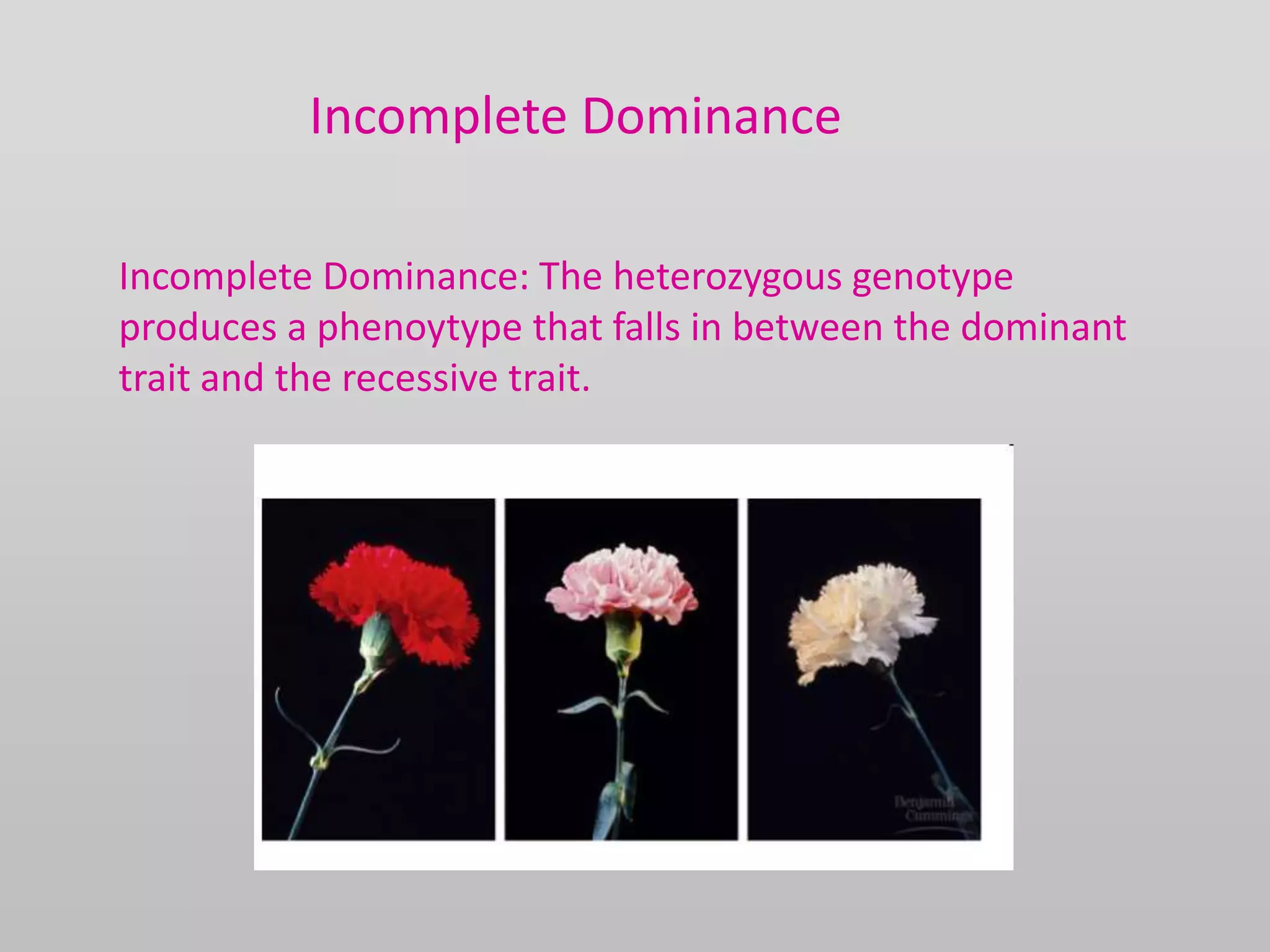
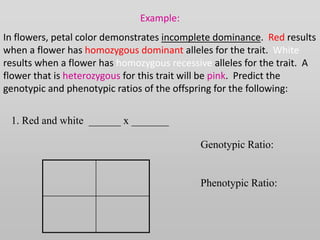
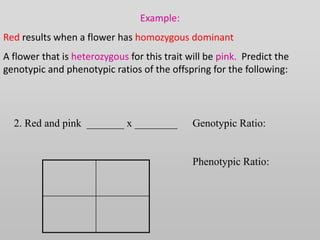
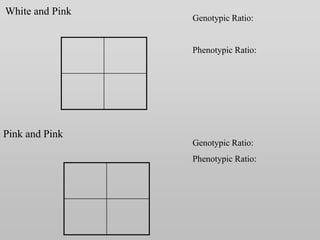
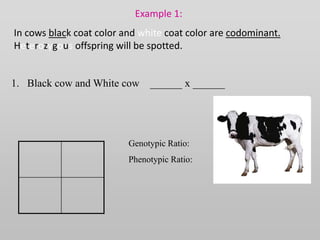
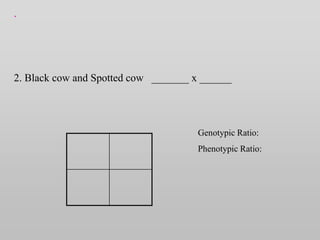
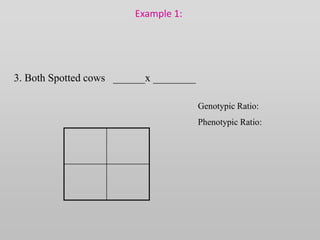
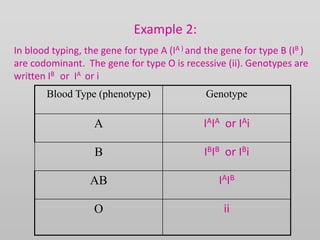
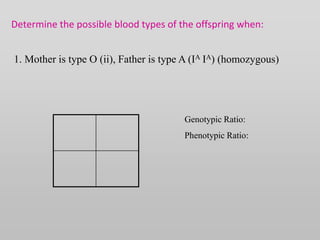
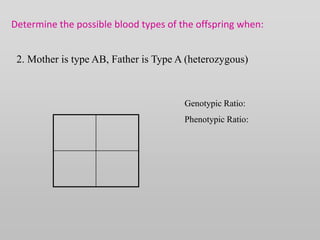
The document discusses two genetic concepts: incomplete dominance and codominance. In incomplete dominance, the heterozygous genotype produces an intermediate phenotype between the two homozygous genotypes. For example, in flowers red and white petal color show incomplete dominance, where heterozygotes are pink. Codominance occurs when both alleles are fully expressed in the heterozygote. For example, in cattle black and white coat colors are codominant, where heterozygotes are spotted. The document provides examples calculating genotypic and phenotypic ratios for offspring from crosses involving these inheritance patterns.