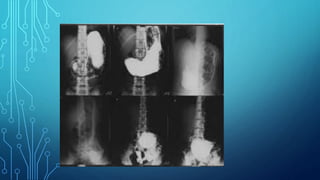
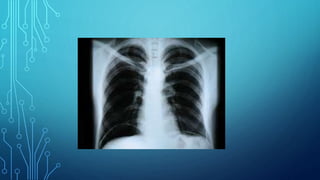
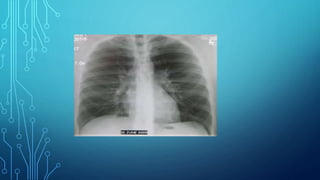
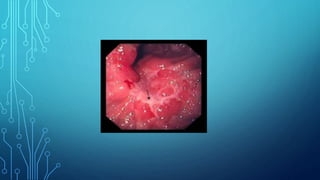
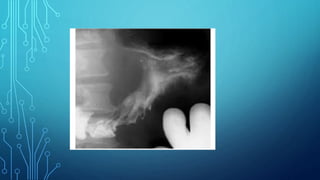
X-ray diagnostic methods can be divided into general and special techniques. General techniques can study any anatomical area using general-purpose X-ray machines, while special techniques use dedicated installations for specific organs. Special techniques also include contrast studies using artificial contrast agents. Fluoroscopy allows real-time imaging on a fluorescent screen but provides a weak image with high radiation exposure, while newer methods like X-ray television transmission provide improved fluoroscopy with lower exposure. Radiography provides static images recorded on film or digitally, and can image any area with natural or artificial contrast. Digital radiography provides faster imaging, post-processing and electronic archiving compared to traditional radiography.