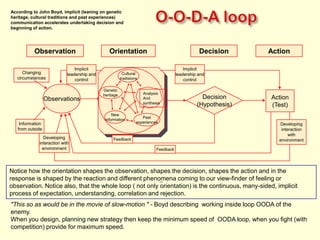
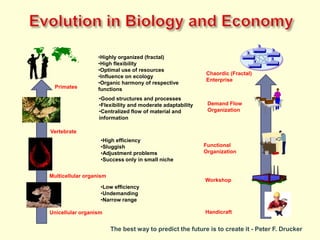
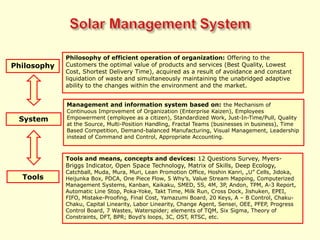
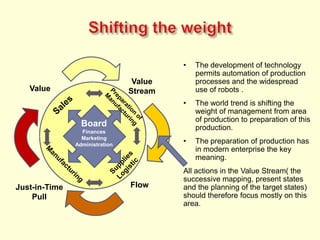
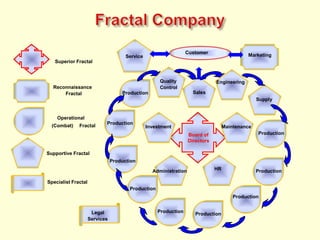
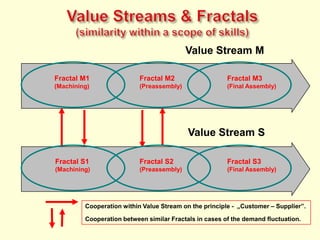
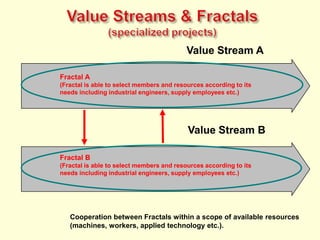
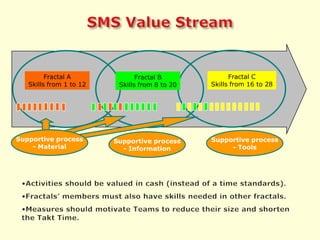
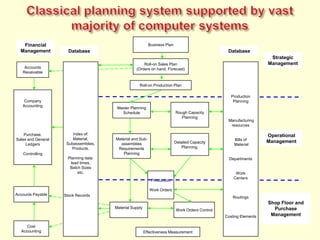
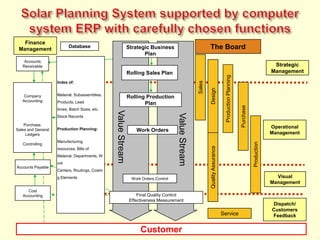
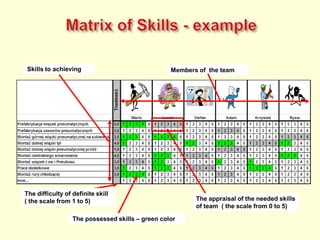
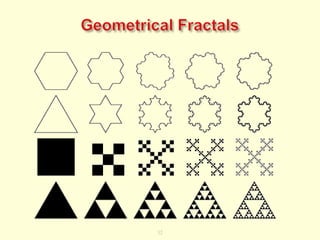
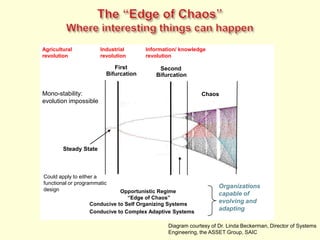
The document discusses new organizational models for the 21st century based on principles from nature. It describes fractal organizations as self-similar, self-organizing units that are connected in a network. Fractal enterprises allow for independent, customer-focused teams that cooperate like natural systems. The document also discusses lean management, the theory of constraints, bionic systems, holonic manufacturing, and chaordic organizations as approaches inspired by nature's patterns of spontaneity, mobility, and harmony.


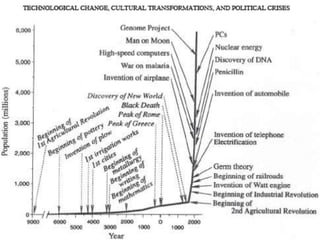






























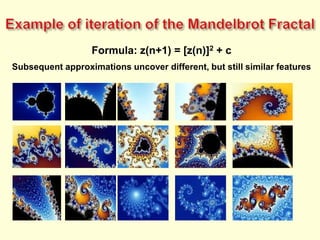

















![Example of iteration of the Mandelbrot FractalFormula: z(n+1) = [z(n)]2 + cSubsequent approximations uncover different, but still similar features](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxicenturyorganization-110217030243-phpapp02/85/XXI-Century-Organization-54-320.jpg)