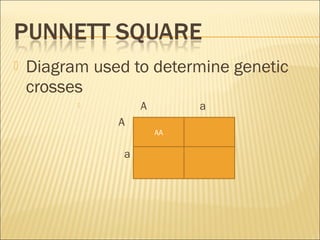
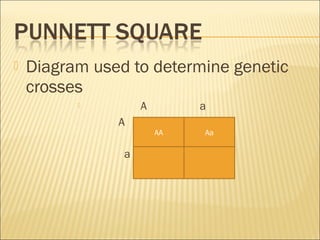
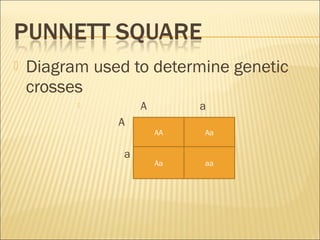
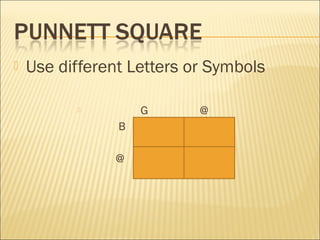
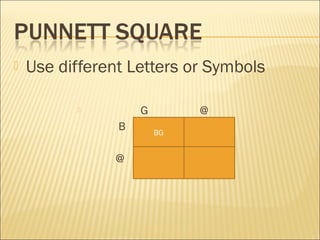
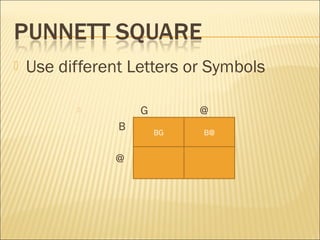
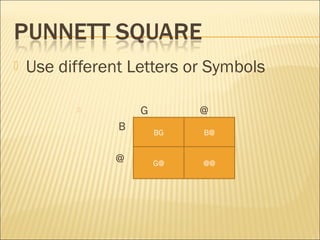
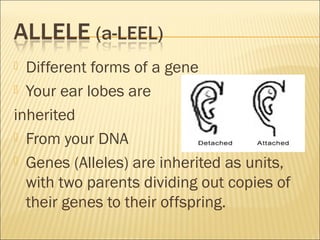
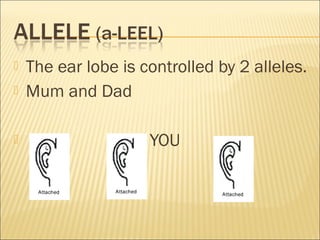
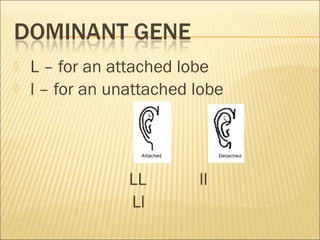
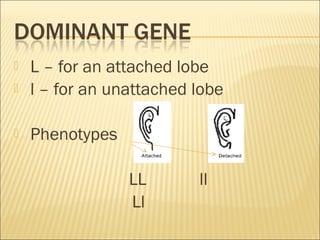
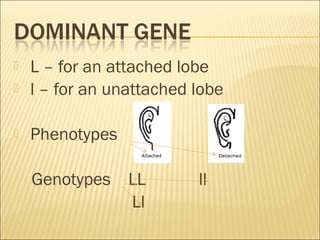
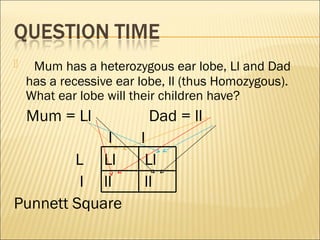
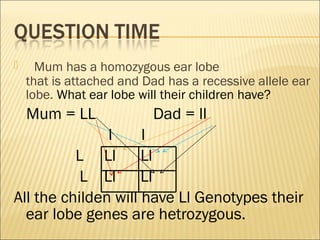
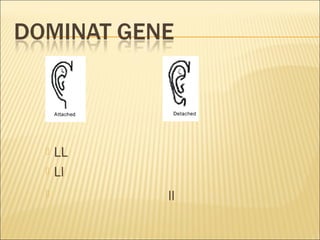
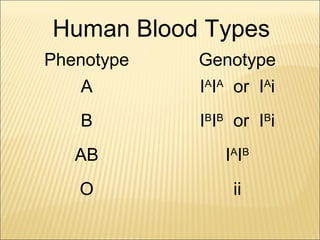
The document discusses basic genetics concepts including Punnett squares, dominance and recessiveness of alleles, and the significance of homozygous and heterozygous traits. It illustrates how traits like ear lobe shape and plant flower colors are inherited, as well as the influence of multiple alleles on traits such as blood type. Additionally, it emphasizes the interaction between genes and environmental factors in determining characteristics.