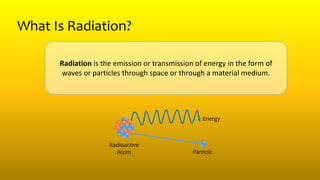
1) Radiation is the emission or transmission of energy through space or matter and comes in the form of waves or particles. The various quantities of radiation include activity, exposure, kerma, absorbed dose, relative biological effectiveness (RBE), effective dose, and equivalent dose.
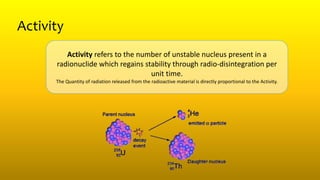
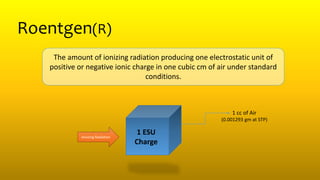
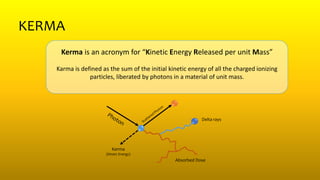
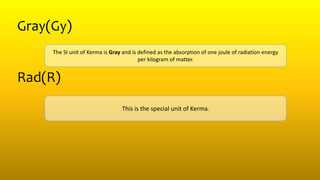
2) Activity refers to the number of unstable nuclei that decay per unit time and is measured in becquerels (Bq) or curies (Ci). Exposure is a measure of ionization in air due to radiation. Kerma measures the kinetic energy transferred to charged particles per unit mass. Absorbed dose measures energy absorbed per unit mass.
3) Effective dose takes into account RBE, which varies by radiation type and biological factors